The global worm and wheel gearbox market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across industries such as material handling, automotive, energy, and manufacturing. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global gearboxes market was valued at approximately USD 25.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029, with worm gearboxes accounting for a significant share due to their reliability in high-torque, low-speed applications. Similarly, Grand View Research reports that the global gearbox market size was valued at USD 24.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030, citing rising industrial automation and infrastructure development as key drivers. As demand for efficient power transmission solutions grows, manufacturers of worm and wheel gearboxes are innovating to improve efficiency, durability, and customization. In this evolving landscape, identifying the leading suppliers becomes critical for engineers, procurement managers, and OEMs aiming to optimize performance and reliability. Below are the top 10 worm and wheel gearbox manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 10 Worm And Wheel Gearbox Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ZF Product Range Industrial Gearboxes
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zf.com
Key Highlights: Drive Gearboxes GFA/GPT. ZF Drive Gears are ideal driveline components for wheel, track or roller-driven mining applications and large construction machines….
#2 BJ-Gear A/S
Domain Est. 2005
Website: bj-gear.com
Key Highlights: BJ-Gear A/S produces high-tech transmission solutions with customisation and service in focus. We manufacture our gearboxes and linear solutions in our factory ……
#3 Worm Reduction Gearbox
Domain Est. 2011
Website: kiscogears.com
Key Highlights: Today, we are a leading manufacturer and exporter of Worm Reduction Gearbox, Horizontal Double Gearbox … Worm & Worm Wheel Sets; Kisco Aluminium Series ……
#4 Grove Gear Gearing Products
Domain Est. 2021
Website: regalrexnord.com
Key Highlights: Grove Gear manufactures standard and custom gear drives for industrial and specialty applications. The product line is the most extensive line of gear reducers ……
#5 Worm Drives and Worm Gearboxes
Domain Est. 1995
Website: nord.com
Key Highlights: Worm drives from NORD DRIVESYSTEMS are the durable, long lasting worm gearbox solution for applications around the globe….
#6 Precision Worm Gear Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1996
Website: wmberg.com
Key Highlights: Worm gears are the best choice for high drive reduction. The addition of a throat permits the wheel to fully envelope the threads of the worm….
#7 Steel & Stainless Steel Worm Wheel Gearboxes
Domain Est. 2007
Website: ondrivesus.com
Key Highlights: Steel and stainless steel worm wheel gearboxes produce low noise output and an output can be used to transmit higher torque or reduce rotational speed….
#8 Premium Transmission
Domain Est. 2014
Website: premium-transmission.com
Key Highlights: We are the pioneers of Worm gearboxes in India. Our solutions energize progress, driving efficiency, reliability, and sustainability across various sectors….
#9 Worm gearboxes made in Germany
Domain Est. 2017
Website: tandler-gearboxes.com
Key Highlights: We offer custom worm gearboxes made in Germany and developed according to customer specifications. These gearboxes are used when high transmission ratios are ……
#10 Best Worm Wheel Gears
Domain Est. 2021
Website: pnpdrive.com
Key Highlights: As professional worm wheel suppliers, Essor excels in manufacturing high precision worms and worm gears, especially in rotary table, machining automation, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Worm And Wheel Gearbox

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Worm and Wheel Gearboxes
The global market for worm and wheel gearboxes is expected to witness steady growth and notable transformation by 2026, driven by industrial automation, energy efficiency demands, and advancements in manufacturing technologies. This analysis explores key market trends shaping the worm and wheel gearbox sector in 2026 under the H2 framework, focusing on Hybrid Technologies, High Efficiency Demands, and Horizontal Integration.
H2.1: Hybrid Technologies Driving Innovation
By 2026, hybrid technologies are playing a pivotal role in enhancing the performance and application range of worm and wheel gearboxes. Manufacturers are increasingly integrating smart sensors and IoT-enabled monitoring systems into traditional gearbox designs. These “smart gearboxes” allow for real-time performance tracking, predictive maintenance, and remote diagnostics—especially critical in industrial automation, robotics, and renewable energy systems.
Additionally, hybrid designs combining worm gears with planetary or helical stages are gaining traction. These hybrid configurations improve torque transmission, reduce wear, and offer better efficiency than conventional worm gearboxes, addressing one of their historical drawbacks: lower mechanical efficiency.
The trend is particularly evident in industries such as electric vehicles (EVs), where compact, high-torque transmission systems are needed. While worm gearboxes are not primary drivetrain components in EVs, their use in auxiliary systems—like steering mechanisms and cooling pumps—is expanding due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness.
H2.2: High Efficiency Demands Reshaping Product Design
Energy efficiency regulations and sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to innovate. Traditional worm gearboxes are known for their high reduction ratios and self-locking capabilities but often suffer from efficiency losses due to sliding friction between the worm and wheel.
By 2026, there is a strong market shift toward high-efficiency worm gearboxes designed with advanced materials (e.g., phosphor bronze, engineered polymers) and surface treatments (e.g., PTFE coatings, superfinishing). These improvements reduce friction and heat generation, boosting efficiency from typical ranges of 50–90% to consistently above 85% in optimized models.
Moreover, the rise of Industry 4.0 and green manufacturing standards is accelerating demand for energy-efficient components. End-users in sectors like food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment prioritize gearboxes that minimize energy consumption and maintenance downtime. This efficiency focus is also encouraging the adoption of hybrid or alternative gearbox types in applications where worm gears were once the default.
H2.3: Horizontal Integration Across Industrial Ecosystems
Horizontal integration—the alignment of worm and wheel gearbox manufacturers with broader industrial ecosystems—is a defining trend in 2026. Instead of operating as standalone component suppliers, gearbox companies are forming strategic partnerships with automation solution providers, robotics firms, and OEMs.
This integration enables customized gearbox solutions tailored to specific machinery needs. For example, in material handling and conveyor systems, gearboxes are now co-developed with control systems and motors to ensure seamless compatibility and optimized performance.
Furthermore, global supply chain reconfiguration post-pandemic has led to regional manufacturing hubs in Asia-Pacific and Eastern Europe. This geographical integration supports faster delivery, reduced logistics costs, and better responsiveness to local market demands. China, India, and Germany remain key manufacturing and innovation centers, with increasing investments in R&D and automation.
Conclusion
By 2026, the worm and wheel gearbox market is evolving rapidly under the influence of Hybrid Technologies, High Efficiency Demands, and Horizontal Integration. While facing competition from more efficient gear types, worm gearboxes remain relevant due to their unique advantages in high-ratio reduction, compact design, and self-locking features. Continued innovation and strategic alignment with industrial trends will determine the long-term competitiveness of this essential mechanical component.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Worm and Wheel Gearboxes (Quality & IP)
Sourcing worm and wheel gearboxes involves more than just finding a supplier with the right specifications. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to operational failures, legal risks, and long-term cost increases. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material and Manufacturing Quality
One of the most frequent issues is receiving gearboxes made from substandard materials or with inconsistent manufacturing processes. Low-grade metals or improper heat treatment can lead to premature wear, reduced load capacity, and catastrophic failure under stress. Buyers often assume specifications equate to quality, but without proper quality control and supplier audits, dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and alignment may fall short—impacting efficiency and lifespan.
Inadequate IP Due Diligence
Purchasing worm gearboxes—especially from low-cost manufacturers—can expose buyers to intellectual property infringement risks. Some suppliers may replicate designs protected by patents or trademarks without authorization. Using such components in your own products could lead to legal disputes, product recalls, or import bans. Always verify that the supplier owns the design rights or has legitimate licensing, particularly when sourcing from regions with lax IP enforcement.
Misleading IP Ratings (Ingress Protection)
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating indicates resistance to dust and moisture, but many suppliers inflate or inaccurately report these values. A gearbox advertised as IP65 may not actually be dust-tight or protected against water jets if testing standards aren’t followed. Relying on unverified claims can result in equipment failure in harsh environments. Always request third-party test reports or conduct your own validation, especially for outdoor or industrial applications.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable suppliers provide full traceability, including material certifications, test reports, and manufacturing records. However, many low-cost vendors offer minimal or falsified documentation. This absence makes it difficult to investigate failures, comply with industry regulations, or ensure consistency across batches—especially critical in regulated sectors like food processing or aerospace.
Hidden Design Copying and Reverse Engineering Risks
Some suppliers may offer “compatible” or “replacement” worm gearboxes that closely mimic well-known branded products. While marketed as cost-effective alternatives, these units may be unauthorized copies, infringing on original designs. Beyond IP concerns, copied gearboxes often lack the exact tolerances, materials, or heat treatments, leading to poor performance and reliability.
Overlooking Long-Term Support and Spare Parts Availability
Cheaper gearboxes may appear cost-effective initially, but if the supplier lacks technical support or spare parts inventory, downtime and replacement costs can skyrocket. Ensure the supplier offers long-term availability, technical documentation, and responsive customer service—especially if the gearbox is integrated into mission-critical systems.
Failure to Verify Performance Claims
Suppliers may exaggerate torque ratings, efficiency, or service life based on ideal lab conditions. Real-world performance can differ significantly due to lubrication quality, alignment, or operating temperature. Always validate performance claims through independent testing or by requesting field data from existing customers.
Conclusion
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, independent quality verification, and attention to intellectual property compliance. Investing time in due diligence upfront can save significant costs and legal complications down the line. Prioritize transparency, documentation, and proven reliability over initial price savings.
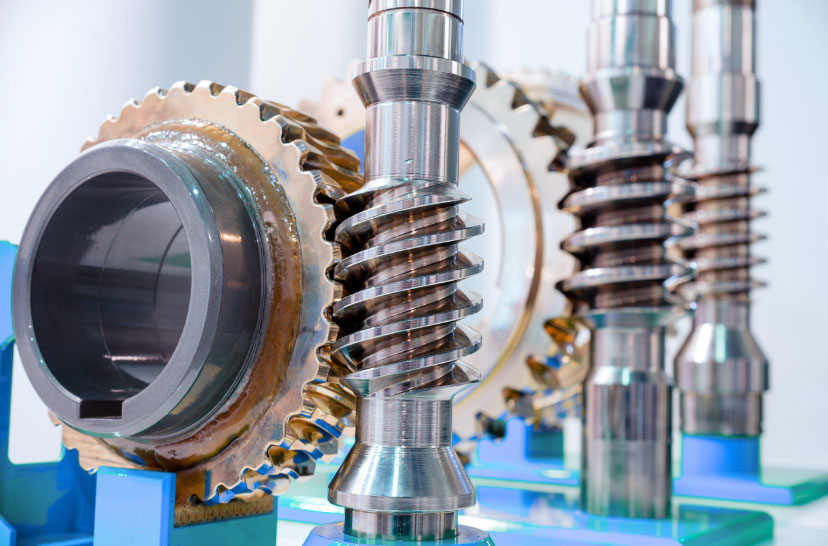
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Worm and Wheel Gearbox
Product Classification and HS Code
Identify the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for the worm and wheel gearbox to ensure accurate customs clearance. Typical classifications fall under Chapter 84 (Machinery and Mechanical Appliances). Common HS codes include 8483.40 (gearboxes and other speed changers) or 8483.90 (parts of gearboxes), depending on design and application. Confirm with local customs authorities or a trade compliance expert to avoid misclassification and potential delays.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Worm and wheel gearboxes must be securely packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use wooden crates or heavy-duty corrugated boxes with internal foam or custom inserts to immobilize the unit. Include protective coatings or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper to prevent rust, especially for international shipments exposed to humidity. Clearly label packages with orientation arrows, “Fragile,” and “Do Not Stack” as needed.
Transportation and Shipping Modes
Choose appropriate transportation modes (air, sea, or land) based on delivery timeline, cost, and destination. For sea freight, ensure compliance with IMDG Code if shipped in containers. For air freight, adhere to IATA regulations—verify weight and dimensional limits. Secure gearboxes to prevent shifting during transit, particularly for long-haul trucking or ocean containers.
Import/Export Documentation
Prepare essential documentation including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading (or air waybill), and certificate of origin. For certain countries, additional paperwork such as a Certificate of Conformity (CoC), CE marking documentation (for EU), or a Letter of Authorization may be required. Ensure all documents accurately describe the product and include correct HS codes.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Ensure gearboxes comply with destination country regulations. For the European Union, adherence to the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and provision of a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) is mandatory. In the U.S., follow OSHA and ANSI safety standards where applicable. Include required technical files, user manuals in local language, and safety labels (e.g., rotation direction, oil level markings).
Environmental and RoHS Compliance
Verify that materials used in the gearbox (e.g., lubricants, coatings, metals) comply with environmental directives such as the EU’s RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH. Provide documentation confirming the absence of restricted substances. For eco-sensitive regions, consider biodegradable lubricants and recyclable packaging materials.
Duty and Tax Considerations
Calculate applicable import duties, VAT, or GST based on the declared value and HS code. Utilize Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) where eligible to reduce tariffs—ensure proper Certificate of Origin is submitted. Account for additional fees such as customs processing, port handling, or anti-dumping duties if applicable.
Product Labeling and Marking
Label each gearbox with essential information: model number, serial number, manufacturer details, CE or other certification marks, input/output specifications, weight, and manufacturing date. Ensure labels are durable and legible, resistant to oil, moisture, and abrasion. Include multilingual warnings and handling instructions if shipping globally.
After-Sales and Warranty Logistics
Establish a support framework for returns, repairs, or replacements. Define warranty terms and conditions in compliance with local consumer laws (e.g., EU Consumer Rights Directive). Prepare Return Material Authorization (RMA) procedures and ensure spare parts availability to support long-term serviceability.
Recordkeeping and Audit Readiness
Maintain comprehensive records of all compliance documents, test reports, shipping manifests, and customs filings for a minimum of five years (or per local regulation). These records support audits, traceability, and dispute resolution during customs inspections or regulatory checks.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Worm and Wheel Gearbox:
Sourcing a worm and wheel gearbox requires a strategic evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, supplier reliability, and total cost of ownership. These gearboxes are particularly valued for applications requiring high torque output, compact design, and inherent self-locking capabilities, making them ideal for lifts, conveyors, material handling, and other industrial machinery.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include gear ratio, efficiency, backlash, material quality, environmental resistance, and compliance with industry standards. While worm gearboxes offer advantages such as smooth and quiet operation, their relatively lower efficiency compared to other gearbox types should be factored into long-term energy costs.
Selecting reputable suppliers with proven manufacturing capabilities, strong technical support, and timely delivery is critical to ensuring product performance and reliability. Additionally, evaluating options for customization, maintenance support, and warranty terms can enhance operational uptime and reduce lifecycle costs.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing decision—balancing performance needs with cost, quality, and service—will ensure the optimal integration of a worm and wheel gearbox into your system, supporting efficient and reliable operation over the long term.