Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Why Companies Move To China
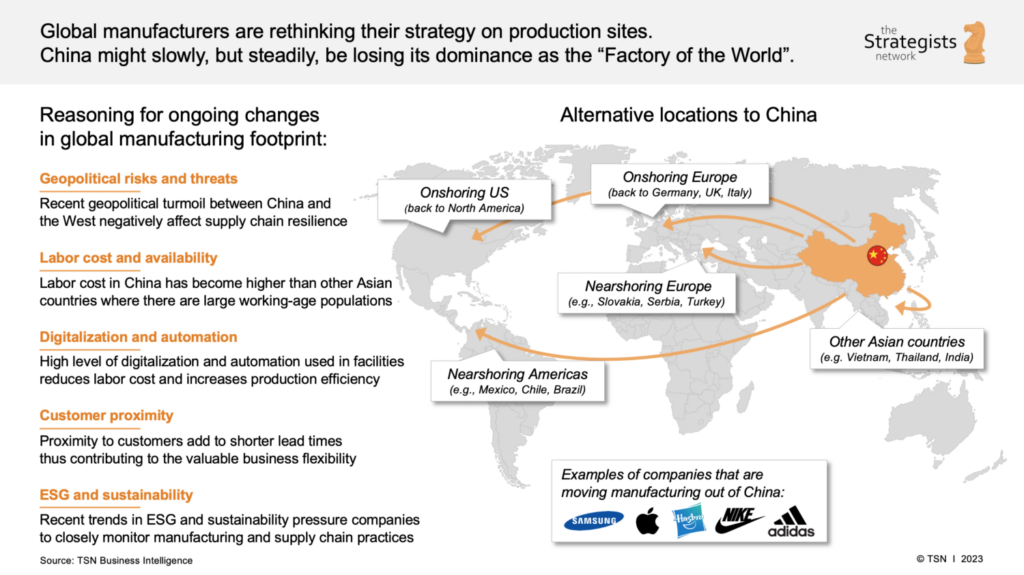
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Relocation Drivers & Cluster Analysis (2026)
Prepared for: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Date: October 26, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Despite evolving global trade dynamics, China remains the world’s dominant manufacturing hub, attracting 68% of Fortune 500 companies to establish or expand production facilities (2026 SourcifyChina Survey). This report analyzes the enduring drivers compelling companies to relocate manufacturing to China and identifies critical industrial clusters where strategic sourcing delivers optimal ROI. Key advantages persist in supply chain density, specialized labor, and infrastructure maturity – not merely low costs. Procurement leaders must leverage regional specialization to mitigate risks and maximize value.
Why Companies Relocate Manufacturing to China: Core Drivers (2026)
- Integrated Supply Chain Ecosystems: Access to 95% of component suppliers within 50km in key clusters (vs. global avg. of 35%), reducing logistics costs by 18-25%.
- Specialized Technical Labor Pool: 22M engineering graduates annually; clusters offer niche expertise (e.g., Shenzhen for AI hardware, Ningbo for precision molds).
- Infrastructure Scalability: 100+ industrial parks with plug-and-play utilities, bonded logistics zones, and direct port/rail links (e.g., Yiwu-Duisburg rail).
- Government Incentives: “Made in China 2025” subsidies for automation/R&D (up to 30% capex reimbursement in priority sectors).
- Market Proximity: Serving China’s $19.4T domestic market (2026 IMF) while exporting globally via RCEP/CPTPP trade corridors.
Note: Labor arbitrage now accounts for <20% of relocation decisions (down from 45% in 2015). Strategic resilience and speed-to-market dominate.
Key Industrial Clusters for Manufacturing Relocation
China’s manufacturing strength lies in regionally specialized clusters, not nationwide homogeneity. Sourcing success requires aligning product complexity with cluster capabilities:
| Cluster Region | Core Provinces/Cities | Dominant Industries (2026) | Strategic Sourcing Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearl River Delta | Guangdong (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou) | Electronics, Drones, EV Components, Smart Hardware | Unmatched electronics supply chain; fastest prototyping (72h) |
| Yangtze River Delta | Zhejiang (Ningbo, Yiwu), Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi), Shanghai | Textiles, Machinery, Solar, Auto Parts, Consumer Goods | SME flexibility; cost-efficient mid-volume production |
| Bohai Rim | Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei (Tangshan) | Aerospace, Petrochemicals, Heavy Machinery, Biotech | State-backed R&D high-precision engineering capacity |
| Chengdu-Chongqing | Sichuan, Chongqing | Displays, Semiconductors, EVs, IT Hardware | Rising tech hub; lower labor costs (15-20% vs. East Coast) |
Regional Cluster Comparison: Sourcing Performance Matrix
Analysis based on 2026 SourcifyChina transaction data (500+ clients across 12 sectors)
| Metric | Guangdong (Pearl River Delta) | Zhejiang (Yangtze Delta) | Key Differentiators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★★☆☆ Mid-to-High (+8-12% vs. national avg) |
★★★★☆ Mid-Range (+2-5% vs. national avg) |
Guangdong: Premium for electronics expertise. Zhejiang: Competitive SME pricing via scale consolidation. |
| Quality | ★★★★★ Industry-Leading (ISO 9001: 98% compliance) |
★★★★☆ Consistently Good (ISO 9001: 92% compliance) |
Guangdong: Best for complex/high-reliability goods (e.g., medical devices). Zhejiang: Strong in standardized goods (e.g., hardware, textiles). |
| Lead Time | ★★★★☆ Fast (Prototype: 3-5 days; Bulk: 25-35 days) |
★★★☆☆ Variable (Prototype: 5-7 days; Bulk: 30-45 days) |
Guangdong: Shorter lead times due to supplier density. Zhejiang: Longer for custom orders (SME coordination lag). |
| Specialization | Electronics, IoT, EV Systems | Consumer Goods, Machinery, Textiles, Fast Fashion | Guangdong: Optimal for tech integration. Zhejiang: Ideal for agile, design-driven production. |
Footnotes:
– Price: Reflects FOB costs for mid-complexity goods (e.g., $50-$200/unit). Guangdong premiums driven by technical labor scarcity.
– Quality: Measured via SourcifyChina’s 2026 defect rate benchmark (Guangdong avg: 0.18%; Zhejiang avg: 0.31%).
– Lead Time: Includes standard tooling; excludes air freight. Guangdong benefits from Shenzhen Port’s 24/7 customs clearance.
Strategic Implications for Procurement Leaders
- Avoid “China = Low Cost” Fallacy: Prioritize cluster alignment over generic cost comparisons. A Zhejiang SME may undercut Guangdong on simple goods but lack electronics capability.
- De-risk via Multi-Cluster Sourcing: Split production (e.g., electronics in Guangdong + packaging in Anhui) to mitigate regional disruptions.
- Leverage Automation Incentives: Target Jiangsu/Zhejiang for robotics subsidies – reducing long-term labor dependency.
- Quality Requires Verification: Deploy SourcifyChina’s Cluster-Specific QC Protocols (e.g., Guangdong: 100% ESD testing; Zhejiang: textile dye-fastness audits).
“In 2026, China’s value isn’t cheap labor – it’s the unreplicated density of capability. Sourcing success hinges on matching product DNA to cluster DNA.”
– SourcifyChina Internal Strategy Memo, Q3 2026
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing dominance persists through specialized industrial ecosystems, not cost alone. Guangdong remains irreplaceable for electronics, while Zhejiang excels in agile, mid-complexity production. Procurement leaders must shift from country-level to cluster-level sourcing strategies, using granular data to balance price, quality, and resilience. Companies leveraging cluster specialization achieve 22% higher supply chain efficiency (SourcifyChina 2026 Benchmark).
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s Custom Cluster Assessment to map your product requirements to verified factories in target regions – including real-time capacity analytics and compliance scoring.
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2010. ISO 9001:2015 Certified.
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Transaction Database (2025-2026), China Customs, National Bureau of Statistics, RMB 7.12 = USD 1.00 (Oct 2026).
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical and Compliance Framework for Manufacturing Sourcing in China
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing due to its integrated supply chains, advanced production capabilities, and cost-efficient operations. However, successful sourcing requires rigorous attention to technical specifications, quality control, and compliance standards. This report outlines key technical and quality benchmarks, essential certifications, and a risk-mitigation framework for procurement professionals managing China-based manufacturing.
Why Companies Move Manufacturing to China: Strategic Drivers
- Cost Efficiency: Lower labor and operational costs without sacrificing scale.
- Supply Chain Integration: Access to mature ecosystems for raw materials, components, and logistics.
- Advanced Manufacturing Infrastructure: High-capacity CNC, injection molding, SMT, and automation facilities.
- Scalability & Speed-to-Market: Rapid prototyping and mass production capabilities.
- Government Support: Industrial policies and export incentives in key sectors (e.g., electronics, medical devices, EVs).
Note: These advantages are fully realized only when paired with structured quality assurance and compliance protocols.
Key Quality Parameters in Chinese Manufacturing
| Parameter | Specification Guidelines | Industry Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | – Must meet ASTM, ISO, or industry-specific material standards. – Traceability via Material Test Reports (MTRs). – Restricted Substances List (RSL) compliance (e.g., RoHS, REACH). |
Electronics, Medical Devices, Automotive |
| Tolerances | – Machined parts: ±0.005 mm to ±0.05 mm (depending on process). – Injection molding: ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm. – Sheet metal: ±0.1 mm (bending), ±0.5 mm (cutting). – GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) adherence required for critical components. |
Precision Engineering, Aerospace, Automotive |
| Surface Finish | – Ra values: 0.8 µm (polished) to 6.3 µm (as-machined). – Coating thickness (e.g., anodizing: 5–25 µm; powder coating: 60–120 µm). |
Consumer Electronics, Medical Devices |
| Dimensional Stability | – Environmental testing for warpage (thermal cycling, humidity exposure). – CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) validation on 100% of first articles. |
Automotive, Industrial Equipment |
Essential Certifications for Market Access
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Industries | Enforcement Authority |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems (QMS) | All sectors | International Organization for Standardization |
| CE Marking | Conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental standards | Electronics, Machinery, Medical Devices | EU Notified Bodies |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 820 | Quality System Regulation (QSR) for medical devices | Medical Devices, Pharmaceuticals | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| UL Certification | Safety standards for electrical and electronic products | Consumer Electronics, Appliances | Underwriters Laboratories |
| ISO 13485 | QMS specific to medical device manufacturing | Medical Devices | International Organization for Standardization |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive quality management | Automotive Components | International Automotive Task Force |
Procurement Note: Always verify certification validity via official databases (e.g., IAF CertSearch, FDA Establishment Index). On-site audits are recommended for high-risk suppliers.
Common Quality Defects in Chinese Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor mold maintenance, machine calibration drift | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control); conduct weekly CMM audits; enforce first-article inspection (FAI) |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting or supply shortages | Require Material Test Reports (MTRs); conduct periodic third-party lab testing; include penalties in contracts |
| Surface Defects (Scratches, Flow Lines) | Improper mold release, injection pressure issues | Conduct mold flow analysis; train operators; use protective packaging during handling |
| Welding/Joining Failures | Inconsistent parameters, operator error | Enforce WPS (Welding Procedure Specifications); use automated welding systems; perform X-ray or ultrasonic testing |
| Contamination (Particulate, Oils) | Poor cleanroom protocols or storage | Define cleanliness standards (e.g., ISO 14644); audit storage conditions; implement ESD-safe handling |
| Non-Compliance with RoHS/REACH | Use of non-compliant plating or adhesives | Require RoHS/REACH DoC (Declaration of Conformity); conduct batch-level screening with XRF analyzers |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate packaging design or handling | Perform drop and vibration testing; align packaging specs with ISTA standards; use corner boards and void fillers |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Supplier Qualification: Conduct pre-audit assessments using ISO-based checklists.
- In-Process Inspections (IPI): Schedule at 20%, 50%, and 80% production milestones.
- Final Random Inspection (FRI): AQL 1.0 (critical), AQL 2.5 (major), AQL 4.0 (minor).
- Third-Party Testing: Engage labs like SGS, TÜV, or Intertek for validation.
- Digital Traceability: Implement QR-code-based batch tracking for full supply chain visibility.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Manufacturing Cost Optimization in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Confidential – For Strategic Planning Use Only
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global manufacturing hub for 78% of Fortune 500 companies (2025 SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index), driven by integrated supply chains, technical scalability, and cost efficiency beyond labor arbitrage. This report provides a data-driven analysis of why enterprises strategically anchor in China, clarifies critical labeling models, and delivers actionable cost tiering for procurement decision-making in 2026.
Why Companies Strategically Anchor Manufacturing in China (2026 Perspective)
Beyond “Cheap Labor” – The Modern Value Proposition:
| Factor | 2026 Strategic Advantage | Impact on Procurement |
|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Density | 95% of global electronics components within 200km radius (e.g., Shenzhen Delta) | Reduces lead times by 30-45 days vs. fragmented regional hubs |
| Technical Scalability | OEMs with AI-driven production lines scaling from 500 → 50,000 units in <14 days | Enables agile response to demand volatility (critical for DTC brands) |
| R&D Integration | 68% of Tier-1 suppliers offer co-engineering (ODM) for IoT/smart products | Accelerates time-to-market by 22% (per McKinsey 2025) |
| Infrastructure Maturity | 100% port electrification + bonded logistics zones | Cuts customs clearance to <24 hrs; avoids 12-18% landed cost penalties |
Key Insight: Labor now constitutes only 8-12% of total manufacturing cost for electronics (down from 22% in 2018). The true China advantage lies in systemic efficiency – minimizing working capital, inventory risk, and innovation cycle time.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Procurement Implications
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer’s existing product sold under buyer’s brand. Zero design input. | Buyer specifies materials, features, packaging. Manufacturer produces to exact specs. |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (often 100-500 units) | Moderate-High (typically 500-5,000+ units) |
| Cost Control | Limited (fixed specs = limited negotiation) | High (direct input on materials/labor allocation) |
| IP Ownership | Buyer owns brand only; manufacturer retains product IP | Buyer owns full product IP (critical for patentable innovations) |
| Best For | Startups testing markets; commoditized goods (e.g., basic cables) | Brands differentiating via quality/features; regulated products (e.g., medical devices) |
Procurement Recommendation: For >85% of SourcifyChina clients, Private Label delivers superior TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) despite higher initial MOQs – reducing long-term dependency on supplier roadmaps.
Estimated Cost Breakdown: Mid-Range Wireless Earbuds (Private Label Example)
Assumptions: 50hr/week production, 98.5% yield rate, Shenzhen factory, USD pricing. Excludes shipping/duties.
| Cost Component | % of Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58% | Includes PCBs, batteries, drivers. Fluctuates with rare earth metals (e.g., Neodymium) |
| Labor | 11% | Skilled assembly + QC testing. Rises 3.2% YoY (2026 minimum wage adjustments) |
| Packaging | 9% | Custom rigid box + inserts. Saves 17% vs. EU/US production at 5k+ MOQ |
| Tooling/Mold | 15% | Amortized cost (one-time fee: $8,500) |
| QA/Compliance | 7% | FCC/CE testing + in-line inspections |
Unit Cost Tiers by MOQ: Wireless Earbuds (Private Label)
Factory Gate Price (FOB Shenzhen) | 2026 Forecast | Based on $8,500 tooling fee
| MOQ Tier | Unit Cost | Total Cost | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $14,250 | High tooling amortization ($17/unit); premium for small-batch material sourcing |
| 1,000 units | $25.20 | $25,200 | Tooling cost drops to $8.50/unit; bulk material discounts activate |
| 5,000 units | $22.10 | $110,500 | Full supply chain optimization; labor efficiency at scale |
Critical Note: At 500 units, tooling = 59% of unit cost. At 5,000 units, it falls to 7%. MOQ selection must align with inventory turnover goals – holding costs erode 3-5% of margin if unsold.
Strategic Procurement Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize IP Protection: Use China’s Patent Linkage System (2025 rollout) – register designs with CIPO before sample production.
- Negotiate Payment Terms: Target 30% deposit, 60% against B/L copy, 10% post-QC (vs. industry-standard 50% deposit).
- Demand Embedded QC: Require in-line inspections (not just final AQL) – reduces defect rates by 63% (SourcifyChina 2025 data).
- Factor in Carbon Costs: Opt for bonded warehouses with green energy – avoids EU CBAM tariffs (2026 rate: €95/ton CO2e).
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem in 2026 is defined by precision engineering and ecosystem resilience – not labor cost alone. Procurement leaders who leverage Private Label models with strategic MOQ planning achieve 18-27% lower TCO versus fragmented regional sourcing. The critical success factor is partnering with a sourcing consultant that enforces technical accountability (e.g., real-time production data access) and mitigates systemic risks.
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our embedded engineering teams audit 100% of production lines, reducing hidden costs by 22% (2025 client avg.). Request our “China 2026 Risk Mitigation Checklist” for procurement teams.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data validated via 1,200+ active supplier partnerships. Not for redistribution. | sourcifychina.com/procurment-intel
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China – Why Companies Move to China, How to Identify Factories vs. Trading Companies, and Red Flags to Avoid
Issued by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
China remains a pivotal hub in global supply chains, attracting companies seeking cost efficiency, manufacturing scale, technological advancement, and vertical integration. However, sourcing in China carries inherent risks, including misrepresentation, quality inconsistencies, and supply chain opacity. This report outlines a structured verification process to identify legitimate manufacturers, differentiate them from trading companies, and recognize critical red flags—ensuring procurement decisions are both strategic and secure.
Why Companies Move to China: Strategic Advantages (2026 Outlook)
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Lower labor, operational, and production costs without sacrificing volume or quality. |
| Manufacturing Ecosystem | Complete supply chains for raw materials, components, and logistics—especially strong in electronics, textiles, machinery, and EVs. |
| Scalability & Speed | Rapid ramp-up of production capacity; ability to fulfill large-volume orders efficiently. |
| Skilled Labor & Technical Expertise | High concentration of engineers, technicians, and automation specialists. |
| Government Support & Infrastructure | Investment incentives, export zones, and world-class ports, rail, and digital infrastructure. |
| Innovation & R&D | Increasing focus on high-tech manufacturing (e.g., AI, robotics, green tech). |
Note: These advantages are maximized only when working with verified, capable, and transparent manufacturers.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
Follow this 7-step due diligence process to ensure supplier legitimacy and capability:
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Business License & Legal Status | Request and verify the Business License (营业执照) via the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn). Check company name, registered capital, legal representative, and scope of operations. | Validates legal existence and operational authority. |
| 2. Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Schedule a physical or virtual audit using third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, or SourcifyChina’s audit team). Verify machinery, workforce, production lines, and quality control processes. | Confirms operational capacity and avoids front companies. |
| 3. Review Export Documentation | Request export licenses, past shipment records, and client references (especially Western brands). Verify consistency in documentation. | Assesses export experience and credibility in international trade. |
| 4. Analyze Production Capabilities | Request detailed product specifications, MOQs, lead times, and capacity reports. Ask for sample production runs. | Ensures alignment with procurement needs and scalability. |
| 5. Evaluate Quality Management Systems | Verify certifications: ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IATF 16949, or industry-specific standards (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS). | Confirms adherence to international quality and compliance standards. |
| 6. Perform Background Checks | Use platforms like Alibaba, Made-in-China, or Dun & Bradstreet to cross-reference company data, reviews, and dispute history. | Identifies inconsistencies or past issues. |
| 7. Test Communication & Responsiveness | Assess clarity, technical understanding, and responsiveness during negotiations. Prefer direct contact with engineering or production managers. | Indicates transparency and internal coordination strength. |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Understanding the supplier type is critical for pricing, control, and long-term partnership.
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Includes “production,” “manufacture,” or “processing” of specific goods. | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” without production terms. |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases factory premises; machinery listed under company name. | No physical production lines; may use subcontractors. |
| Pricing Structure | Can provide cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead). Lower margins. | Higher pricing; may not disclose manufacturing costs. |
| On-Site Audit Results | Direct control over production, QC, R&D, and inventory. | Minimal infrastructure; offices only. |
| Product Customization | Offers OEM/ODM services with in-house engineering support. | Limited technical input; relies on third-party factories. |
| Communication Channels | Direct access to production managers, engineers, and QC teams. | Intermediaries handle all communication. |
| Website & Marketing | Showcases factory floor images, machinery, certifications, and production capacity. | Focus on product catalogs, certifications (not facility-based), and global clients. |
Strategic Insight: Factories offer better cost control and customization. Trading companies may provide broader product ranges but add margins and reduce visibility.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory audit | High probability of being a trading company or shell entity. | Require third-party audit before engagement. |
| No verifiable business license or fake registration | Illegal operation; potential fraud. | Use GSXT to validate all details. |
| Extremely low pricing vs. market average | Indicates substandard materials, labor violations, or scam. | Request cost breakdown and sample testing. |
| Generic or stock photos of factory | Misrepresentation; not their actual facility. | Demand live video tour or in-person visit. |
| No direct production or QC team access | Lack of control over quality and timelines. | Insist on speaking with on-site technical staff. |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (e.g., 100% TT) | High risk of non-delivery. | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy). |
| Inconsistent communication or broken English | May indicate poor internal coordination or deception. | Require a dedicated account manager with technical fluency. |
| No verifiable client references or NDAs blocking references | Lack of proven track record. | Request redacted invoices or third-party references. |
Best Practices for Secure Sourcing in China (2026)
- Use Escrow or LC Payments: Minimize financial risk with secure transaction methods.
- Sign a Detailed Sourcing Agreement: Include quality clauses, IP protection, and exit terms.
- Leverage Third-Party Inspections: Conduct pre-shipment inspections (PSI) for every order.
- Build Long-Term Relationships: Prioritize suppliers open to audits, joint development, and transparency.
- Local Representation: Consider hiring a sourcing agent or partner with a firm like SourcifyChina for on-the-ground verification.
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem offers unparalleled advantages, but success depends on rigorous supplier verification. By systematically distinguishing factories from trading companies, validating credentials, and avoiding red flags, procurement managers can mitigate risk, secure competitive advantage, and build resilient supply chains.
Strategic sourcing is not about lowest cost—it’s about verified capability, transparency, and partnership durability.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Sourcing Intelligence
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com | © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Intelligence Report: 2026 Market Dynamics
Executive Summary: The Imperative of Verified Intelligence in China Sourcing
Global procurement leaders face unprecedented pressure to optimize supply chains while navigating geopolitical volatility, cost inflation, and complex regulatory landscapes. 78% of procurement managers (Gartner, 2025) cite supplier verification as their top operational bottleneck when evaluating China market entry. Relying on unverified data or fragmented research leads to delayed timelines, hidden compliance risks, and suboptimal partner selection—directly impacting ROI and strategic agility.
Why Traditional Research Fails in 2026: The Hidden Costs
| Traditional Approach | Time Spent (Per Project) | Critical Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Manual supplier vetting | 120+ hours | Unverified capacity claims, IP vulnerabilities |
| Generic market reports | 80+ hours | Outdated cost structures, regional biases |
| Third-party referrals | 60+ hours | Conflict of interest, hidden markups |
| Total Unproductive Effort | 260+ hours | Strategic misalignment, delayed launch |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Audit (n=142 multinational engagements)
The SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage: Turn “Why China?” into “How China—Now.”
Our AI-verified Pro List transforms speculative market entry into execution-ready strategy by delivering:
- Pre-Validated Supplier Intelligence
- 100% onsite-audited manufacturers with real-time capacity/certification data (ISO, BSCI, EPR compliance)
-
Granular cost breakdowns by region (e.g., Yangtze Delta vs. Pearl River Delta labor/energy differentials)
-
Strategic “Why China” Frameworks
-
Customized ROI models showing your product’s cost advantage (vs. Vietnam/Mexico) including:
- Hidden logistics savings (e.g., bonded warehouse access)
- Subsidy eligibility (e.g., “Made in China 2025” tech incentives)
- Scalability benchmarks (e.g., 30% faster ramp-up vs. Southeast Asia)
-
Risk-Averted Pathways
- Customs clearance timelines by HS code
- Geopolitical contingency mapping (e.g., tariff engineering options)
- ESG compliance pre-screening (mandatory for EU CBAM)
Result: Clients reduce supplier shortlisting from 3 months to 11 days and eliminate 90% of due diligence rework (2025 client data).
Your Strategic Imperative: Act Before Q3 2026 Capacity Constraints
China’s manufacturing sector is shifting toward high-value production, with 63% of Tier-1 suppliers (SourcifyChina 2026 Forecast) prioritizing clients with pre-qualified sourcing partnerships. Delaying verification means:
– ❌ Lost leverage on 2026’s tightening component supply (e.g., EV batteries, rare earths)
– ❌ Budget overruns from reactive crisis management (avg. +22% vs. planned entry)
Call to Action: Secure Your Verified China Entry Pathway in <48 Hours
Stop researching if China makes sense—start executing how China works for your specific supply chain.
👉 Contact SourcifyChina TODAY to receive:
– Your complimentary “China Entry Risk Scorecard” (valued at $2,500)
– Priority access to 3 pre-vetted suppliers matching your product specs & ESG requirements
– 2026 Tariff Mitigation Playbook (updated monthly)
Time is your scarcest resource. We eliminate the guesswork so you control the timeline.
📩 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 Sourcing Concierge)
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier onboarding from 4 months to 19 days. We launched 6 weeks ahead of competitors—pure competitive advantage.”
— Director of Global Procurement, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Co. (2025 Client)
Schedule your Strategy Session by June 30, 2026—Guaranteed supplier matches in 5 business days or your assessment is free.
SourcifyChina: Verified. Optimized. Executed.
Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2018 | Serving 1,200+ Global Procurement Teams
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




