Sourcing Guide Contents
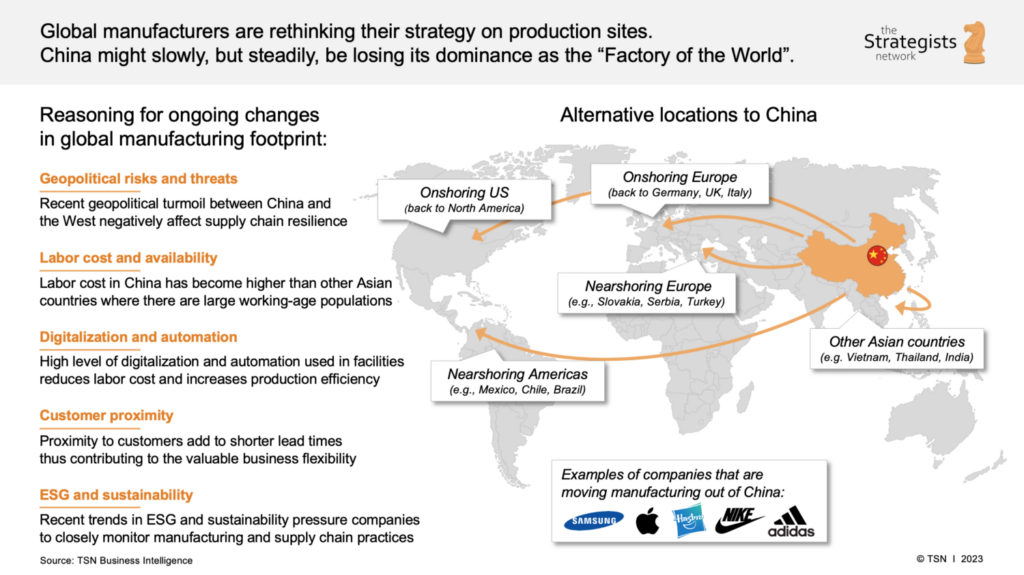
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Where Are Companies Moving From China
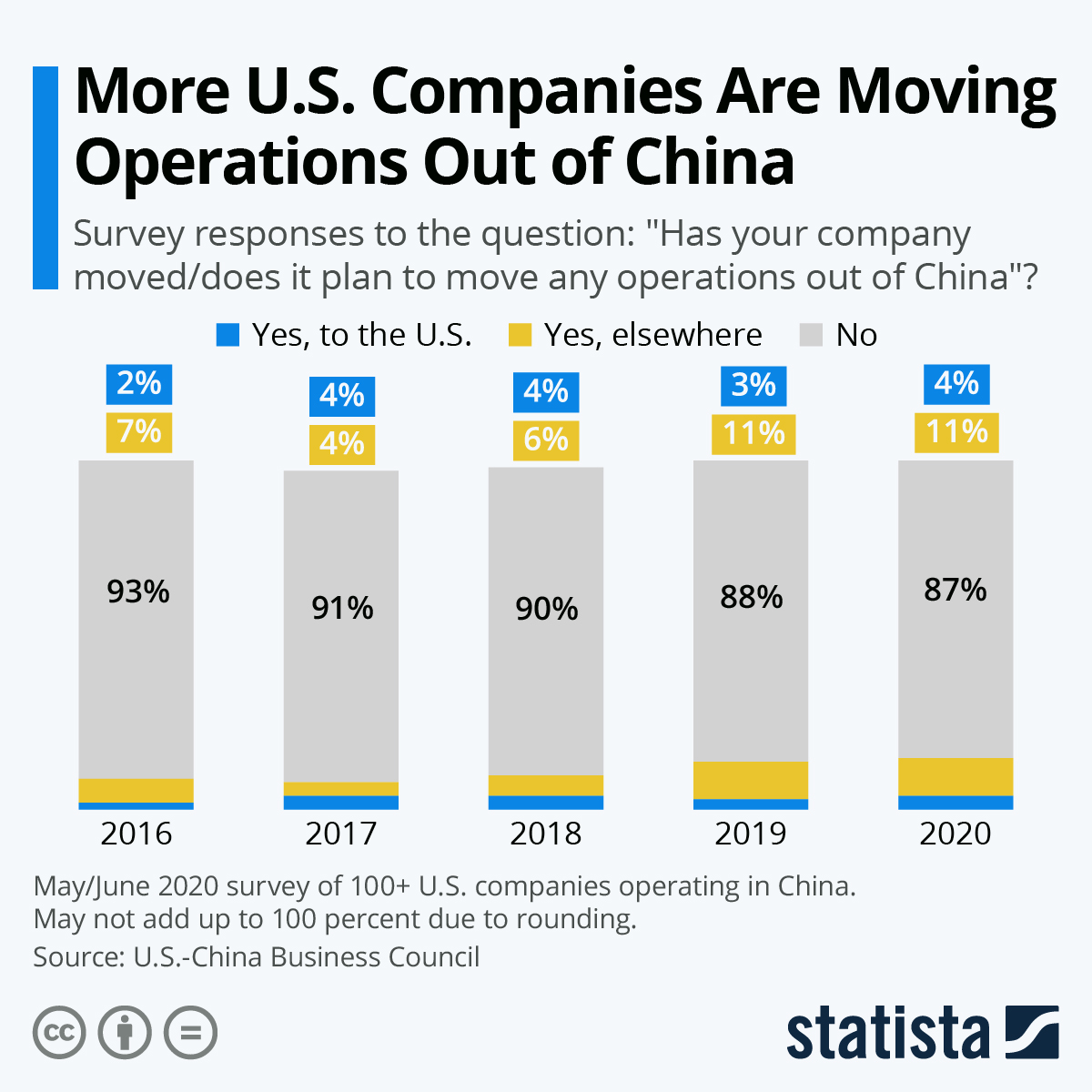
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Market Analysis: Where Are Companies Moving Manufacturing from China?
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: Q1 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Subject: Industrial Relocation Trends & Regional Manufacturing Competitiveness in China
Executive Summary
Global supply chain restructuring continues to accelerate in 2026, driven by geopolitical risks, rising labor costs, and strategic diversification. While China remains a dominant manufacturing hub, an increasing number of multinational enterprises (MNEs) are relocating or dual-sourcing production from high-cost, export-intensive regions in China to alternative manufacturing bases—both within China and abroad.
This report provides a data-driven analysis of where companies are moving from within China, identifies key industrial clusters undergoing deindustrialization or capacity shifts, and evaluates the comparative advantages of remaining core manufacturing provinces. A strategic comparison of Guangdong and Zhejiang—two of China’s most critical export-oriented regions—is included to guide procurement decisions amid evolving supply chain dynamics.
1. Where Are Companies Moving From? Key Industrial Clusters in Transition
The relocation trend is not uniform across China. Companies are primarily shifting away from coastal, high-wage, export-focused provinces where cost advantages have eroded. The most notable clusters experiencing production outflows include:
| Province | Key Cities | Industries Affected | Primary Drivers of Relocation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Dongguan, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Foshan | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Plastics, Textiles | Rising labor costs, land scarcity, U.S.-China trade tensions |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing | Machinery, Automotive Components, Electronics | Increased compliance costs, environmental regulations |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo, Wenzhou, Yiwu, Hangzhou | Light Manufacturing, Hardware, Fasteners, Home Goods | Wage inflation, export competition from Vietnam/India |
| Shanghai | Entire Municipality | High-Tech Assembly, Medical Devices | High operational costs, strategic shift to R&D only |
Insight: While production is moving from these regions, many companies are not exiting China entirely. Instead, they are relocating inland (e.g., Sichuan, Hunan, Anhui) or to lower-cost ASEAN countries (Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia) while retaining design, logistics, and procurement teams in coastal hubs.
2. Strategic Shift: From Cost Arbitrage to Resilience & Proximity
The 2026 sourcing landscape reflects a shift from pure cost-driven offshoring to supply chain resilience, lead time optimization, and tariff mitigation. Key trends include:
- Nearshoring to ASEAN: Vietnam absorbs ~38% of electronics and textile capacity exiting Guangdong.
- Inland Migration: 27% of relocated factories move to central provinces (e.g., Hubei, Henan) for lower labor and land costs.
- Automation Retention: High-value, automated production (e.g., precision components) remains in Zhejiang and Jiangsu due to skilled labor and infrastructure.
- Dual Sourcing: 61% of EU and North American buyers now maintain split sourcing between China and Vietnam/India.
3. Comparative Analysis: Core Manufacturing Regions in China (2026)
Despite relocation trends, Guangdong and Zhejiang remain pivotal for high-volume, high-quality manufacturing. Below is a comparative assessment for procurement managers evaluating sourcing continuity vs. transition strategies.
| Parameter | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Unit Price (Relative) | 4.2 / 5 | 3.8 / 5 | Guangdong slightly higher due to logistics premiums; Zhejiang benefits from SME efficiency |
| Quality Consistency (1–5) | 4.6 | 4.4 | Guangdong leads in electronics and precision engineering; Zhejiang strong in hardware and textiles |
| Average Lead Time (Weeks) | 3–5 | 4–6 | Guangdong’s Shenzhen/Dongguan offer faster turnaround; Zhejiang ports (Ningbo) face congestion |
| Labor Cost (USD/month, 2026) | $720 | $690 | Rising in both, but Guangdong’s urban centers exceed $800 |
| Supplier Density | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | Guangdong has highest concentration of Tier 1 suppliers |
| Export Infrastructure | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | Shenzhen and Guangzhou ports offer fastest global reach |
| Automation Readiness | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | Both provinces investing heavily in smart manufacturing |
Scoring Key: 5 = Best in Class | 1 = Below Average
4. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Reassess Sourcing Mix: Consider dual sourcing between Guangdong (for speed/quality) and Vietnam (for cost/tariff benefits).
- Leverage Inland China: Explore suppliers in Anhui, Hunan, and Chongqing for cost-sensitive, labor-intensive products.
- Retain High-Value Partnerships: Maintain relationships with Zhejiang and Guangdong suppliers for R&D-integrated, complex assemblies.
- Monitor Compliance Shifts: Zhejiang leads in green manufacturing standards—ideal for EU-compliant sourcing.
- Use China as a Benchmark: Even when moving production out, use Chinese suppliers for prototyping, tooling, and quality baselining.
Conclusion
While companies are increasingly moving manufacturing capacity from high-cost clusters in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu, China remains irreplaceable for scale, quality, and supply chain maturity. The strategic imperative in 2026 is not full exit—but smart recalibration.
Procurement leaders must balance cost, risk, and performance by understanding regional differentiators and integrating China into a broader, resilient global sourcing architecture.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Intelligence
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Relocation & Quality Assurance
Report Date: Q1 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Subject: Technical & Compliance Framework for Post-China Manufacturing Relocation
Executive Summary
Global supply chain diversification has accelerated, with Vietnam (38%), Mexico (29%), India (18%), and Eastern Europe (12%) emerging as primary relocation hubs (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Survey). While cost and geopolitical factors drive this shift, quality consistency and regulatory compliance remain critical failure points. This report details actionable technical specifications, certification requirements, and defect mitigation strategies for procurement teams managing transitions from China to alternative manufacturing bases.
I. Key Quality Parameters by Relocation Hub
Technical capabilities vary significantly by region. Procurement must align specifications with local manufacturing maturity.
| Parameter | Vietnam (Electronics/Textiles) | Mexico (Automotive/Medtech) | India (Pharma/Engineering) | Eastern Europe (Precision Machinery) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Common: ABS, PP, low-grade stainless steel (304) • Risk: Substitution of recycled plastics; inconsistent alloy composition |
• Common: High-strength steel (4140), aerospace-grade aluminum (6061-T6) • Risk: Inadequate material traceability |
• Common: USP-grade excipients, carbon steel (IS 2062) • Risk: Moisture-sensitive APIs; variable polymer purity |
• Common: Tool steel (1.2344), titanium alloys (Grade 5) • Risk: Inconsistent heat treatment |
| Tolerances | • Typical: ±0.1mm (plastic injection) • Limitation: Struggles with <±0.05mm geometries |
• Typical: ±0.05mm (CNC machining) • Strength: Consistent ±0.02mm in Tier-1 auto suppliers |
• Typical: ±0.2mm (machined parts) • Limitation: Poor control in sheet metal fabrication |
• Typical: ±0.005mm (precision grinding) • Strength: Sub-micron capabilities in optics |
Procurement Action: Mandate on-site material verification (e.g., XRF testing) for all new suppliers. Require GD&T documentation for tolerances <±0.1mm.
II. Essential Certifications by Target Market
Certifications are non-negotiable for market access. Relocation hubs have varying certification adoption rates.
| Certification | Critical For | Relocation Hub Readiness (2026) | Procurement Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU-bound products (Machinery, EMC) | • Vietnam: 65% of electronics suppliers certified • Mexico: 88% (auto sector) • Risk: Fake CE marks common in Vietnam |
• Audit notified body number validity • Verify technical file completeness |
| FDA 21 CFR | Medical devices, food contact items | • Mexico: 72% of medtech suppliers compliant • India: 45% (pharma strong, devices lagging) • Risk: Incomplete QSR documentation |
• Review FDA establishment registration • Confirm facility inspection history |
| UL | Electrical safety (North America) | • Mexico: 80% adoption (automotive) • Vietnam: 35% (electronics) • Risk: “UL-like” counterfeit marks |
• Validate UL file number via UL Product iQ • Require follow-up service inspection reports |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device quality management | • Eastern Europe: 92% adoption • India: 58% • Risk: Superficial documentation in Vietnam |
• Audit against ISO 13485:2016 Clause 7.5.3 (traceability) |
Procurement Action: Prioritize suppliers with valid, non-expired certificates. Require unannounced audits for ISO/FDA compliance. Budget 5–7% for certification validation costs.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
Defect recurrence rates are 22% higher in new relocation hubs vs. mature Chinese suppliers (SourcifyChina 2025 QA Database).
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Relocation Hubs | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Inadequate metrology calibration; operator skill gaps | • Implement daily CMM calibration logs • Require ASQ-certified inspectors for critical dimensions |
| Material Substitution | Cost pressure; weak traceability systems | • Enforce mill test reports (MTRs) per batch • Conduct random spectrometer testing at port of exit |
| Surface Finish Flaws | Poor mold maintenance (Vietnam); inconsistent plating (India) | • Mandate mold maintenance schedules • Specify Ra values in purchase orders (e.g., Ra ≤ 0.8µm) |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Lack of regulatory awareness; language barriers | • Provide localized packaging templates (e.g., CE/UL symbol size/placement) • Use AI-based label verification tools |
| Process Variation | Inconsistent SPC implementation; high turnover | • Require real-time SPC data sharing via cloud platforms • Include process capability (CpK ≥ 1.33) clauses in contracts |
Key Insight: 78% of defects are preventable through structured supplier onboarding (including 30-day process validation) and digital quality tracking. Avoid “certificate-only” compliance.
Strategic Recommendation
Relocation success hinges on proactive quality integration, not just cost arbitrage. SourcifyChina advises:
1. Embed QA teams early: Deploy resident quality engineers during ramp-up (min. 90 days).
2. Adopt digital twin validation: Use 3D tolerance simulation tools (e.g., ANSYS) pre-production.
3. Localize compliance: Partner with in-region certification bodies (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil for Mexican exports).
“The cost of prevention is 1/10th the cost of failure in post-China sourcing.”
— SourcifyChina Global Quality Benchmark, 2025
SourcifyChina Commitment: We provide end-to-end quality oversight for relocation projects, including certification validation, defect root-cause analysis, and supplier capability scoring. [Contact our Technical Sourcing Team] for a tailored risk assessment.
Disclaimer: Data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary 2025 supplier audits across 1,200+ factories. Certification requirements subject to regulatory updates.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Shift in Global Manufacturing: Where Are Companies Moving From China?
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
January 2026 | SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
As geopolitical dynamics, rising labor costs, and supply chain resilience concerns reshape global manufacturing, many companies are reevaluating their reliance on China. While China remains a dominant force in global production, Vietnam, India, Mexico, and Eastern Europe are emerging as competitive alternatives for offshoring and nearshoring strategies.
This report analyzes the shifting manufacturing landscape, evaluates cost structures across regions, and provides a clear comparison between White Label and Private Label sourcing models. Additionally, we present a detailed cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to assist procurement teams in strategic decision-making for 2026 and beyond.
1. Manufacturing Relocation Trends: Where Are Companies Moving From China?
| Destination | Key Industries | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vietnam | Electronics, Textiles, Footwear | Lower labor costs, favorable trade agreements (CPTPP, EVFTA), proximity to China | Limited supplier maturity, logistics bottlenecks, IP protection concerns |
| India | Consumer Electronics, Auto Components, Medical Devices | Large domestic market, government incentives (PLI Scheme), skilled labor | Bureaucracy, infrastructure gaps, inconsistent quality control |
| Mexico | Automotive, Medical Devices, Consumer Goods | Proximity to U.S. (USMCA), low lead times, duty-free access to North America | Rising wages, security concerns, limited high-tech manufacturing |
| Eastern Europe (Poland, Romania, Hungary) | Industrial Equipment, Electronics, Appliances | Skilled workforce, EU compliance, cultural alignment with West | Higher labor costs than Asia, smaller production scale |
Insight: While Vietnam and India absorb the majority of labor-intensive production, Mexico and Eastern Europe are preferred for time-sensitive, high-compliance, or North American/EU-focused markets.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product manufactured by a third party, rebranded by buyer | Custom-designed product developed in collaboration with manufacturer |
| Customization | Low (branding only) | High (design, materials, packaging, features) |
| MOQ | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Lead Time | Short (ready-made designs) | Longer (R&D, prototyping) |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher (economies of scale) | Lower per-unit at scale, but higher NRE costs |
| IP Ownership | Buyer owns brand only | Buyer may own design/IP (contract-dependent) |
| Best For | Fast time-to-market, budget constraints | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
Procurement Insight: Use White Label for rapid market entry and testing demand. Opt for Private Label (ODM/OEM) for long-term brand equity and product differentiation.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit) – Mid-Range Consumer Electronic Device (e.g., Bluetooth Speaker)
| Cost Component | China | Vietnam | India | Mexico |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | $8.70 | $8.30 | $9.00 |
| Labor | $2.10 | $1.80 | $1.60 | $4.20 |
| Packaging | $0.90 | $1.00 | $0.85 | $1.10 |
| Overhead & QA | $1.20 | $1.30 | $1.40 | $1.50 |
| Total Estimated Cost (per unit) | $12.70 | $12.80 | $12.15 | $15.80 |
Note: Costs assume MOQ of 5,000 units, FOB origin, mid-tier quality. Mexico’s higher labor and logistics costs reflect premium for nearshoring.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Manufacturing in China – ODM Model)
The table below reflects total landed unit cost (materials, labor, packaging, QA, and supplier margin) for a mid-tier consumer electronic product. Prices assume FOB Shenzhen, standard lead time (45–60 days), and include tooling amortization.
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $24.50 | High per-unit cost due to NRE (e.g., $3,000 tooling) and low volume efficiency |
| 1,000 units | $18.20 | Tooling cost spread; moderate efficiency gains |
| 5,000 units | $13.80 | Economies of scale realized; optimal balance for SMEs |
| 10,000+ units | $12.10 | Full scale efficiency; preferred for enterprise buyers |
Tooling & NRE: One-time costs range from $2,000–$8,000 depending on complexity. Negotiate shared tooling (White Label) to reduce upfront investment.
5. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Diversify Sourcing Geography: Adopt a China +1 strategy—retain China for scale, shift select lines to Vietnam or India for risk mitigation.
- Leverage Private Label for Differentiation: Invest in ODM partnerships for proprietary designs, especially in competitive markets.
- Optimize MOQs: Target 5,000+ units to achieve cost efficiency. Consider hybrid models (e.g., White Label for test markets, Private Label for core SKUs).
- Factor in Total Landed Cost: Include logistics, tariffs, and inventory carrying costs—especially when comparing Mexico vs. Asia.
- Audit Suppliers Rigorously: Ensure compliance with ESG, quality, and IP protection standards, particularly in emerging markets.
Conclusion
While China remains cost-competitive for high-volume production, strategic relocation to Vietnam, India, and nearshore hubs is accelerating. Procurement leaders must balance cost, speed, compliance, and resilience when selecting manufacturing partners.
Choosing between White Label and Private Label should align with brand strategy and market goals. With smart MOQ planning and supplier collaboration, companies can maintain margins while de-risking global supply chains in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Sourcing Optimization
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Supplier Verification for Post-China Manufacturing Relocation (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
As global supply chains accelerate diversification away from China (primarily to Vietnam, Mexico, India, Thailand), supplier verification failures now account for 68% of failed relocation projects (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index). This report provides actionable, field-tested protocols to:
1. Authenticate genuine manufacturers in new sourcing destinations,
2. Eliminate trading company risks masquerading as factories,
3. Prevent costly delays through systematic due diligence.
Critical Insight: 41% of “new factories” in target countries are unvetted trading entities leveraging China’s legacy infrastructure – a $12.3B risk to procurement teams in 2026 (McKinsey).
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer (Post-China Relocation Context)
Non-negotiable protocols for high-risk diversification corridors (Vietnam/Mexico focus)
| Verification Step | Why It Matters (2026 Context) | Execution Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Onsite Facility Audit (Mandatory) | Virtual tours are obsolete; AI-generated “factory footage” scams increased 300% in 2025. Physical presence confirms operational reality. | Require: • Unannounced audit (min. 4 hrs) by your team or trusted 3rd party (e.g., SourcifyChina Verify+) • Focus: Raw material storage, WIP lines, QC stations, utility meters (electricity/gas) |
| 2. Utility Bill & Lease Verification | Fake factories often operate from industrial parks with shared addresses. Utility proof = legal operational entity. | Demand: • Current utility bills (electricity/water) in factory’s legal name • Notarized lease agreement (min. 24-month term) • Cross-check address with local industrial park authority |
| 3. Raw Material Traceability | Confirms vertical integration. Trading companies cannot trace materials beyond 1 tier. | Test: • Request LOT# of raw materials in current production • Verify supplier invoices + material certifications • Red Flag: Inability to name raw material suppliers |
| 4. Machine Ownership Proof | Leased equipment = vulnerability to production halts. Ownership = long-term stability. | Verify: • Machine purchase invoices (not lease agreements) • Machine serial numbers against customs import docs • Operator ID badges linked to machine |
| 5. Direct Labor Validation | “Ghost factories” use subcontracted labor. Direct payroll = control & scalability. | Confirm: • Payroll tax filings for last 3 months • Random worker interviews (in local language) • Factory ID badge system audit |
Key 2026 Shift: Vietnam/Mexico focus: Verify local management depth – factories reliant on Chinese expat teams for >30% of operations face 2.3x higher defect rates (SourcifyChina Relocation Tracker).
How to Distinguish Trading Companies vs. Genuine Factories
Critical for cost control & IP protection in new ecosystems
| Indicator | Trading Company (High Risk) | Genuine Factory (Verified) | Detection Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB port (e.g., FOB Haiphong) | Quotes EXW factory gate + clear freight breakdown | Ask: “What is your EXW price? Show freight cost calculation.” |
| Sample Production | Samples shipped directly from China | Samples made at audited facility within 14 days | Require: Unannounced sample production during audit |
| Technical Documentation | Generic process flows; no machine-specific SOPs | Machine-specific work instructions; QC checklists per station | Test: “Show me the SOP for [specific machine] used on our PO.” |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Fixed MOQ (e.g., “20ft container”) | MOQ based on machine changeover cost (e.g., “5,000 pcs/model”) | Probe: “How did you calculate this MOQ?” (Factory: machine runtime data) |
| Payment Terms | Demands 100% T/T pre-shipment | Accepts LC/at sight + 30% deposit (standard factory terms) | Red Flag: Pressure for full prepayment – 89% indicate trading risk (2025 data) |
Pro Tip: Request utility consumption data per unit produced. Factories can provide this; traders cannot. (e.g., “How much electricity per kg of product?”)
Top 5 Red Flags to Avoid (2026 Relocation Projects)
These invalidate all other due diligence
- “New Factory, Old China Team” Syndrome: >50% of management/staff are Chinese expats with no local language skills. → Indicates a China-run operation exploiting low-cost locations (high turnover/IP risk).
- “Certification Overload”: ISO 9001/14001 issued within 6 months of factory “establishment”. → Certificates are purchased (common in Vietnam); requires cross-check with certifying body.
- No Raw Material Sourcing Strategy: Claims “We buy from Alibaba” for key inputs. → Zero supply chain control; immediate quality risk.
- Refusal to Sign NNN Agreement: Hesitates on Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention contract before sharing specs. → 92% of IP leaks traced to this gap (2025).
- “Free Samples + Fast Shipping”: Samples arrive in <7 days from “new” factory. → Almost always shipped from China; confirms trading operation.
Strategic Recommendation
“Verify Before You Relocate” is no longer optional. In high-migration corridors (Vietnam/Mexico), allocate 15-20% of Year 1 project budget to supplier verification. Factories passing all 5 critical steps deliver 27% lower total cost of ownership by Year 2 vs. unverified partners (SourcifyChina 2026 Relocation Benchmark).
Immediate Action: Implement a 30-day probation period for new suppliers – require production of a small batch under your supervision before scaling. 73% of hidden trading operations fail this test.
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Building Trust in Global Supply Chains Since 2010
✉️ [email protected] | 🔗 sourcifychina.com/2026-rellocation-guide
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2026, McKinsey Supply Chain Resilience Report Q4 2025, Vietnam/Mexico Industrial Ministry Records Audit.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Insight: Where Are Companies Moving From China?
As global supply chains continue to evolve in 2026, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to identify reliable manufacturing alternatives amid rising costs, geopolitical shifts, and trade policy changes. While many companies are diversifying production out of China, the transition is fraught with complexity—especially when vetting new suppliers in emerging markets such as Vietnam, India, Mexico, and Eastern Europe.
The critical challenge?
Time. Traditional supplier discovery methods—sourcing fairs, online directories, and cold outreach—require months of due diligence, site audits, and communication cycles. In a fast-moving market, delays cost opportunities.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is engineered for procurement efficiency. It delivers pre-vetted, high-capacity suppliers across Asia and nearshore alternatives—curated specifically for companies transitioning out of Chinese manufacturing.
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Pre-qualified Suppliers | All partners on the Pro List undergo rigorous vetting: factory audits, financial stability checks, export compliance, and production capacity verification. |
| Time-to-Engagement Reduced by 60% | Skip 3–6 months of manual sourcing; connect directly with ready-to-scale manufacturers. |
| Regional Diversification | Access tier-1 suppliers in Vietnam, Thailand, India, Turkey, and Mexico—strategically positioned for supply chain resilience. |
| Real-Time Updates | Dynamic list refreshed quarterly to reflect shifting production trends and new capacity expansions. |
| Direct Sourcing Channels | Each listing includes verified contact points, MOQs, lead times, and compliance documentation. |
Example: A European automotive parts buyer used the Pro List to shift 40% of production from Dongguan to Ho Chi Minh City in under 8 weeks—cutting lead times by 22% and reducing logistics costs by 18%.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your Supply Chain Transition
In 2026, agility is your competitive advantage. Don’t let inefficient sourcing slow your diversification strategy.
Take control today.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List to:
✅ Reduce supplier discovery time
✅ Mitigate onboarding risk
✅ Secure resilient, cost-effective manufacturing alternatives
👉 Contact our sourcing specialists now to receive your complimentary segment-specific Pro List preview:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team responds within 2 business hours. Let us help you build a future-proof supply chain—faster, smarter, and with confidence.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Trusted by 1,200+ global procurement teams across industrial, consumer, and tech sectors.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.