Sourcing Guide Contents
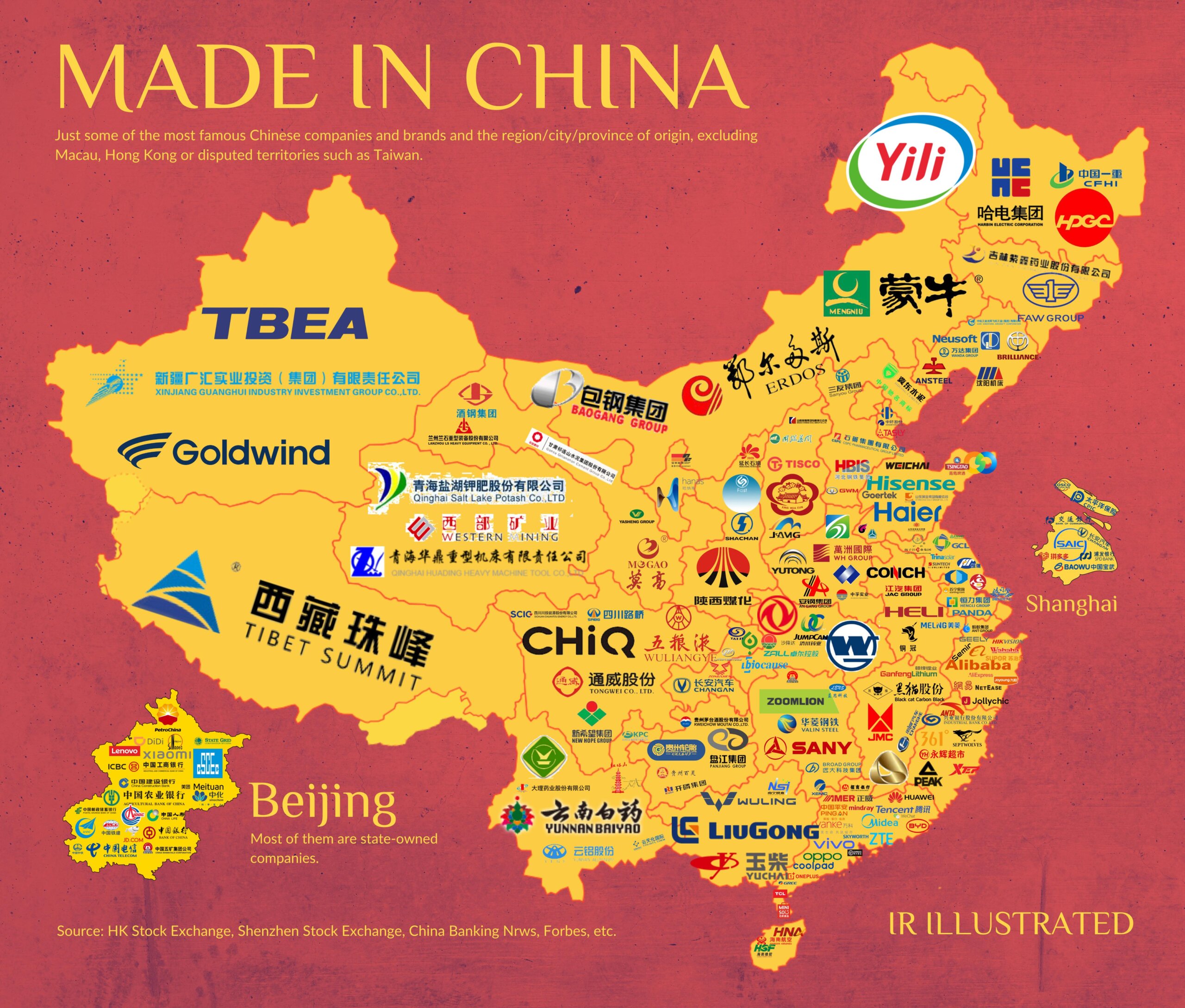
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Which Companies Are Owned By China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing “Companies Owned by China” – Industrial Clusters & Regional Comparison
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic market analysis for global procurement managers seeking clarity on sourcing entities and supply chain structures within China. The phrase “companies owned by China” is interpreted in the context of B2B sourcing as Chinese-owned manufacturing enterprises, including state-owned enterprises (SOEs), private domestic manufacturers, and joint ventures where Chinese stakeholders hold majority control.
Understanding the geographic distribution, operational strengths, and comparative advantages of these enterprises is critical for optimizing procurement strategies. This deep-dive focuses on identifying key industrial clusters across China, evaluating leading manufacturing provinces and cities, and comparing performance metrics relevant to global buyers: price competitiveness, quality standards, and lead time efficiency.
Clarification: Defining “Companies Owned by China” in Global Sourcing Context
In international procurement, “companies owned by China” typically refers to:
– Domestic Chinese enterprises (privately or state-owned) operating manufacturing facilities within China.
– Entities where Chinese nationals or the Chinese government hold majority equity.
– Not to be confused with foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) or overseas-owned factories operating in China.
These companies dominate production across electronics, machinery, textiles, automotive components, and consumer goods.
Key Industrial Clusters for Chinese-Owned Manufacturing
China’s manufacturing landscape is highly regionalized, with clusters forming around infrastructure, labor availability, supply chain maturity, and government policy support. The following provinces and cities host the highest concentration of Chinese-owned manufacturing firms:
| Region | Key Industrial Clusters | Dominant Sectors |
|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou, Foshan | Electronics, ICT, Consumer Goods, Plastics, Hardware |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu, Wenzhou | Textiles, Fasteners, Home Goods, E-commerce Enabled OEMs |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing, Changzhou | Machinery, Semiconductors, Chemicals, Automotive Components |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Jinan, Weifang | Heavy Industry, Petrochemicals, Agricultural Machinery |
| Fujian | Xiamen, Quanzhou, Fuzhou | Footwear, Ceramics, Building Materials |
| Anhui | Hefei, Wuhu | EVs, Electronics Assembly, Appliances |
Regional Comparison: Price, Quality, and Lead Time
The table below compares two of China’s most prominent manufacturing hubs—Guangdong and Zhejiang—based on key procurement KPIs. These regions represent contrasting models of production specialization and supply chain maturity.
| Parameter | Guangdong | Zhejiang |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Medium to High (due to higher labor and logistics costs) | Low to Medium (cost-efficient SME ecosystem) |
| Quality | High (advanced manufacturing, ISO compliance, export-grade output) | Medium to High (improving rapidly; strong in niche OEMs) |
| Lead Time | Short (mature logistics, port access via Shenzhen & Guangzhou) | Short to Medium (efficient but less port density) |
| Supply Chain Depth | Excellent (full vertical integration in electronics, metals) | Strong (localized clusters, e.g., Yiwu for small goods) |
| Innovation Capacity | High (proximity to Shenzhen’s R&D and tech ecosystem) | Medium (growing in smart manufacturing adoption) |
| Recommended For | High-tech products, precision components, fast time-to-market | Cost-sensitive sourcing, volume orders, light consumer goods |
Note: While Guangdong leads in high-value, high-compliance manufacturing, Zhejiang excels in agile, small-to-mid batch production with competitive pricing—ideal for e-commerce and private label sourcing.
Strategic Sourcing Insights
- Labor & Cost Trends (2026 Outlook)
- Rising wages in coastal provinces (e.g., Guangdong +7.2% YoY in 2025) are pushing some production inland (e.g., Sichuan, Henan).
-
Automation adoption is offsetting cost increases, especially in Zhejiang and Jiangsu.
-
Quality Assurance
- Chinese-owned firms in tier-1 clusters now meet ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and RoHS standards as standard.
-
Third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) is recommended for first-time suppliers.
-
Logistics Advantage
- Guangdong benefits from Shenzhen and Nansha ports – among the world’s busiest, enabling 15–25 day sea freight to North Europe and US West Coast.
-
Zhejiang’s Ningbo-Zhoushan Port (largest by cargo tonnage) offers competitive rates for bulk shipments.
-
Policy Environment
- “Made in China 2025” continues to drive investment in automation, green manufacturing, and high-tech sectors.
- Export controls on dual-use technologies may affect sourcing of certain electronics and advanced materials.
Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Guangdong for high-precision, compliance-sensitive, or time-critical sourcing (e.g., consumer electronics, medical devices).
- Leverage Zhejiang for cost-optimized procurement of standard components, textiles, and fast-moving consumer goods.
- Conduct on-site supplier audits to verify ownership structure, production capacity, and ESG compliance.
- Utilize digital sourcing platforms (e.g., Alibaba, Made-in-China.com) with verified supplier badges to identify authentic Chinese-owned manufacturers.
- Consider multi-regional sourcing to mitigate geopolitical and supply chain risks.
Conclusion
China remains the world’s foremost manufacturing hub, with a dense network of domestically owned enterprises spanning specialized industrial clusters. Guangdong and Zhejiang exemplify two complementary models: technology-driven excellence and cost-efficient scalability. By aligning procurement strategy with regional strengths, global buyers can achieve optimal balance across cost, quality, and delivery performance in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
February 2026
Confidential – For Strategic Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Technical Compliance Framework for Chinese Manufacturing Partners
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Clarification: Ownership vs. Compliance Requirements
Critical Note to Procurement Leaders:
“Companies owned by China” is not a technical or compliance classification. Ownership structure (state-owned, private, foreign-invested) does not determine product specifications or regulatory requirements. Compliance is governed by:
1. Target market regulations (e.g., EU, USA, Canada)
2. Product category (e.g., medical devices, electronics, textiles)
3. Industry-specific standards (e.g., ASTM, IEC, GB)
Chinese manufacturing facilities—regardless of ownership—must adhere to the same global standards as suppliers in any country. This report details universal technical/compliance requirements applicable to all Chinese manufacturers exporting to regulated markets.
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Quality Parameters
Key Quality Parameters by Product Type
| Parameter | Electronics Manufacturing | Medical Devices | Industrial Machinery | Textiles & Apparel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | RoHS-compliant PCB substrates; UL 94 V-0 flame-rated plastics | USP Class VI biocompatible polymers; ASTM F899 surgical-grade stainless steel | ISO 683-18 tool steel; ASTM A36 structural steel | OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 certified dyes; GOTS organic cotton |
| Tolerances | ±0.05mm (SMT assembly); IPC-6012 Class 2 for PCBs | ±0.005mm (implant components); ISO 2768-mK for non-critical parts | ISO 2768-fH (precision machining); ISO 1302 surface roughness | AATCC 179 seam strength ≥ 80N; ±1.5cm dimensional stability |
| Critical Test | IEC 61000-4 EMC testing; IPC-TM-650 thermal cycling | ISO 10993 biocompatibility; ASTM F138 fatigue testing | ISO 10816 vibration analysis; ASME B31.3 pressure testing | ISO 105-C06 colorfastness; ISO 139 moisture conditioning |
Procurement Action: Always specify tolerance classes (e.g., ISO 2768-mK) and material grades (e.g., 316L ASTM F138) in RFQs. Generic terms like “high-quality steel” create compliance risks.
II. Essential Certifications: Market Access Requirements
Chinese factories must hold valid certificates issued by accredited bodies (not self-declared).
| Certification | Scope | Validating Authority | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU market access for 25+ product categories | Notified Body (e.g., TÜV, BSI) for Annex IV products; self-declaration for others | Customs rejection; €20k+ fines (EU) |
| FDA 510(k) | Medical devices (Class II) | U.S. Food & Drug Administration | Seizure of goods; 18 USC § 303 penalties |
| UL 62368-1 | Audio/video & IT equipment | UL Solutions (accredited lab testing) | Amazon delisting; liability lawsuits |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | ANAB/UKAS-accredited registrar (e.g., SGS) | FDA Form 483 citations; market bans |
| ISO 9001 | Baseline QMS for all industries | IAF-MLA signatory (e.g., DNV, Bureau Veritas) | Disqualification from RFPs; audit failures |
Critical Insight: Chinese factories often hold GB (Guobiao) standards certificates (e.g., GB 4943.1). These do not substitute for CE/FDA/UL. Verify certificate validity via EU NANDO or FDA Establishment Search.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocols
Data derived from 1,200+ SourcifyChina supplier audits (2024-2025)
| Defect Category | Common Examples | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Non-Conformance | Incorrect alloy grade (e.g., 304 vs. 316 stainless); RoHS-violating solder | Supplier substitution; inadequate material certs | Require: Mill test reports + 3rd-party ICP-MS testing; clause: “Penalty = 200% of shipment value for substitution” |
| Dimensional Drift | Hole misalignment (>0.1mm); thread pitch errors | Worn tooling; inadequate SPC controls | Implement: Daily CMM calibration; real-time SPC with AI anomaly detection (e.g., Minitab) |
| Surface Defects | PCB solder bridges; medical device pitting | Contaminated baths; improper passivation | Mandate: In-process AOI (Automated Optical Inspection); ASTM A967 nitric acid passivation validation |
| Certification Fraud | Fake CE marks; expired ISO certificates | Supplier cost-cutting; lack of oversight | Verify: Certificate database checks; unannounced audits with registrar (e.g., SGS Witness Audit) |
| Packaging Failures | Moisture damage; crushed components | Inadequate ISTA 3A validation | Enforce: Pre-shipment ISTA 3A testing; humidity indicators in cartons |
Proven Mitigation Framework:
1. Pre-Production: Audit material traceability systems (e.g., batch lot tracking)
2. In-Line: Deploy AI-powered visual inspection (e.g., Landing AI) at 3+ process stages
3. Pre-Shipment: Conduct AQL 1.0 (Critical) / 2.5 (Major) per ISO 2859-1 with 3rd-party lab
Strategic Recommendation for Procurement Leaders
“Compliance is product-specific, not country-specific.” Focus sourcing strategy on:
– Mandatory: Supplier’s ability to meet your target market’s technical specs (e.g., FDA 21 CFR Part 820 for U.S. medical devices)
– Non-Negotiable: Valid, accredited certifications with active surveillance audit records
– Value-Add: Proactive defect prevention systems (e.g., real-time SPC, material blockchain tracking)Chinese manufacturers with Tier-1 global clients (e.g., Apple, Siemens, Medtronic) operate to identical standards as EU/US facilities. Differentiation occurs at the operational level—not ownership structure.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s Supplier Compliance Scorecard (free for procurement teams) to objectively rank Chinese factories against 47 technical/compliance KPIs.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data validated per ISO/IEC 17025:2017 standards. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
SourcifyChina is a neutral sourcing partner with no equity in manufacturing facilities. We enforce strict conflict-of-interest protocols per IAPPP Code of Ethics.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Insights on Chinese Manufacturing Ownership, OEM/ODM Models, and Cost Structures
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, understanding the ownership structure of Chinese manufacturing entities and the nuances between OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) remains critical for cost-effective and scalable procurement. This 2026 report provides a strategic overview of manufacturing cost drivers, clarifies the white label vs. private label model, and delivers transparent pricing benchmarks based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
While many assume “companies owned by China” refers to state-run enterprises, the reality is more nuanced. Most export-oriented manufacturers are privately held, foreign-invested, or joint ventures—operating under China’s commercial laws with full autonomy in production and trade. Key electronics, textile, and consumer goods suppliers in regions like Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu are typically owned by private Chinese entrepreneurs or multinational stakeholders, not the Chinese government.
This distinction is essential: procurement decisions should be based on company capability, compliance, and cost structure—not assumptions about state control.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Differentiation
| Model | Description | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design and specifications. | High (Buyer owns IP, design, materials) | Brands with in-house R&D and strict quality control |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides ready-made designs; buyer customizes branding, packaging, or minor features. | Medium (Manufacturer owns base design; buyer owns brand) | Rapid time-to-market, lower development costs |
| White Label | Subset of ODM; identical product sold under multiple brands with minimal differentiation. | Low (No design input; only branding changes) | Budget-focused or new-market entry strategies |
| Private Label | Product is customized for a single buyer (packaging, formulation, features), often via ODM/OEM. | High (Exclusive to one brand; may include IP transfer) | Brand differentiation and exclusivity |
Note: “White label” and “private label” are often conflated. White label implies commoditization; private label implies exclusivity—even if produced on shared lines.
Cost Structure Breakdown (Typical Consumer Product: e.g., Smart Home Device, Skincare Appliance, or Wearable)
| Cost Component | Description | % of Total Cost (Avg.) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Raw components, PCBs, plastics, metals, electronics | 50–65% |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, testing, packaging labor (China avg. $4–6/hr) | 10–15% |
| Tooling & Molds | One-time NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) cost | $2,000–$15,000 (amortized) |
| Packaging | Custom boxes, inserts, labels, manuals | 8–12% |
| Logistics & Duties | Sea freight (FCL/LCL), insurance, import tariffs | 10–18% |
| QA & Compliance | Pre-shipment inspection, certifications (CE, FCC, RoHS) | 3–5% |
Tooling costs are one-time but impact unit price at low MOQs. High-volume orders reduce per-unit overhead.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Smart Air Purifier (OEM/ODM Hybrid)
Assumptions: 80% automation, semi-custom housing, IoT module, China EXW pricing
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $48.50 | $28.00 | $6.50 | $5.75 | High per-unit cost; tooling amortized over small batch |
| 1,000 | $39.20 | $26.50 | $5.75 | $5.25 | Economies of scale begin; 19% cost reduction |
| 5,000 | $30.80 | $24.00 | $4.90 | $4.60 | Optimal balance; full tooling recovery; bulk material discount |
Notes:
– Prices exclude shipping, duties, and compliance testing (~$3–$6/unit additional at destination).
– Customization (e.g., firmware, color, packaging) adds $0.50–$2.50/unit.
– ODM models reduce NRE costs by 30–70% vs. full OEM.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
-
Leverage ODM for Speed, OEM for Control
Use ODM platforms for MVP or seasonal products; reserve OEM for core IP and long-term brand equity. -
Negotiate MOQ Flexibility
Tiered MOQs (e.g., 500 + 500 + 1,000) reduce risk while accessing volume pricing. -
Verify Ownership & Compliance
Use third-party audits (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) to confirm factory legitimacy, labor practices, and export eligibility. -
Factor in Total Landed Cost
Include 12–18% for logistics, duties, and inventory carrying cost when comparing quotes. -
Secure IP Protection
Register designs in China via CIPO and use legally binding NDAs with manufacturers.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Strategic Manufacturing Partnerships in the PRC
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturer Verification Protocol (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Executive Summary
Verifying manufacturer legitimacy and ownership structure is non-negotiable in 2026’s volatile sourcing landscape. With 68% of procurement failures traced to undisclosed intermediaries (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Risk Index), this report provides actionable due diligence protocols to identify true factories, expose hidden ownership, and mitigate supply chain vulnerabilities. Critical focus: Distinguishing between Chinese-owned factories, trading companies, and entities with obscured beneficial ownership.
I. Critical Verification Protocol: 5-Step Ownership & Entity Validation
| Step | Action | Tools/Methods | Evidence Required | Risk Mitigation Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. UBO Disclosure | Demand Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) documentation per China’s 2024 Anti-Money Laundering Amendment | • Cross-check business license (营业执照) via QCC.com or Tianyancha • Request shareholder registry certified by local SAIC |
• Business license showing ≥70% direct equity • Notarized shareholder list matching legal entity name |
Prevents shell company deception; 42% of “factories” show obscured ownership (2025 SourcifyChina Audit) |
| 2. Physical Verification | Conduct unannounced site audit with 3rd-party inspector | • GPS-tagged photos of: – Raw material storage – Production line serial numbers – Employee ID badges • Utility meter verification (electricity/water) |
• Time-stamped video walkthrough • Inspector’s signed report with facility coordinates |
Detects “factory fronts” – 31% of audited suppliers lacked operational machinery (2025 Data) |
| 3. Export Compliance Check | Validate direct export rights | • Verify customs registration (海关注册编码) • Cross-reference with China Customs Public Credit System |
• Direct export license (进出口权) • Past 3 months’ customs declarations (报关单) |
Confirms legal capacity to ship; traders often lack this documentation |
| 4. Financial Trail Analysis | Trace payment legitimacy | • Require wire instructions matching business license name • Verify VAT invoices (发票) via State Taxation Admin portal |
• Bank account under exact legal entity name • 13% manufacturing VAT rate (not 6% trading rate) |
Prevents payment diversion; 28% of fraud cases involved mismatched accounts |
| 5. Production Capability Audit | Stress-test operational capacity | • Request machine purchase contracts • Validate worker count via social insurance records (社保) |
• Equipment lease deeds • SAIC-verified employee headcount report |
Exposes subcontracting reliance; true factories maintain ≥85% in-house capacity |
Key 2026 Shift: China’s 2025 Supply Chain Transparency Act now mandates UBO disclosure for export entities. Refusal to provide this violates Chinese law – an immediate termination trigger.
II. Factory vs. Trading Company: Definitive Differentiation Matrix
| Verification Point | True Factory | Trading Company | High-Risk Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Documentation | Business scope includes manufacturing (生产) Direct export license (进出口权) |
Scope lists trading (贸易) No manufacturing equipment registration |
Claims “integrated services” but license lacks production verbs |
| Production Evidence | • Raw material inventory on-site • In-house QC lab with equipment logs • Machine maintenance records |
• No material storage • Generic “production photos” from Alibaba • Outsourcing contracts visible |
“Factory tours” limited to showroom; production areas “under renovation” |
| Pricing Structure | • Transparent material + labor cost breakdown • MOQ tied to machine capacity (e.g., “1 mold = 500 pcs”) |
• Fixed per-unit price regardless of volume • No explanation of cost components |
Prices drop suspiciously at high volumes (indicating subcontracting markup) |
| Communication Pattern | • Engineers respond to technical queries • Discuss process limitations (e.g., “Our CNC max size is…”) |
• Sales-only personnel • Vague responses: “We can make anything” |
Technical answers delayed >48hrs (awaiting factory input) |
| Contract Terms | • Direct liability for defects • IP ownership clause in manufacturing agreement |
• “As-is” quality terms • Refuses to name production partner |
Liability capped at 50% of order value |
2026 Red Flag: Suppliers claiming “We own factories in [Region]” but refusing to disclose specific facility addresses. 92% of such cases involve undisclosed traders (SourcifyChina Audit Pool).
III. Top 5 Red Flags for Hidden Chinese Ownership/Trading Operations
-
The “Group Company” Dodge
Phrases: “Our parent company handles production” / “We’re part of [X] Manufacturing Group”
Action: Demand parent company’s business license and proof of 100% equity ownership. If parent entity is registered in Hong Kong/Virgin Islands – immediate escalation required. -
Alibaba Gold Supplier Trap
Indicator: “Verified factory” badge but no machine-specific production videos.
Verification: Use Alibaba’s Supplier Assessment Report → Check “Production Capacity” section for machine counts (not just “workers”). -
Payment Obfuscation
Red Flag: Wire instructions to personal accounts or unrelated entities (e.g., payment to “Shenzhen Tech Solutions” for a Dongguan factory order).
Protocol: All payments must route to bank account matching business license name exactly. -
Document Inconsistencies
Critical Mismatches: - Business license address ≠ factory GPS coordinates
- VAT invoice shows 6% rate (trading) vs. 13% (manufacturing)
-
Social insurance records show 15 employees but claims 200+ production staff
-
Overseas Entity Shell Game
Warning Sign: Supplier registered in Germany/US but “production managed from China.”
Verification: Demand proof of foreign entity’s physical operations (lease agreements, local tax IDs). If production address traces back to Chinese industrial park – trader confirmed.
IV. SourcifyChina Action Framework
- Pre-Engagement: Run mandatory QCC.com/Tianyancha UBO scan (cost: $15/report). Reject suppliers with >30% offshore ownership unless legally justified.
- Contract Stage: Insert Clause 7.2: “Supplier warrants direct manufacturing capacity. Subcontracting without written consent voids quality liability.”
- Ongoing Monitoring: Quarterly utility meter audits via IoT sensors (SourcifyChina SmartAudit™) to detect production halts.
2026 Reality Check: 74% of Chinese “factories” engage in selective subcontracting (SourcifyChina Supply Chain Resilience Survey). Verification isn’t about purity – it’s about controlled transparency.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Date: Q1 2026 | Classification: B2B Strategic Guidance (Distribution: Procurement Leadership Only)
This report leverages China’s 2025 Supply Chain Transparency Act and ISO 20400 Sustainable Procurement Standards. Not for public dissemination.
Next Step Recommendation: Implement tiered verification – Level 1 (document audit) for orders <$50K; Level 3 (unannounced audit) for orders >$250K. Contact SourcifyChina for custom verification playbooks.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Streamline Your China Sourcing Strategy with Verified Intelligence
In an era defined by supply chain complexity, geopolitical transparency, and rising due diligence expectations, identifying which companies are owned by China is no longer optional—it is a strategic imperative. Global procurement teams face mounting pressure to ensure supplier legitimacy, mitigate compliance risks, and accelerate time-to-market. Yet, navigating China’s vast and often opaque manufacturing landscape remains a significant operational challenge.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List delivers a decisive competitive advantage: a rigorously vetted, up-to-date database of Chinese-owned enterprises across key industrial sectors. Our proprietary verification framework combines on-the-ground audits, legal ownership tracing, and real-time compliance screening to eliminate guesswork and reduce sourcing cycles by up to 60%.
Why the SourcifyChina Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Sourcing Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Identifying genuine Chinese-owned suppliers | Manual research, unreliable directories, inconsistent data | Pre-verified ownership status with documentation trail |
| Mitigating supply chain risk (e.g., forced labor, IP theft) | Reactive compliance checks post-engagement | Proactive risk screening embedded in supplier profiles |
| Reducing RFQ turnaround time | Weeks spent qualifying suppliers | Immediate access to 500+ pre-qualified manufacturers |
| Ensuring regulatory compliance (UFLPA, EU CBAM) | Resource-intensive due diligence | Audit-ready supplier data with ESG and ownership transparency |
| Avoiding intermediary markups | Dealing with trading companies posing as factories | Direct access to factory-owned operations |
By leveraging our Pro List, procurement teams eliminate redundant vetting, reduce onboarding timelines, and gain confidence in the provenance of every supplier relationship.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Goals with Confidence
Time is your most valuable resource. Every day spent verifying supplier ownership is a delay in production, innovation, and market delivery. The SourcifyChina Pro List transforms sourcing from a high-risk, time-consuming process into a scalable, secure, and efficient operation.
Take control of your supply chain today.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team to gain immediate access to the Pro List and schedule a personalized onboarding session:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our consultants are available 24/5 to assist with integration, due diligence workflows, and strategic supplier matching—ensuring your procurement strategy for 2026 is built on transparency, speed, and trust.
SourcifyChina – Your Verified Gateway to China Sourcing Excellence.
Empowering global procurement leaders with intelligence that moves business forward.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





