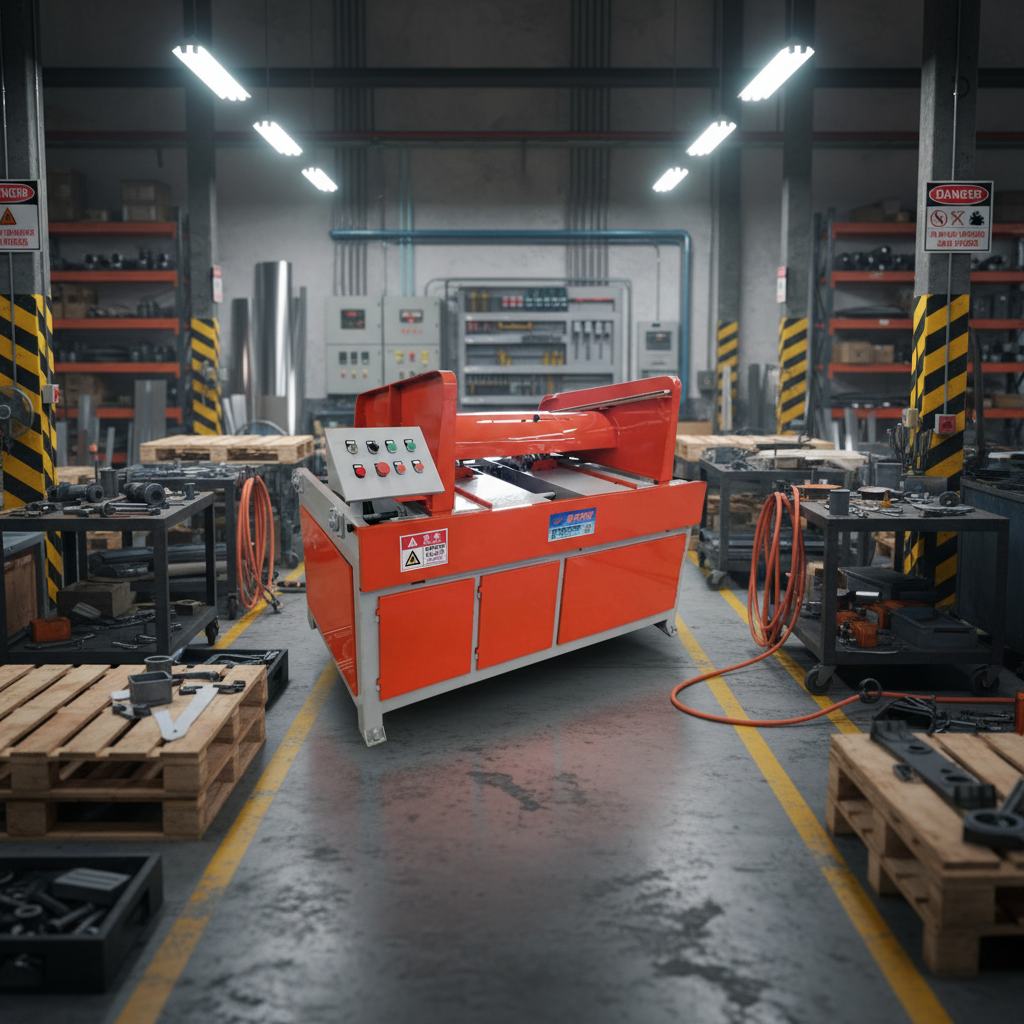
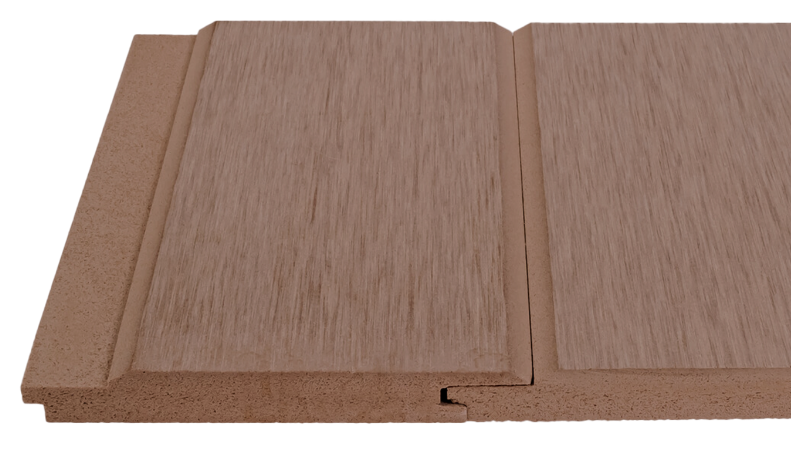
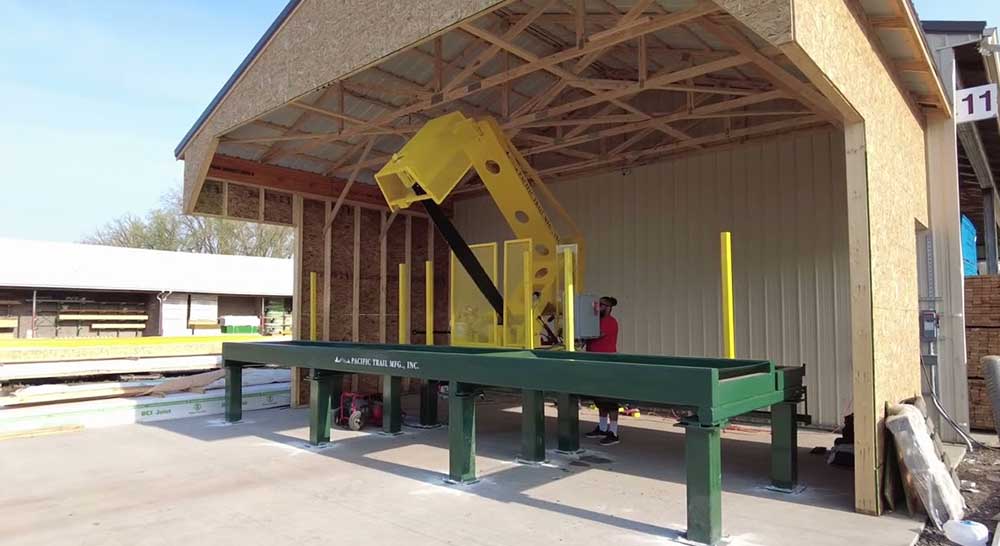
The global woodworking machinery market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand from construction, furniture manufacturing, and interior design sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global woodworking machinery market size was valued at USD 4.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. A key segment within this industry is precision cutting equipment, particularly wood groove cutting saws, which are essential for joinery, cabinetry, and flooring applications. As automation and CNC technology become more prevalent, manufacturers are focusing on innovation, accuracy, and efficiency. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and product reliability, the following nine companies have emerged as leading wood groove cutting saw manufacturers shaping the future of precision woodworking.
Top 9 Wood Groove Cutting Saw Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Charles G.G. Schmidt & Co.,Inc.
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cggschmidt.com
Key Highlights: During our 92 years of service to the woodworking industry, we have been the consistent source for the highest quality state-of-the-art tooling, as well as ……
#2 Ballew Saw and Tool, Amana, Onsrud, Freeborn, Freud, Dynabrade
Domain Est. 2003
Website: ballewsaw.com
Key Highlights: Ballew Saw and Tool, Amana, Onsrud, Freeborn, Freud, Dynabrade all industrial cutting tools in stock….
#3 Grooving
Domain Est. 2011
Website: dimartooling.com
Key Highlights: Saw Blades. Offering a comprehensive range of quality saw blades for all industrial applications has established Dimar as a global leader in this field….
#4
Domain Est. 1996
Website: fletcher-terry.com
Key Highlights: Equipment spare parts for Fletcher Cutters, AMP’s Underpinners and Saws, cutting blades and wheels, repair kits, and equipment accessories….
#5 Forrest Saw Blades
Domain Est. 1997
Website: forrestblades.com
Key Highlights: Serious woodworkers count on American-made Forrest saw blades for smooth, quiet cuts, every time… without splintering, scratching or tearouts….
#6 Whiteside Machine Company
Domain Est. 1999
Website: whitesiderouterbits.com
Key Highlights: Made from high quality steel and tipped with micro-grain carbide, our years of experience provides you a full line of router bits your workshop will cherish….
#7 V
Domain Est. 1999
Website: festool.com
Key Highlights: V-groove cutter · Disc groove cutter · Hinge location cutters/dowel drills · Profile cutter · Hand rail cutter · Edge router · Other routers….
#8 Woodline USA
Domain Est. 2002
Website: woodline.com
Key Highlights: Woodline USA carries thousands of carbide-tipped and solid carbide router bits, carbide-tipped shaper cutters, and many other woodworking tools and accessories….
#9 Saws
Domain Est. 2004
Website: festoolusa.com
Key Highlights: This illustrated guide will explain to you how you can saw and cut GFRP panels precisely and safely….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wood Groove Cutting Saw

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Wood Groove Cutting Saws
The wood groove cutting saw market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting end-user demands, and broader industry trends in woodworking and construction. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Increased Demand for Precision and Automation:
By 2026, the demand for high-precision groove cutting in cabinetry, flooring, and furniture manufacturing will intensify. This will fuel adoption of computer numerical control (CNC) groove cutting saws and automated sliding tables. Manufacturers will prioritize tools offering micron-level accuracy and repeatable performance to meet tight tolerances in modern designs, reducing waste and labor costs.
2. Growth in Cordless and Portable Solutions:
Advancements in lithium-ion battery technology will continue to enhance the power and runtime of cordless groove cutting saws. By 2026, these portable tools are expected to gain significant market share, especially among on-site contractors, custom installers, and DIY enthusiasts who value mobility and flexibility without sacrificing cutting depth or blade stability.
3. Integration with Smart Technology:
Smart features such as Bluetooth connectivity, mobile app integration, and digital depth/angle displays will become more common. These innovations allow users to store cutting profiles, receive maintenance alerts, and improve workflow efficiency—particularly appealing to professional workshops aiming for digital shop floor integration.
4. Focus on Dust Extraction and Operator Safety:
Regulatory standards and health awareness will push manufacturers to design groove cutting saws with superior dust management systems. By 2026, models featuring optimized dust ports, integrated vacuum compatibility, and improved blade guards will be standard, aligning with OSHA and EU safety directives and reducing long-term health risks.
5. Expansion in Engineered Wood Processing:
The rising use of engineered wood composites (e.g., MDF, plywood, LVL) in construction and furniture will require groove saws capable of clean, splinter-free cuts in abrasive materials. Blades with specialized carbide tips and optimized tooth geometry will see increased demand, and saws with adjustable RPM settings will be favored to handle material variability.
6. Sustainability and Eco-Design:
Environmental considerations will influence product design and materials. Expect more saws made with recycled components, energy-efficient motors, and packaging that minimizes plastic use. Consumers and B2B buyers alike will increasingly favor brands with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) commitments.
7. Regional Market Diversification:
While North America and Western Europe remain strong markets, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia—will experience accelerated growth due to urbanization and expanding woodworking industries. Localized production and region-specific product adaptations will be key strategies for global manufacturers.
In summary, by 2026, the wood groove cutting saw market will be defined by smarter, cleaner, and more adaptable tools that cater to both industrial efficiency and the needs of mobile professionals. Companies that innovate in automation, ergonomics, and sustainability will lead the competitive landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Wood Groove Cutting Saws (Quality and IP)
Sourcing wood groove cutting saws—whether for in-house manufacturing, resale, or integration into machinery—can be fraught with challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Avoiding these pitfalls is essential to ensure performance, reliability, legal compliance, and brand reputation.
Poor Material and Build Quality
One of the most frequent issues is receiving saws made from substandard materials or with inconsistent craftsmanship. Low-grade carbide tips, poorly tensioned blades, or inferior steel substrates lead to rapid wear, inaccurate cuts, and blade warping under heat. These flaws result in increased downtime, higher replacement costs, and compromised end-product quality.
Inconsistent Dimensional Accuracy
Many suppliers, especially low-cost manufacturers, fail to maintain tight tolerances in blade diameter, tooth geometry, and groove depth calibration. Inconsistent saws produce uneven grooves, affecting joint integrity in woodworking applications like tongue-and-groove flooring or cabinetry. This variability undermines precision and may necessitate post-processing or rework.
Lack of Performance Testing and Certification
Reputable saws undergo rigorous performance testing for heat resistance, RPM tolerance, and cutting efficiency. However, some sourced products lack verifiable test data or certifications (e.g., ISO, CE). Without these, buyers face increased risk of equipment failure, safety hazards, and non-compliance with regional safety standards.
Misrepresentation of Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate or falsify technical specifications—such as maximum RPM, kerf width, or recommended feed rates. This misrepresentation can lead to dangerous operating conditions, including blade disintegration or motor overload, especially when integrated into automated machinery.
Intellectual Property Infringement
A significant legal risk involves sourcing saws that imitate patented blade designs, tooth configurations, or proprietary coatings from established brands (e.g., Freud, DeWalt, or Leitz). Using or distributing such products—even unknowingly—can expose buyers to IP litigation, customs seizures, and reputational damage.
Unclear or Absent IP Documentation
Suppliers may fail to provide proof of IP ownership, design rights, or freedom-to-operate documentation. Without proper licensing or original design evidence, buyers assume full legal liability for infringement claims, which can halt production or result in costly settlements.
Supply Chain Transparency Gaps
Opaque supply chains make it difficult to trace a saw’s origin or verify the authenticity of components. Counterfeit or reconditioned blades may be passed off as new, particularly in regions with weak regulatory enforcement. This lack of traceability jeopardizes both quality assurance and compliance.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Warranty
Low-cost suppliers often provide minimal technical support, replacement parts, or warranty coverage. When issues arise, resolving them becomes time-consuming and expensive, especially if the supplier lacks local service centers or refuses responsibility for defective batches.
Overlooking Regulatory Compliance
Woodworking tools must meet regional safety and environmental standards. Saws that lack proper labeling, safety certifications, or compliance with directives like the EU’s Machinery Directive can be barred from import or sale, resulting in financial loss and logistical complications.
Failure to Conduct Supplier Audits
Relying solely on product samples or supplier claims without auditing manufacturing facilities increases the risk of quality and IP issues. On-site assessments help verify production capabilities, quality control processes, and IP compliance practices, reducing the likelihood of future disputes.
By recognizing and proactively addressing these common pitfalls, businesses can source wood groove cutting saws that meet both performance expectations and legal requirements, ensuring long-term operational success and market credibility.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wood Groove Cutting Saw
Product Classification and HS Code
The Wood Groove Cutting Saw is typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) Code 8467.21, which covers circular saw blades, whether or not with their own hand-operated driving mechanisms. Accurate classification is essential for determining import duties, taxes, and applicable trade regulations in the destination country. Always verify the specific HS code with local customs authorities as classifications may vary slightly by region.
Import/Export Regulations
Import and export of power tools like the Wood Groove Cutting Saw are subject to national and international trade regulations. Exporters must comply with export controls, including obtaining necessary licenses if shipping to restricted regions. Importers are responsible for meeting local requirements, such as product conformity assessments, customs declarations, and payment of applicable tariffs. Proper documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, must accompany all shipments.
Safety and Electrical Compliance
The Wood Grove Cutting Saw must comply with electrical safety standards relevant to the destination market. In the European Union, compliance with the CE marking directive (including Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU) is mandatory. In the United States, adherence to OSHA safety standards and UL certification (e.g., UL 62841 for hand-held motor-operated tools) is required. Products must include appropriate safety warnings, user manuals in the local language, and meet grounding and insulation requirements.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Packaging must ensure safe transportation and protect the saw from damage during transit. All units should be securely boxed with cushioning materials and labeled with essential information, including product name, model number, voltage, power rating, serial number, manufacturer details, and compliance marks (e.g., CE, UL). Hazard symbols, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”), and country of origin must be clearly displayed on the outer packaging.
Environmental and RoHS Compliance
The Wood Groove Cutting Saw must conform to environmental regulations such as the EU’s Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive 2011/65/EU, which limits the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous materials in electrical equipment. Additionally, compliance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives may require producers to register and support recycling programs. Similar regulations may apply in other regions, including China RoHS and California Proposition 65.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Shipments should comply with international transport standards, including IATA regulations for air freight and IMDG Code for sea transport if batteries are included. Use of sturdy, recyclable packaging materials is encouraged. Ensure correct classification for freight purposes, and consider insurance for high-value consignments. Coordinate with logistics partners to maintain temperature and humidity controls where necessary and avoid exposure to moisture.
Customs Clearance and Duties
Prepare all documentation in advance to facilitate smooth customs clearance. This includes a detailed commercial invoice, bill of lading or airway bill, packing list, and any required conformity certificates. Accurate valuation of goods is critical to avoid delays or penalties. Be aware of free trade agreements that may reduce or eliminate tariffs (e.g., USMCA, EU-South Korea FTA) and leverage them where applicable.
After-Sales and Warranty Compliance
Provide clear warranty terms in accordance with local consumer protection laws (e.g., EU Consumer Rights Directive, U.S. Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act). Maintain service and spare parts availability in target markets. Record customer data securely, complying with data protection laws such as GDPR or CCPA, especially when processing warranty claims or service requests.
Recordkeeping and Audit Readiness
Maintain comprehensive records of compliance documentation, test reports, certifications, shipping details, and import/export licenses for a minimum of five years. These records must be readily available for audits by regulatory authorities or certification bodies to demonstrate ongoing compliance with logistics and product safety requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing a wood groove cutting saw requires careful consideration of several key factors including cutting precision, blade quality, motor power, compatibility with different wood types and thicknesses, and overall durability. Whether for industrial production, woodworking workshops, or DIY projects, selecting the right groove cutting saw enhances efficiency, ensures clean and accurate grooves, and contributes to longer tool lifespan. Evaluating supplier reliability, after-sales support, and cost-effectiveness is equally important to ensure consistent performance and value for investment. By prioritizing quality and suitability for specific applications, businesses and craftsmen can make informed decisions that optimize productivity and achieve superior woodworking results.