The wire erosion process, also known as wire electrical discharge machining (wire EDM), has become a cornerstone technology in precision manufacturing, particularly in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and tool and die making. This non-traditional machining method enables the cutting of intricate shapes and hard metals with exceptional accuracy and minimal material stress, driving its adoption across high-tech manufacturing sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global wire EDM market was valued at USD 4.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7.2% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by rising demand for high-precision components and advancements in automation and CNC integration. Similarly, Grand View Research noted that increasing industrialization and the shift toward smart manufacturing are accelerating investments in advanced machining technologies, further expanding the wire erosion equipment market. As competition intensifies and innovation accelerates, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in delivering reliable, high-performance wire EDM solutions. Here are the top 9 wire erosion process manufacturers shaping the future of precision manufacturing.
Top 9 Wire Erosion Process Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Wire
Domain Est. 1999
Website: gfms.com
Key Highlights: From our wire cutting EDM machines and ultraprecise machining of miniaturized components down to high-speed electrical discharge and spark erosion processes …Missing: erosion ma…
#2 EDM
Website: sktechnology.de
Key Highlights: We produce the finest contours, cuts and corner radii using EDM technology. Depending on the component requirements, we use two processes: wire erosion and EDM….
#3 Electrical Discharge Machines
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mitsubishielectric.com
Key Highlights: Mitsubishi Electric Die-sinking EDMs and Wire-cut EDMs enhance productivity with high-speed and high-accuracy….
#4 Makino Electrical Discharge Machining
Domain Est. 1996
Website: makino.com
Key Highlights: Wire EDM machines are able to carefully remove excess material without exerting a strong cutting force and is most commonly used in mold and die manufacturing ……
#5 Fine Wire EDM
Domain Est. 1997
Website: edmdept.com
Key Highlights: Expert Fine Wire EDM services for micro-precision parts. We use micro diameter wire to create holes as small as 30 microns. Get a quote today!…
#6 Metal Fabrication Machinery
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mcmachinery.com
Key Highlights: MC Machinery Systems, a supplier of metal fabrication machines, provides EDM, milling, laser, press brake, finishing, and automation solutions….
#7 Electrical Discharge Machining Companies
Domain Est. 2000
Website: electricaldischargemachining.com
Key Highlights: Find the leading electrical discharge machining companies who produce custom products from various materials, including aluminum, steel, copper, and brass….
#8 EDM Wire Erosion
Domain Est. 2003
Website: qualitetch.com
Key Highlights: We can offer EDM wire erosion services to give the best accuracy possible, and for those metals whose chemical composition make photo etching impossible….
#9 Wire EDM
Domain Est. 2019
Website: fathommfg.com
Key Highlights: Wire EDM · Build Complex Parts with Tight Tolerances · Precision Cutting of Tough Materials · Cost-Effective Manufacturing Option….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wire Erosion Process
H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Wire Erosion Process
The wire erosion process, also known as Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (Wire EDM), is expected to witness significant evolution and expansion by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technology, rising demand for precision components, and the integration of Industry 4.0 principles. This analysis explores key market trends shaping the Wire EDM landscape in 2026 across technological innovation, industry adoption, regional dynamics, and competitive developments.
-
Technological Advancements and Automation
By 2026, Wire EDM machines are anticipated to feature increased levels of automation, including AI-driven process optimization, real-time monitoring, and closed-loop feedback systems. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors enables predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics, reducing downtime and improving machining accuracy. Additionally, advancements in power supply technology—such as next-generation pulse generators—are enhancing cutting speeds and surface finish quality, making Wire EDM more competitive with conventional machining processes. -
Rising Demand in Aerospace, Medical, and Automotive Sectors
The aerospace and defense industries remain major drivers for Wire EDM adoption due to the need for high-precision machining of hard-to-cut materials like titanium, Inconel, and other superalloys. In the medical sector, the production of intricate surgical instruments and implants requires micron-level tolerances, which Wire EDM delivers effectively. The electric vehicle (EV) market is also contributing to growth, particularly in the manufacturing of precision components for motors and battery systems. -
Growth in Asia-Pacific and Emerging Markets
The Asia-Pacific region, led by China, India, and Japan, is projected to dominate the Wire EDM market by 2026 due to rapid industrialization, government initiatives supporting advanced manufacturing, and the expansion of high-tech supply chains. Local production of EDM machines and decreasing equipment costs are making the technology more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), further fueling market penetration. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt energy-efficient machining solutions. Modern Wire EDM systems are being designed with reduced power consumption, improved dielectric fluid recycling, and minimal waste generation. These eco-friendly innovations are becoming a competitive differentiator and align with global green manufacturing trends. -
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Collaborations
Major players such as Mitsubishi Electric, Makino, Sodick, and GF Machining Solutions are intensifying R&D investments and forming strategic partnerships with software providers and automation firms. The convergence of CAD/CAM systems with EDM-specific software is streamlining programming and setup, reducing human error and cycle times. Additionally, the rise of hybrid machining centers—combining Wire EDM with milling or grinding—is creating new opportunities for complex part fabrication. -
Challenges and Barriers
Despite positive momentum, challenges remain. High initial investment costs, skilled labor shortages, and the need for specialized maintenance can hinder adoption, particularly in developing economies. Furthermore, competition from alternative non-traditional machining methods, such as laser and waterjet cutting, necessitates continuous innovation to maintain Wire EDM’s edge in precision and material versatility.
Conclusion
In 2026, the Wire Erosion Process market is poised for robust growth, underpinned by technological innovation, expanding industrial applications, and a shift toward smart, sustainable manufacturing. Companies that leverage automation, invest in user-friendly interfaces, and adapt to regional market needs will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this high-precision segment of advanced manufacturing.
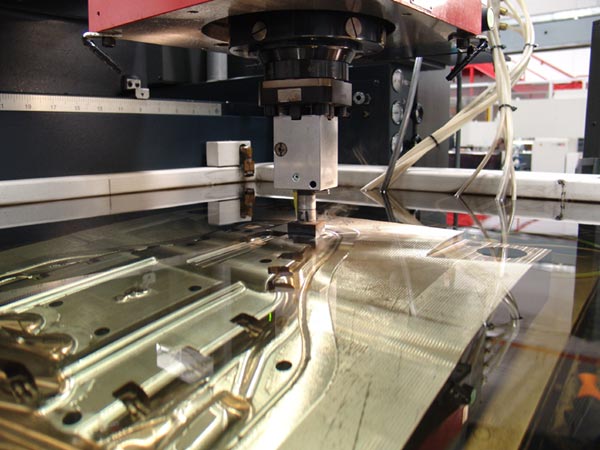

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Wire Erosion Processes (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing wire erosion (also known as Wire Electrical Discharge Machining or Wire EDM) services can offer precision and complexity benefits, but it comes with significant risks related to quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to project delays, compromised part performance, and legal exposure.
Inadequate Quality Assurance and Process Control
One of the most frequent issues when outsourcing wire erosion is inconsistent part quality due to poor process oversight by the supplier. Wire EDM requires precise control of parameters such as wire tension, dielectric fluid condition, spark frequency, and positioning accuracy. If the vendor lacks robust quality systems—such as regular machine calibration, documented process validation, or in-process inspection—dimensional inaccuracies, surface finish defects, or taper errors may occur. Additionally, inexperienced operators may not recognize subtle signs of wire breakage or machine drift, leading to undetected flaws. Without clear acceptance criteria and third-party inspection reports, buyers risk receiving non-conforming parts that compromise downstream assembly or performance.
Insufficient Verification of Machine Capability and Maintenance
Not all wire EDM machines deliver the same level of precision or reliability. Sourcing from vendors without verifying their equipment specifications—such as machine age, manufacturer (e.g., Makino, Mitsubishi, Sodick), axis resolution, and automation features—can result in mismatched capabilities. Older or poorly maintained machines may introduce variability, especially for tight-tolerance or high-accuracy applications. Furthermore, some suppliers may overload their machines with high-volume jobs, increasing wear and reducing accuracy. Buyers must audit machine logs, maintenance schedules, and perform first-article inspections to ensure that the supplier’s infrastructure supports the required quality standards.
Weak Intellectual Property Protection Agreements
Wire erosion often involves machining complex or proprietary components, making IP protection critical. A major pitfall is proceeding without a comprehensive Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) or IP ownership clause tailored to manufacturing services. Some suppliers may retain digital toolpaths, CAM files, or inspection data, creating risks of unauthorized replication or reverse engineering. In jurisdictions with lax IP enforcement, this risk increases significantly. Additionally, shared work environments or subcontracting without consent can expose designs to unintended parties. Buyers must ensure contracts explicitly state that all process data, tooling, and designs remain the client’s exclusive property and outline secure data handling and destruction protocols.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
High-integrity applications (e.g., aerospace, medical devices) require full traceability of machining parameters, material certifications, and inspection records. A common sourcing mistake is accepting parts without standardized documentation packages. Without logs of cutting paths, wire types, or post-process validation, it becomes difficult to troubleshoot failures or validate compliance with industry standards (e.g., AS9100, ISO 13485). This lack of traceability also complicates root cause analysis and liability assignment if defects emerge in the field.
Overlooking Subcontracting and Supply Chain Transparency
Some EDM service providers outsource work to third parties without informing the client, especially during peak demand. This undermines quality control and IP security, as the original supplier may have no oversight over the subcontractor’s practices. Buyers should require transparency about whether work will be performed in-house and include contractual prohibitions against unauthorized subcontracting. Uncontrolled supply chains can also introduce inconsistencies in materials, processes, and quality standards.
Failure to Align on Tolerances and Surface Finish Expectations
Miscommunication about technical requirements is a frequent source of disputes. Wire EDM can achieve micron-level accuracy, but only if specifications are clearly defined and mutually understood. Vague drawings, ambiguous surface finish callouts (e.g., “smooth finish”), or missing GD&T annotations lead to rework or rejected parts. Buyers should ensure that all tolerances, corner radii, and surface roughness values (e.g., Ra, Rz) are explicitly stated and confirmed by the supplier before production begins.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through rigorous supplier vetting, detailed contracts, and clear technical specifications—companies can leverage wire erosion services effectively while safeguarding quality and intellectual property.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wire Erosion Process
This guide outlines the essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for implementing and operating a Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (Wire EDM) process in a manufacturing environment. Adhering to these standards ensures operational efficiency, personnel safety, environmental protection, and regulatory compliance.
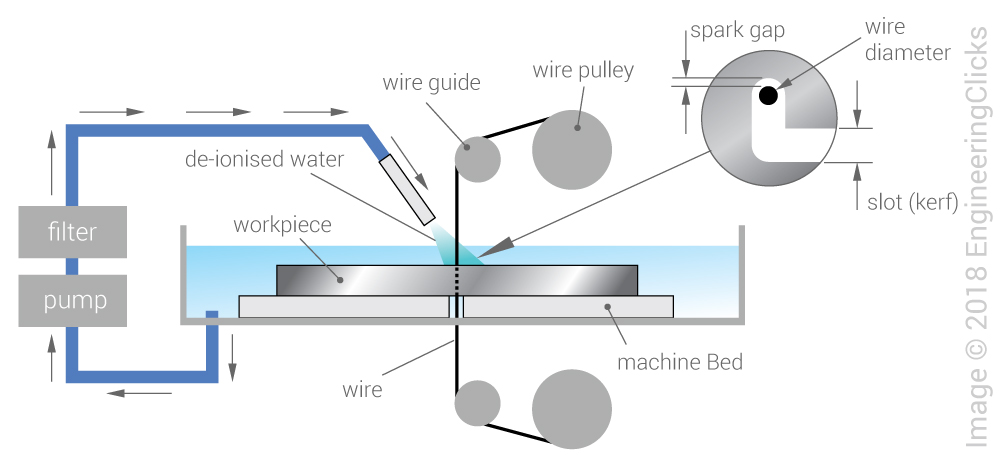
Process Overview and Equipment Requirements
Wire EDM utilizes a thin, electrically charged wire to cut conductive materials with high precision through controlled spark erosion. Key equipment includes the Wire EDM machine, dielectric fluid system, wire spooling mechanism, CNC control unit, and filtration system. Proper installation requires stable power supply (typically 3-phase), adequate floor space with vibration isolation, climate-controlled environment (18–24°C), and sufficient ventilation. Equipment must comply with ISO 230 (machine accuracy testing) and IEC 60204-1 (safety of machinery – electrical equipment).
Material Handling and Inventory Management
Conductive raw materials (e.g., tool steels, titanium, inconel) must be stored in a dry, clean environment to prevent oxidation or contamination. Incoming materials should be inspected for dimensional accuracy and material certification (e.g., mill test reports per ASTM or EN standards). Wire electrodes (usually brass or coated zinc) require shelf-life monitoring and storage away from moisture. Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system and track wire consumption to optimize procurement. Use non-magnetic handling tools to prevent debris adhesion.
Dielectric Fluid Management and Environmental Compliance
Deionized water is the primary dielectric fluid in Wire EDM. Maintain proper resistivity (typically 10–20 µS/cm) and filtration to ensure cutting stability and surface finish. Used dielectric fluid may contain fine metal particulates and must be treated per local environmental regulations before disposal. Facilities must comply with EPA (or equivalent) standards for wastewater discharge and hazardous waste classification (e.g., RCRA in the U.S.). Implement closed-loop filtration systems where possible to minimize fluid consumption and waste. Conduct regular fluid analysis and maintain logs for audit purposes.
Operational Safety and Personnel Training
Operators must be trained in machine operation, emergency shutdown, and personal protective equipment (PPE) use, including safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing. High-voltage components and moving wire spools present electrical and mechanical hazards. Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures per OSHA 1910.147 must be followed during maintenance. Conduct regular safety drills and maintain machine guarding as per ISO 13849 (safety of machinery – control systems). Training records and certifications must be documented and up to date.
Quality Assurance and Process Documentation
All Wire EDM processes must follow documented work instructions aligned with ISO 9001 quality management standards. Maintain inspection records, including first article inspections (FAI), in-process checks, and final dimensional verification using calibrated equipment (e.g., CMM, optical comparators). Monitor key process parameters (wire tension, feed rate, spark frequency) and log data for traceability. Non-conforming parts must be quarantined and dispositioned per corrective action procedures (e.g., 8D reports).
Regulatory and Industry Standards Compliance
Ensure compliance with relevant local and international regulations, including:
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910 (U.S. workplace safety)
– REACH and RoHS (EU chemical and hazardous substance restrictions)
– ISO 14001 (environmental management systems)
– ITAR/EAR (if machining controlled defense or dual-use materials)
Maintain a compliance audit trail, including equipment certifications, calibration records, training logs, and waste disposal manifests. Conduct internal audits at least annually.
Maintenance and Equipment Calibration
Establish a preventive maintenance (PM) schedule for Wire EDM machines, including wire guides, filters, pumps, and power supply components. Follow manufacturer-recommended intervals and document all maintenance activities. Calibration of CNC controls, tension sensors, and measuring instruments must be traceable to national standards (e.g., NIST) and performed at defined intervals (typically annually). Use accredited calibration service providers and retain certificates for compliance audits.
Waste Disposal and Recycling Procedures
Metal sludge generated from dielectric fluid filtration is classified as hazardous waste in many jurisdictions due to heavy metal content. Collect sludge in approved containers and dispose of through licensed hazardous waste handlers with proper manifests. Recycle spent brass wire through certified metal recyclers. Maintain disposal records for a minimum of five years to comply with environmental and financial auditing requirements.
Shipping and Final Product Handling
Finished Wire EDM components must be cleaned, dried, and packaged to prevent corrosion during transit. Use anti-corrosive VCI (vapor corrosion inhibitor) packaging for long-term storage or international shipping. Label packages with proper handling instructions and material certifications if required. Follow export regulations (e.g., Incoterms) and customs documentation requirements for international logistics.
Conclusion for Sourcing Wire Erosion Process:
The wire erosion process, also known as wire-cut Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), is a highly precise and reliable manufacturing method ideal for shaping hard conductive materials with complex geometries and tight tolerances. When sourcing this process, it is essential to partner with a supplier that possesses advanced machinery, technical expertise, quality certifications, and a proven track record in delivering consistent results.
Key considerations in sourcing include the supplier’s capability to handle specific material types and part complexities, adherence to quality standards (such as ISO certifications), turnaround time, cost-effectiveness, and post-processing services. Additionally, effective communication, engineering support, and the ability to scale production are crucial for long-term success.
In conclusion, outsourcing wire erosion to a competent and reliable vendor enables businesses to achieve high-precision components without the capital investment in specialized equipment. A strategic sourcing approach ensures optimal performance, reduced lead times, and enhanced product quality, ultimately supporting competitiveness in industries such as aerospace, medical devices, tool and die manufacturing, and automotive engineering.