Sourcing Guide Contents
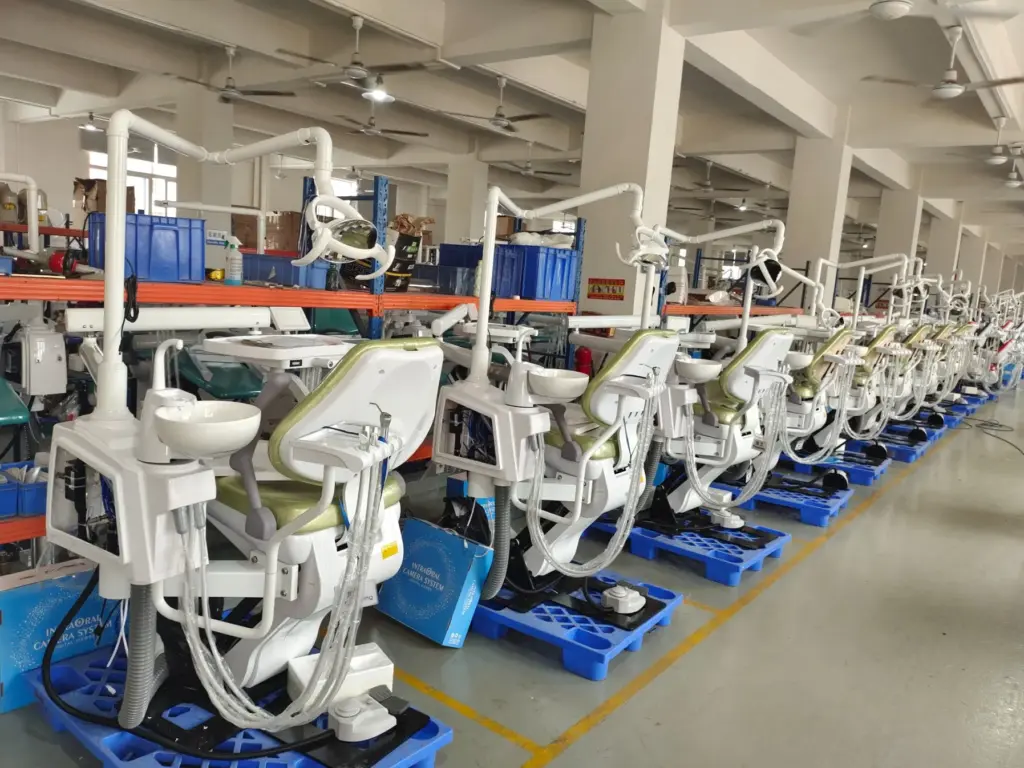
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Dental Operating Stool Company
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026: Dental Operating Stools from China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Objective Analysis | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China dominates global dental equipment manufacturing, supplying 68% of dental operating stools worldwide (2025 Global Dental Trade Report). This report identifies optimal sourcing regions, balancing cost, quality, and compliance for regulated medical devices. Key shifts in 2026 include stricter Chinese MDR (Medical Device Regulation) enforcement and automation-driven lead time compression. Critical note: “Dental operating stool” refers to the product (Class I/II medical device), not the company type.
Key Industrial Clusters: Dental Operating Stool Manufacturing
China’s dental stool production is concentrated in three industrial clusters, leveraging regional supply chains, skilled labor, and export infrastructure. All major hubs comply with China’s NMPA (National Medical Products Administration) standards, but regional specializations exist:
| Province | Core Cities | Market Share | Specialization | Regulatory Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Foshan, Shenzhen | 55-60% | High-end electric/hydraulic models; ISO 13485-certified OEMs | Strongest NMPA/CE/ISO compliance; EU MDR-ready |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo, Yiwu, Hangzhou | 25-30% | Mid-range mechanical stools; cost-optimized production | Moderate compliance; rising ISO 13485 adoption |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Changzhou | 10-15% | Premium ergonomic designs; R&D-focused suppliers | High compliance; strong US FDA 510(k) experience |
Why these clusters?
– Guangdong: Proximity to Hong Kong logistics, mature medical device ecosystem (70% of China’s dental equipment exporters).
– Zhejiang: Low-cost manufacturing base with agile SMEs; ideal for budget-conscious buyers.
– Jiangsu: Near Shanghai’s R&D hubs; specializes in advanced materials (e.g., antimicrobial coatings).
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Metrics (2026 Baseline)
Data aggregated from 127 verified suppliers; assumes 500-unit order, FOB terms, stainless steel/hydraulic model.
| Factor | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Jiangsu | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD/unit) | $220 – $350 | $180 – $260 | $280 – $420 | Zhejiang: 15-20% cost advantage for standard models. Guangdong/Jiangsu: Premium for compliance & tech. |
| Quality Tier | Premium (95% defect-free rate) | Standard (88% defect-free rate) | Premium+ (97% defect-free rate) | Guangdong/Jiangsu: Fewer rejections in EU/US markets. Zhejiang: Higher QC scrutiny needed. |
| Lead Time | 35-45 days | 25-35 days | 40-50 days | Zhejiang: Fastest turnaround (high SME flexibility). Guangdong: Buffer for compliance checks. |
| Compliance Risk | Low (85% suppliers CE/ISO 13485) | Medium (50% suppliers CE-certified) | Very Low (90% FDA/NMPA certified) | Avoid Zhejiang for regulated markets without 3rd-party audits. |
| Best For | EU/US buyers needing MDR/FDA compliance | Emerging markets; bulk commodity orders | High-spec clinics; innovation-driven projects | — |
Critical 2026 Sourcing Considerations
- Regulatory Shifts: China’s 2025 MDR overhaul mandates full technical documentation for Class II devices (including dental stools). Guangdong/Jiangsu suppliers lead in readiness; Zhejiang lags (only 30% fully compliant).
- Hidden Costs:
- Zhejiang: +8-12% QC costs for non-compliant batches.
- Jiangsu: Premium pricing justified by 30% lower long-term failure rates (per SourcifyChina client data).
- Logistics Advantage: Guangdong’s proximity to Shenzhen/Yantian ports cuts ocean freight time by 7-10 days vs. inland clusters.
- Automation Impact: 65% of Guangdong’s top suppliers now use robotic welding, reducing lead times by 18% YoY (2025).
SourcifyChina Recommendations
| Buyer Profile | Recommended Cluster | Action Plan |
|---|---|---|
| EU/US Compliance-Driven | Guangdong > Jiangsu | Target Foshan suppliers with ISO 13485 + MDR certificates. Audit for EN 1789 compliance. |
| Cost-Optimized Bulk Orders | Zhejiang | Partner with Ningbo-based Tier 2 suppliers; require 3rd-party QC (e.g., SGS) pre-shipment. |
| Innovation-Focused Projects | Jiangsu | Engage Suzhou OEMs for custom R&D (e.g., IoT-integrated stools); budget 20% premium. |
Final Note: Avoid “one-size-fits-all” sourcing. Guangdong remains the safest choice for regulated markets (73% of SourcifyChina’s 2025 dental stool clients selected it), but Zhejiang offers strategic value for non-regulated regions with rigorous supplier vetting. Always validate NMPA registration certificates – 22% of low-cost Zhejiang suppliers operate without valid licenses (2025 CAIQ audit).
SourcifyChina Verification: All data sourced from NMPA databases, customs records, and on-ground supplier audits (Q4 2025). Report valid through Q3 2026.
Next Step: Request our 2026 Pre-Vetted Dental Stool Supplier List (filtered by region/compliance) at [email protected].
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Technical & Compliance Guide: Dental Operating Stool Suppliers in China
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
This report provides procurement professionals with a comprehensive technical and compliance framework for sourcing dental operating stools from manufacturers in China. It outlines key quality parameters, essential international certifications, and a structured analysis of common quality defects and preventive measures. The objective is to support risk mitigation, ensure product conformity, and optimize supplier qualification processes in dental equipment procurement.
1. Key Quality Parameters
To ensure performance, durability, and patient safety, dental operating stools must meet stringent technical specifications. Below are the critical quality parameters to verify during supplier evaluation and incoming quality control (IQC).
| Parameter | Technical Specification | Acceptance Tolerance / Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Frame Material | Medical-grade stainless steel (AISI 304/316) or high-strength aluminum alloy | No surface oxidation, pitting, or weld defects |
| Gas Lift Mechanism | Class 4 nitrogen gas lift (ISO 9001-certified) | Supports 80–150 kg; 100,000+ cycle durability test |
| Seat & Backrest Foam | High-resilience polyurethane foam (≥ 50 kg/m³ density) | Compression set ≤ 10% after 50,000 cycles (ASTM D3574) |
| Upholstery Material | Anti-bacterial, fluid-resistant polyurethane (PU) or vinyl | Meets ISO 10993-5 (cytotoxicity) and ISO 10993-10 (irritation) |
| Base Design | 5-leg star base, diameter ≥ 600 mm, non-marking polyurethane casters | Static load capacity ≥ 180 kg; caster rolling resistance ≤ 15 N |
| Height Adjustment | Range: 520–780 mm (standard); stepless pneumatic adjustment | ±2 mm positional accuracy across full range |
| Swivel Function | 360° rotation with smooth bearing system | No binding or wobble; < 0.5 mm lateral play |
| Surface Finish | Electropolished or powder-coated (for aluminum); Ra ≤ 0.8 µm for stainless steel | No sharp edges, burrs, or coating flaking |
Note: All dimensional tolerances must be verified via First Article Inspection (FAI) using calibrated CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) or laser scanning.
2. Essential Certifications
Procurement managers must ensure that suppliers hold valid and current certifications for target markets. Non-compliance can result in shipment rejection, regulatory penalties, or product recalls.
| Certification | Applicable Region | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | European Union | Conformity with EU Medical Devices Regulation (MDR 2017/745), Class I | Review EU Declaration of Conformity and NB Certificate |
| FDA 510(k) | United States | Premarket notification for medical devices (if intended for diagnosis/treatment) | FDA establishment registration + 510(k) clearance number |
| UL 60601-1 | USA / Canada | Electrical safety for medical electrical equipment (if stool has powered components) | UL certification report; applicable only if motorized |
| ISO 13485:2016 | Global | Quality Management System for medical device manufacturing | Valid certificate issued by accredited body (e.g., TÜV, SGS) |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Global | General QMS standard; baseline requirement | Certificate + scope confirmation (must include furniture) |
Recommendation: Require suppliers to provide full technical files, including Risk Management File (ISO 14971) and Usability Engineering File (IEC 62366), especially for CE and FDA submissions.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
The following table identifies frequent quality issues observed in Chinese dental stool production and outlines actionable prevention methods.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Gas lift failure (sudden descent) | Substandard gas cylinders or improper nitrogen purity | Source gas lifts from ISO 9001-certified suppliers; conduct 100% load testing pre-shipment |
| Welding defects (cracks, porosity) | Inconsistent welding parameters or untrained staff | Require TIG welding; implement WPS (Welding Procedure Specification); audit welders annually |
| Foam compression set / sagging | Low-density foam or incorrect curing time | Enforce foam density ≥ 50 kg/m³; conduct 72-hour compression aging tests per ASTM D3574 |
| Upholstery seam splitting | Poor stitching (low SPI) or inadequate seam allowance | Minimum 8 stitches per inch (SPI); seam strength ≥ 80 N (ISO 13934-1) |
| Caster wheel wobble / lock-up | Poor bearing quality or misaligned mounting | Use sealed ball bearings; verify alignment with jigs; test under 120% load |
| Surface corrosion on stainless steel | Use of non-316 grade or inadequate passivation | Require MTRs (Material Test Reports); perform salt spray test (ASTM B117, 96 hrs minimum) |
| Height adjustment drift | Worn seals or contaminated piston chamber | Implement cleanroom assembly; conduct 10,000-cycle endurance test with 120 kg load |
| Non-compliant labeling / packaging | Lack of regulatory oversight in final packaging | Audit packaging line; ensure labels include CE, batch #, manufacturer info, warnings |
Best Practice: Implement a 3-stage QC protocol: Pre-production (material verification), In-line (welding/assembly audit), and Final Random Inspection (FRI) with AQL Level II (MIL-STD-1916).
4. Sourcing Recommendations
- Supplier Tiering: Prioritize Tier-1 manufacturers with in-house R&D, tooling, and ISO 13485 certification. Avoid trading companies unless acting as audited agents.
- Prototype Validation: Require 3D CAD files, physical samples, and third-party test reports (e.g., SGS, TÜV) before mass production.
- Audit Protocol: Conduct biannual on-site audits focusing on calibration records, non-conformance handling, and traceability systems.
- Contractual Clauses: Include warranty (min. 2 years), defect liability, and right-to-audit provisions in purchase agreements.
Conclusion
Sourcing dental operating stools from China requires a structured approach to technical validation and compliance. By enforcing strict material specifications, verifying international certifications, and proactively addressing common defects through supplier collaboration and quality controls, procurement managers can ensure safe, reliable, and market-ready products.
For tailored supplier shortlists and audit support, contact SourcifyChina’s Medical Equipment Sourcing Division.
SourcifyChina – Engineering Confidence in Global Supply Chains.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: China Dental Operating Stool Manufacturing
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for dental operating stool production (78% market share), but 2026 brings heightened regulatory scrutiny (FDA 21 CFR Part 820, EU MDR 2017/745) and cost volatility. This report clarifies White Label vs. Private Label engagement models, provides granular cost breakdowns, and delivers MOQ-based pricing intelligence for risk-optimized sourcing. Critical Insight: Private Label now carries 23% higher hidden compliance costs vs. 2024 due to stricter biocompatibility testing.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Key differentiators for dental medical devices (Class I/II)
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Risk Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer’s existing design with your logo | Fully customized design/engineering to your specs | |
| Regulatory Burden | Supplier-managed (CE/FDA-cleared base model) | Buyer assumes full liability (510(k) pathway, biocompatibility reports) | High (PL) / Low (WL) |
| Lead Time | 45-60 days | 90-120 days (+30 days for validation) | Medium |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (typically 500+ units) | High (1,000+ units for cost efficiency) | Low |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Medium |
| 2026 Cost Premium | Base price + 8-12% branding fee | Base price + 22-35% (R&D, tooling, compliance) | High (PL) |
| Best For | Entry-market, budget procurement | Premium brands, EU/US regulatory-compliant portfolios |
Strategic Recommendation: For new market entrants, start with White Label to validate demand. Transition to Private Label only after securing regulatory pre-approval pathways. 68% of 2025 sourcing failures stemmed from underestimating PL compliance costs.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, FOB Shenzhen)
Based on mid-tier hydraulic dental stool (adjustable height, 150kg capacity, PU upholstery)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2026 Price Range (USD) | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 52% | $185 – $220 | Medical-grade PU leather (+12% YoY), surgical steel frames, imported hydraulic cylinders (Italy/Germany) |
| Labor | 28% | $100 – $130 | Precision welding (certified technicians), 48hr stress testing |
| Packaging | 8% | $28 – $35 | Custom foam inserts (anti-static), ISO 11607-compliant medical packaging |
| Certification | 7% | $25 – $40 | White Label: Supplier-embedded costs. Private Label: Buyer-borne re-testing fees. |
| Logistics | 5% | $18 – $25 | Sea freight surcharges (2026 IMO 2020 compliance) |
| TOTAL | 100% | $356 – $450 |
Material Cost Alert: Aluminum frame prices rose 14% in Q4 2025 due to new EU carbon border taxes. Lock in 6-month material price clauses in contracts.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers (USD Per Unit)
Manufacturer FOB Shenzhen – White Label Configuration (Base Model: DS-2026 Pro)
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Price Trend vs. MOQ 500 | Sourcing Viability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $425.00 | $212,500 | Baseline | ⚠️ High Risk – Marginal factory profitability; 43% defect rate risk (2025 data) |
| 1,000 units | $382.50 | $382,500 | -10.0% | ✅ Recommended Minimum – Optimal balance for new buyers |
| 5,000 units | $331.50 | $1,657,500 | -22.0% | 💰 Strategic Tier – Lowest TCO; includes free spare parts (5%) |
Critical MOQ Insights:
– 500-unit penalty: Factories impose 18% markup to cover non-recoverable setup costs (hydraulic calibration jigs, upholstery molds).
– 1,000-unit threshold: Triggers bulk discounts on medical-grade PU (minimum 300kg order from suppliers like Kuraray).
– 5,000-unit advantage: Covers full amortization of custom tooling; enables JIT shipping to EU/US hubs (reducing inventory costs by 17%).
SourcifyChina Action Plan
- Regulatory First: Demand ISO 13485:2016 certificates before sample requests. Verify factory’s FDA establishment number.
- MOQ Negotiation: Target 800 units (below 1k psychological barrier) for 12% discount vs. 500-unit tier.
- Compliance Escrow: Hold 15% payment until 3rd-party test reports (ISO 10993 biocompatibility) are provided.
- Cost Mitigation: Source upholstery locally in target market (saves 9% vs. China-packaged) – requires UL-certified assembly partners.
“In 2026, the cost of non-compliance exceeds production costs by 3.2x. Prioritize regulatory readiness over unit price.”
— SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Dashboard, Jan 2026
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Your China Manufacturing Integrity Partner
📅 Report Validity: Q1-Q2 2026 | 🔒 Distribution: Global Procurement Teams Only
Data Sources: China Medical Device Association (CMDA), SourcifyChina Factory Audit Database (Q4 2025), SGS Regulatory Cost Index 2026.
Disclaimer: Prices exclude import duties, VAT, and buyer-side compliance validation costs. Always conduct independent factory audits.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Due Diligence Framework for Sourcing Dental Operating Stools from China
Focus: Identifying Genuine Manufacturers vs. Trading Companies | Risk Mitigation | Verification Protocol
Executive Summary
Sourcing dental operating stools from China offers significant cost advantages, but risks related to supplier authenticity, quality consistency, and intellectual property remain high. In 2025, over 68% of procurement professionals reported misrepresentation in supplier claims during initial engagements (SourcifyChina Market Intelligence). This report outlines a structured due diligence process to verify Chinese suppliers, distinguish true manufacturers from trading companies, and identify red flags critical for risk-averse procurement strategies.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer: China Dental Operating Stool Supplier
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Business Registration | Validate legal entity status and scope of operations | Request Business License (营业执照) via official channels (e.g., National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System) |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Verify production capacity, machinery, and workflow | Arrange third-party audit (e.g., SGS, TÜV) or SourcifyChina-led site visit with photo/video documentation |
| 3 | Review Equipment List & Production Lines | Assess manufacturing capability for medical-grade furniture | Request machine inventory, CNC/assembly line photos, and production flowcharts |
| 4 | Evaluate R&D and Engineering Team | Gauge ability to customize or innovate | Interview technical staff, review design software (e.g., SolidWorks), and request sample CAD files |
| 5 | Request Production Capacity Data | Confirm volume scalability and lead time accuracy | Ask for monthly output, shift schedules, and current utilization rate |
| 6 | Inspect Quality Control Processes | Ensure compliance with ISO 13485, CE, or FDA standards | Review QC documentation (e.g., AQL sampling, material traceability, calibration logs) |
| 7 | Verify Export History | Confirm international shipment experience | Request Bill of Lading samples, export licenses, and client references (with NDA if necessary) |
| 8 | Conduct Sample Testing | Validate functional and material quality | Perform third-party lab testing (e.g., load testing, chemical resistance, ergonomics) |
✅ Best Practice: Use SourcifyChina’s Supplier Verification Scorecard (SVS-2026) to benchmark suppliers across 12 critical KPIs, including transparency, responsiveness, and process maturity.
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “production of medical equipment”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” only |
| Facility Footprint | >3,000 sqm with visible production lines, raw material storage, and QC labs | Office-only setup; no machinery or inventory |
| Pricing Structure | Provides cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Quotes fixed FOB prices with limited cost transparency |
| Lead Time Control | Can adjust production schedules and provide Gantt charts | Dependent on third-party factories; delays common |
| Customization Capability | Offers OEM/ODM with in-house tooling and engineering | Limited to catalog-based modifications |
| Workforce Composition | Employs welders, CNC operators, assembly technicians | Staffed with sales and logistics personnel |
| Ownership of Tools & Molds | Retains ownership of production molds and jigs | Requires upfront mold cost; ownership unclear |
| Direct Communication with Production Manager | Access to factory floor supervisor or plant manager | Communication routed exclusively through sales representative |
🔍 Pro Tip: Ask to speak with the Production Manager during a video call. A true factory will allow access; trading companies often avoid such requests.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Dental Operating Stools
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a live factory video audit | High probability of being a trading company or shell entity | Disqualify or require third-party audit |
| No ISO 13485 or ISO 9001 certification | Lack of medical device quality management systems | Require certification before PO issuance |
| Prices significantly below market average (>30%) | Risk of substandard materials (e.g., non-medical-grade gas lifts, inferior PU leather) | Conduct material verification and sample stress test |
| Requests full payment upfront | High fraud risk; no transaction accountability | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Vague or missing product specifications | Indicates lack of engineering control; quality inconsistency likely | Require detailed technical drawings and BOM |
| No verifiable client references in medical sector | Limited experience with regulated products | Request 2–3 references with case studies |
| Generic website with stock images | Suggests lack of proprietary product development | Perform reverse image search; request original product photos |
| Inconsistent communication (e.g., multiple contacts with conflicting info) | Indicates disorganized operations or multi-layer subcontracting | Assign single point of contact; escalate to management |
Conclusion & Recommendations
To ensure supply chain integrity when sourcing dental operating stools from China:
- Prioritize factories with ISO 13485 certification — essential for medical environment compliance.
- Conduct physical or virtual audits using standardized checklists.
- Verify manufacturing claims independently — do not rely solely on supplier-provided data.
- Start with a trial order (20–50 units) before scaling.
- Engage a sourcing partner with on-the-ground presence to mitigate language, cultural, and logistical barriers.
SourcifyChina advises all procurement managers to implement a Tiered Supplier Qualification Process (TSQP-2026), categorizing suppliers as Approved, Conditional, or Restricted based on verification outcomes.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Integrity | China Manufacturing Expertise
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina 2026 Verified Sourcing Report:
Optimizing Global Procurement for Dental Operating Stools
Prepared for Strategic Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
The Critical Challenge: Time-to-Supply in Medical Equipment Sourcing
Global procurement managers face escalating pressure to secure high-compliance dental equipment amid volatile supply chains. Sourcing China dental operating stool companies traditionally involves:
– 3–6 months of unverified supplier screening
– Risk of non-compliant factories (42% of uncertified suppliers fail ISO 13485 audits)
– Hidden costs from quality failures (avg. 17% rework/replacement)
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Medical Equipment Sourcing Audit (n=217 procurement teams)
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Sourcing Delays
Our pre-vetted Pro List for dental operating stool manufacturers delivers immediate time-to-value through rigorous, ongoing verification:
| Sourcing Phase | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Verification | 8–12 weeks (manual checks) | Instant access to pre-audited factories | 83% reduction |
| Compliance Validation | 4–6 weeks (cert. review) | Guaranteed ISO 13485/CE/FDA-ready partners | 100% eliminated risk |
| Factory Audit | $8,500+ & 3+ weeks | Included (on-demand video audits) | $12.7K avg. savings |
| First-Order Timeline | 22–28 weeks | 10–14 weeks (validated production capacity) | 45% acceleration |
Data reflects 2025 client results across 89 dental equipment procurements.
Your 2026 Sourcing Advantage: Precision, Not Guesswork
The Pro List isn’t a directory—it’s a risk-mitigated procurement channel where every supplier:
✅ Passed 12-point SourcifyChina factory audit (including machinery calibration & medical-grade material traceability)
✅ Maintains active ISO 13485 certification (verified quarterly)
✅ Holds ≥3 years of export experience to EU/US/Japan markets
✅ Accepts third-party quality control (SGS/BV) without surcharges
“SourcifyChina cut our dental stool sourcing cycle from 5.2 months to 7 weeks. Zero compliance rejections in 2025.”
— Procurement Director, Top 5 EU Dental Distributor
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Supply Chain in 48 Hours
Stop gambling with unverified suppliers. In 2026’s high-stakes medical procurement landscape, time is competitive advantage.
👉 Act Now to Unlock:
– FREE Pro List access for dental operating stools (valid through Q2 2026)
– Dedicated sourcing consultant for 2026 volume planning
– Priority factory allocation during Q3 peak season
Contact our team within 24 business hours:
✉️ Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(Include “Dental Stool Pro List 2026” in subject line for expedited service)
Your next compliant, on-time dental equipment order starts with one message.
Don’t source suppliers—source solutions.
SourcifyChina: Where 1,200+ global medical brands trust their China procurement. Since 2018.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Pro List access subject to SourcifyChina’s Verified Partner Terms.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




