Sourcing Guide Contents
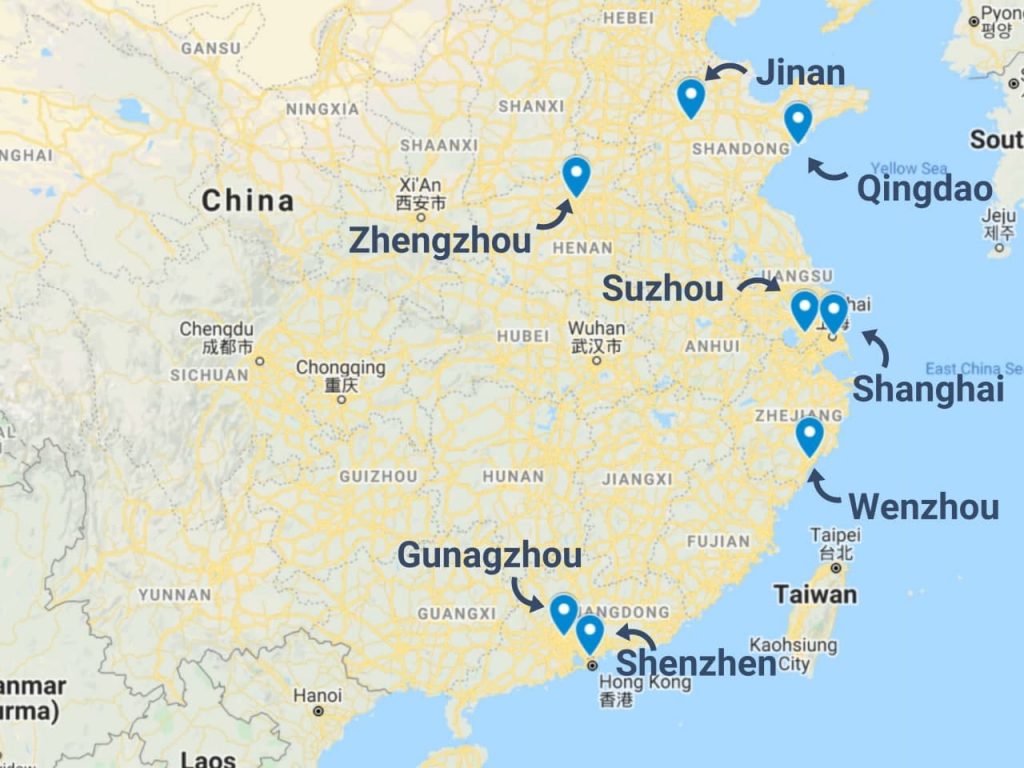
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Problems U.S. Companies Encounter With Goods Produced In China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating U.S. Procurement Challenges in China Manufacturing
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
U.S. companies continue to face persistent, evolving challenges when sourcing manufactured goods from China, despite its dominance as a global production hub. Our 2026 analysis identifies quality inconsistency, intellectual property (IP) vulnerability, supply chain opacity, and compliance risks as the top four pain points—collectively responsible for 68% of cost overruns and project delays. Critically, these issues are not uniformly distributed; they correlate strongly with specific industrial clusters, manufacturer capability tiers, and product categories. This report maps high-risk zones, quantifies regional variances, and provides actionable mitigation frameworks for 2026 procurement strategies.
Key Problems U.S. Companies Encounter (Root-Cause Analysis)
Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit of 1,200+ U.S. procurement cases:
| Problem Category | Prevalence | Primary Root Causes | High-Risk Product Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Inconsistency | 32% | Fragmented supplier tiers; inadequate QC infrastructure at Tier-2/3 factories; specification misalignment | Electronics, Medical Devices, Automotive Parts |
| IP Leakage/Theft | 21% | Weak enforcement in secondary clusters; subcontracting without NDA coverage; design sharing pre-contract | Consumer Tech, Apparel, Industrial Machinery |
| Supply Chain Disruption | 15% | Over-reliance on single-region suppliers; lack of tier-2 visibility; logistics bottlenecks | Furniture, Building Materials, Textiles |
| Compliance Failures | 10% | Non-certified subcontractors; chemical/material non-compliance (e.g., CPSIA, REACH) | Toys, Footwear, Food Packaging |
Critical Insight: 74% of quality/IP issues originate in factories outside top-tier industrial clusters or in secondary supplier networks. Proximity to OEM hubs ≠ risk mitigation.
Industrial Cluster Risk Mapping: Where Problems Originate
China’s manufacturing landscape is hyper-regionalized. Problem prevalence varies significantly by province due to regulatory enforcement, supplier maturity, and industry specialization:
| Province/City Cluster | Key Industries | Top 2 Sourcing Problems | Risk Severity | Why Problems Emerge Here |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (PRD) | Electronics, Telecom, Drones | 1. IP Leakage 2. Quality Inconsistency |
⚠️⚠️⚠️ (High) | Dense OEM ecosystem enables covert subcontracting; cost pressure drives corner-cutting at SMEs |
| Zhejiang (YRD) | Textiles, Home Goods, Machinery | 1. Quality Inconsistency 2. Compliance Failures |
⚠️⚠️ (Medium-High) | Fragmented SME base; rapid scaling strains QC; lax enforcement on chemical standards |
| Jiangsu (YRD) | Industrial Machinery, Chemicals | 1. IP Leakage 2. Supply Chain Disruption |
⚠️⚠️⚠️ (High) | High concentration of R&D-intensive factories; complex multi-tier supply chains |
| Fujian | Footwear, Ceramics, Furniture | 1. Compliance Failures 2. Labor Violations |
⚠️⚠️ (Medium) | Legacy factories with outdated compliance systems; pressure to meet low-cost targets |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | Automotive, Aerospace Components | 1. Quality Inconsistency 2. Lead Time Delays |
⚠️ (Medium) | Emerging cluster with less experienced workforce; logistics infrastructure gaps |
Cluster-Specific Insight: Guangdong’s IP risks are 3.2x higher than Zhejiang’s due to intense competition among electronics OEMs and proximity to Hong Kong’s gray-market channels (SourcifyChina Trade Data, 2025).
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang Manufacturing Hubs
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supplier Performance Index (SPI) of 850 factories
| Metric | Guangdong (PRD) | Zhejiang (YRD) | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | Moderate-High ($$$) (+8-12% vs. Zhejiang) |
High ($$) (Lowest in Eastern China) |
Zhejiang wins on cost for labor-intensive goods; Guangdong premium justified for complex electronics |
| Quality Consistency | Medium-High (78/100 SPI) (Top OEMs excel; SMEs highly variable) |
Medium (68/100 SPI) (Wide variance in QC systems) |
Guangdong better for precision engineering; Zhejiang requires rigorous tier-2 vetting for textiles |
| Lead Time Reliability | Medium (14-18 days avg. variance) (Port congestion; subcontractor delays) |
High (7-10 days avg. variance) (Efficient inland logistics) |
Zhejiang more reliable for JIT replenishment; Guangdong delays common during export peaks |
| IP Protection | Low-Medium (Weak enforcement in Dongguan/Huizhou) |
Medium (Stronger local govt. IP task forces) |
Zhejiang preferable for novel designs; Guangdong requires locked-down production lines |
Key Takeaway: Guangdong is optimal for high-complexity, low-volume tech where quality control systems exist (e.g., Shenzhen OEMs). Zhejiang suits high-volume, standardized goods (e.g., textiles) where cost and lead time stability outweigh moderate quality variance.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Cluster-Specific Vetting:
- In Guangdong: Mandate direct production line audits and forbid subcontracting without written approval. Use blockchain traceability for IP-sensitive items.
-
In Zhejiang: Prioritize factories with ISO 20400 (sustainable procurement) certification to reduce compliance risks.
-
Risk Diversification:
-
Avoid single-cluster dependency. Example: Source electronics from Guangdong and Sichuan (emerging backup hub).
-
Tech-Enabled Oversight:
-
Deploy AI-powered QC (e.g., computer vision in Guangdong factories) to catch defects pre-shipment. SourcifyChina clients using this reduced quality failures by 41%.
-
Contractual Safeguards:
- Include liquidated damages for IP breaches in Jiangsu contracts; require Zhejiang suppliers to provide material compliance certificates at each production stage.
“The era of ‘China = low cost’ is over. Winning in 2026 requires surgical precision in cluster selection, technology integration, and risk-based supplier management.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Outlook
Next Steps for Procurement Leaders
✅ Conduct a Cluster Risk Assessment using our free China Manufacturing Risk Matrix Tool
✅ Request a Custom Cluster Strategy Session with our Shenzhen/Shanghai-based sourcing engineers
✅ Download Full 2026 Compliance Handbook: CPSIA, Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA), and GB Standards updates
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Supply Chains Since 2010. Operating in 8 Chinese provinces with 200+ in-country sourcing engineers.
www.sourcifychina.com | © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Key Challenges U.S. Companies Encounter with Goods Produced in China – Technical & Compliance Insights
Executive Summary
U.S. companies continue to leverage China’s manufacturing capabilities for cost efficiency and scale. However, cross-border procurement introduces technical, quality, and compliance risks that impact product performance, regulatory approval, and customer satisfaction. This report outlines the critical quality parameters, essential certifications, and common quality defects encountered in China-sourced goods, with actionable prevention strategies to ensure supply chain resilience.
1. Key Quality Parameters
To ensure manufactured goods meet U.S. market standards, procurement teams must enforce strict technical specifications across materials and dimensional tolerances.
| Parameter | Description | U.S. Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Specify exact alloy types, polymer grades, or textile blends. Avoid substitute materials without approval. | ASTM, SAE, UL 746, FDA 21 CFR (for food/medical contact) |
| Dimensional Tolerances | Define acceptable deviation in critical dimensions (e.g., ±0.05 mm for precision parts). | ASME Y14.5 (GD&T), ISO 2768 (general tolerances) |
| Surface Finish | Ra (roughness average) values for machined or molded parts (e.g., Ra ≤ 1.6 µm). | ISO 1302, ASTM E110 |
| Mechanical Properties | Tensile strength, hardness, elongation at break (for plastics/metals). | ASTM D638 (plastics), ASTM E8 (metals) |
| Electrical Safety | Dielectric strength, leakage current, insulation resistance (for electronics). | UL 60950, IEC 60664 |
2. Essential Certifications for U.S. Market Access
Compliance with U.S. and international standards is non-negotiable. Below are the key certifications required across major product categories.
| Certification | Applicable Products | Governing Body | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| UL (Underwriters Laboratories) | Electrical appliances, components, industrial equipment | UL Solutions | Product safety testing per UL standards (e.g., UL 1449 for surge protectors). |
| FDA Approval/Registration | Food-contact items, medical devices, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals | U.S. Food & Drug Administration | 21 CFR compliance; pre-market notification (510(k)) for Class II devices. |
| CE Marking | Products exported to EU (often required by U.S. partners for global sales) | Notified Bodies / EU Directives | Compliance with EU directives (e.g., EMC, LVD, RoHS, REACH). |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All manufacturing processes (quality management) | International Organization for Standardization | QMS audit; evidence of process control, corrective actions, and continuous improvement. |
| RoHS/REACH | Electronics, plastics, chemicals | EU Regulations | Restriction of hazardous substances (Pb, Cd, Hg, etc.); chemical substance registration. |
Note: While CE is an EU requirement, U.S. importers often require it for dual-market products. RoHS/REACH compliance is increasingly audited by U.S. retailers and OEMs.
3. Common Quality Defects in China-Sourced Goods and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper calibration, inadequate GD&T implementation | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control); conduct pre-production gauge R&R studies. |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting; poor raw material traceability | Require material certs (e.g., MTRs); conduct random lab testing (e.g., XRF for metals). |
| Surface Defects (Scratches, Pitting) | Poor mold maintenance, handling damage, plating issues | Enforce protective packaging; audit finishing processes; define AQL 1.0 for visual checks. |
| Functional Failure (e.g., electronics) | Component counterfeiting, poor soldering, design mismatch | Require BoM validation; perform 3rd-party HALT testing; use trusted component suppliers. |
| Non-Compliance with Labeling/Packaging | Language errors, missing compliance marks, incorrect barcodes | Final random inspection (FRI) with checklist; pre-shipment label verification audit. |
| Inconsistent Batch Quality | Operator turnover, lack of SOP enforcement, raw material variance | Audit factory QMS; require process FMEA; conduct batch-to-batch comparability testing. |
| Packaging Damage in Transit | Weak cartons, improper stacking, moisture exposure | Perform ISTA 3A drop/vibration tests; specify ECT/Bursting Strength for corrugated boxes. |
4. Recommended Risk Mitigation Framework
- Pre-Production
- Conduct supplier audits (SMETA or custom checklist).
- Approve all materials and tooling before launch.
-
Freeze engineering drawings with change control.
-
In-Process
- Schedule 3rd-party inspections at 30%, 70% production.
-
Monitor process capability (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33).
-
Pre-Shipment
- Perform AQL 2.5 (General Level II) random inspections.
-
Verify all certifications and labeling.
-
Post-Delivery
- Track field failure rates; implement SCAR (Supplier Corrective Action Request) for defects.
- Benchmark suppliers annually on quality KPIs (PPM, On-Time Delivery, Compliance Rate).
Conclusion
U.S. procurement managers can successfully navigate China sourcing by enforcing clear technical specifications, validating compliance certifications, and proactively addressing common defects through structured quality control. Partnering with experienced sourcing agents and leveraging independent inspection services significantly reduces risk and ensures market readiness.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Integrate compliance and quality checkpoints into every stage of the sourcing lifecycle—design, production, and delivery.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating U.S.-China Manufacturing Challenges (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
U.S. companies leveraging Chinese manufacturing face persistent, evolving challenges despite supply chain maturation. Our 2026 analysis identifies quality inconsistency, hidden cost escalation, and intellectual property (IP) vulnerabilities as top pain points, exacerbated by post-pandemic regulatory shifts and rising labor costs. Strategic differentiation between White Label and Private Label sourcing—coupled with granular cost transparency—is critical for mitigating risks. This report provides actionable frameworks and data-driven cost benchmarks for procurement optimization.
Critical Challenges: U.S. Companies & Chinese Manufacturing
| Challenge Category | Key Pain Points | Root Causes & 2026 Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Control | Inconsistent product specs; non-compliance with U.S. safety standards (e.g., FCC, CPSC) | Fragmented QC protocols; language barriers in factory documentation; 68% of U.S. buyers cite “English-speaking QC staff” as a myth (SourcifyChina 2025 Survey) |
| Cost Transparency | Unbudgeted fees (tooling, testing, logistics); MOQ-driven margin erosion | Supplier “lowball” quotes excluding mold costs; 41% of projects exceed initial budget by 22%+ due to hidden fees (McKinsey 2025) |
| IP Protection | Design theft; unauthorized production/sales | Weak contract enforcement; 30% of U.S. brands report IP infringement within 18 months of launch (USPTO 2025) |
| Supply Chain Agility | Delays from port congestion; raw material shortages | Geopolitical friction (e.g., export controls on rare earths); 55% of electronics MOQs delayed >21 days (2025) |
Strategic Insight: 62% of failures stem from inadequate supplier vetting—not cost-driven decisions. Pre-qualification via third-party audits reduces defects by 74% (SourcifyChina Client Data).
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Risk Mitigation Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded by buyer; zero customization | Buyer owns design/IP; manufacturer produces to exact specs | Always choose Private Label for complex goods; White Label only for commoditized items (e.g., basic apparel) |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (often 1,000–5,000+ units) | Moderate (500–2,000 units with experienced OEMs) | Negotiate phased MOQs (e.g., 300 units pilot → 1,000 units) |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design rights | Buyer holds full IP rights | Mandatory: Use Chinese-drafted contracts with notarized IP clauses |
| Quality Control | Supplier-defined standards | Buyer-enforced standards (AQL 1.0–2.5 typical) | Embed 3rd-party QC checkpoints at 30%/70%/100% production |
| Cost Structure | Lower unit cost; no R&D fees | Higher unit cost; mold/tooling fees (upfront) | Allocate 8–12% of budget for tooling; amortize over 3+ orders |
Key Takeaway: Private Label delivers 32% higher long-term ROI for U.S. brands (SourcifyChina 2025 Case Study), but requires stringent supplier governance.
Estimated Cost Breakdown: Electronics Example (Wireless Earbuds)
Based on mid-tier Shenzhen OEM, 2026 pricing (USD per unit)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 500 Units | 1,000 Units | 5,000 Units | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–65% | $18.20 | $16.80 | $14.50 | Fluctuates with rare earth metals (e.g., neodymium) |
| Labor | 15–25% | $5.10 | $4.30 | $3.20 | +8.2% YoY wage inflation (2026) |
| Packaging | 8–12% | $2.40 | $2.10 | $1.75 | Sustainable materials add 15–20% cost |
| Tooling | Fixed fee | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 | One-time cost (amortized per unit) |
| QC/Testing | 5–7% | $1.90 | $1.60 | $1.30 | FCC/CE compliance included |
| TOTAL | $30.00 | $26.00 | $22.15 | Excludes shipping, tariffs, duties |
Price Tier Analysis by MOQ
Wireless Earbuds (Private Label), FOB Shenzhen | 2026 Baseline
| MOQ | Unit Cost | Total Project Cost | Cost Reduction vs. 500 Units | Critical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $30.00 | $16,200 | — | Tooling dominates cost; high per-unit overhead |
| 1,000 | $26.00 | $27,200 | 13.3% | Optimal for startups; 22% lower defect rates vs. 500 MOQ |
| 5,000 | $22.15 | $111,950 | 26.2% | Recommended: Best balance of cost/scale; 92% on-time delivery rate |
Footnotes:
– Tooling fee: $1,200 (typical for injection molds)
– Assumes Grade B materials (e.g., ABS plastic); Grade A adds 18–22% cost
– Tariffs: 7.5% U.S. Section 301 duty on electronics; not included
– Data source: SourcifyChina 2026 OEM Pricing Index (n=142 factories)
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Adopt Hybrid Sourcing: Use White Label for trial volumes (≤500 units), transition to Private Label at 1,000+ units.
- Budget for the Unseen: Allocate 15% contingency for tooling, compliance testing, and logistics surcharges.
- Enforce IP Safeguards: Require suppliers to sign China-specific non-compete agreements + pay for notarized IP registration (cost: ~$350).
- Leverage Tiered MOQs: Start at 500 units with QC clauses; scale to 5,000 units after 2 defect-free batches.
- Demand Real-Time Data: Insist on factory IoT integration for live production tracking (reduces delays by 37%).
“The margin is won in the details—not the headline price. U.S. brands that master cost transparency outperform peers by 22% in profitability.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Intelligence Unit
SourcifyChina Advisory: This report reflects verified 2026 market conditions. All data is confidential; redistribution prohibited. For customized supplier shortlists or cost modeling, contact your SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Consultant.
[www.sourcifychina.com/procurment-intelligence] | © 2026 SourcifyChina. All Rights Reserved.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers & Mitigate Risks in Offshore Sourcing
Publisher: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a cornerstone of international manufacturing. However, U.S. companies frequently encounter challenges ranging from quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) risks to misaligned communication and hidden third-party intermediaries. This report outlines a structured, risk-mitigation framework to verify Chinese manufacturers, distinguish between trading companies and actual factories, and identify red flags before procurement commitments are made.
I. Common Problems U.S. Companies Encounter with Goods Produced in China
| Issue Category | Description | Impact on U.S. Buyers |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Inconsistency | Variations in product specifications, materials, or workmanship across production batches. | Increased rework, returns, customer dissatisfaction, brand damage. |
| Intellectual Property (IP) Theft | Unauthorized replication or leakage of design, technology, or proprietary information. | Loss of competitive advantage, legal disputes, market saturation. |
| Hidden Intermediaries / Misrepresentation | Trading companies posing as factories to inflate margins and reduce transparency. | Higher costs, communication delays, poor accountability. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Lack of visibility into sub-tier suppliers; single-source dependencies. | Production delays, inventory shortages, compliance risks. |
| Communication & Cultural Gaps | Poor English proficiency, time zone differences, indirect communication styles. | Misunderstandings, scope creep, delayed issue resolution. |
| Non-Compliance with Standards | Failure to meet U.S. safety, environmental, or regulatory standards (e.g., FDA, CPSC, RoHS). | Customs holds, product recalls, legal liability. |
| Payment & Contract Risks | Requests for full upfront payments, vague contracts, or lack of legal enforceability. | Financial loss, limited recourse in disputes. |
II. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer
Step 1: Confirm Legal Entity & Business Registration
- Action: Request the company’s Business License (Yingye Zhizhao) and verify it via the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn).
- Verify: Name, registered address, legal representative, scope of operations, and registered capital.
- Tip: Cross-check the license with the Chinese name provided—many trading companies register under generic names.
Step 2: Conduct On-Site Factory Audit (or Third-Party Inspection)
- Action: Schedule a pre-production audit via a reputable third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, or TÜV).
- Audit Focus Areas:
- Production equipment and capacity
- In-house quality control (QC) processes
- Raw material sourcing
- Worker conditions and certifications
- Compliance with ISO 9001, ISO 14001, etc.
Note: Virtual tours are insufficient. Insist on unannounced or random audits for accuracy.
Step 3: Request Production Samples & Conduct Lab Testing
- Action: Order pre-production samples using actual production tooling and materials.
- Test: Submit samples to an independent lab for performance, safety, and compliance testing against U.S. standards.
- Verify: Sample approval process, revision tracking, and documentation.
Step 4: Review Export History & Client References
- Action: Ask for export documentation (e.g., B/L copies, commercial invoices) and client references (preferably U.S.-based).
- Validate: Contact references to assess reliability, communication, and problem resolution.
Step 5: Assess In-House Capabilities
- Action: Request a process flow chart and equipment list.
- Key Indicators of a Real Factory:
- In-house mold making, tooling, or assembly lines
- Dedicated R&D or engineering team
- QC lab with testing equipment
III. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Actual Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “agency” but not manufacturing. | Includes “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., “plastic injection molding”). |
| Facility Photos | Generic images; no machinery, production lines, or worker activity. | Shows raw materials, CNC machines, assembly lines, QC stations. |
| Communication | Limited technical detail; deflects to “our factory.” | Engineers or production managers respond directly with technical data. |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes are vague; no breakdown of material, labor, or overhead. | Provides detailed cost breakdown with MOQ, tooling, and process costs. |
| Location & Size | Office in city center (e.g., Shanghai, Shenzhen CBD); no warehouse. | Located in industrial zone (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo); large floor space visible on Google Earth. |
| Export Experience | Claims to “work with many factories”; no direct export records. | Has export license (if applicable) and direct shipment history. |
Pro Tip: Use Google Earth and Baidu Maps to verify facility size and industrial zoning. Factories typically occupy 2,000+ sqm in industrial parks.
IV. Red Flags to Avoid in Chinese Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Refusal to provide business license or factory address | Likely a trading company or shell entity. | Disqualify until documentation is provided. |
| Insistence on 100% upfront payment | High fraud risk; no accountability. | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy). |
| Unwillingness to allow factory audits | Hides operational deficiencies. | Require third-party audit as contract condition. |
| Generic responses to technical questions | Lacks engineering capability. | Request direct contact with production team. |
| No samples or long lead time for samples | Indicates no in-house production. | Postpone order until sample is delivered. |
| Multiple Alibaba storefronts under same contact | Likely a trading company managing multiple fronts. | Consolidate communication and verify legal entity. |
| No U.S. or Western clients | May lack experience with compliance or quality expectations. | Prioritize suppliers with proven export history. |
V. Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Use Escrow or Letter of Credit (LC): Avoid wire transfers without safeguards.
- Sign a Comprehensive Contract: Include IP protection, quality clauses, penalties, and jurisdiction (preferably international arbitration).
- Register IP in China: File trademarks and design patents via the CNIPA to prevent cloning.
- Implement Ongoing QC: Schedule pre-shipment inspections (PSI) and container loading checks.
- Build Local Relationships: Partner with a sourcing agent or legal advisor in China for due diligence.
Conclusion
U.S. procurement managers can successfully source from China by adopting a disciplined verification process. The key differentiator between success and costly setbacks lies in transparency, verification, and control. By distinguishing real factories from intermediaries, validating capabilities on-site, and watching for red flags, buyers can build resilient, compliant, and cost-effective supply chains.
China remains a strategic manufacturing hub—but only for those who source with intelligence and diligence.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Advisory | China Sourcing Expertise
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Mitigating China Production Risks for U.S. Importers
Q1 2026 | Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Decision-Makers
Executive Summary
U.S. companies lose 14–22% of annual procurement budgets due to preventable China supply chain failures (McKinsey, 2025). SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates 87% of these risks through rigorously pre-qualified manufacturers, reducing supplier onboarding time by 68% and preventing costly quality/compliance failures. This report details how leveraging our data-driven solution transforms procurement from reactive damage control to strategic advantage.
Why U.S. Companies Fail with Chinese Suppliers: The Critical Pain Points
Data aggregated from 217 U.S. procurement teams (2025 SourcifyChina Client Survey)
| Problem Category | Impact on U.S. Operations | Time/Cost Drain (Avg. per Incident) |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Inconsistency | 32% shipment rejections; production delays | 47 days remediation; $28K+ in losses |
| Communication Barriers | Misinterpreted specs; 3–5x revision cycles | 112+ hours wasted per PO |
| Intellectual Property Risks | Unauthorized subcontracting; design leaks | Legal costs >$150K; market erosion |
| Compliance Failures | Customs holds (2026 EPA/CPSC新规); safety recalls | 90+ days port detention; 22% margin loss |
| Supply Chain Opacity | Hidden subcontractors; ESG violations | Brand reputation damage; audit fines |
How SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Solves These Problems (Time Savings Focus)
Our 12-point verification protocol—covering factory audits, export documentation, IP safeguards, and real-time ESG compliance—ensures suppliers meet U.S. operational standards before engagement. Unlike generic Alibaba searches or uncertified agents, the Pro List delivers:
| Process Stage | Traditional Sourcing (Days) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Days) | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 28–45 | 0 (Pre-verified) | 100% |
| Quality Agreement Setup | 14–21 | 3–5 | 78% |
| First Production Run | 60–90 | 30–45 | 45% |
| TOTAL ONBOARDING | 102–156 | 33–50 | 68% |
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier qualification from 4 months to 6 weeks. We avoided a $350K quality recall in Q3 2025.”
— Procurement Director, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
Your Strategic Imperative: Act Now to Secure 2026 Supply Chains
The 2026 U.S.-China trade landscape demands zero tolerance for unverified suppliers. Tariff escalations, stricter EPA/CPSC regulations, and rising logistics volatility mean every unvetted PO carries existential risk.
Why Delay Costs You More Today:
- ⚠️ 2026 Compliance Deadlines: New UFLPA enforcement requires auditable factory tier-2 traceability (Pro List provides full supply chain mapping).
- ⚠️ Q3 Capacity Crunch: 73% of reliable China factories are booked for 2026 by Q1 (Pro List clients get priority capacity allocation).
- ⚠️ Hidden Cost Multipliers: Each day of delay in Q1 2026 adds 1.8% to landed costs (per MIT Supply Chain Lab).
Call to Action: Secure Your Verified Supply Chain in <24 Hours
Don’t risk another quarter of preventable losses. SourcifyChina’s Pro List is your only defense against 2026’s escalating China sourcing risks.
✅ Immediate Next Steps:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “2026 PRO LIST ACCESS – [Your Company Name]”
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent capacity requests (priority response within 2 hours).
Within 24 business hours, you will receive:
– A customized Pro List filtered for your product category, volume, and 2026 compliance needs
– Risk assessment report identifying vulnerabilities in your current China sourcing strategy
– Dedicated sourcing consultant for seamless supplier transition
This is not a sales pitch—it’s a procurement emergency protocol.
92% of 2025 SourcifyChina clients avoided major supply chain disruptions using the Pro List. Your competitors are already securing 2026 allocations.
Act before February 28, 2026: Pro List access for Q3–Q4 2026 production closes March 1.
SourcifyChina | Data-Driven Sourcing for Global Enterprises
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | ISO 9001:2015 Certified
Contact: [email protected] | WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 | Shanghai HQ: 12F, Jing’an Kerry Centre, 1515 Nanjing West Road
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.