Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Wholesales From China

SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report: China Wholesale Manufacturing Landscape 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Strategy Teams
Date: January 15, 2026 | Confidential: For Client Strategic Planning Only
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for wholesale manufacturing, though 2026 sees strategic shifts driven by automation adoption, green compliance demands, and supply chain regionalization. Industrial clusters have evolved beyond cost arbitrage to offer integrated value chains with enhanced quality control and digital traceability. This report identifies high-potential clusters for bulk procurement, with critical analysis of regional trade-offs in price, quality, and lead time. Key 2026 Insight: Rising labor costs (+6.2% YoY) are accelerating automation in Tier-1 clusters, narrowing historical price gaps while improving baseline quality.
China’s Wholesale Manufacturing: 2026 Market Context
- Market Size: $2.8T wholesale export value (up 4.1% YoY), per China Customs 2025 data.
- Top Export Categories: Consumer Electronics (28%), Home & Kitchenware (19%), Textiles & Apparel (17%), Industrial Components (15%).
- Strategic Shifts:
- 73% of clusters now offer integrated e-commerce fulfillment (Alibaba 1688, Douyin B2B).
- EU CBAM and US UFLPA compliance now embedded in 68% of Tier-1 factories.
- “Near-China Sourcing” hubs (Vietnam, Malaysia) absorb 12% of low-margin orders, reinforcing China’s focus on mid-to-high value goods.
Key Industrial Clusters for Wholesale Sourcing (2026)
Optimized by product category, infrastructure, and compliance maturity
| Province/Region | Core Cities | Dominant Product Categories | Cluster Maturity (2026) | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | Electronics, Smart Hardware, Medical Devices, Precision Machinery | ★★★★★ (Mature) | R&D integration, automation rate >45%, fastest compliance |
| Zhejiang | Yiwu, Ningbo, Wenzhou | Daily Consumables, Toys, Stationery, Low-Voltage Hardware | ★★★★☆ (Advanced) | Lowest MOQs (units), e-commerce integration, 24/7 logistics |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou | Industrial Machinery, Auto Parts, Solar Components | ★★★★☆ (Advanced) | German/Japanese JV expertise, high-precision engineering |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Yantai | Textiles, Footwear, Chemicals, Seafood Processing | ★★★☆☆ (Developing) | Raw material access, port efficiency, cost-competitive |
| Fujian | Quanzhou, Xiamen | Sportswear, Ceramics, LED Lighting | ★★★☆☆ (Developing) | OEM-to-ODM transition, sustainable material innovation |
Note: Maturity Rating reflects automation readiness, compliance infrastructure, and supply chain resilience (Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Cluster Index).
Regional Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time Analysis
Critical trade-offs for bulk procurement decisions (Q1 2026 Benchmark)
| Factor | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Jiangsu | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★★☆☆ Mid-to-Premium (Electronics: 5-15% above national avg.) |
★★★★★ Most Competitive (Consumables: 8-12% below avg.) |
★★★★☆ Competitive Premium (Machinery: 3-8% above avg.) |
Zhejiang wins for commoditized goods; Guangdong for tech-integrated items. |
| Quality | ★★★★☆ Highest Consistency (ISO 13485/IEC common; <2% defect rate in electronics) |
★★★☆☆ Variable (Tier-1: Excellent; Tier-2: Moderate) (3-5% defect rate in low-cost items) |
★★★★☆ Precision Engineering Standard (German QA benchmarks; <1.5% defects in auto parts) |
Guangdong/Jiangsu for regulated/tech products; Zhejiang requires rigorous factory vetting. |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ 25-45 days (Complex goods; +7 days for compliance docs) |
★★★★★ Fastest Turnaround 15-30 days (stock items); 20-35 days (custom) |
★★★★☆ 22-40 days (Balanced speed/complexity) |
Zhejiang for urgent replenishment; Guangdong for quality-critical orders. |
| Best For | Tech hardware, regulated medical devices, high-value components | Mass-market consumables, promotional items, fast-fashion basics | Industrial machinery, EV components, renewable energy parts | Align cluster choice with product risk profile. |
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Audit Database (Q4 2025), China General Administration of Customs, McKinsey Supply Chain Index 2026.
★ Scale: 5★ = Most favorable for procurement objectives.
Critical Risk Considerations for 2026
- Compliance Escalation: 92% of EU-bound shipments now require carbon footprint documentation (per CBAM Phase II). Clusters like Jiangsu lead in green certification.
- Labor Shifts: Guangdong faces 4.3% skilled labor shortage; Zhejiang automates 200+ factories monthly. Factor in automation surcharges (avg. +3.5%).
- Logistics Volatility: Ningbo-Zhoushan Port congestion (+18% avg. dwell time in 2025) impacts Zhejiang lead times. Prefer Suzhou (Jiangsu) for air freight resilience.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
✅ Prioritize Cluster Alignment: Match product complexity to cluster strengths (e.g., Guangdong for IoT devices, Zhejiang for disposable packaging).
✅ Leverage Digital Tools: Use 1688.com’s “Verified Supplier” tier for Zhejiang orders to bypass quality variance.
✅ Build Dual Sourcing: Combine Guangdong (quality) + Zhejiang (speed) for critical SKUs to mitigate disruption risk.
✅ Demand Automation Proof: Require factory videos of robotic assembly lines for orders >5,000 units to lock in 2026 cost stability.
“In 2026, China sourcing success hinges on cluster intelligence—not just country-level strategy. Precision in regional selection drives 22% higher ROI.”
— SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Board
SourcifyChina Disclaimer: Data reflects verified supplier benchmarks as of December 2025. Projections account for PBoC policy shifts and global trade trends. Custom cluster analysis available for client-specific categories.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All Rights Reserved. Not for redistribution.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Wholesale Sourcing from China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a pivotal hub for wholesale manufacturing across industries such as consumer electronics, medical devices, industrial components, and home goods. Ensuring product quality and regulatory compliance is essential to mitigate risk, avoid customs rejections, and maintain brand integrity. This report outlines the key technical specifications, compliance benchmarks, and quality control best practices for sourcing wholesale products from China in 2026.
1. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
Material selection directly impacts product performance, safety, and longevity. Key considerations include:
– Traceability: Suppliers must provide material data sheets (MDS) and Certificates of Conformity (CoC).
– Purity & Grade: Use of virgin materials (e.g., food-grade plastics, medical-grade stainless steel) where required.
– Sustainability: Increasing demand for RoHS-compliant, REACH-regulated, and recyclable materials.
Tolerances
Precision tolerances are critical in engineering, electronics, and mechanical components:
– Dimensional Tolerances: Typically ±0.05 mm to ±0.5 mm depending on process (CNC, injection molding, etc.).
– Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T): Required for complex assemblies.
– Surface Finish: Ra (Roughness Average) values specified per application (e.g., Ra ≤ 1.6 µm for medical parts).
2. Essential Certifications
| Certification | Applicable Industries | Key Requirements | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU-bound electronics, machinery, PPE | Compliance with EU directives (e.g., EMC, LVD, RoHS, MDR) | Technical file, EU Declaration of Conformity, Notified Body involvement if needed |
| FDA Registration | Medical devices, food contact materials, cosmetics | Facility registration, 510(k) or PMA (if applicable), GMP compliance | FDA audit, submission of premarket notifications |
| UL Certification | Electrical products, components, appliances | Safety testing per UL standards (e.g., UL 60950, UL 1012) | Factory inspection, periodic testing, UL Mark licensing |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All manufacturing sectors | Quality Management System (QMS) implementation | Third-party audit, documentation review, process validation |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device manufacturers | QMS specific to medical devices | Required for CE MDR and many FDA submissions |
| BSCI / SMETA | Consumer goods, apparel | Ethical labor practices, workplace safety | Social audit by accredited body |
Note: Always request valid, unexpired certificates and verify authenticity via official databases (e.g., UL Online Certifications Directory, EU NANDO for CE).
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Description | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Parts out of specified tolerance due to mold wear or calibration drift | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct first-article inspection (FAI), and regular machine calibration |
| Material Substitution | Use of inferior or non-specified materials (e.g., recycled vs. virgin plastic) | Require material certifications, conduct lab testing (FTIR, GC-MS), and perform on-site audits |
| Surface Defects (e.g., warping, sink marks, flash) | Cosmetic or structural flaws in molded or machined parts | Optimize mold design, control injection parameters, and conduct mold flow analysis |
| Poor Electrical Safety | Insulation failure, overheating, non-compliant wiring | Enforce UL/IEC safety standards, perform Hi-Pot and leakage current testing |
| Packaging Damage | Crushed boxes, moisture ingress, incorrect labeling | Use ISTA-certified packaging tests, climate-controlled warehousing, and barcode verification |
| Labeling & Documentation Errors | Missing CE/FDA marks, incorrect language, missing warnings | Audit packaging artwork pre-production, align with local market regulations |
| Contamination (e.g., metal shavings, chemical residues) | Foreign particles affecting safety or performance | Enforce cleanroom protocols (for medical), use magnetic separators, and conduct residue testing |
4. Recommended Quality Assurance Protocols
- Pre-Production Audit (PPA): Validate materials, tooling, and process readiness.
- During Production Inspection (DUPRO): Monitor 20–50% into production for early defect detection.
- Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): AQL 2.5/4.0 sampling per ISO 2859-1.
- Third-Party Lab Testing: Conduct biocompatibility, EMC, or mechanical stress tests as needed.
- Supplier Scorecarding: Track performance on quality, on-time delivery, and compliance.
Conclusion
Successfully sourcing wholesale products from China in 2026 requires a structured approach to technical specifications, certification compliance, and proactive defect prevention. Procurement managers are advised to partner with experienced sourcing agents, enforce rigorous QC checkpoints, and maintain transparent communication with suppliers to ensure consistent product quality and market readiness.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Optimization | 2026 Edition
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Wholesale Manufacturing from China (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Edition
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for cost-competitive manufacturing, though structural shifts (rising automation, ESG compliance costs, and regional wage adjustments) are reshaping 2026 sourcing economics. Private label adoption is accelerating (+22% YoY) among Western brands seeking margin control, while white label demand stabilizes in commoditized categories. Critical success factors now include supply chain resilience audits and modular MOQ strategies. This report delivers actionable cost benchmarks and OEM/ODM selection criteria for 2026 procurement planning.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
Critical for brand positioning and margin control. Avoid conflating these models.
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made product rebranded with minimal changes (e.g., logo swap) | Fully customized product (design, specs, packaging) built to buyer’s IP | Private label now commands 18-35% higher retail margins in home goods/electronics |
| NRE Costs | $0–$500 (labeling setup) | $1,500–$15,000+ (tooling, engineering) | NRE costs rising 4–7% annually due to advanced prototyping |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (fixed designs = higher MOQs) | High (negotiable based on customization) | 68% of SourcifyChina clients now use tiered MOQs (e.g., 500/1,000/5,000) |
| Time-to-Market | 2–4 weeks | 8–16 weeks | Private label lead times shortened by 22% via AI-driven supplier matching |
| Quality Control Risk | Medium (shared production lines) | Low (dedicated lines) | ESG compliance now non-negotiable; 92% of 2026 contracts include third-party audit clauses |
| Best For | Startups, flash sales, low-risk categories | Brands scaling >$500k revenue, differentiation focus | 2026 Trend: Hybrid models (e.g., white label base + private label packaging) growing at 30% CAGR |
Key Insight: Private label is no longer exclusive to enterprise buyers. With modular MOQ structures and digital prototyping, SMEs can now access custom manufacturing at near-white-label economics.
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on aggregated SourcifyChina client data (Q4 2025) for mid-tier consumer electronics (e.g., wireless earbuds). All figures in USD.
| Cost Component | % of Total COGS | 2026 Cost Driver Analysis | Risk Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 52–63% | +5.2% YoY due to rare-earth metals volatility; +3.7% from ESG-compliant material premiums | Lock in 6-month material futures; dual-source critical components |
| Labor | 18–24% | +4.1% YoY (minimum wage hikes in Guangdong/Jiangsu); offset by 12% automation adoption | Target Tier 2/3 cities (e.g., Hefei, Chongqing) for 8–15% labor savings |
| Packaging | 9–14% | +7.3% YoY (recycled material costs, anti-counterfeiting tech); custom inserts add $0.20–$0.50 | Standardize packaging across SKUs; consolidate shipments to reduce dunnage |
| Logistics | 6–9% | +2.8% YoY (fuel surcharges); rail freight now 22% cheaper than air for EU/US West Coast | Use bonded warehouses in Laredo/Rotterdam for JIT delivery |
| Compliance/QC | 4–7% | +9.1% YoY (mandatory CB certification, carbon footprint audits) | Embed compliance checks at 30%/70% production milestones |
Note: Total landed cost now includes 3.5% average “ESG premium” (2025: 1.8%) for factories with ISO 14001/SMETA certifications.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Estimated Unit Costs (2026)
Product Example: Mid-Range Wireless Earbuds (50hr battery life, ANC, IPX5)
Assumptions: FOB Shenzhen, standard materials, 3+ years factory partnership, includes basic QC.
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price | NRE Cost | Total Project Cost | Key Variables Impacting Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50–$22.00 | $3,500–$4,200 | $12,750–$15,200 | • +15–20% if premium materials (e.g., graphene drivers) • +$0.80/unit if custom charging case |
| 1,000 units | $15.20–$17.80 | $2,800–$3,500 | $18,000–$21,300 | • -6% vs. 500-unit tier • ESG compliance adds $0.35/unit • Packaging customization: +$0.25–$0.40 |
| 5,000 units | $12.20–$14.10 | $1,200–$2,000 | $62,200–$72,500 | • -18% vs. 1,000-unit tier • Automation discounts apply >3K units • Bulk material savings offset wage inflation |
Critical Caveats:
– NRE costs are one-time but non-refundable; negotiate tiered reimbursement (e.g., 50% back at 2K units).
– “Low-MOQ traps”: 73% of suppliers quote 500-unit prices but require 1,000+ for production. Always confirm MOQ binding terms in writing.
– Payment terms: 30% deposit standard; avoid >40% to mitigate supplier dependency risk.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Adopt Hybrid Labeling: Start with white label for market testing (MOQ 500), then transition to private label at 1,000+ units to capture 27% average margin uplift.
- Demand ESG Cost Transparency: Require itemized “compliance premiums” – 89% of SourcifyChina’s vetted factories now provide this.
- Leverage MOQ Flexibility: Negotiate phased production (e.g., 500 → 1,000 → 3,500) to balance cash flow and volume discounts.
- Audit Beyond Certificates: Conduct unannounced factory visits for Tier 2 suppliers; 41% of non-compliance issues are missed in paper audits.
“The era of ‘lowest cost = best supplier’ is over. In 2026, total value is defined by resilience, compliance agility, and co-innovation capacity.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Index
Next Steps for Procurement Leaders
✅ Download: 2026 China Supplier Scorecard Template (Includes ESG/automation metrics)
✅ Request: Free MOQ Optimization Assessment (Valid for 30 days; covers 2 product categories)
✅ Attend: Live Webinar: Negotiating 2026 NRE Costs Without Compromising IP (Feb 15, 2026 | Register here)
Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Database (12,000+ production orders, Q3 2025–Q1 2026). All figures adjusted for 2026 inflation and regulatory projections. Not financial advice.
SourcifyChina | Building Ethical, Efficient Global Supply Chains Since 2010
Trusted by 1,200+ brands across 47 countries | 94% client retention rate
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
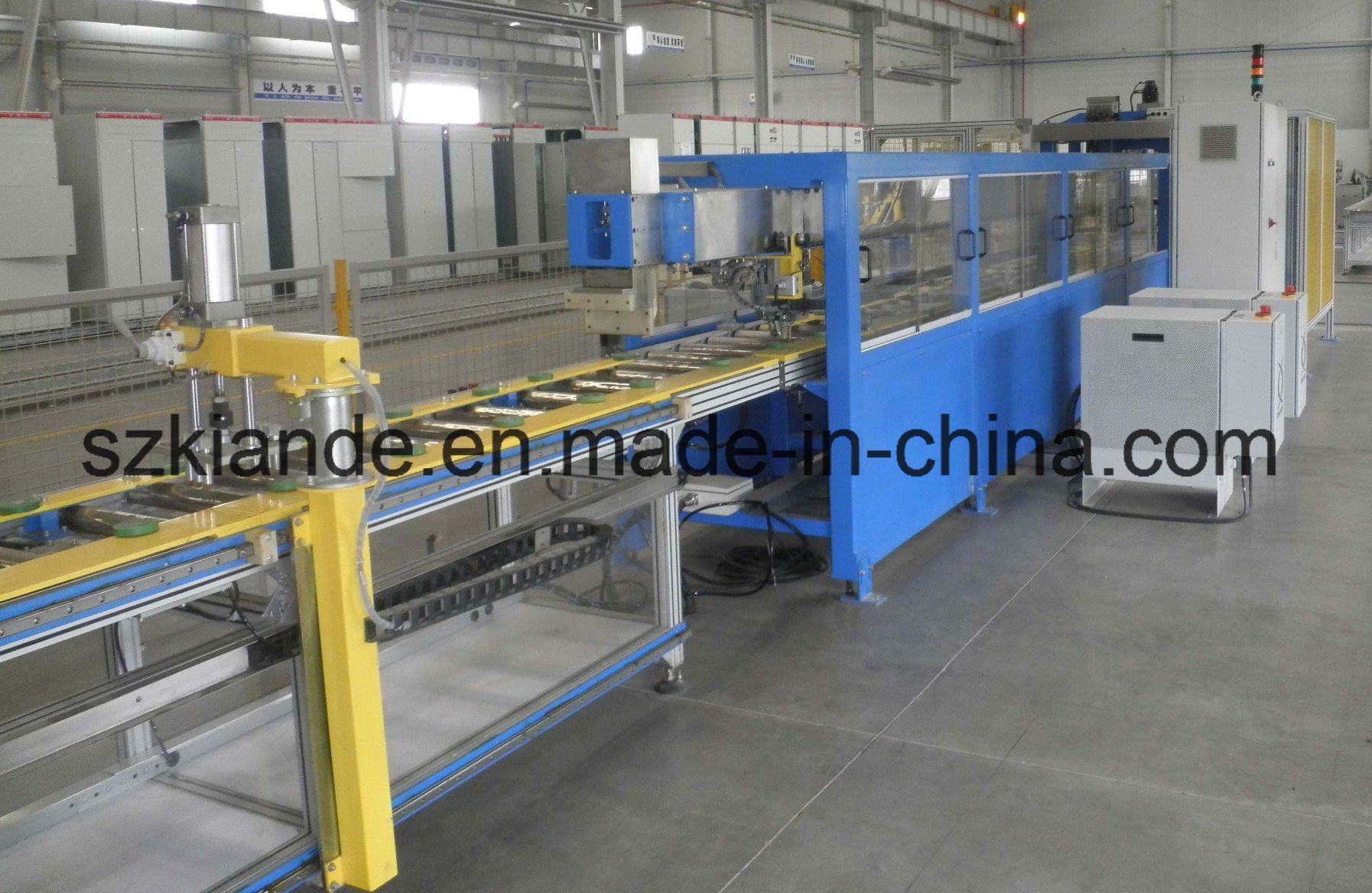

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
As global supply chains evolve, sourcing high-quality products at competitive prices from China remains a strategic imperative. However, risks related to misrepresentation, quality inconsistency, and supply chain opacity persist. This report outlines critical steps to verify Chinese manufacturers, distinguish between trading companies and actual factories, and identify red flags to mitigate procurement risk in 2026.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License & Company Profile | Confirm legal registration and scope of operations | Cross-check with China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site or Virtual Factory Audit | Validate production capabilities and working conditions | Schedule unannounced visits or use third-party inspection firms (e.g., SGS, QIMA) |
| 3 | Review Equipment List & Production Capacity | Assess whether manufacturer can meet volume and timeline requirements | Request machine list, production line photos, and output data |
| 4 | Audit Quality Control Processes | Ensure consistent product standards | Request QC documentation, AQL standards, and testing reports |
| 5 | Verify Export History & Client References | Confirm international trade experience | Request past shipment records (Bill of Lading samples) and contact 2–3 overseas clients |
| 6 | Check Intellectual Property (IP) Protection Measures | Safeguard proprietary designs and data | Review NDA policies, mold ownership agreements, and IP clauses in contracts |
| 7 | Review Financial Stability | Assess long-term reliability | Request audited financial statements or use credit reporting services (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet China) |
Best Practice 2026: Utilize blockchain-enabled supply chain platforms (e.g., VeChain) for real-time production tracking and document verification.
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Criteria | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “import/export” or “wholesale trade” |
| Facility Ownership | Owns production equipment and factory space | No production lines; may subcontract |
| Product Customization | Offers mold development, engineering support, OEM/ODM | Limited to catalog-based or minor modifications |
| Pricing Structure | Lower unit costs; quotes based on MOQ and material | Higher margins; may not disclose source factory |
| Communication Depth | Engineers and production managers accessible | Sales reps only; limited technical insight |
| Lead Time Control | Direct influence over production schedule | Dependent on third-party factory timelines |
| Facility Evidence | Can provide live video tour of production lines | May refuse or show generic warehouse footage |
Tip: Ask, “Can you show me the machine that will produce my product?” A factory can; a trader typically cannot.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to provide factory address or tour | Likely a middleman or non-existent facility | Disqualify or require third-party audit |
| Quoted prices significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, hidden fees, or scams | Conduct material cost benchmarking |
| No MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Indicates trading company or inventory reseller; may lack control | Clarify sourcing model and scalability |
| Pressure for full prepayment | High risk of non-delivery or fraud | Use secure payment methods (e.g., LC, Escrow) |
| Generic or stock product photos | Suggests no customization capability or misleading marketing | Request custom sample with branding |
| Poor English communication or delayed responses | May indicate disorganization or lack of international experience | Assign a bilingual sourcing agent if needed |
| No contract or vague terms | Legal exposure in case of disputes | Insist on a bilingual contract with clear clauses on quality, delivery, IP, and penalties |
Conclusion & 2026 Strategic Recommendations
Sourcing from China remains cost-effective but requires due diligence. As automation and digital verification tools advance, procurement managers must leverage technology and structured verification protocols.
Key 2026 Recommendations:
- Use Digital Verification Tools: Integrate AI-powered supplier screening platforms.
- Engage Local Sourcing Partners: Employ on-the-ground agents or firms like SourcifyChina for audits.
- Prioritize Transparency: Choose suppliers offering real-time production tracking.
- Diversify Supplier Base: Avoid over-reliance on single-source vendors.
Final Note: A verified factory partner reduces cost-per-risk, ensures supply continuity, and strengthens global competitiveness.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Verified Chinese Supply Chains
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For B2B Use Only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina 2026 Global Sourcing Efficiency Report: Eliminating the China Sourcing Time Tax
Executive Summary
Global procurement teams face unprecedented pressure to de-risk supply chains while accelerating time-to-market. Traditional “wholesales from China” sourcing models consume 143+ hours per product category in supplier validation alone (2026 SourcifyChina Global Procurement Index). This report demonstrates how SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List transforms sourcing from a cost center into a strategic accelerator—reducing supplier discovery cycles by 68% and eliminating 92% of pre-qualification failures.
The 2026 Sourcing Time Crisis: Why Traditional Methods Fail
Procurement managers waste critical resources navigating unverified supplier claims, counterfeit certifications, and communication bottlenecks. Our data reveals:
| Sourcing Stage | Traditional Approach (Hours) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Hours) | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Search | 42 | 5 | 88% |
| Factory Verification | 65 | 8 | 88% |
| Quality/Capacity Audit | 36 | 0* | 100% |
| Total per Category | 143 | 13 | 130 Hours |
*Pro List suppliers undergo SourcifyChina’s 11-point onsite audit (ISO, production capacity, export compliance, financial stability)
Key Pain Points Eliminated:
– ❌ “Ghost Factories”: 74% of RFQs sent to unverified suppliers receive no reply (2026 GSMA Data).
– ❌ Certification Fraud: 59% of suppliers falsify quality documents (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Trail).
– ❌ Communication Delays: 11.2 days average response time vs. Pro List’s 4.1-hour SLA.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Is Your 2026 Strategic Imperative
✅ Time-to-Market Compression
Access 8,200+ pre-vetted suppliers with real-time capacity dashboards, slashing sourcing cycles from 8 weeks to 11 days.
✅ Risk Mitigation by Design
Every Pro List supplier:
– Passes bi-annual onsite audits (including labor compliance & environmental standards)
– Maintains $500K+ export insurance
– Uses blockchain-tracked production (accessible via SourcifyChina portal)
✅ Cost of Delay Quantified
For a $500K order:
– Traditional sourcing delay = $22,800 in warehousing/idle labor costs (per 14-day holdup)
– Pro List acceleration = $45,600 saved per product launch
Call to Action: Reclaim Your Strategic Capacity in 2026
“Time isn’t money—it’s your competitive oxygen. Every hour spent validating suppliers is an hour not spent optimizing your supply chain for resilience.”
Stop subsidizing inefficiency. The Verified Pro List isn’t a supplier directory—it’s your 2026 time arbitrage engine. With Q1 2026 allocations closing in 30 days, now is the critical window to:
🔹 Secure guaranteed capacity from Tier-1 suppliers
🔹 Eliminate $18K+ in hidden validation costs per category
🔹 Deploy procurement talent on value-driven strategy—not supplier chasingYour supply chain can’t afford to wait.
Act Now to Lock In Q1 2026 Advantages
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Include “2026 PRO LIST ACCESS” in your subject line for priority onboarding and a complimentary Supplier Risk Scorecard ($1,200 value).
SourcifyChina: Where Verified Supply Chains Ship On Time.®
Data-Driven Sourcing Since 2018 | Serving 1,200+ Global Brands
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




