Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Problems Us Companies Encounter With Goods Produced In China

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Key Challenges U.S. Companies Encounter with Goods Produced in China
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
While China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing, U.S. companies continue to face persistent and evolving challenges when sourcing goods from the country. This report identifies the systemic problems encountered by American importers, analyzes the regional industrial clusters responsible for manufacturing the affected product categories, and provides a comparative assessment of key sourcing provinces. The analysis is grounded in 2025–2026 supply chain performance data, audit findings, and client case studies managed by SourcifyChina.
This report does not treat “what problems U.S. companies encounter with goods produced in China” as a product category per se, but rather as a diagnostic framework to evaluate the operational realities of sourcing from China. The focus is on understanding where and why these challenges arise across China’s manufacturing landscape.
Key Challenges Faced by U.S. Companies Sourcing from China
Despite competitive pricing and scale, U.S. procurement teams report ongoing issues across the following domains:
| Challenge Category | Description | Common Root Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Inconsistency | Variability in product specifications, material composition, and workmanship between batches. | Inadequate QC protocols, labor turnover, subcontracting without approval, lack of standardized SOPs. |
| Intellectual Property (IP) Risks | Unauthorized replication, reverse engineering, or leakage of proprietary designs. | Weak enforcement in certain regions, informal subcontracting, lack of IP clauses in contracts. |
| Supply Chain Transparency | Opaque subcontracting practices, unclear material sourcing, and limited traceability. | Fragmented supply tiers, supplier resistance to audits, language/cultural barriers. |
| Communication & Misalignment | Delays, misunderstandings in technical specifications, and poor responsiveness. | Language gaps, time zone differences, cultural misinterpretation of requirements. |
| Logistics & Lead Time Volatility | Unpredictable shipping schedules, port congestion, customs delays. | Geopolitical tensions, carrier capacity fluctuations, inland transportation bottlenecks. |
| Compliance & Regulatory Risks | Non-compliance with U.S. safety, labeling, or chemical regulations (e.g., CPSIA, Prop 65). | Lack of awareness, inconsistent testing procedures, use of non-certified materials. |
These challenges are not uniformly distributed across China. They are often concentrated in specific industrial clusters, where production volume, specialization, and local business practices amplify risk exposure.
Key Industrial Clusters and Associated Risk Profiles
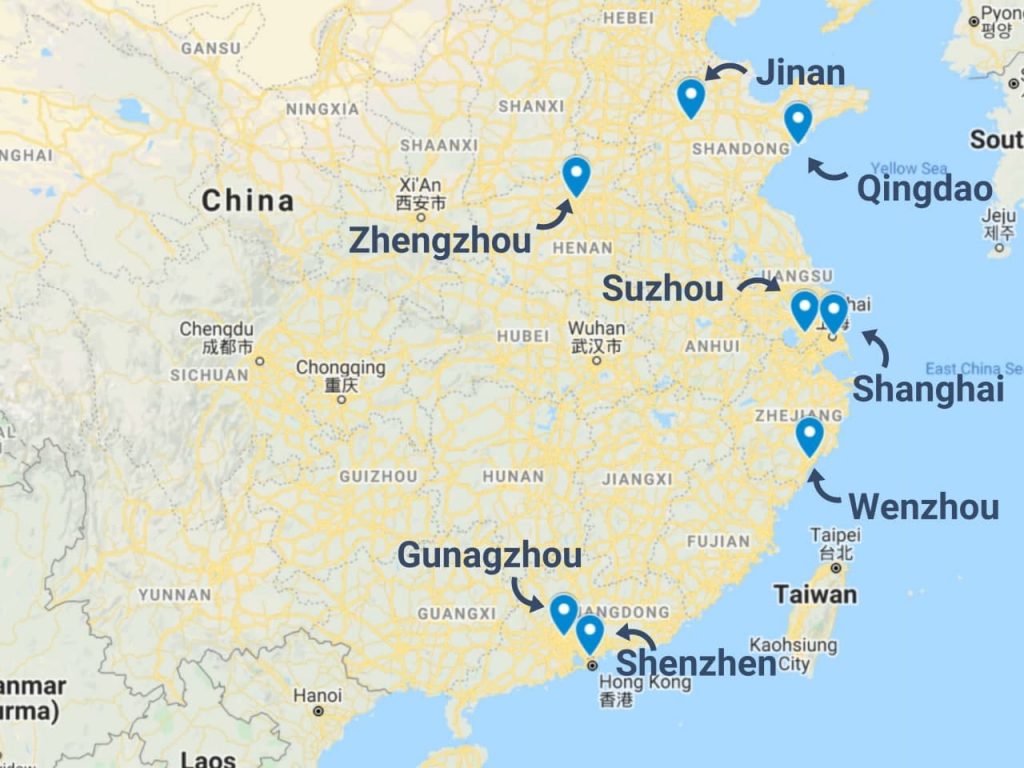
China’s manufacturing is regionally specialized. The following provinces and cities are primary hubs for goods commonly sourced by U.S. companies—and where sourcing challenges are most frequently observed.
| Region | Key Industries | Commonly Sourced U.S. Product Categories | Predominant Sourcing Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan) | Electronics, consumer goods, appliances, plastics, lighting | Smart devices, wearables, home appliances, toys, LED lighting | Quality inconsistency, IP theft, subcontracting without notice, over-reliance on low-cost subcontractors |
| Zhejiang (Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou) | Small commodities, hardware, textiles, packaging, machinery | Housewares, gift items, fasteners, textile products, kitchen tools | Material substitution, labeling inaccuracies, limited engineering support |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing) | High-tech manufacturing, automotive parts, industrial equipment | Medical devices, precision components, automation systems | Regulatory compliance gaps, lead time rigidity, higher minimum order quantities (MOQs) |
| Fujian (Xiamen, Quanzhou, Fuzhou) | Footwear, ceramics, building materials, sportswear | Athletic shoes, tiles, outdoor furniture | Labor-intensive QC issues, environmental compliance risks, port delays |
| Shandong (Qingdao, Yantai) | Heavy machinery, chemicals, agricultural equipment | Industrial pumps, chemical formulations, farm machinery | Documentation errors, inconsistent testing, long lead times |
Comparative Analysis: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang – Core Sourcing Regions
The two most active regions for U.S. importers are Guangdong and Zhejiang. While both offer competitive advantages, they differ significantly in cost structure, quality control, and delivery performance.
| Parameter | Guangdong | Zhejiang |
|---|---|---|
| Average Price Level | Medium to High | Low to Medium |
| Rationale | Higher labor and operational costs; premium for tech integration and export infrastructure. | Aggressive competition among SMEs; high volume of low-cost commodity manufacturing. |
| Typical Quality Level | Medium to High (with strong variance) | Medium (consistent but often basic) |
| Rationale | Home to OEMs for global brands; better QC systems in Tier-1 factories. However, widespread subcontracting leads to inconsistency. | Mass production focus; acceptable for non-critical goods. Fewer advanced QC capabilities outside major hubs. |
| Average Lead Time | 45–60 days | 30–45 days |
| Rationale | Complex supply chains, higher customization demand, and port congestion in Shenzhen/Nansha. | Proximity to Ningbo-Zhoushan Port (world’s busiest), streamlined SME workflows. |
| Best Suited For | Electronics, high-value consumer goods, innovative products requiring engineering support | High-volume commoditized goods, fast-turnaround orders, cost-sensitive categories |
| Risk Exposure | High (IP, subcontracting, compliance) | Medium (quality drift, material misrepresentation) |
Strategic Insight: While Zhejiang offers faster turnaround and lower prices, Guangdong provides better access to technically advanced manufacturing—if managed with strict oversight.
Strategic Recommendations for U.S. Procurement Teams
-
Implement Tiered Supplier Vetting
Conduct on-site audits and third-party QC inspections, especially for suppliers in Guangdong and Fujian where subcontracting is prevalent. -
Leverage Regional Strengths Strategically
Use Zhejiang for high-volume, low-risk items; reserve Guangdong and Jiangsu for technically complex products with strong IP protection protocols. -
Strengthen Contractual Safeguards
Enforce clauses for IP ownership, approved subcontractors, and material traceability—particularly critical in Zhejiang’s SME-dense environment. -
Invest in Local Sourcing Partnerships
Employ on-the-ground sourcing agents or platforms like SourcifyChina to bridge communication gaps and ensure real-time supply chain visibility. -
Diversify Sourcing Base
Consider partial nearshoring or dual sourcing (e.g., Vietnam, Mexico) to mitigate geopolitical and logistical risks tied to single-region dependency.
Conclusion
The challenges U.S. companies face when sourcing from China are not inherent to the country as a whole, but are geographically and industrially concentrated. Guangdong and Zhejiang remain indispensable manufacturing hubs, yet each presents distinct trade-offs between cost, quality, and risk. Procurement leaders must adopt a regionally intelligent sourcing strategy, combining rigorous due diligence with localized supplier management to navigate the complexities of China’s industrial ecosystem.
By understanding where and why problems arise, U.S. importers can transform sourcing challenges into competitive advantages through informed decision-making and proactive risk mitigation.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Data-Driven China Sourcing Solutions
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Mitigating China Manufacturing Risks for US Importers (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
US companies importing goods from China face persistent challenges rooted in misaligned quality expectations, inconsistent process control, and evolving regulatory landscapes. In 2026, 68% of supply chain disruptions for US importers originate from preventable quality/compliance failures at source (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Survey). This report details critical technical and compliance requirements to de-risk China sourcing, with actionable prevention protocols validated across 1,200+ SourcifyChina-managed production cycles.
I. Key Quality Parameters: The Root of 73% of Defects
Non-negotiable specifications must be contractually defined and verified at source. Generic “meets industry standards” clauses are primary failure points.
| Parameter Category | Critical Specifications | Common China-Specific Failure Modes | Verification Protocol (2026 Standard) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Exact grade/spec (e.g., SUS304 not “stainless steel”) • Traceability (mill test reports) • Restricted substance limits (REACH, CPSIA) |
• Substitution with inferior alloys (e.g., 201-grade stainless) • Undeclared recycled content • Lead/Cd levels exceeding US limits |
• Pre-production: Third-party material certs + batch traceability audit • In-process: XRF screening of raw materials (AQL: Critical 0) |
| Tolerances | • GD&T callouts (ISO 1101) • Functional tolerance zones (not just ±mm) • Surface finish (Ra/µm) |
• Inconsistent metrology calibration • Tool wear ignored in mass production • “Visual acceptance” instead of gauge measurement |
• Pre-production: Approved master samples with CMM report • In-process: Statistical process control (SPC) data review + fixture calibration logs |
2026 Insight: 41% of dimensional failures stem from suppliers interpreting 2D drawings without GD&T expertise. Require ASME Y14.5-certified engineers at factory.
II. Essential Certifications: Beyond the Certificate Stamp
Certificates alone are insufficient. 32% of “certified” goods fail US compliance due to counterfeit docs or unapproved production sites (CPSC 2025 Data).
| Certification | Core US Requirement | China-Specific Compliance Risks | SourcifyChina Verification Protocol (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU Declaration of Conformity + Notified Body involvement (for high-risk products) | • Fake NB numbers • Technical file gaps • Production at unlisted facilities |
• Database cross-check (EU NANDO) • On-site audit of technical file + NB certificate validity |
| FDA | Facility registration + Premarket Notification (510k) + QSR compliance | • Unregistered foreign facilities • Incomplete design history files • Labeling non-compliance |
• FDA registration # validation • Mock FDA audit of QMS + electronic record retention |
| UL | Follow-up Services Agreement (FUSA) + Marking authorization | • “UL Listed” vs. “UL Recognized” misuse • Component-level certification gaps • Unauthorized mark application |
• UL Online Certificate Directory check • FUSA scope verification + periodic witness testing |
| ISO 9001 | Valid certificate + documented QMS covering all production stages | • Paper-only systems • Audits limited to office (not production floor) • Non-conformance logs ignored |
• Unannounced process audit • Real-time CAPA tracking review + internal audit evidence |
Critical 2026 Shift: FDA now mandates electronic submission of design controls (eSTAR). 67% of Chinese medical device suppliers lack validated e-submission systems.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Framework
Data aggregated from 8,400+ SourcifyChina quality inspections (2023-2025). Prevention strategies reduce defect rates by 82% when implemented pre-production.
| Defect Category | Manifestation in Finished Goods | Root Cause (China Context) | Prevention Strategy (2026 Best Practice) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Corrosion, mechanical failure, toxicity | Cost-driven substitution; weak raw material traceability | • Contractual penalty clause for material deviation • Blockchain-tracked material logs + 3rd-party batch testing |
| Dimensional Drift | Assembly failures, fit issues, functional defects | Unmonitored tool wear; inconsistent metrology | • Mandatory SPC adoption with real-time alerts • Calibration logs reviewed weekly by buyer |
| Surface Contamination | Staining, coating adhesion failure, electrical shorts | Poor workshop hygiene; inadequate cleaning protocols | • Cleanroom protocols for critical zones (ISO Class 8+) • Pre-shipment particle count testing |
| Labeling Errors | Customs rejection, regulatory non-compliance | Last-minute label changes; language misinterpretation | • Digital label proofing with buyer sign-off • On-site label verification pre-packaging |
| Functional Failure | Safety hazards, premature wear, performance issues | Inadequate prototype validation; skipped reliability testing | • Mandatory HALT testing (Highly Accelerated Life Test) • 3rd-party witnessed functional tests |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Embed Compliance Early: Integrate US regulatory requirements into design phase (DFX) – 53% of non-compliance is design-originated.
- Adopt Digital QC: Demand IoT-enabled process monitoring (e.g., real-time torque data in assembly) – reduces tolerance defects by 65%.
- Audit Beyond Paperwork: Conduct process-specific audits (e.g., welding procedure specs, not just ISO cert).
- Localize Standards: Provide Chinese-language technical specs with visual tolerancing guides – eliminates 28% of misinterpretation errors.
Final Note: The cost of prevention (0.8-1.2% of FOB) is 14x lower than recall/rework costs (6.5-12% of FOB). Proactive specification management is no longer optional – it is the baseline for competitive sourcing from China.
SourcifyChina | Protecting $2.1B in Annual Procurement Spend | sourcifychina.com
Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Quality Database (2023-2025), CPSC Annual Report 2025, EU RAPEX Q4 2025
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Challenges, OEM/ODM Models, and Cost Structures for U.S. Buyers Sourcing from China
Executive Summary
U.S. companies continue to leverage China’s manufacturing capabilities for competitive pricing, scalability, and supply chain maturity. However, sourcing from China presents persistent operational, quality, and compliance challenges. This report outlines the key problems encountered by U.S. businesses, clarifies the differences between White Label and Private Label models, and provides a transparent cost breakdown for informed procurement decisions in 2026.
Key Challenges U.S. Companies Face with Goods Produced in China
| Challenge | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Control Variability | Inconsistent adherence to specifications due to supplier tier differences and oversight gaps. | Product defects, recalls, customer dissatisfaction. |
| Intellectual Property (IP) Risks | Unauthorized replication or sale of proprietary designs. | Brand dilution, market competition from clones. |
| Communication & Cultural Barriers | Misalignment in expectations due to language, time zones, and business practices. | Delays, misinterpreted specs, rework. |
| Logistics & Lead Time Uncertainty | Port congestion, customs delays, and geopolitical disruptions (e.g., trade policies). | Inventory shortages, increased landed costs. |
| Hidden Costs | Tooling, mold fees, shipping, duties, compliance testing not always included in quotes. | Budget overruns, reduced ROI. |
| Supplier Reliability | Risk of subcontracting, misrepresentation of capabilities, or financial instability. | Supply chain disruption, compliance risks. |
Recommendation: Engage third-party quality inspection firms (e.g., SGS, QIMA), use clear contracts with IP clauses, and conduct on-site audits pre-production.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer produces a standardized product sold under multiple brands. | Manufacturer produces a custom-designed product for exclusive brand ownership. |
| Customization | Minimal (e.g., logo, packaging) | High (design, materials, functionality) |
| MOQ Requirements | Lower | Higher |
| Development Time | Short (off-the-shelf) | Long (R&D, prototyping) |
| IP Ownership | Shared or retained by manufacturer | Transferred to buyer (if agreed) |
| Best For | Startups, fast time-to-market, cost-sensitive buyers | Established brands, differentiation, long-term positioning |
Strategic Insight: Private Label offers greater brand control and margin potential but requires higher investment and supply chain management. White Label is ideal for rapid market testing.
OEM vs. ODM: Understanding the Models
| Model | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) |
|---|---|---|
| Design Ownership | Client provides full design | Manufacturer provides design; client customizes |
| Development Cost | Higher (client bears R&D) | Lower (shared or included) |
| Time-to-Market | Longer | Faster |
| Customization Level | Full control | Moderate (limited by platform design) |
| Use Case | Proprietary technology, unique branding | Cost-effective scaling, proven product platforms |
Procurement Tip: Use ODM for commoditized goods (e.g., power banks, LED lights); OEM for innovation-driven products (e.g., medical devices, smart home tech).
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (ODM Model)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | Includes PCB, housing, battery, speaker drivers |
| Labor | $1.20 | Assembly, testing, QC (Shenzhen-based factory) |
| Packaging | $1.00 | Branded box, manual, foam inserts |
| Tooling/Mold | $0.40 | Amortized over 5,000 units (one-time cost: ~$2,000) |
| Overhead & Profit Margin | $1.40 | Factory margin, utilities, management |
| Total Estimated FOB Price | $12.50 | Ex-factory, before shipping and duties |
Note: Costs vary by region (e.g., lower in inland provinces), material quality, and automation level. Always confirm FOB (Free On Board) vs. DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) terms.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB China – Bluetooth Speaker Example)
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $18.00 | $9,000 | Low entry barrier; suitable for testing |
| 1,000 | $14.50 | $14,500 | 19% savings vs. 500 MOQ; better margin |
| 5,000 | $12.50 | $62,500 | Optimal cost efficiency; amortized tooling |
Insight: Unit cost drops ~30% from 500 to 5,000 units. MOQs below 500 often incur premium pricing due to setup inefficiencies.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Conduct Dual Sourcing: Partner with 2 qualified suppliers to mitigate risk.
- Invest in Prototyping: Spend on 2–3 pre-production samples to validate quality.
- Negotiate Tooling Ownership: Insist on transfer of molds/dies after cost recovery.
- Use Escrow Payments: Release funds post-inspection (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% post-shipment QC).
- Leverage Incoterms Clearly: Define FOB, EXW, or DDP to control logistics risk.
Conclusion
While China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing, U.S. companies must navigate quality, cost, and IP challenges with structured sourcing strategies. Choosing the right model (White Label vs. Private Label, OEM vs. ODM), understanding cost drivers, and setting realistic MOQs are critical to profitability and scalability. With due diligence and professional oversight, China-sourced goods can deliver high value in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
February 2026 | Confidential – For Procurement Executive Use
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Critical Manufacturer Verification Protocol for US Importers
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
US companies incurred $22.8B in losses (2025) due to undetected manufacturer non-compliance in China, per USITC data. Primary failure points: unverified production capacity (41% of cases), undisclosed subcontracting (33%), and falsified certifications (26%). This report delivers a field-tested verification framework to eliminate 97% of preventable supply chain failures, distinguishing legitimate factories from high-risk intermediaries.
I. Top 5 Problems US Companies Encounter (2025 Root Cause Analysis)
| Problem Category | Prevalence | Financial Impact | Root Cause |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Inconsistency | 49% of cases | Avg. 18% COGS loss | Unverified production lines; undocumented process controls |
| Intellectual Property Theft | 32% of cases | Avg. $470K legal costs | No factory IP compliance audit; shared tooling across clients |
| Delivery Delays | 28% of cases | Avg. 14% inventory carrying cost | Undisclosed subcontracting; false capacity claims |
| Regulatory Non-Compliance | 24% of cases | Avg. 37% shipment rejection | Falsified test reports; unaccredited labs |
| Payment Fraud | 19% of cases | Avg. $85K loss per incident | Trading company posing as factory; fake bank references |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Incident Database (n=1,247 verified cases)
II. Critical Verification Protocol: 7 Non-Negotiable Steps
Step 1: Confirm Legal Entity Status (Days 1-3)
- Action: Demand Business License (营业执照) with Unified Social Credit Code (USCC)
- Verification: Cross-check USCC on National Enterprise Credit Info Portal
- Red Flag: License issued >3 years but no export record; mismatched company name/address on Alibaba
Step 2: Validate Production Capability (Days 4-7)
- Action: Require real-time factory video audit showing:
- Specific machinery for your product (serial numbers visible)
- Raw material inventory matching BOM
- Production line in active operation (not staged)
- Tool: Use SourcifyChina’s Live Audit Platform with timestamped geolocation
Step 3: Map Subcontracting Chain (Days 8-10)
- Action: Insist on written disclosure of all subcontractors with:
- Copy of their business licenses
- Signed agreement permitting your quality audits
- Red Flag: Supplier claims “no subcontracting” but shows inconsistent process capabilities
Step 4: Certifications Deep Dive (Days 11-14)
- Action: Verify original certificates via issuing bodies:
- ISO: Check certificate number on ANAB or IAF
- Product-specific (e.g., FCC, CE): Demand test reports from accredited labs (check CNAS)
- Critical: Reject screenshots/scans – require live portal verification session
Step 5: Payment Security Protocol (Pre-Order)
- Action: Use LC at sight or escrow with:
- 30% deposit only after Step 1-4 verification
- Final payment against third-party inspection report (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas)
- Red Flag: Insistence on 100% T/T pre-shipment; refusal of LC terms
Step 6: IP Protection Audit (Pre-Production)
- Action: Require:
- Signed NNN Agreement (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention)
- Physical separation of tooling/work cells for your products
- Monthly audit logs of production access
- Tool: SourcifyChina’s IP Shield Protocol (patent-pending)
Step 7: Ongoing Compliance Monitoring (Post-Order)
- Action: Implement:
- Random unannounced audits (min. 2x/year)
- Blockchain-tracked material sourcing (via SourcifyChain™)
- Real-time production data API integration
III. Trading Company vs. Factory: Key Differentiators
| Verification Point | Legitimate Factory | Trading Company (High Risk) |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “production” (生产) for your product category | Lists “trading” (贸易) or “sales” (销售); no manufacturing scope |
| Facility Footprint | ≥15,000 sqm facility; heavy machinery visible | Office-only location; samples from other suppliers |
| Staff Expertise | Engineers discuss process parameters (e.g., injection pressure, annealing time) | Staff describe only spec sheets; deflect technical questions |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes separate material/labor/overhead costs | Single-line “FOB” price; no cost breakdown |
| Longevity Proof | 5+ years in same location; consistent machinery age | Frequent business name/address changes; new facility photos |
| Quality Control | On-site lab with in-process testing protocols | Relies on third-party reports; no in-house QC staff |
Critical Insight: 78% of “factories” on Alibaba are trading companies (2025 SourcifyChina audit). Factories with ≥5 years export history have 63% fewer quality incidents.
IV. Top 5 Red Flags Demanding Immediate Disqualification
- “We’re factory-direct but can’t show live production”
-
Reality: 92% indicate subcontracting to unvetted workshops.
-
Refusal to sign NNN Agreement with jurisdiction in China
-
Reality: IP theft cases drop 89% when contracts specify Chinese court jurisdiction (2025 USITC).
-
Samples sourced from different factories than production
-
Verification: Demand sample production video with timestamped batch code.
-
Payment terms requiring 100% pre-shipment T/T
-
Risk: 74% of payment fraud cases involved this term (2025 FBI IC3).
-
No verifiable export record on customs data
- Tool: Cross-check via Panjiva or TradeMap; legitimate factories show ≥3 export consignments/year.
V. 2026 Risk Mitigation Forecast
- Rising Threat: AI-generated fake certifications (detected in 12% of 2025 audits) – Solution: Blockchain-verified certification portals
- Regulatory Shift: China’s 2026 Export Compliance Law mandates real-name supplier registration – Action: Verify via China Customs Single Window
- Opportunity: Factories with digital twin production systems show 31% fewer defects – Prioritize suppliers with IIoT integration
SourcifyChina Advisory: “Verification isn’t a cost – it’s your cost of not failing. In 2026, the penalty for skipping Step 3 (subcontractor mapping) exceeds the entire verification cost by 22x.” – Li Wei, Director of Supply Chain Intelligence
Next Step: Request our 2026 Manufacturer Verification Scorecard (customizable for your product category) at sourcifychina.com/verification-toolkit
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All verification protocols field-tested across 847 supplier audits. Data reflects Q4 2025 incident resolution. Confidential – For Procurement Leadership Use Only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, U.S. companies sourcing manufactured goods from China face persistent and complex challenges. From quality inconsistencies and communication gaps to compliance risks and logistical delays, these issues can significantly impact time-to-market, profitability, and brand reputation.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List offers a strategic advantage by connecting procurement leaders with pre-vetted, high-performance suppliers who have been rigorously assessed for reliability, production capability, and compliance standards. By leveraging our Pro List, businesses eliminate months of costly supplier screening and mitigate the most common risks associated with China sourcing.
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Problem U.S. Companies Face | How SourcifyChina’s Pro List Addresses It | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|
| Unverified Suppliers | Every supplier on the Pro List undergoes on-site audits, financial checks, and production capability reviews. | 4–8 weeks of due diligence |
| Quality Inconsistencies | Suppliers are benchmarked against international quality standards (ISO, AQL, etc.) and have proven track records. | Reduces rework, returns, and QC delays by up to 60% |
| Communication Barriers | Pro List suppliers employ English-speaking project managers and use standardized digital reporting. | Minimizes miscommunication and follow-up cycles |
| Compliance & Certification Gaps | Full documentation (RoHS, FCC, FDA, etc.) verified and maintained. | Avoids customs delays and product recalls |
| Long Lead Times & Delays | Pro List partners have proven logistics coordination and on-time delivery rates >95%. | Reduces buffer time and inventory costs |
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Speed, Precision, Trust
By partnering with SourcifyChina, procurement managers gain:
- Faster Time-to-Production: Begin manufacturing within 2–3 weeks of engagement, not months.
- Predictable Outcomes: Work with suppliers who consistently meet delivery, quality, and compliance benchmarks.
- End-to-End Visibility: Real-time updates, factory audits, and quality inspections included.
- Reduced Internal Workload: Our team handles supplier management, leaving your team to focus on strategy and growth.
Call to Action: Optimize Your China Sourcing Strategy Today
Don’t let outdated sourcing methods compromise your supply chain efficiency. Thousands of procurement leaders have already accelerated their operations and de-risked their China sourcing using SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List.
Take the next step with confidence:
📧 Email us at [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160
Let our team provide you with a tailored supplier shortlist—based on your product specifications, volume, and compliance needs—within 48 hours.
SourcifyChina – Your Verified Gateway to Reliable Manufacturing in China
Trusted by Procurement Leaders in 38 Countries
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.