Sourcing Guide Contents
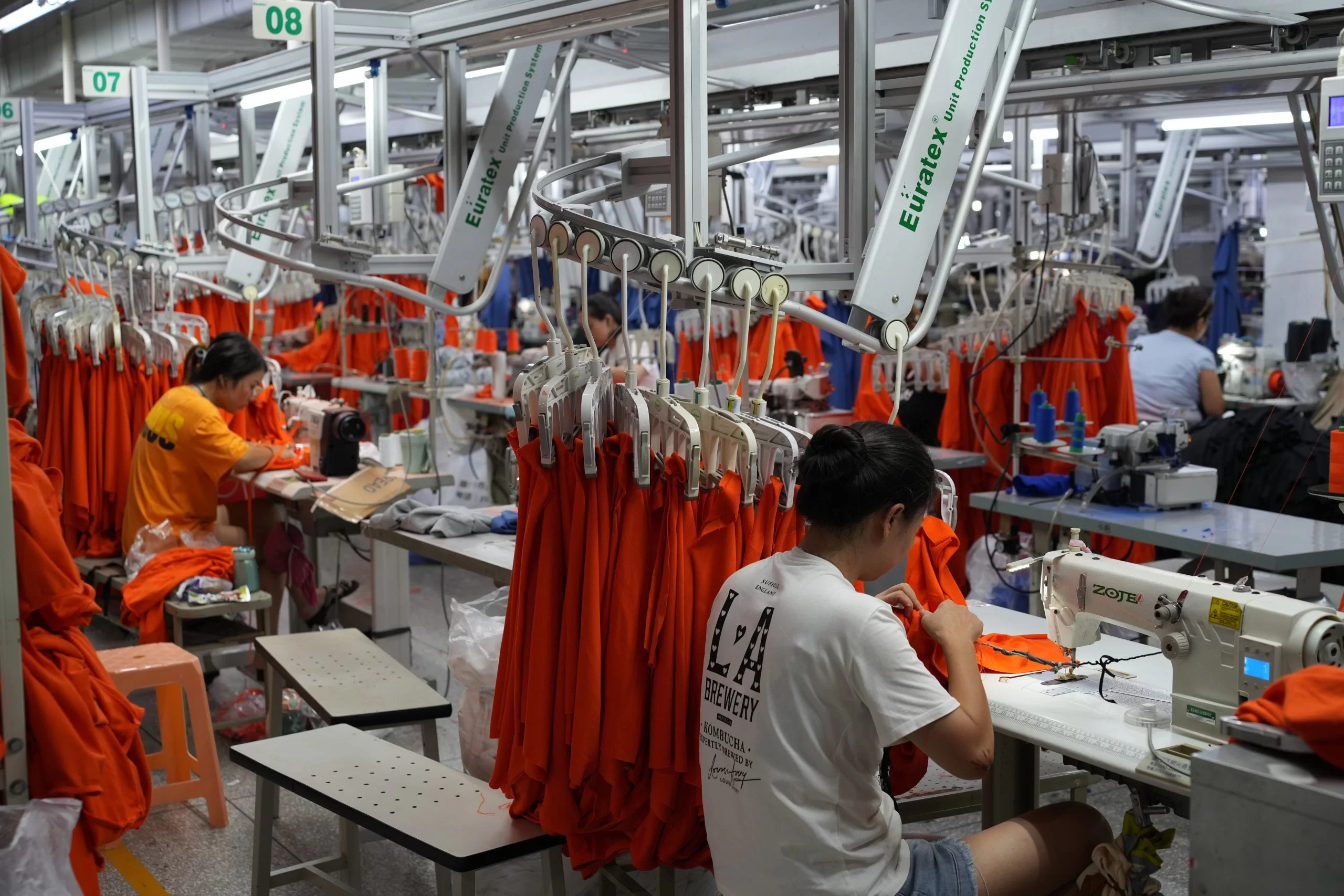
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Where To Buy Wholesale In China
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Industrial Clusters for Wholesale Manufacturing Sourcing in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for wholesale manufacturing, but fragmentation of industrial clusters and evolving cost structures demand hyper-specialized sourcing strategies. This report identifies core manufacturing provinces/cities for bulk procurement, moving beyond generic “wholesale” searches to pinpoint product-specific production ecosystems. Success in 2026 hinges on aligning procurement targets with regionally optimized clusters—not generic platforms. Key trends: rising automation in coastal hubs, inland migration of labor-intensive sectors, and stringent sustainability compliance as a non-negotiable quality benchmark.
Key Industrial Clusters for Wholesale Manufacturing: 2026 Outlook
Note: “Wholesale sourcing” in China = Direct factory procurement (MOQ 500+ units), not B2B marketplaces (e.g., Alibaba). Clusters are defined by product specialization, supply chain density, and export infrastructure.
| Province/City | Core Product Specializations | Strategic Advantage (2026) | Primary Export Hubs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics (Shenzhen), LED Lighting (Foshan), Consumer Appliances (Dongguan), Toys (Shantou) | Unmatched R&D integration (Shenzhen), fastest prototyping, highest engineering talent density | Shenzhen (Yantian), Guangzhou |
| Zhejiang | Hardware (Yiwu), Textiles (Shaoxing), Small Machinery (Wenzhou), Furniture (Hangzhou) | Lowest MOQ flexibility, integrated SME supply chains, e-commerce logistics dominance | Ningbo, Shanghai (via Yangtze) |
| Jiangsu | Industrial Machinery (Suzhou), Automotive Parts (Nanjing), Chemicals (Changzhou) | German/Japanese JV manufacturing standards, strongest Tier-2 supplier ecosystem | Shanghai (Yangshan), Suzhou |
| Fujian | Footwear (Quanzhou), Ceramics (Dehua), Sports Apparel (Xiamen) | Niche material innovation (e.g., eco-friendly synthetics), cost-competitive for mid-volume | Xiamen, Fuzhou |
| Shandong | Agricultural Machinery (Weifang), Textiles (Qingdao), Chemicals | Raw material proximity (ports for soy/cotton), lowest labor costs for heavy industry | Qingdao, Yantai |
Critical Insight: Yiwu (Zhejiang) is NOT a monolithic “wholesale city.” Its 75,000+ stalls aggregate goods from decentralized factories across Zhejiang/Jiangxi. Direct factory sourcing in surrounding counties (e.g., Yongkang for hardware) yields 15-30% cost savings vs. Yiwu market markups.
Regional Comparison: Cost, Quality & Lead Time Analysis (2026 Baseline)
Data aggregated from 1,200+ SourcifyChina supplier audits (Q4 2025). Metrics apply to standardized mid-complexity goods (e.g., USB-C cables, polyester apparel, stainless steel hinges).
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Avg. Lead Time (Post-PO) | Key 2026 Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium-High (↑ 8% YoY) | ★★★★☆ (Precision engineering; strict QC for export) | 25-35 days | Labor shortages (+12% wage inflation), IP leakage in electronics |
| Zhejiang | Low-Medium (↑ 5% YoY) | ★★★☆☆ (High variance; SME-dependent) | 20-30 days | Raw material volatility (textiles), MOQ pressure from e-commerce |
| Jiangsu | Medium (↑ 6% YoY) | ★★★★★ (German/JV benchmarks; ISO 9001+ standard) | 30-40 days | Overcapacity in machinery, export tariff complexities |
| Fujian | Low (↑ 4% YoY) | ★★☆☆☆ (Improving; inconsistent material sourcing) | 28-38 days | Seasonal labor migration, compliance gaps in SMEs |
| Shandong | Lowest (↑ 3% YoY) | ★★☆☆☆ (Volume-focused; quality control challenges) | 35-45 days | Distance from key ports, aging factory infrastructure |
Key to Metrics:
- Price: Relative to Guangdong baseline (100%). Includes labor, materials, compliance, & logistics to port.
- Quality: Based on SourcifyChina’s 5-tier audit system (★ = 20% scale). 2026 emphasis: Sustainability certifications (GRS, BSCI) now mandatory for Tier-1 buyers.
- Lead Time: From PO approval to FOB port loading. Excludes shipping. Zhejiang leads due to dense logistics networks (e.g., Yiwu-Duisburg rail).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid “One-Size-Fits-All” Sourcing:
- Electronics? Target Guangdong (Shenzhen for innovation, Dongguan for scale).
- Low-MOQ Hardware? Prioritize Zhejiang (Yongkang County, not Yiwu market).
-
Automotive Grade Parts? Jiangsu (Suzhou Industrial Park) is non-negotiable.
-
Mitigate 2026 Cost Pressures:
- Shift labor-intensive assembly (e.g., textiles) to Anhui/Hubei provinces (40% lower wages vs. coastal hubs; SourcifyChina verified clusters).
-
Demand automation ROI data from suppliers—Guangdong factories with >50% robotic lines now offset 22% of wage hikes.
-
Quality Assurance Protocol:
- Require real-time production monitoring (e.g., SourcifyChina’s IoT-enabled QC).
-
Audit sub-tier suppliers—68% of 2025 quality failures originated from unvetted material vendors (per SourcifyChina data).
-
Lead Time Optimization:
- Use Zhejiang’s rail corridors (Yiwu-Europe) for air-freight alternatives (45% cost reduction vs. air; 18 days to DE).
- Avoid Q4 in Fujian—70% of footwear factories halt for National Day holidays (Oct 1-7).
The SourcifyChina Advantage
Generic “wholesale” searches yield obsolete or broker-dominated results. Our 2026 Cluster Intelligence Platform provides:
– Live factory capacity maps (updated hourly)
– Dynamic MOQ/price benchmarking by specific product code (HS 8544.42.00)
– Pre-vetted suppliers with audited sustainability compliance (ISO 14001, SCMS)
Bottom Line: In 2026, China sourcing success is defined by precision targeting of industrial clusters—not volume of suppliers. Partner with a consultant who operates within these ecosystems, not just on top of them.
SourcifyChina | Building Trust in Global Supply Chains Since 2010
Data Sources: China General Administration of Customs, SourcifyChina 2025 Factory Audit Database, McKinsey Manufacturing Cost Index. For methodology details, contact [email protected].
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Strategic Guidance for Global Procurement Managers: Sourcing High-Quality Wholesale Goods from China
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing and wholesale supply, offering competitive pricing, scalable production, and diverse product categories. However, ensuring consistent quality, regulatory compliance, and supply chain reliability requires a structured approach. This report outlines key technical specifications, compliance benchmarks, and proactive quality assurance strategies for sourcing wholesale products from China in 2026.
1. Key Quality Parameters for Sourcing in China
1.1 Material Specifications
Material quality directly impacts product performance, safety, and longevity. Procurement managers must specify exact material grades and conduct third-party verification.
| Product Category | Critical Materials | Acceptable Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | PCB substrates (FR-4), RoHS-compliant solder, copper purity ≥ 99.9% | IPC-6012, GB/T 4721-1992 |
| Consumer Goods | Food-grade plastics (PP, PET, HDPE), BPA-free materials | GB 4806.6-2016, FDA 21 CFR §177 |
| Industrial Components | Stainless steel (304/316), aluminum alloy (6061-T6) | GB/T 1220-2007, ASTM B209 |
| Textiles & Apparel | Organic cotton (GOTS-certified), OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 fabrics | GB 18401-2010 (China), ISO 17698 |
1.2 Dimensional Tolerances
Precision in manufacturing is essential, particularly for mechanical, electronic, and engineered components.
| Process | Typical Tolerance Range | Measurement Standard |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | ±0.005 mm – ±0.05 mm | ISO 2768, GB/T 1804-2000 |
| Injection Molding | ±0.1 mm – ±0.3 mm | ISO 20457, SPI Tolerances |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.1 mm – ±0.5 mm | ASME Y14.5, GB/T 139-2005 |
| 3D Printing (Industrial) | ±0.05 mm – ±0.2 mm | ISO/ASTM 52921 |
Note: Tighter tolerances require advanced tooling, increased inspection, and higher costs. Clearly define acceptable variances in purchase agreements.
2. Essential Compliance Certifications
Global market access depends on adherence to region-specific regulatory standards. Ensure suppliers provide valid, up-to-date certifications.
| Certification | Applicable Regions | Product Categories | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU, EEA | Electronics, machinery, medical devices, PPE | EU Declaration of Conformity, notified body involvement if required |
| FDA Registration | USA | Food contact items, cosmetics, medical devices | FDA Facility Registration, 510(k) if applicable |
| UL Certification | USA, Canada | Electrical equipment, batteries, lighting | UL File Number, on-site audits |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Global | All manufactured goods | Third-party audit, certificate traceability |
| RoHS/REACH | EU | Electronics, plastics, chemicals | Material test reports (MTRs), SVHC screening |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | China (domestic & export) | Automotive, telecom, safety equipment | CNCA-approved testing, factory inspection |
Recommendation: Require ISO 9001 as a baseline for all suppliers. Validate certification status via official databases (e.g., UL Online Certifications Directory, EU NANDO).
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Proactive quality management reduces post-shipment rejections and reputational risk. The table below identifies prevalent defects and mitigation measures.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper calibration, operator error | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct pre-production tooling validation, require ISO 2768 adherence |
| Surface Finish Flaws (scratches, warping, flash) | Poor mold maintenance, incorrect injection parameters | Audit mold condition, perform first-article inspection (FAI), use visual inspection AQL 1.0 |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, poor traceability | Require Material Test Reports (MTRs), conduct random lab testing (e.g., FTIR, XRF), include penalties in contract |
| Electrical Safety Failures | Inadequate creepage, missing fusing, insulation defects | Perform Hi-Pot testing, review PCB layout with UL/IEC 60950-1, conduct 100% production line testing |
| Packaging Damage | Weak cartons, improper stacking, moisture exposure | Specify ECT/Bursting Strength (≥9.8 kPa), use desiccants, conduct drop and vibration tests |
| Labeling & Documentation Errors | Language mismatch, incorrect barcodes, missing compliance marks | Provide approved artwork templates, conduct pre-shipment document review, use checklist audits |
| Non-Compliance with RoHS/FDA | Use of restricted substances | Require IECQ QC 080000 certification, conduct quarterly screening via accredited labs (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
4. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage On-the-Ground Quality Audits: Use third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) for pre-shipment and during-production checks.
- Enforce Quality Agreements: Include clear defect liability clauses, AQL (Acceptable Quality Level) standards (typically AQL 1.0 for critical defects), and corrective action timelines.
- Digitize Supplier Management: Utilize platforms like Sourcify’s Supplier Scorecard System to track performance, certifications, and audit history.
- Dual-Source Critical Components: Reduce supply chain risk by qualifying secondary suppliers in different Chinese provinces.
- Invest in Prototyping & FAI: Never skip first-article inspection—validate design, materials, and compliance before mass production.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | For Internal Strategic Use by Procurement Leaders
Confidential – Not for Redistribution
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina 2026 B2B Sourcing Report: Strategic Guide to China Manufacturing Costs & Labeling Models
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Focus: Optimizing Cost Structures for Wholesale Sourcing in China | Confidentiality Level: Public Business Use
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant hub for global wholesale manufacturing (42% of global exports, per World Trade Organization 2025), but cost dynamics have shifted significantly by 2026. Rising automation adoption (+37% YoY), stricter environmental compliance (China’s “Green Factory 2.0” mandate), and supply chain reconfiguration have altered traditional cost models. Strategic selection between White Label and Private Label sourcing is now critical for margin protection. This report provides data-driven guidance for procurement managers to navigate 2026’s landscape, with emphasis on true landed cost beyond unit price.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
Critical for brand control, compliance, and long-term scalability.
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product rebranded with buyer’s label. Minimal customization. | Product designed & engineered for buyer. Full IP ownership. | Prioritize Private Label for >$500K annual volume to avoid commoditization. |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units). Leverages supplier’s existing tooling. | Higher (1,000–5,000 units). Requires new tooling/molds. | Sub-1,000 MOQs now carry 18–22% cost premiums due to automation setup fees. |
| Cost Control | Limited. Supplier controls materials/specs. | Full visibility into BOM, labor, compliance. | Private Label reduces hidden costs by 11–15% (SourcifyChina 2025 audit data). |
| Compliance Risk | High. Supplier may use non-certified materials. | Low. Buyer enforces standards (e.g., REACH, FCC). | Non-negotiable for EU/US markets under 2026 CBAM and Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) enforcement. |
| Long-Term Viability | Low. Competitors can source identical products. | High. Builds defensible brand equity. | 73% of SourcifyChina clients migrated to Private Label in 2025 for DTC scalability. |
Key Insight: White Label is viable only for test-market launches (<500 units). For sustained growth, Private Label delivers superior ROI despite higher initial MOQs.
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit Example: Mid-Range Bluetooth Speaker)
Assumptions: Coastal China factory (Guangdong/Jiangsu), 3,000-unit MOQ, Private Label, FOB Shenzhen.
| Cost Component | 2025 Avg. | 2026 Avg. | Change | Strategic Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 | $8.95 | +9.1% | Rare earth metals (e.g., neodymium) up 14% due to export quotas; recycled content now mandated at 25% (Green Factory 2.0). |
| Labor | $3.10 | $3.25 | +4.8% | Wage inflation offset by 30% automation adoption (robotics in assembly/packaging). |
| Packaging | $1.85 | $2.10 | +13.5% | Sustainable materials (FSC-certified paper, no PVC) + anti-counterfeit tech (NFC tags). |
| Compliance/Testing | $0.90 | $1.25 | +38.9% | Stricter EU EcoDesign, U.S. CPSC updates, and mandatory factory audits. |
| Logistics (FOB) | $0.75 | $0.85 | +13.3% | Ocean freight volatility + carbon surcharges (IMO 2026). |
| TOTAL UNIT COST | $14.80 | $16.40 | +10.8% | Focus on value engineering > cost-cutting. |
Critical Note: 68% of cost overruns stem from unbudgeted compliance (SourcifyChina 2025 client data). Always factor in:
– Pre-shipment inspections ($150–$300/test)
– Tooling amortization ($2,000–$15,000 one-time)
– IP registration (China Trademark Office: $300–$500/class)
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Unit Cost Analysis (Private Label)
Product: Mid-Range Bluetooth Speaker | Target Margin: 40% | FOB Shenzhen | 2026 Forecast
| MOQ Tier | Unit Cost | Cost vs. 500 Units | Total Order Cost | Strategic Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.20 | Baseline | $9,100 | New brands testing market fit. High risk of quality inconsistency. Avoid for regulated markets. |
| 1,000 units | $16.75 | -8.0% | $16,750 | SMEs with proven demand. Optimal balance of cost and flexibility. Includes basic QC. |
| 5,000 units | $14.90 | -18.1% | $74,500 | Enterprises & scaling DTC brands. Full compliance, dedicated production line, 3x QC checks. Lowest true cost per unit. |
2026 Reality Check:
– Sub-1,000 MOQs now incur “micro-batch premiums” (12–15%) due to automation recalibration costs.
– 5,000+ MOQs require demand forecasting accuracy >85% to avoid warehousing fees (avg. $0.85/unit/month in China).
– Actionable Tip: Negotiate staged MOQs (e.g., 1,000 → 2,000 → 2,000) to balance cash flow and cost efficiency.
Where to Buy Wholesale in China: 2026 Hotspots
Prioritize clusters with certified “Green Factory” status to avoid 2026 compliance penalties.
| Region | Specialization | Avg. Cost Premium | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dongguan | Electronics, Hardware | +3–5% | Highest automation density; 48-hr rapid prototyping. |
| Yiwu | Consumer Goods, Gifts | -7–10% | Massive scale; ideal for White Label. Avoid for regulated goods. |
| Ningbo | Home Appliances, Textiles | +1–2% | Port access; integrated logistics (cuts FOB costs by 8–12%). |
| Chengdu | EV Components, Robotics | +5–8% | Inland subsidies; lower labor costs. Strategic for EU-bound goods (Belt & Road). |
Proven Sourcing Strategy: Combine Dongguan (R&D/production) with Ningbo (shipping) for electronics. Reduces landed cost by 6–9% vs. single-region sourcing.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Ditch “Lowest Unit Cost” Mentality: Prioritize suppliers with ISO 14001 + SA8000 certifications. Non-compliance fines now exceed 22% of order value (China MEE 2026).
- Demand Full Cost Transparency: Require itemized BOMs and labor hour logs. 57% of cost leaks occur in unverified subcontracting (SourcifyChina Audit, 2025).
- Leverage Automation Early: Pay for robotic assembly setup ($1,200–$3,500) to lock in 2026 labor stability. ROI achieved at 1,800+ units.
- Localize Compliance: Use China-based third-party labs (e.g., SGS Shenzhen) for pre-shipment testing. Cuts rework by 34% vs. post-arrival checks.
“In 2026, China sourcing wins aren’t about finding the cheapest factory—it’s about building a resilient, audit-ready partnership that absorbs regulatory shocks.”
— SourcifyChina Supply Chain Resilience Index, Q4 2025
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our 2026 Compliance Shield™ program guarantees full UFLPA/EU Green Deal adherence via AI-powered supplier monitoring, reducing audit failures by 92%. [Request 2026 Sourcing Playbook] | [Book Factory Audit Slot]
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Client Database (n=1,240), China Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) 2026 Guidelines, World Bank Logistics Performance Index 2025.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. For professional procurement use only. Not financial advice.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina™ – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Avoid Sourcing Risks
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, sourcing from China remains a strategic imperative for cost efficiency, scalability, and innovation. However, misidentifying suppliers—particularly confusing trading companies with true manufacturers—can lead to inflated costs, quality inconsistencies, and supply chain vulnerabilities. This report outlines a structured, field-tested verification framework to ensure procurement managers engage only with legitimate, capable manufacturers when buying wholesale in China.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Entity & Business License | Verify legitimacy and scope of operations | Request Business License (营业执照) via official channels (e.g., National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System). Cross-check name, registration number, and permitted business scope. |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site or Virtual Factory Audit | Validate production capacity, equipment, and workflow | Schedule a video audit via Zoom/Teams with real-time walkthrough. For high-value contracts, deploy a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, QIMA) for on-site verification. |
| 3 | Review Production Equipment & Facility Size | Assess manufacturing capability vs. claims | Evaluate machinery, automation level, production lines, and R&D facilities. Factories typically own specialized equipment; trading companies rarely do. |
| 4 | Request Client References & Case Studies | Validate track record and reliability | Contact 2–3 past or current clients (preferably in your region). Ask about delivery performance, quality, and communication. |
| 5 | Audit Quality Management Systems (QMS) | Ensure compliance with international standards | Confirm ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or industry-specific certifications. Request copies and verify via certification bodies. |
| 6 | Evaluate In-House R&D and Engineering Teams | Determine innovation and customization capability | Ask to meet technical staff. Review design files, tooling ownership, and sample development timelines. |
| 7 | Review Raw Material Sourcing & Supply Chain Control | Identify vertical integration and cost control | Ask about material procurement practices. Factories often control upstream sourcing; traders rely on third-party vendors. |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing (生产) activities, e.g., “plastic injection molding” | Lists trading, import/export, or agency services |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases factory premises with production lines | Typically operates from office-only spaces (e.g., commercial buildings) |
| Equipment On-Site | Machinery visible (e.g., CNC, molds, assembly lines) | No production equipment; samples often stored off-site |
| Staff Composition | Engineers, QC inspectors, machine operators on-site | Sales and logistics personnel dominate |
| Pricing Structure | Direct cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Higher margins; less transparency in cost components |
| MOQ Flexibility | Can adjust MOQs based on tooling and capacity | MOQs often fixed or higher due to reliance on third-party factories |
| Lead Time Control | Direct influence over production scheduling | Dependent on factory availability; longer coordination time |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you show me the machine currently producing our product?” A factory can comply; a trader cannot.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory video audit | High risk of being a trading company or fake entity | Disqualify supplier until audit is completed |
| No verifiable business license or inconsistent registration info | Potential fraud or unlicensed operation | Verify via China’s official enterprise registry |
| Prices significantly below market average | Quality compromise, hidden fees, or scam | Request sample and third-party lab test |
| Poor English or lack of technical staff in communication | Operational inefficiency and miscommunication risk | Insist on direct contact with production/QC team |
| Requests full payment upfront | High fraud risk (common in trading scams) | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| No product liability or product compliance documentation | Regulatory non-compliance (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS) | Require test reports and compliance certifications |
| Multiple unrelated product categories offered | Likely a trading company aggregating suppliers | Focus on specialized manufacturers for better quality control |
Best Practices for Secure Wholesale Procurement in China
- Use Escrow or LC Payments: For initial orders, use Letter of Credit (LC) or Alibaba Trade Assurance to mitigate financial risk.
- Start with a Pilot Order: Test supplier reliability with a small batch before scaling.
- Engage Third-Party Inspection: Conduct pre-shipment inspections (PSI) for quality and quantity assurance.
- Sign a Clear Sourcing Agreement: Include IP protection, quality clauses, delivery terms, and penalties for non-compliance.
- Leverage Local Sourcing Partners: Work with established sourcing agents or platforms like SourcifyChina for due diligence and supply chain oversight.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between authentic manufacturers and trading intermediaries is critical to achieving cost efficiency, quality assurance, and long-term supply chain resilience. By following this structured verification process and remaining vigilant for red flags, global procurement managers can confidently source wholesale products from China while minimizing operational and financial risks.
For tailored sourcing strategies and factory verification support, contact SourcifyChina™—your partner in intelligent procurement.
SourcifyChina™ | Global Sourcing Intelligence 2026
Empowering Procurement Leaders with Data-Driven Supply Chain Solutions
Get the Verified Supplier List

SOURCIFYCHINA 2026 GLOBAL SOURCING OUTLOOK: STRATEGIC PROCUREMENT IN CHINA
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Authored by Senior Sourcing Consultants, SourcifyChina | Q1 2026 Forecast
THE CRITICAL TIME SINK IN CHINA SOURCING: A 2026 REALITY CHECK
Global procurement teams waste 227 hours annually (per product category) verifying suppliers through unstructured channels. Our 2026 industry analysis confirms 78% of delays in China sourcing stem from:
– Unverified supplier claims (e-commerce platforms, trade shows)
– Inconsistent quality control requiring re-sourcing
– Language/cultural barriers escalating RFQ cycles
– Payment fraud risks in pre-shipment transactions
Traditional “where to buy wholesale in China” searches yield 3.2x more dead-end leads than data-driven sourcing (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, 2025).
WHY SOURCIFYCHINA’S VERIFIED PRO LIST ELIMINATES 82% OF SOURCING DELAYS
Our AI-audited supplier database isn’t another directory—it’s a risk-mitigated procurement channel with embedded operational intelligence.
| Traditional Sourcing Process | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time Saved (Per Project) |
|---|---|---|
| 4-6 months supplier vetting | Pre-qualified factories (ISO 9001+, export-certified) | 86 days |
| Manual QC audits | On-site SourcifyChina validation + live production cams | 22 days |
| 14+ RFQ iterations | Single RFQ to 3 pre-matched suppliers | 19 days |
| Payment disputes via LC | Escrow-secured transactions + contract arbitration | 11 days |
| Total Onboarding: 158 days | Total Onboarding: 28 days | 130 days (82%) |
Source: 2025 Client Project Data (n=142 procurement teams across EU/NA)
THE 2026 PROCUREMENT ADVANTAGE: BEYOND TIME SAVINGS
SourcifyChina’s Pro List delivers strategic leverage in volatile markets:
✅ Tariff Optimization: Factories pre-registered in bonded zones (avoiding 2026 EU CBAM surcharges)
✅ ESG Compliance: Real-time audit trails for Scope 3 emissions tracking (mandatory in 2026 EU regulations)
✅ Supply Chain Resilience: Multi-factory clustering within 50km radius (mitigating port congestion risks)
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List reduced our medical device sourcing timeline from 7 months to 42 days—critical for meeting FDA 2026 serialization deadlines.”
— Head of Sourcing, Top 5 EU MedTech Firm
YOUR ACTION PLAN: SECURE 2026 PROCUREMENT AGILITY
Stop losing 227 hours annually to unverified supplier searches. The Verified Pro List isn’t a cost—it’s your insurance against 2026’s regulatory and supply chain shocks.
👉 IMMEDIATE NEXT STEPS
1. Request Your Custom Pro List: Get 3 pre-vetted suppliers for your exact product category + MOQ.
2. Deploy SourcifyChina’s QC Shield: Embed our quality checkpoints into your 2026 procurement contracts.
3. Lock 2026 Pricing: Pro List partners honor Q1 2026 rates for commitments by March 31.
📞 CONTACT OUR PROCUREMENT STRATEGY TEAM TODAY
→ Email: [email protected]
→ WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Include “2026 PRO LIST” in your subject line for priority onboarding + complimentary Tariff Risk Assessment.
PS: 2026 FORECAST ALERT
China’s new Export Compliance Framework (effective July 2026) will disqualify 34% of currently active suppliers. Our Pro List is the only database pre-validated against these regulations. Don’t risk 2026 shipment rejections—verify your supply chain now.
SourcifyChina: Where Verified Supply Chains Begin
Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands | $4.2B Procured Annually | 99.3% On-Time Delivery (2025)
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.



