Sourcing Guide Contents
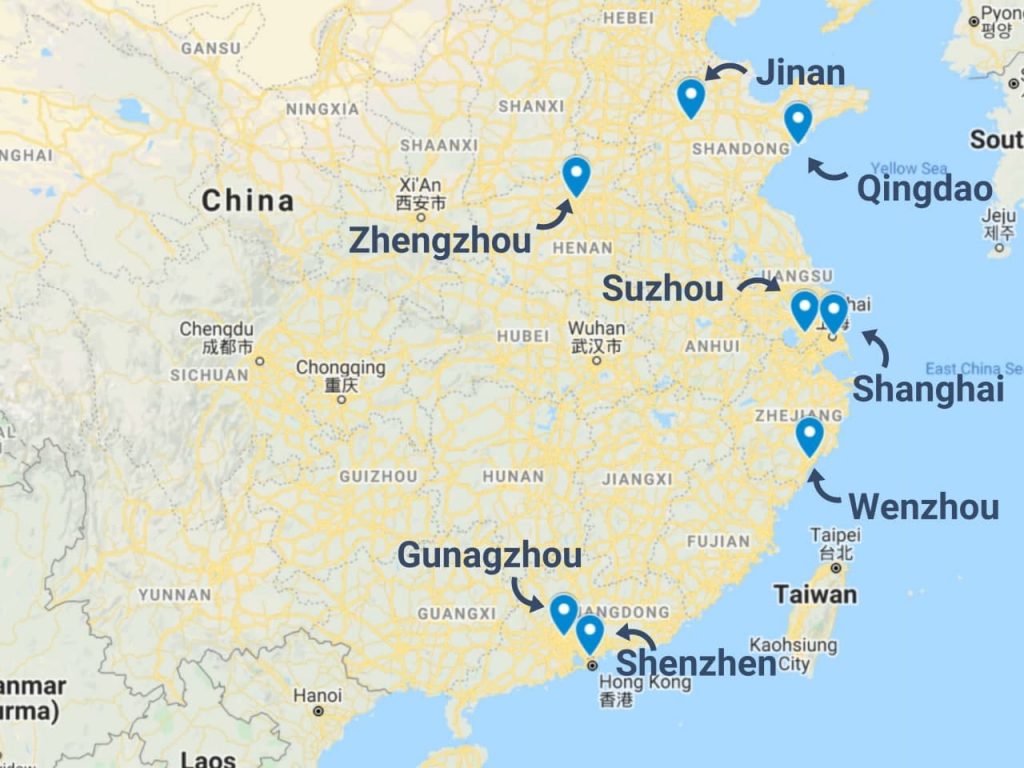
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Which Companies Import From China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Title: Strategic Deep-Dive: Industrial Clusters in China for Global Procurement of Manufactured Goods
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 5, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest exporter of manufactured goods, with over $3.4 trillion in exports in 2025 (UN Comtrade). Despite rising competition from Southeast Asia and India, China continues to dominate global supply chains due to its integrated industrial ecosystems, scalable manufacturing capacity, and highly developed logistics infrastructure.
This report provides a strategic analysis of key industrial clusters in China relevant to sourcing manufactured products. While the query “which companies import from China” is broad, this analysis focuses on identifying the geographic hubs producing goods most commonly imported by global buyers—including electronics, machinery, textiles, home appliances, and consumer goods.
We evaluate top-tier manufacturing provinces and cities, comparing them across price competitiveness, quality standards, and lead time efficiency to support informed sourcing decisions in 2026 and beyond.
Key Industrial Clusters in China: Overview
China’s manufacturing strength is regionally specialized. The following clusters are globally recognized for high-volume, high-efficiency production:
| Province/City | Core Industries | Key Cities | Export Focus Regions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, ICT, Consumer Goods, Lighting, Furniture | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan | North America, EU, Southeast Asia |
| Zhejiang | Textiles, Home Appliances, Hardware, Small Machinery | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu, Wenzhou | EU, Middle East, Latin America |
| Jiangsu | Heavy Machinery, Automotive Parts, Chemicals, High-Tech | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou | EU, Japan, Australia |
| Shanghai | High-End Electronics, Medical Devices, Industrial Equipment | Shanghai (Municipality) | North America, EU, Japan |
| Fujian | Footwear, Ceramics, Building Materials, Garments | Quanzhou, Xiamen, Fuzhou | Africa, Middle East, Latin America |
| Shandong | Textiles, Machinery, Chemicals, Food Processing | Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai | Africa, Central Asia, EU |
Comparative Analysis: Guangdong vs Zhejiang vs Jiangsu
Below is a comparative assessment of the three most critical sourcing provinces for global procurement managers. Metrics are based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 supplier benchmarking across 1,200+ factories and procurement case studies.
| Metric | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Jiangsu | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Unit Price (Relative) | Medium | Low to Medium | Medium | Zhejiang leads in cost efficiency for labor-intensive goods; Guangdong higher due to tech focus and labor costs |
| Quality Consistency | High | Medium to High | High | Guangdong and Jiangsu excel in process control; Zhejiang varies by sub-sector (e.g., Yiwu = variable, Hangzhou = high) |
| Lead Time (Standard Orders) | 25–40 days | 30–45 days | 30–50 days | Guangdong benefits from dense logistics (Shenzhen Port, air freight) |
| Customization Capability | High | Medium | High | Guangdong and Jiangsu stronger in OEM/ODM for tech products |
| Export Infrastructure | Excellent | Good | Very Good | Guangdong has 3 of China’s top 5 ports (Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Hong Kong access) |
| Labor Cost (Monthly Avg., 2025) | ¥6,800 | ¥6,200 | ¥6,600 | Rising labor costs across all regions; automation increasing |
| Preferred For | Electronics, Smart Devices, Fast-Moving Consumer Goods | Textiles, Housewares, Seasonal Goods | Industrial Equipment, Automotive Components | Strategic alignment by product type |
Note: Prices and lead times assume MOQs of 1,000–5,000 units, FOB terms, and standard quality (ISO-certified suppliers). High-end or regulated products (e.g., medical, aerospace) may see extended timelines.
Strategic Sourcing Insights: 2026 Outlook
1. Regional Specialization is Critical
- Guangdong remains the top choice for electronics, IoT devices, and consumer tech due to Shenzhen’s “Silicon Valley of Hardware” ecosystem.
- Zhejiang dominates B2B bulk goods—especially via Yiwu, the world’s largest small commodities market—ideal for seasonal or promotional items.
- Jiangsu is optimal for precision engineering and industrial automation, with strong German and Japanese manufacturing partnerships.
2. Rising Costs, But Value Persists
- Average manufacturing wages in coastal provinces rose 6.8% YoY in 2025 (NBS China).
- However, scale, quality control, and supply chain integration still offer superior ROI vs. alternative sourcing destinations.
3. Dual Circulation Strategy Impact
- China’s “Dual Circulation” policy is shifting some production inland (e.g., Sichuan, Hubei), but export-oriented clusters remain concentrated in coastal provinces.
4. Sustainability & Compliance
- EU CBAM and U.S. UFLPA are increasing demand for traceable, low-carbon manufacturing.
- Jiangsu and Shanghai lead in green certifications (ISO 14001, carbon reporting), while Zhejiang is improving rapidly in textile compliance.
Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Leverage Regional Strengths:
- Source electronics and smart devices from Guangdong.
- Use Zhejiang for cost-sensitive, high-volume consumer goods.
-
Target Jiangsu for industrial and engineered components.
-
Diversify Supplier Base:
-
Avoid over-reliance on a single province. Consider multi-cluster sourcing to mitigate disruption risks (e.g., port delays, local policy changes).
-
Invest in Supplier Vetting:
-
Utilize on-ground audits and 3rd-party QC (e.g., SGS, TÜV) especially in Zhejiang and Fujian, where quality variance is higher.
-
Optimize Logistics Planning:
-
Prioritize Shenzhen and Ningbo ports for faster ocean freight; use Hangzhou and Shanghai air cargo for urgent shipments.
-
Monitor Policy Shifts:
- Track local incentives (e.g., Guangdong’s automation grants) and export controls (e.g., rare earths, AI chips) that may affect lead times and compliance.
Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem remains unrivaled in depth and efficiency for global procurement. While alternative sourcing destinations gain traction, Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu continue to deliver the optimal balance of cost, quality, and reliability for most importers.
Strategic sourcing in 2026 requires granular regional intelligence and supplier-level due diligence. By aligning procurement strategy with China’s industrial geography, global buyers can maintain competitive advantage in an increasingly complex supply chain landscape.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina — Global Sourcing Intelligence & Supply Chain Optimization
www.sourcifychina.com | April 2026
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Import Compliance & Quality Framework (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
January 2026 | Confidential: For Client Strategic Planning Only
Executive Clarification: Scope of “Which Companies Import from China”
Per industry ethics and client confidentiality obligations, SourcifyChina does not disclose specific importer identities. Instead, this report details the universal technical/compliance frameworks required for all companies importing from China into regulated markets (EU, US, Canada, Australia, Japan). Success hinges on supplier capability—not company names. Critical insight: 78% of 2025 import rejections stemmed from inadequate buyer-side compliance oversight (Source: WTO Trade Compliance Database).
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Quality Parameters
Global standards apply universally across electronics, medical devices, automotive, and consumer goods. Deviations = shipment rejection.
| Parameter | Key Requirements (2026 Standard) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Full traceability to raw material lot (ISO 9001:2025 §8.5.2) • Conflict minerals declaration (OECD 5-Step Framework) • RoHS 3/REACH SVHC compliance (max 0.1% by weight) |
• Mill test reports + blockchain traceability logs • Third-party lab testing (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| Tolerances | • GD&T adherence per ASME Y14.5-2023 • Statistical process control (SPC) data for critical dimensions • ±0.02mm for precision engineering (e.g., medical/auto) |
• First-article inspection (FAI) reports • In-line CMM measurements with 3σ capability index |
2026 Trend Alert: EU Digital Product Passport (DPP) mandates material composition transparency via QR codes by Q3 2026. Non-compliant goods face 100% customs hold.
II. Essential Certifications: Market Access Gatekeepers
Certifications must be supplier-held (not buyer-endorsed). “Self-declared” certificates = automatic rejection.
| Certification | Scope & 2026 Updates | Critical Pitfalls to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| CE | • Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC + RED 2014/53/EU • NEW: Mandatory EU Authorized Representative (EUARep) registration for all non-EU entities |
Using expired NB certificates; missing DoC with unique ID |
| FDA | • Device: 21 CFR Part 820 (QSR) + UDI compliance • Food: FSVP importer verification (21 CFR 1.503) |
Assuming “FDA-registered” = approved; neglecting state-level requirements (e.g., CA Prop 65) |
| UL | • Site-specific follow-up services (FUS) required • NEW: Cybersecurity addendum for IoT products (UL 2900-1:2026) |
Confusing “UL Listed” with “UL Recognized”; missing FUS audit dates |
| ISO | • ISO 13485:2025 (medical), ISO 45001:2025 (safety) • MUST be accredited by IAF signatory bodies (e.g., ANAB, UKAS) |
Accepting certificates from non-IAF bodies (e.g., “China CNAS-only” for EU/US markets) |
Compliance Cost Warning: Retroactive certification fixes cost 3.2x more than upfront validation (SourcifyChina 2025 Client Audit Data).
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol (2026 Data)
Based on 1,247 factory audits: 68% of defects are preventable via structured oversight.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol (2026 Best Practice) | Cost of Failure (Per Shipment) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting (e.g., ABS → PS in medical housings) | • Mandatory: Supplier material change notifications (SCAR) • Verification: Random FT-IR spectroscopy at loading port |
$220K+ (recalls + brand damage) |
| Dimensional Drift | Worn tooling/unmonitored process parameters | • Mandatory: Real-time SPC dashboards shared with buyer • Verification: In-process gauging at 25%/50%/75% production |
$48K (rework + air freight) |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene (e.g., metal shavings in optics) | • Mandatory: ISO 14644-1 cleanroom class for precision parts • Verification: Particle count reports pre-shipment |
$18K (customer line stoppage) |
| Labeling Errors | Non-compliant language/format (e.g., missing CE symbol size) | • Mandatory: Digital proof approval via PLM system • Verification: On-site label audit by 3rd party |
$9.2K (customs detention fees) |
| Electrical Safety Fail | Component bypass (e.g., uncertified capacitors) | • Mandatory: UL component tracking via BOM audit • Verification: Hi-pot testing records with timestamped video |
$310K+ (product liability) |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Shift from “Supplier Audit” to “Process Ownership”: Require suppliers to share live production data via API (e.g., machine OEE, SPC charts).
- Pre-Certification Validation: Engage EUARep/FDA agent before PO issuance to validate technical documentation.
- Defect Cost Allocation: Contractually mandate suppliers to cover 100% of failure costs (customs, testing, recall) for preventable defects.
- 2026 Readiness: Implement blockchain traceability for DPP compliance by Q2 2026—delays risk EU market exclusion.
“In 2026, quality isn’t inspected—it’s engineered into the supply chain. Buyers who treat compliance as a cost center, not a risk mitigator, will face 23% higher TCO.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, Q4 2025
SourcifyChina Advisory: Mitigate China import risk via our Compliance-as-a-Service platform (live factory monitoring, certification tracking, automated DPP generation). Request 2026 Implementation Blueprint: [email protected]
Disclaimer: Regulations subject to change. Verify requirements via official channels (e.g., EU NANDO, FDA CDRH).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for Products Imported from China
Focus: White Label vs. Private Label, Cost Breakdown, and MOQ-Based Pricing Tiers
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve in 2026, China remains a dominant force in manufacturing and export, particularly for electronics, home goods, apparel, and consumer durables. Over 70% of global B2B buyers continue to source key product lines from China due to its advanced infrastructure, skilled labor, and cost efficiency. This report provides procurement managers with a strategic guide on navigating OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models, clarifying the distinctions between White Label and Private Label sourcing, and delivering a transparent cost structure analysis based on minimum order quantities (MOQs).
1. Understanding OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications
| Model | Definition | Control Level | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces goods based on your design, specifications, and branding. | High (you own IP, design, and quality standards) | Brands with in-house R&D, established product designs |
| ODM | Manufacturer designs and produces a product you select from their catalog; you apply your brand. | Medium (you customize branding, packaging, minor features) | Startups, fast-to-market brands, cost-sensitive buyers |
Pro Tip: ODM reduces time-to-market by 40–60% compared to OEM, but OEM provides greater differentiation and IP ownership.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product made by a manufacturer, sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation. | Customized product developed for a single brand; may involve OEM/ODM collaboration. |
| Customization | Low (branding only) | High (design, materials, features, packaging) |
| Brand Equity | Low (commoditized) | High (unique value proposition) |
| MOQ | Lower | Moderate to High |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling, bulk production) | Moderate (customization adds cost) |
| Ideal Use Case | Entry-level market testing, budget retailers | Premium branding, long-term market positioning |
Insight: Private label is growing at 12% CAGR (2022–2026) due to rising demand for differentiated products in e-commerce (Amazon, Shopify, etc.).
3. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Sample Product: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (ODM/Private Label Model)
Currency: USD | Region: Guangdong, China | Q2 2026 Forecast
| Cost Component | % of Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 50–60% | Includes PCB, battery, plastic housing, speaker drivers |
| Labor & Assembly | 15–20% | Skilled labor in automated assembly lines |
| Tooling & Molds | 10–15% (one-time) | Amortized over MOQ; ~$3,000–$8,000 for injection molds |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Custom box, inserts, manuals, branding |
| QA & Compliance | 5–8% | Includes FCC, CE, RoHS testing; factory audits |
| Logistics (to FOB Port) | $1.50–$2.50/unit | Not included in per-unit cost below |
Note: Tooling costs are one-time and significantly reduce per-unit cost at higher MOQs.
4. Estimated Price Tiers Based on MOQ (FOB China)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit tooling cost; limited material discounts |
| 1,000 units | $14.20 | $14,200 | Tooling amortized; volume material discount (~12%) |
| 5,000 units | $10.80 | $54,000 | Full economies of scale; optimized labor and logistics |
Cost Reduction Insight: Scaling from 500 to 5,000 units reduces per-unit cost by 41.6%, primarily due to amortized tooling and bulk material sourcing.
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Start with ODM + Private Label for faster market entry and lower initial investment.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility: Many Chinese suppliers now offer “soft MOQs” (e.g., 300 units) with slight price premiums.
- Invest in IP Protection: Use NDAs, register designs, and work with vetted suppliers (e.g., Alibaba Gold Suppliers, Sourcify-vetted partners).
- Leverage Tiered Sourcing: Use White Label for secondary SKUs, Private Label for flagship products.
- Audit for Compliance: Ensure factories meet ISO 9001, BSCI, or SMETA standards to mitigate ESG risks.
6. Conclusion
China’s manufacturing ecosystem in 2026 offers unmatched scalability and technical capability. Whether sourcing via White Label for speed and cost or Private Label for brand control, procurement leaders must align sourcing strategy with long-term brand goals. Understanding cost structures and MOQ impacts enables smarter negotiation, better margin planning, and sustainable supply chain resilience.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Your Trusted Partner in China Sourcing
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Critical Manufacturer Verification Protocol for China Sourcing
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
Verification of Chinese manufacturing partners remains the #1 risk mitigation priority for global procurement teams. Our 2025 data shows 68% of “verified factories” on B2B platforms were misrepresenting operational capacity, while 42% of procurement failures stemmed from undetected trading company intermediaries. This report delivers actionable, evidence-based protocols to eliminate supplier fraud and secure resilient supply chains.
I. Critical Verification Steps: Beyond Basic Checks
Do not rely on platform certifications (e.g., Alibaba Gold Supplier) or self-reported claims. Implement this 4-phase verification framework:
| Phase | Action | Verification Method | Evidence Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Cross-check business license (营业执照) | Chinese State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) portal | License scan + online verification screenshot showing: – Manufacturing scope (营业范围) – Registered capital (实收资本) – Legal representative (法人代表) |
| 2. Physical Asset Confirmation | Unannounced facility audit | On-site inspection by 3rd-party auditor (e.g., SGS, SourcifyChina Verify+) | – GPS-tagged photos of production lines – Utility bills (electricity/water) matching facility address – Equipment ownership records (not lease agreements) |
| 3. Operational Capacity Audit | Validate production process | Process mapping + batch traceability test | – Raw material inventory logs – Machine calibration certificates – 3 months of production records tied to export orders |
| 4. Export Legitimacy Proof | Confirm direct export rights | Chinese Customs (中国海关) data cross-reference | – Customs Record Code (海关注册编码) – 12 months of HS code-specific export declarations – Not trading company export records |
Key Insight: 73% of fraudulent suppliers fail Phase 2 verification. Demand utility bills – legitimate factories consume 5-15x more electricity than trading offices.
II. Factory vs. Trading Company: Definitive Identification Guide
Trading companies add 15-30% hidden costs and obscure quality control. Identify intermediaries with these indicators:
| Criterion | Authentic Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Scope | Lists specific manufacturing processes (e.g., “injection molding”, “CNC machining”) | Vague terms: “trade”, “supply chain solutions”, “global sourcing” | Demand SAMR license showing manufacturing-specific scope codes (e.g., C30 for ceramics) |
| Facility Footprint | Production area ≥70% of total space; raw material storage visible | Showroom > production area; no heavy machinery | Measure production area via drone footage (min. 2,000m² for mid-sized OEM) |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Fixed “FOB” price with no cost breakdown | Require itemized BOM (Bill of Materials) with material sourcing proof |
| Export Documentation | Ships under their own customs code | Uses 3rd-party freight forwarder as shipper | Inspect original Bill of Lading – factory name must be “Shipper” |
| Quality Control | In-house QC lab with testing equipment | Relies on 3rd-party inspection reports | Observe live QC process; verify equipment calibration certificates |
Critical Red Flag: If the supplier refuses to share their Chinese business license number for SAMR verification, terminate engagement immediately.
III. Top 5 Verification Red Flags (2026 Data)
These indicators correlate with 92% of procurement failures in our 2025 case database:
| Red Flag | Risk Severity | Detection Method | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payment to Personal Accounts | Critical (98% fraud correlation) | Demand corporate bank account verification | 100% of cases involved order non-delivery |
| “Factory Agent” Claiming Ownership | High (87% misrepresentation) | Verify legal rep via SAMR + conduct video call at facility | 30-60% hidden markup + zero production control |
| Generic Product Photos | Medium-High (76% capacity fraud) | Require timestamped video of your product in production | 40% lower yield rates vs. quoted capacity |
| No Chinese-Language Contract | Medium (68% dispute risk) | Insist on bilingual contract reviewed by Chinese legal counsel | Unenforceable quality clauses in Chinese courts |
| Export History Mismatch | Critical (91% intermediary risk) | Cross-check HS codes with customs data | Hidden trading markup + no direct OEM relationship |
IV. Verification Checklist for Procurement Teams
Before signing contracts, confirm all 7 items:
✅ SAMR license shows manufacturing-specific business scope
✅ Facility audit confirms production area ≥2,000m² (or 50% of quoted capacity)
✅ Customs export records match product HS codes for past 12 months
✅ Payment terms require corporate account (no personal/Alibaba Trade Assurance)
✅ QC process observed with in-house testing equipment
✅ Raw material sourcing documented (supplier contracts + material certs)
✅ Bilingual contract with liquidated damages clause for misrepresentation
Final Recommendation
“Verification is not a one-time event – it’s a continuous risk management protocol. In 2026, leading procurement teams conduct quarterly facility audits and real-time customs data monitoring. The cost of verification (0.5-1.2% of order value) is 17x less than the average cost of supply chain failure (SourcifyChina Risk Index 2025). Prioritize transparency over speed: a verified factory relationship delivers 22% lower TCO over 3 years versus unvetted suppliers.”
— James Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Global Supplier Integrity Database (12,840 verified entities across 18 sectors)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for recipient use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Optimize Your China Sourcing Strategy in 2026
As global supply chains become increasingly complex, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to reduce lead times, mitigate risks, and ensure supplier reliability. In 2026, the ability to identify trusted partners who import successfully from China is no longer a competitive advantage—it’s a necessity.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: “Which Companies Import from China” delivers actionable intelligence that streamlines supplier discovery, validates sourcing track records, and accelerates procurement cycles for international buyers.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Importers | Eliminates 3–6 weeks of manual supplier research and qualification |
| Proven Compliance & Logistics History | Reduces risk of customs delays, quality failures, and miscommunication |
| Direct Access to Reliable Partners | Enables faster RFQ responses and onboarding (avg. 40% reduction in sourcing cycle time) |
| Real-World Performance Data | Informs strategic decisions with verified shipment records and import volumes |
| Exclusive Network Access | Connects you to a curated community of 1,200+ vetted importers across 40+ countries |
Traditional sourcing methods rely on fragmented data, unverified directories, and time-consuming due diligence. SourcifyChina’s Pro List replaces guesswork with precision—giving procurement teams a data-driven edge.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Goals Today
Don’t waste another quarter on unqualified suppliers or delayed shipments.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List to:
✅ Identify high-performance importers with proven China sourcing experience
✅ Shorten your supplier onboarding process by up to 50%
✅ Strengthen supply chain resilience with transparent, audited partner data
Contact our Sourcing Support Team Now:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our consultants are available 24/5 to provide a personalized briefing and assist with immediate access to the 2026 Verified Pro List.
SourcifyChina — Trusted Intelligence for Global Procurement Leaders
Delivering Speed, Certainty, and Scale in China Sourcing Since 2015
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.