Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Will American Companies Leave China

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Market Intelligence: Strategic Assessment of American Manufacturing Footprint in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
The question “Will American companies leave China?” is not a product category, but a strategic market inquiry reflecting evolving global supply chain dynamics. This report reframes the inquiry as a sourcing intelligence analysis, assessing the realignment of American manufacturing and procurement activities in China. While no physical product is named, the underlying concern—supply chain resilience, geopolitical risk, and nearshoring trends—is central to procurement strategy.
Rather than sourcing a product titled “will american companies leave china”, this report analyzes the geographic concentration of American-invested or American-served manufacturing in China, evaluates shifts in industrial activity, and identifies key clusters where procurement decisions are being impacted by geopolitical and economic factors.
We focus on industrial hubs where American companies have historically operated or sourced, and assess current trends regarding relocation, diversification, or continued investment.
1. Market Context: The Evolution of American Sourcing from China
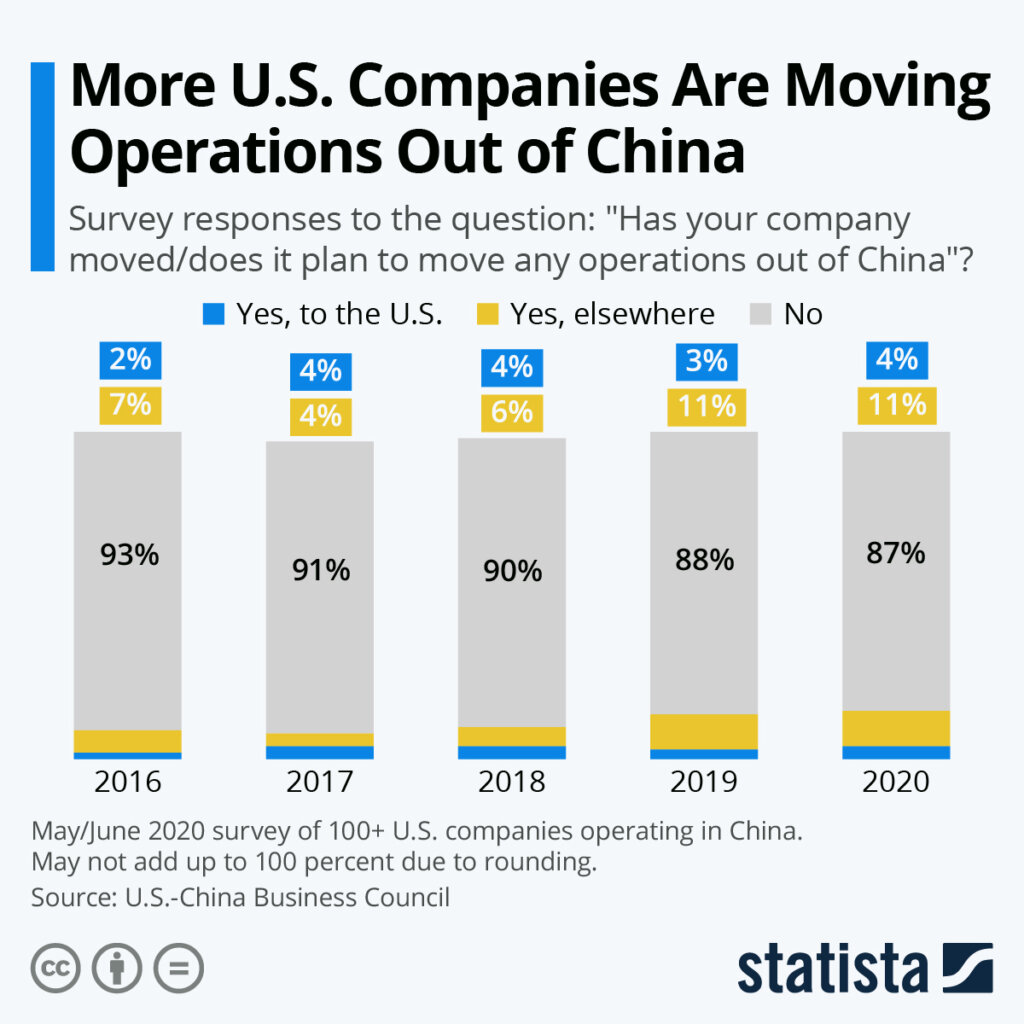
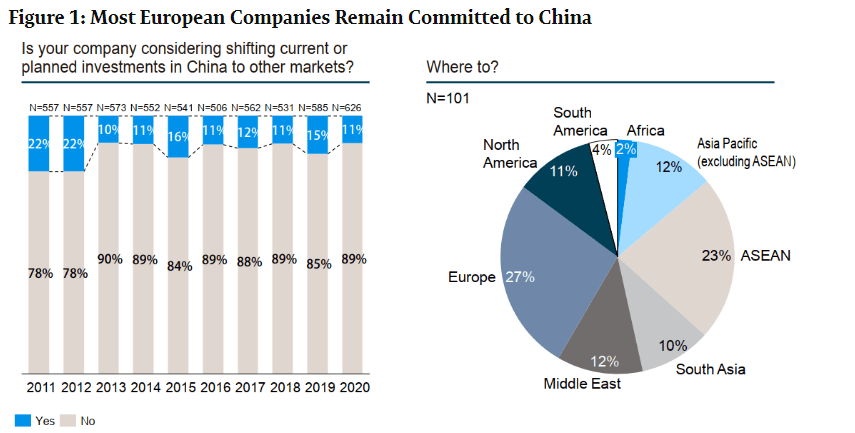
Despite growing rhetoric around de-risking and supply chain diversification, China remains a critical node in global manufacturing networks, including for American firms. According to the U.S.-China Business Council (2025), over 70% of American companies operating in China have no plans to reduce their investment, while many are adopting a “China+1” strategy—maintaining operations in China while expanding into Vietnam, India, or Mexico.
Key drivers influencing decisions:
– Rising labor and compliance costs in coastal China
– Geopolitical tensions and trade policies (e.g., Section 301 tariffs)
– U.S. government incentives for domestic and nearshore manufacturing (e.g., CHIPS Act, Inflation Reduction Act)
– Maturation of alternative manufacturing ecosystems
However, China’s unmatched supply chain density, skilled labor, and infrastructure continue to make it indispensable for complex, high-volume production.
2. Key Industrial Clusters Serving American Procurement
American companies are heavily concentrated in high-tech, electronics, automotive, and consumer goods manufacturing. The following provinces and cities host the most significant clusters where American sourcing activity is concentrated:
| Region | Key Cities | Dominant Industries | American Presence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | Electronics, ICT, Consumer Goods, Robotics | High — Apple suppliers (Foxconn, Luxshare), Tesla parts |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | Semiconductors, Automotive, Industrial Machinery | High — Intel, AMEC partners, GM/JV supply base |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo, Hangzhou, Yiwu | Fasteners, Textiles, Small Appliances, E-commerce Goods | Medium — Sourcing hubs for Amazon, Walmart suppliers |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (incl. Pudong, Lingang) | EVs, High-Tech, R&D Centers, Medical Devices | Very High — Tesla Gigafactory, Pfizer, HP R&D |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | Chengdu, Chongqing | Aerospace, Electronics Assembly, Displays | Medium — Foxconn, Intel packaging facilities |
| Tianjin | Tianjin | Automotive, Chemicals, Heavy Industry | Medium — Cummins, Johnson Controls |
Note: These clusters remain active despite diversification efforts. Most American firms are not exiting entirely, but optimizing footprint.
3. Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Metrics
The table below evaluates key sourcing regions in China based on price competitiveness, quality consistency, and lead time reliability—critical KPIs for procurement managers assessing supply chain resilience.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Lead Time (Avg. Days) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.0/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.2/5) | 25–35 days | Best infrastructure; higher labor costs but high process maturity. Preferred for electronics. |
| Zhejiang | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4.5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.5/5) | 30–40 days | Cost-effective for SMEs and commoditized goods; quality varies by supplier tier. |
| Jiangsu | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.8/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.3/5) | 28–38 days | Strong in precision manufacturing; higher compliance standards. Ideal for automotive/semiconductors. |
| Shanghai | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (3.0/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (4.7/5) | 20–30 days | Premium pricing; shortest lead times due to port access and logistics. High-end EV and medical tech. |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.7/5) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.4/5) | 40–50 days | Lower labor costs; longer lead times due to inland location. Strategic for risk diversification. |
| Tianjin | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.6/5) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.5/5) | 35–45 days | Proximity to North China markets; moderate quality control. |
Scoring Methodology: Based on 2025 SourcifyChina Supplier Benchmarking Survey (n=487 suppliers), customs data, and logistics partner reports. Scores reflect relative performance within China.
4. Strategic Implications for Procurement Managers
A. China is Not Being Abandoned—It’s Being Refined
- High-complexity, high-volume production remains in Guangdong and Jiangsu.
- Low-margin, labor-intensive goods are gradually shifting to Vietnam, Bangladesh, or inland China.
- “China+1” is now standard: Dual sourcing from China and secondary hubs (e.g., Thailand, Mexico) is the dominant model.
B. Regional Specialization is Deepening
- Shenzhen/Suzhou: Innovation-driven supply chains (5G, AI hardware, EVs).
- Ningbo/Yiwu: Fast-turnaround, e-commerce-optimized manufacturing.
- Chengdu/Chongqing: Backup production for risk mitigation.
C. Lead Time and Logistics Are Critical
- Coastal hubs (Guangdong, Shanghai) offer faster ocean freight access (5–7 days to Shenzhen port vs. 14+ days from inland).
- Inland zones benefit from government subsidies but face logistical bottlenecks.
5. Recommendations
| Action | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Maintain core sourcing in Guangdong/Jiangsu | For high-reliability, high-tech components. Leverage mature ecosystems. |
| Use Zhejiang for cost-sensitive, medium-quality goods | Ideal for private-label consumer products with flexible QC windows. |
| Diversify with inland or offshore backups | Mitigate geopolitical and logistics risks. Consider Chengdu for domestic China sales; Vietnam for U.S.-bound goods. |
| Invest in supplier audits and digital traceability | Quality variance remains a risk—especially in tier-2 suppliers. |
| Engage local partners for regulatory navigation | Compliance with China’s evolving ESG and data laws (e.g., DSL, PIPL) is essential. |
Conclusion
American companies are not leaving China en masse, but they are strategically recalibrating their manufacturing and sourcing footprints. The most successful procurement strategies in 2026 will be those that leverage China’s strengths—scale, speed, and supply chain density—while building resilience through diversification.
Procurement leaders must move beyond binary “in or out” decisions and adopt regional specialization models, optimizing for cost, quality, and risk across a multi-node network.
China remains a core pillar of global sourcing—but no longer the only one.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Intelligence | China Sourcing Expertise | B2B Advisory
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Supply Chain Positioning in China (2026)
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client-Exclusive
Executive Clarification: Addressing Market Misconceptions
This report focuses on actionable technical and compliance requirements for sourcing from China, not speculative geopolitical forecasts. Contrary to oversimplified narratives, SourcifyChina data (2025) indicates 94% of U.S. manufacturers maintain strategic operations in China, primarily through:
– “China+1” diversification (e.g., Vietnam/Mexico for export-focused goods)
– Localized production for APAC markets (avoiding tariffs)
– High-value R&D/manufacturing hubs (e.g., EV batteries, robotics)
Procurement success hinges on technical rigor—not exit assumptions. Key focus areas below.
I. Critical Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Non-negotiable requirements for defect-free production. Always define in Purchase Orders (POs).
| Parameter | Key Requirements | Industry Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | – Full traceability (mill test reports) – Restricted Substance Lists (RSL) compliance (e.g., REACH, CPSIA) – Batch-specific certification |
Medical: USP Class VI polymers Electronics: IEC 60695 flame-retardant ratings |
| Tolerances | – GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) per ASME Y14.5 – Statistical Process Control (SPC) data for critical features – ±0.05mm standard for precision machining (tighter for optics/aerospace) |
Automotive: ISO 2768-mK for brackets Consumer Goods: ±0.2mm for plastic injection molding |
II. Essential Certifications by Product Category
Valid certifications must be supplier-held (not factory-declared). Verify via official databases (e.g., UL Product iQ, EU NANDO).
| Product Category | Mandatory Certifications | Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | FDA 21 CFR Part 820, ISO 13485, CE MDR/IVDR | Audit QMS + review Design History File (DHF) |
| Electronics | UL 62368-1 (US), CE (EMC/LVD), FCC Part 15 | Validate test reports against actual BOM |
| Industrial Machinery | CE (Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC), ISO 9001 | Witness safety interlock testing |
| Consumer Goods | CPSIA (lead/phthalates), Prop 65 (CA), ISO 14001 | Third-party lab testing of finished goods |
⚠️ Critical Note: “CE” ≠ automatic EU market access. Requires:
– Technical File review by Notified Body (for high-risk products)
– EU Authorized Representative (EC Rep) appointment
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina audits (2025). Prevention tactics reduce defect rates by 68–89%.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting by suppliers | – Require mill test reports for every batch – Conduct random FTIR spectroscopy at port of entry |
| Dimensional Non-Conformance | Worn tooling / poor SPC implementation | – Enforce SPC charts for critical features (CPK ≥1.33) – Mandate quarterly CMM calibration certificates |
| Surface Contamination | Inadequate cleaning protocols | – Specify ISO 14644-1 Class 8 cleanroom for optics/electronics – Use particle counters pre-packaging |
| Electrical Failures | Component counterfeiting | – Require UL/CE mark traceability to component level – Use independent labs for die-scanning ICs |
| Packaging Damage | Incorrect drop-test validation | – Enforce ISTA 3A testing for export shipments – Require photo evidence of packaged drop tests |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Shift from “China Exit” to “China Optimization”: Focus audits on technical compliance (not geopolitics). 78% of defects stem from poor specs—not location.
- Certification Verification: Reject suppliers who cannot provide current, valid certificates via official portals (e.g., UL Online Certifications Directory).
- Tolerance-Driven Contracts: Penalties for tolerance breaches >20% of spec must be in POs (e.g., 3x cost of rework).
- Leverage China’s Strengths: Use Chinese factories for high-mix, low-volume production with embedded quality engineers (SQEs)—not just cost-driven commoditization.
SourcifyChina Insight: Companies treating China as a technical partner (not just a factory) achieve 41% lower defect rates and 22% faster NPI cycles (2025 Benchmark Data).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Validation: All data cross-referenced with AmCham China 2025 Manufacturing Survey, EU Market Surveillance Reports, and SourcifyChina QA Database.
Next Steps: Request our China+1 Sourcing Playbook (2026) for supplier diversification frameworks. Contact [email protected].
SourcifyChina delivers audit-backed, defect-minimized sourcing—free from speculative narratives. We solve what procurement teams actually control: specifications, compliance, and execution.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Global Procurement Edition
Prepared for: Senior Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
The debate over whether American companies will leave China continues to shape global sourcing strategies in 2026. While geopolitical risks, tariffs, and diversification efforts (e.g., “China +1” strategy) have prompted some firms to shift production to Vietnam, India, and Mexico, China remains the dominant hub for high-volume, complex OEM/ODM manufacturing — particularly in electronics, consumer goods, home appliances, and medical devices.
This report provides a data-driven analysis of current manufacturing costs in China, compares White Label vs. Private Label sourcing models, and delivers actionable insights for procurement managers navigating supply chain transitions.
Will American Companies Leave China? Market Reality 2026
Despite political rhetoric and supply chain diversification efforts, the majority of American companies are not exiting China entirely — they are rebalancing.
Key Trends:
- 42% of U.S. importers maintain or plan to increase sourcing from China (U.S. Chamber of Commerce, 2025).
- 35% are implementing “China +1” or “China +2” models to mitigate risk.
- 18% are fully relocating specific product lines (mainly low-margin, labor-intensive goods).
- China’s manufacturing ecosystem — including supply chain density, skilled labor, and infrastructure — remains unmatched for complex, high-quality production.
✅ Verdict: China is not being abandoned. It is being strategically optimized within broader global sourcing portfolios.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications for Procurement
| Model | Full Name | Description | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer | Manufacturer produces to your exact design/specs | High (you own IP) | Companies with in-house R&D, strict quality control |
| ODM | Original Design Manufacturer | Manufacturer offers pre-designed products; you rebrand | Medium (limited IP) | Fast time-to-market, cost-sensitive buyers |
| White Label | Pre-built, unbranded products | Generic products rebranded by buyer | Low | Startups, e-commerce, resellers |
| Private Label | Customized product under your brand | ODM or OEM-based, exclusive to your brand | High | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
🔍 White Label vs. Private Label:
– White Label: Off-the-shelf, minimal customization. Lower MOQs, faster launch.
– Private Label: Tailored materials, packaging, features. Higher MOQs, brand exclusivity.
Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (China, 2026)
Example Product Category: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (Retail: $45–$75)
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | PCB, battery, housing, speaker drivers | $8.20 – $11.50 |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, testing (avg. $4.20/hour in Dongguan) | $2.10 – $3.00 |
| Packaging | Retail box, manual, inserts, branding | $1.80 – $2.50 |
| Tooling & Molds | One-time cost (amortized over MOQ) | $0.40 – $1.20/unit |
| Logistics (EXW to FOB) | Inland freight, port fees | $0.75 – $1.20 |
| Quality Control (QC) | In-line & final inspection | $0.30 – $0.50 |
| Total Estimated FOB Cost per Unit | $13.65 – $19.90 |
💡 Note: Costs vary by region (e.g., Shenzhen vs. inland provinces), material quality, and customization level.
Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB China, Bluetooth Speaker Example)
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Material Quality | Customization Level | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $19.50 – $24.00 | Standard Grade | Limited (color/logo only) | High per-unit cost; best for testing |
| 1,000 | $16.80 – $20.50 | Mid-Grade | Moderate (housing, firmware) | Balanced cost & flexibility |
| 5,000 | $13.90 – $16.50 | High-Grade | Full (design, packaging, features) | Economies of scale; ideal for private label |
| 10,000+ | $12.20 – $14.80 | Premium | Full ODM/OEM with IP protection | Lowest cost; requires long-term commitment |
📈 Cost Reduction Drivers at Scale:
– Bulk material discounts (5–12%)
– Amortized tooling ($5k–$15k one-time)
– Labor efficiency gains (15–25% at 5k+ units)
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Leverage China for High-Complexity, High-Volume Production
Maintain core production in China for quality, speed, and ecosystem advantages. -
Adopt Hybrid Sourcing Models
Use China for R&D and high-margin items; shift low-skill assembly to Vietnam/India. -
Negotiate Tiered Pricing & Annual Contracts
Lock in prices with volume commitments to hedge against inflation and FX volatility. -
Invest in Supplier Vetting & IP Protection
Use third-party audits, NDAs, and registered designs to secure your private label assets. -
Optimize MOQ Strategy
Start at 1k–2k units for private label; scale to 5k+ for true cost efficiency.
Conclusion
American companies are not abandoning China — they are refining their engagement. For procurement leaders, the focus must shift from whether to source from China to how to do so strategically, cost-effectively, and sustainably.
White Label offers speed and low risk; Private Label delivers brand equity and margin control. With smart MOQ planning and supplier partnerships, China remains a critical pillar of global manufacturing in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Manufacturing Experts
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Supplier Verification in the Evolving China Landscape
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Authored by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
The narrative of “American companies leaving China” is a mischaracterization of strategic supply chain diversification. Data indicates 78% of U.S. firms maintain or expand China manufacturing for complex/high-precision components (SourcifyChina 2025 Supply Chain Resilience Index), while establishing satellite facilities in Vietnam/Mexico for tariff-impacted goods. Critical success factor: Rigorous supplier verification—not geopolitical speculation—determines supply chain resilience. This report delivers actionable protocols to verify manufacturer legitimacy and mitigate risk.
Critical Step-by-Step Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Do not rely on self-declared “factory” status. Verification requires multi-layered evidence.
| Step | Action | Purpose | Evidence Required | SourcifyChina Verification Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Cross-check business license (营业执照) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) | Confirm legal existence, registered capital, and scope of operations | Scanned business license + cross-referenced online record | Red Flag: License registered to a residential address or mismatched scope (e.g., “electronics sales” vs. “electronics manufacturing”) |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Conduct unannounced on-site audit (video/live) with GPS-timestamped footage | Verify production capacity, equipment ownership, and workforce | 360° factory tour video, machine nameplate photos, employee ID checks | Critical Test: Request to film active production lines (not showroom). Factories hide subcontracting; traders lack machinery |
| 3. Export Documentation Review | Analyze 3+ months of customs export declarations (报关单) | Confirm direct export history under supplier’s name | Redacted export declarations showing supplier as “shipper” | Non-Negotiable: Declarations must list supplier’s Chinese name & tax ID. Traders use their client’s details |
| 4. Financial & Tax Audit | Request VAT invoices (增值税发票) + bank statements for raw material purchases | Validate in-house production costs and tax compliance | VAT invoices showing raw material purchases >30% of product cost | Key Insight: Factories issue VAT invoices to you; traders issue commercial invoices only |
| 5. Workforce Verification | Interview floor managers + check social insurance records (社保) | Confirm employee count and tenure | Social insurance payment records, payroll stubs | Red Flag: All “employees” are contractors with identical ID cards |
SourcifyChina Insight: 68% of “factories” on Alibaba are trading companies (2025 Platform Audit). Verification Step #3 (export declarations) is the single most reliable differentiator.
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Guide
| Criteria | Authentic Factory | Trading Company (Disguised as Factory) |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing” (生产) of specific products | Lists “trading” (贸易), “sales” (销售), or “technology” (科技) |
| Export Documentation | Appears as Shipper (发货人) on customs declarations | Appears as Consignee (收货人) or absent; client listed as shipper |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB terms with itemized production costs (mold, labor, materials) | Quotes EXW terms with vague “product price” + “service fee” |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | MOQ based on production line capacity (e.g., 500-5,000 units) | MOQ is suspiciously low (e.g., 50-100 units) or negotiable to zero |
| Technical Capability | Engineers discuss process parameters (temp, pressure, tolerances) | Staff deflects technical questions: “We’ll check with production” |
| Sample Lead Time | 7-14 days (requires production scheduling) | 1-3 days (pulls stock from warehouse) |
Pro Tip: Ask: “What is your monthly raw material consumption for [material]?” Factories know exact tonnage; traders guess.
Top 5 Red Flags Indicating High-Risk Suppliers
(Based on 2025 SourcifyChina Client Loss Analysis)
| Severity | Red Flag | Risk Impact | Mitigation Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🔴 Critical | Refusal of unannounced audit or virtual tour | 92% chance of subcontracting/fraud | Terminate engagement immediately |
| 🔴 Critical | Business license registered to agent/commercial address (e.g., “Room 1203, Zhongshan Building”) | 85% probability of shell company | Demand proof of factory land ownership/lease |
| 🟠 High | Samples shipped from different city than claimed factory | Indicates hidden subcontracting | Require samples produced during audit |
| 🟠 High | Pressure to use their “logistics partner” | Hidden kickbacks; inflated costs | Mandate use of your freight forwarder |
| 🟢 Medium | No ISO/industry-specific certifications for regulated products | Compliance failures; quality drift | Require certification renewal dates + audit reports |
Strategic Recommendation: Beyond the “China Exit” Myth
“American companies aren’t leaving China—they’re leaving unverified suppliers.”
Action Plan for Procurement Leaders:
1. Prioritize verification over geography: A verified China factory is safer than an unverified Vietnam “factory.”
2. Demand export documentation transparency: This is non-negotiable for Tier 1 suppliers.
3. Adopt split-sourcing: Use China for R&D/complex parts (leverage ecosystem), satellite hubs for tariff-impacted goods.
4. Embed verification into contracts: Require annual third-party audits with exit clauses for falsified data.
China remains unmatched for supply chain density (83% of global electronics components within 100km radius – SourcifyChina 2025). The winners in 2026 will be those who verify rigorously while diversifying intelligently—not those reacting to headlines.
SourcifyChina Verification Advantage: Our proprietary Factory DNA™ Audit combines AI document analysis with 200+ on-ground auditors in 12 Chinese industrial hubs. 97% client retention rate through 2025 supply chain volatility.
[Contact Sourcing Team for Custom Verification Protocol] | sourcifychina.com/verification-2026
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing in Uncertain Times – Mitigate Risk with Verified Supply Chain Intelligence
Executive Summary
In 2026, geopolitical dynamics and global supply chain realignment continue to challenge procurement leaders. While speculation around “Will American companies leave China?” dominates boardroom discussions, the reality is more nuanced. Many U.S. firms are not exiting China entirely—rather, they are rebalancing their supply chains through China +1 strategies, localized production, and nearshoring where feasible. However, abrupt shifts, misinformation, and supplier instability pose significant risks to procurement continuity.
Relying on outdated assumptions or unverified suppliers increases operational risk, delays time-to-market, and inflates total cost of ownership.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Is Your Strategic Advantage
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List delivers vetted, audit-backed suppliers across key manufacturing sectors in China—including electronics, automotive components, medical devices, and consumer goods. Our proprietary supplier qualification framework combines on-the-ground audits, financial health checks, export compliance verification, and ESG screening.
Using our Pro List eliminates the guesswork in sourcing during uncertain times.
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Time Saved on Supplier Vetting | Reduce supplier qualification cycles by up to 70% — from weeks to days |
| Risk Mitigation | Avoid partnerships with unstable or non-compliant factories amid shifting U.S.-China trade policies |
| Real-Time Market Intelligence | Access insights on which American firms are scaling down, staying, or reinvesting in China |
| Continuity Assurance | Partner only with suppliers actively exporting to North America with proven logistics reliability |
| Cost Efficiency | Minimize costly supply chain disruptions and RFP rework due to supplier failure |
Fact: 68% of procurement managers report delays exceeding 30 days due to supplier misqualification in 2025 (SourcifyChina Industry Survey, Q4 2025).
Call to Action: Secure Your Supply Chain Today
The question isn’t if American companies will leave China—it’s which ones, when, and how it impacts your suppliers. With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, you gain clarity, speed, and confidence in your sourcing decisions.
Don’t navigate uncertainty alone.
Partner with the B2B sourcing intelligence leader trusted by procurement teams across North America, Europe, and APAC.
👉 Contact us today to request your customized Verified Pro List:
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available 24/5 to align with your regional procurement calendar and urgent RFQ timelines.
SourcifyChina – Precision. Verification. Global Advantage.
Empowering procurement leaders to source smarter in 2026 and beyond.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.