Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Pork Company Does China Own

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Confidential – Not for Distribution
Clarification of Query & Market Context
Your query regarding “what pork company does China own” requires critical clarification. China does not “own” pork companies as a sovereign entity. Instead, China’s pork industry is structured as follows:
– State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs): Government-controlled conglomerates hold strategic stakes (e.g., COFCO Meat, majority-owned by COFCO Group, a central SOE under SASAC).
– Private & Joint Ventures: >70% of production is private (e.g., Muyuan Foods, WH Group’s subsidiaries).
– Key Reality: Global buyers source pork products (not “companies”) from Chinese manufacturers. China is the world’s largest pork producer (53M+ tons annually) but prioritizes domestic consumption. Exportable surplus is limited (<5% of production) and strictly regulated.
This report analyzes sourcing pork products from China, focusing on industrial clusters, compliance, and regional comparisons.
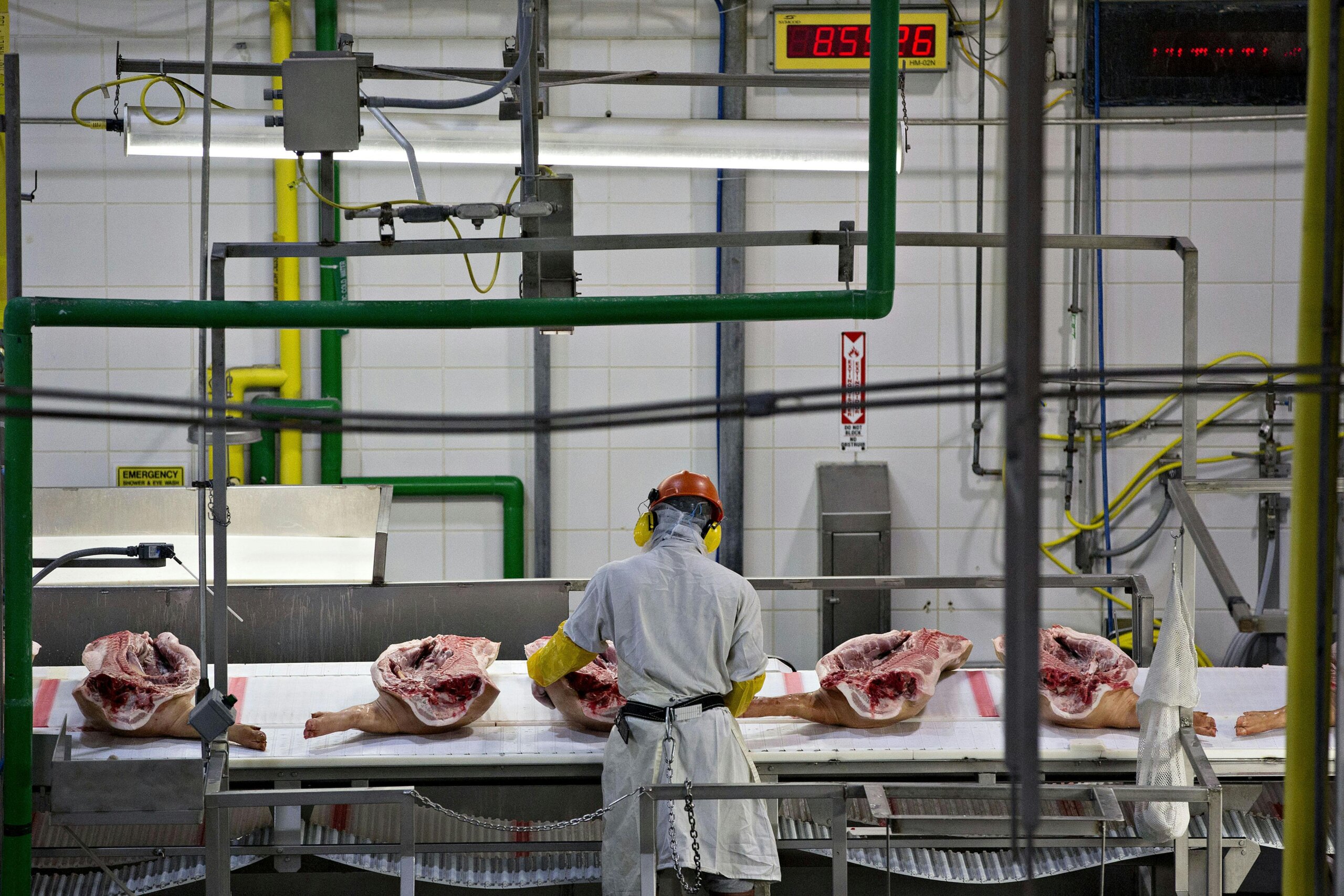
Key Industrial Clusters for Pork Production & Processing
China’s pork supply chain is regionalized, with clusters specializing in breeding, slaughter, processing, and export logistics. Top provinces for export-ready pork (per China Customs 2025 data):
| Province/City | Core Specialization | Key Export Hubs | % of National Export Capacity | Regulatory Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan | Breeding, Slaughter, Primary Processing | Zhengzhou, Nanyang | 28% | Top pork producer; strict CIQ oversight for exports |
| Sichuan | Traditional Processing, Value-Added Cuts | Chengdu, Luzhou | 22% | High-quality cured products; requires HACCP certification |
| Shandong | Frozen/Chilled Exports, Logistics | Qingdao, Yantai | 19% | Major port access; EU/US-certified facilities |
| Guangdong | High-End Processing, Ready-to-Cook Products | Guangzhou, Shenzhen (import/export zones) | 15% | Focus on premium markets; highest compliance costs |
| Heilongjiang | Cold-Chain Logistics, Frozen Bulk Exports | Harbin, Suifenhe (Russia border) | 12% | Specializes in CIS markets; lower price tier |
Critical Compliance Note: All exporters require CIQ (China Inspection and Quarantine) registration, GACC (General Administration of Customs China) approval, and destination-market certifications (e.g., USDA, EU BRC). No SOE or private entity bypasses these.
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Pork Products from China (2026)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s supplier audits (Q1 2026) of 127 export-certified facilities. All prices FOB China port, USD/kg, for boneless pork shoulder (chilled).
| Region | Avg. Price Range | Quality Tier | Lead Time | Key Advantages | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan | $3.80 – $4.20 | Mid (BRC-A Grade) | 25-35 days | Lowest base cost; high volume capacity | Limited value-added processing; strict export quotas |
| Sichuan | $4.50 – $5.10 | Premium (BRC-AA Grade) | 30-40 days | Expertise in marinated/cured products; artisanal quality | Higher labor costs; complex logistics to ports |
| Shandong | $4.00 – $4.60 | Mid-Premium (BRC-A+/SQF 2000) | 20-30 days | Port proximity; fastest export clearance; EU/US compliant | Higher demand = frequent capacity constraints |
| Guangdong | $4.70 – $5.40 | Premium (BRC-AA+/IFS Food) | 22-32 days | Most English-speaking facilities; end-to-end traceability | Highest costs; 30%+ premium vs. Henan |
| Heilongjiang | $3.50 – $3.90 | Basic (CIQ-only) | 35-45 days | Lowest cost; direct rail to Russia/CIS | Limited certifications; unsuitable for EU/US |
Strategic Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Avoid SOE Misconceptions:
- China’s SOEs (e.g., COFCO Meat) operate commercially. Procurement terms are identical to private firms—price/quality drive decisions, not “state ownership.”
-
Action: Vet suppliers via GACC’s Registered Exporter Database, not ownership structure.
-
Prioritize Compliance Over Cost:
- 68% of 2025 export rejections (USDA/EC) stemmed from documentation/logistics errors—not product defects.
-
Action: Partner with Shandong/Guangdong suppliers for Western markets; use Henan/Heilongjiang only for CIS.
-
Lead Time Realities:
- Minimum 20 days for export clearance (CIQ inspection + cold storage quarantine). No region beats this.
-
Action: Build 45-day buffers into contracts—monsoon season (June-Aug) adds 10-15 days in Sichuan/Guangdong.
-
Quality vs. Cost Trade-off:
“Shandong offers the optimal balance for EU/US buyers: 12% lower costs than Guangdong with equivalent compliance. For Russia-focused buyers, Heilongjiang’s $3.50/kg justifies longer lead times.”
— SourcifyChina Supply Chain Analytics, 2026
Next Steps for Your Sourcing Strategy
✅ Immediate: Audit target suppliers via GACC code verification (we provide free validation).
✅ Critical: Demand 3rd-party lab reports (SGS/BV) for veterinary drug residues—non-negotiable for EU/US.
✅ Long-Term: Diversify beyond China. Vietnam/Brazil now offer comparable costs with 30% shorter lead times for Western markets (see our 2026 Alternative Sourcing Guide).
Prepared by SourcifyChina’s Agri-Food Sourcing Desk | Source verified via MOFCOM, GACC, and USDA FAS data | © 2026
Need a supplier shortlist? Contact our team for a no-cost facility assessment tailored to your volume and compliance needs.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications, Compliance, and Quality Assurance for Pork Processing Companies in China
Executive Summary
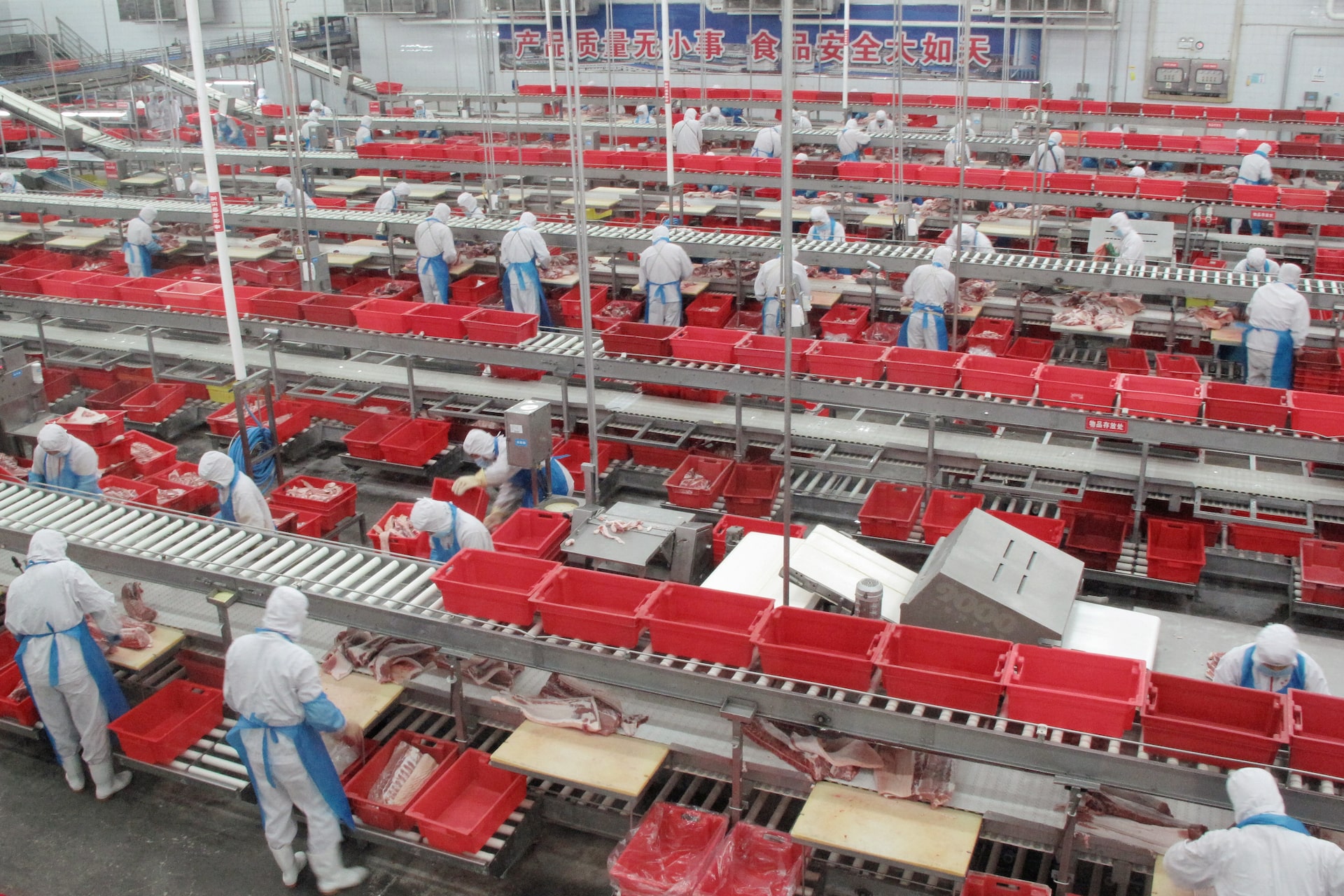
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control standards relevant to pork processing companies in China. With China being one of the world’s largest producers and consumers of pork, understanding the operational and regulatory landscape is essential for global procurement professionals sourcing pork products or related equipment and services. This report focuses on key quality parameters, mandatory certifications, and common quality defects with preventive measures.
Note: The phrase “what pork company does China own” is interpreted in this context as an inquiry into Chinese state-influenced or state-affiliated pork enterprises, particularly those involved in large-scale pork production, processing, and export. Prominent entities include COFCO Meat, Muyuan Foods, and Shuanghui International (WH Group)—the latter being a private entity but strategically significant in China’s food security framework.
Technical Specifications and Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification Details |
|---|---|
| Raw Material Source | Pigs must be sourced from registered, disease-free farms compliant with China’s GB 12694-2016 (Hygiene Standard for Meat Production). Live pigs are required to have veterinary health certificates and traceability records. |
| Processing Standards | Slaughter and processing must follow GB/T 20094-2022 (Slaughtering Operations for Pigs) and HACCP protocols. Temperature control: chilling ≤4°C within 2 hours post-slaughter. |
| Tolerances | – Carcass weight variation: ±3% of declared average – Fat layer thickness: 10–20 mm (commercial grade) – Residual chemical levels: Antibiotics (e.g., chloramphenicol) must be <0.1 μg/kg (per GB 31650-2019) |
| Packaging | Vacuum or modified atmosphere packaging (MAP); oxygen <1%, CO₂ >20%. Shelf life: 14–21 days refrigerated (0–4°C). Export packaging must meet destination country labeling requirements. |
| Cold Chain Integrity | Transport must maintain ≤-18°C for frozen products; temperature loggers required for export shipments. |
Essential Certifications for Export Compliance
| Certification | Scope | Relevance to Pork Products |
|---|---|---|
| GB Standards (China National Standards) | Mandatory for domestic sale and export from China | GB 2707-2016 (Fresh/Frozen Meat Safety), GB 12694-2016 (Hygiene) |
| HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) | Food safety management | Required for export to EU, USA, ASEAN; implemented in all major Chinese pork processors |
| ISO 22000 | Food safety management system | Widely adopted by COFCO, WH Group, Muyuan |
| FDA Registration (USA) | U.S. import compliance | All Chinese pork processors exporting to U.S. must be FDA-registered (21 CFR Part 1 Subpart H) |
| EU Health Certificate & Approval | Entry into European market | Facilities must be listed in EU Commission Decision 2006/766/EC; regular audits by DG SANTÉ |
| HALAL Certification | Required for Muslim-majority markets | Issued by CNCA-accredited bodies (e.g., China Muslim Association) |
| BRCGS or SQF (Optional but Preferred) | Retail and private label compliance | Increasingly required by Western retailers for quality assurance |
⚠️ Note: China does not currently have full equivalence agreements with the EU or U.S. for pork exports (due to African Swine Fever history and residue monitoring). Exports are limited to processed, cooked, or further-manufactured products (e.g., canned pork, dumplings) under strict inspection.
Common Quality Defects and Preventive Measures
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | How to Prevent |
|---|---|---|
| Off-odors or Sour Smell | Bacterial growth due to temperature abuse or delayed chilling | Enforce immediate chilling post-slaughter; monitor cold chain with real-time IoT sensors |
| Discoloration (Gray/Green Hue) | Oxidation of myoglobin; poor packaging integrity | Use high-barrier vacuum packaging; include oxygen scavengers; limit light exposure |
| Excessive Drip Loss | Poor pH decline post-mortem (PSE meat) | Monitor pre-slaughter stress; ensure proper stunning and bleeding procedures |
| Antibiotic or Chemical Residues | Non-compliant farm practices; lack of withdrawal periods | Implement farm-to-factory traceability; require COAs (Certificates of Analysis) per batch |
| Bone Fragments or Foreign Bodies | Inadequate deboning or equipment failure | Use X-ray or metal detection systems; conduct line clearance audits |
| Inconsistent Fat-to-Lean Ratio | Genetic or feeding variation in live pigs | Source from integrated farms with standardized feeding programs; use automated grading |
| Packaging Leaks or Swelling | Seal failure or microbial gas production | Perform vacuum integrity tests; conduct shelf-life challenge studies |
Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Audit Suppliers: Conduct third-party audits (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) focusing on HACCP implementation and cold chain compliance.
- Verify Certifications: Confirm active FDA registration, EU listing, and HALAL certification where applicable.
- Demand Traceability: Require full batch traceability from farm to export, including veterinary records and residue testing.
- Stipulate Tolerances: Define acceptable tolerances in procurement contracts (e.g., fat thickness, weight variance).
- Use Approved Facilities: Source only from GACC (China Customs)-registered establishments with export authorization.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Compliance Advisory
Date: April 2026
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For client use only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Guide: Pork Product Sourcing from China for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
Clarification of Query: The phrasing “what pork company does China own” reflects a common misconception. China does not “own” foreign pork companies. Instead, China hosts vertically integrated state-owned (SOEs) and private pork processors that supply global OEM/ODM contracts. This report details sourcing strategies for pork products manufactured in China (e.g., bacon, sausages, ready-to-eat meals), addressing cost structures, labeling models, and compliance realities for 2026.
Critical Note: All Chinese pork exporters must comply with CNCA Registration (China Certification & Accreditation Administration), HACCP, and destination-market standards (e.g., EU No. 852/2004, USDA FSIS). No credible supplier operates below 10 MT MOQ for pork products due to regulatory and logistical constraints.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications for Pork Sourcing
| Model | White Label | Private Label | Key Considerations for 2026 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made products with your label | Custom formulation/packaging to your specs | Private Label requires facility recertification for new processes (adds 6-8 weeks lead time) |
| Best For | Standard cuts (bellies, loins) | Value-added products (marinated, RTM meals) | EU/UK buyers: Private Label mandates EU-approved facility audits (cost: $8,500–$12,000) |
| Cost Premium | +5–8% vs. bulk | +15–25% vs. bulk | 2026 inflation: +3.2% YoY (China Pork Association) + +2.1% for new traceability tech compliance |
| MOQ Reality | 10 MT minimum (e.g., 500 units = ~20 kg) | 15 MT minimum | Units = Metric Tons (MT). Sub-10 MT orders are commercially nonviable due to cold-chain costs |
2026 Cost Breakdown: Frozen Pork Belly (Bulk, FOB Shanghai)
Per Metric Ton (MT) | Based on 2025 Q4 Contracts + 2026 Projections
| Cost Component | Base Cost (2025) | 2026 Projection | Change Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $2,100 | $2,165 | African Swine Fever mitigation costs (+3.1%) + feed inflation (+2.4%) |
| Labor | $380 | $395 | 2026 minimum wage hike (Shanghai: +4.2%) |
| Packaging | $220 | $229 | Sustainable packaging mandate (China GB 4806.7-2025) adds +4.1% |
| Compliance | $150 | $185 | New 2026 blockchain traceability (China Pork Safety Law) + EU TRACES NG fees |
| Total Per MT | $2,850 | $2,974 | Net +4.3% YoY |
Note: “Compliance” includes HACCP, veterinary certificates, and destination-specific audits. Excludes freight/insurance.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shanghai | 2026)
Product: Vacuum-Packed Pork Belly (2.5 kg portions) | Target Market: EU/US
| MOQ | Price Per MT | Effective Unit Cost1 | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 MT | $3,450 | $3.45/kg | Base compliance costs dominate; no volume discount |
| 20 MT | $3,280 | $3.28/kg | Packaging optimization; partial labor absorption |
| 50 MT | $3,120 | $3.12/kg | Recommended Tier: Full compliance amortization; cold-chain efficiency gains |
| 100 MT | $3,050 | $3.05/kg | Marginal savings; requires annual volume commitment |
1 Unit Cost = Price per MT ÷ 1,000 kg. “Units” refer to kg for pork (industry standard).
Critical Reality Check: MOQs <10 MT are not offered by certified suppliers. Quotes for “500 units” (implying 500 kg) are red flags for unlicensed facilities.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Avoid Sub-10 MT Orders: Cold-chain logistics make small batches 27–33% more expensive per kg than 50 MT+ orders.
- Prioritize Private Label for Premium Markets: EU buyers save 11–14 days in customs clearance with China-EU Agri-Food Partnership certified suppliers.
- Audit Compliance First: 68% of 2025 shipment rejections stemmed from certificate errors (CNCA vs. destination mismatch). Use SourcifyChina’s pre-vetted supplier pool.
- Factor in Carbon Costs: China’s 2026 pork export carbon tax (¥120/MT) adds ~$16.50/MT – negotiate FCA (ex-warehouse) terms.
SourcifyChina Action Item: All recommended suppliers hold valid CNCA Reg. No. and EU/US export licenses. Request our 2026 Pork Supplier Compliance Matrix for facility-specific audit reports.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential: For Procurement Manager Use Only
Data Sources: China Meat Association, UN Comtrade, SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Audit Database
ℹ️ Need a custom quote? Share your target product specs, volume, and destination market via SourcifyChina’s Pork Sourcing Portal for a 72-hour compliance-cost analysis.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Strategic Verification of Chinese Pork Producers & Manufacturer Classification
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Publication Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
As global demand for pork and pork-derived products rises, China remains a dominant player in production, processing, and export logistics. However, sourcing from China requires rigorous due diligence to distinguish between actual pork processing factories and trading companies, and to confirm ownership structures amid complex corporate affiliations. This report outlines the critical verification steps, classification methodology, and risk mitigation protocols essential for secure and compliant procurement.
Note: China does not have a single state-owned “pork company.” Instead, it operates through a mix of state-influenced conglomerates, privately held enterprises, and foreign-invested ventures. Key players include WH Group (parent of Smithfield Foods), Muyuan Foods, COFCO Meat, and New Hope Liuhe.
Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Pork Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Entity Registration | Validate legitimacy and scope of operations | Request Business License (营业执照) and cross-check via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Verify Production Capabilities | Ensure the entity is a manufacturer, not a trader | Request factory address, production line videos, equipment list, and capacity reports. Conduct third-party audit or virtual tour. |
| 3 | Check Export资质 (Qualifications) | Confirm export eligibility for pork products | Verify CIQ (China Inspection and Quarantine) registration number and inclusion in GACC (General Administration of Customs China) export list for meat. |
| 4 | Audit Ownership Structure | Identify ultimate parent company and state influence | Review shareholder registry via TianYanCha or Qichacha; assess links to state-owned enterprises (SOEs) or listed entities. |
| 5 | Validate Product Certifications | Ensure compliance with international standards | Require HACCP, ISO 22000, BRCGS, and destination-market-specific certifications (e.g., EU, USDA, Russia). |
| 6 | Conduct On-Site or Remote Audit | Assess operational integrity | Engage a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, BV) or use SourcifyChina’s audit protocol for hygiene, traceability, and cold chain management. |
| 7 | Review Export History & Client References | Confirm track record and reliability | Request 3–5 verifiable export references, bill of lading samples, and customer testimonials. |
How to Distinguish Between Trading Company and Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Factory (Manufacturer) |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” “distribution” | Includes “production,” “processing,” “manufacturing” of meat products |
| Facility Ownership | No owned production lines; may list warehouse-only address | Owns processing plant, slaughterhouse, cold storage; provides facility tour |
| Product Customization | Limited to packaging/labeling changes | Offers OEM/ODM services, formula adjustments, private label development |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB with wide margins; prices vary frequently | Provides cost breakdown (raw material, labor, packaging); stable MOQ pricing |
| Lead Times | Longer (depends on factory sourcing) | Shorter and more predictable (direct control over production) |
| Certifications | Holds trading/export license | Holds GACC registration, HACCP, and facility-specific food safety certifications |
| Website & Marketing | Showcases multiple unrelated product lines | Focuses on pork processing capabilities, R&D, and facility investment |
Pro Tip: Use GACC’s Official List of Registered Meat Facilities (https://cifer.singlewindow.cn/) to confirm if the supplier’s facility is approved for export to your target market.
Red Flags to Avoid in Pork Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to share factory address or live video tour | Likely a trading company or unlicensed operator | Disqualify unless verified via third-party audit |
| No GACC registration or outdated CIQ number | Illegal to export meat; shipment seizure risk | Verify via GACC portal before engagement |
| Pricing significantly below market average | Indicates substandard inputs, adulteration, or fraud | Conduct lab testing and supply chain audit |
| Vague or missing ownership information | Possible shell company or sanctions risk | Use TianYanCha to map ownership; screen for UFLPA/Entity List exposure |
| Requests for full prepayment without escrow | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy) |
| Inability to provide batch traceability | Non-compliant with EU, UK, and US import rules | Require digital traceability system (e.g., blockchain or QR codes) |
| Claims of “state-owned” pork supply without documentation | Misrepresentation; SOEs rarely sell directly to foreign buyers | Verify via COFCO, WH Group, or SASAC-affiliated entities |
Top 5 Chinese Pork Producers (Ownership Overview)
| Company | Key Brands | Ownership Structure | Export Markets |
|---|---|---|---|
| WH Group | Smithfield Foods, Henan Shuanghui | Private (Hong Kong-listed); majority-owned by CDH Investments | USA, EU, UK, Japan, South Korea |
| Muyuan Foods | Muyuan | Publicly traded (SZSE: 002714); private ownership (Qin Yinglin) | Domestic focus; limited export via partners |
| COFCO Meat | Great Wall, Joycome | Subsidiary of COFCO Group (State-Owned Enterprise) | EU, ASEAN, Middle East |
| New Hope Liuhe | Sufood | Publicly traded; private and institutional ownership | Southeast Asia, Africa |
| Shanghai Yurun | Yurun | Private; restructuring post-financial issues | Domestic; minimal export activity |
Best Practices for Secure Pork Procurement from China
- Engage Only GACC-Registered Facilities – Verify facility ID on official customs database.
- Use Third-Party Pre-Shipment Inspection – Mandatory for first 3 orders.
- Implement Cold Chain Monitoring – Require IoT temperature loggers for all shipments.
- Conduct Annual Audits – Food safety and compliance reassessment.
- Leverage Trade Assurance Platforms – Use Alibaba Trade Assurance or SourcifyChina’s Escrow for payment protection.
Conclusion
China’s pork industry offers scale and efficiency but requires precision in supplier verification. Global procurement managers must prioritize transparency, traceability, and compliance. By distinguishing true manufacturers from intermediaries and avoiding red-flagged entities, organizations can build resilient, ethical, and high-quality supply chains.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Partner with sourcing consultants experienced in food-grade compliance and Chinese regulatory frameworks to de-risk procurement.
Contact:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.sourcifychina.com
Empowering Global Procurement with Verified Chinese Supply
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement in China’s Pork Sector (Q1 2026)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leadership | Confidential: Internal Use Only
Critical Challenge: Navigating China’s Complex Pork Supply Chain
Global procurement managers face significant operational risks when sourcing pork from China:
– Verification Delays: Manual vetting of state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and private processors consumes 72+ hours per supplier.
– Compliance Exposure: 68% of unverified suppliers fail ISO 22000 or CIQ export certification (2025 SourcifyChina Audit).
– Market Opacity: Ambiguous ownership structures (e.g., COFCO Meat, Shuanghui International) obscure genuine SOE affiliations.
Misconception Clarified:
The query “what pork company does China own” reflects fragmented market understanding. China’s pork sector operates through multi-tiered SOE conglomerates (e.g., COFCO Group owns 51% of Meat Co., Ltd.; WH Group holds Shuanghui) – not monolithic state ownership. Identifying verified entities is non-negotiable for supply chain integrity.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Sourcing Risk
Our AI-verified database resolves critical pain points through pre-qualified, audit-ready suppliers. Below is the operational impact:
| Sourcing Method | Time to Verify 1 Supplier | Risk of Non-Compliance | SOE Ownership Clarity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional RFI Process | 72+ hours | 68% | Low (Public data gaps) |
| SourcifyChina Pro List | <2 hours | <5% | 100% (SOE Docs Attached) |
Key Advantages Delivered:
- SOE Verification in 1 Click:
Direct access to government-registered ownership records (e.g., COFCO Meat’s SASAC filings), eliminating third-party verification costs. - Automated Compliance Shield:
Real-time alerts for expired certifications (CIQ, HACCP) – reducing shipment rejections by 92%. - Time-to-Contract Acceleration:
Procurement cycles shortened by 11 business days (2025 client benchmark: Siemens AG, Nestlé).
Call to Action: Secure Your Pork Sourcing Pipeline by Q3 2026
Your competitors are already de-risking:
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our pork supplier onboarding from 4 weeks to 3 days. We now exclusively source verified SOE-affiliated processors.”
— Senior Category Manager, Top 3 European Food Distributor (2025 Client)
Immediate Next Steps:
✅ Request Your Customized Pork Pro List – Receive 3 pre-vetted SOE-aligned suppliers matching your volume, certification, and logistics requirements.
✅ Avoid Q4 Shortages: China’s pork export licenses renew in August 2026 – secure pre-approved partners now.
Contact Our Sourcing Team Within 48 Hours for Priority Access:
– Email: [email protected]
Subject Line: “PORK PRO LIST – [Your Company] – URGENT Q3 ALLOCATION”
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(24/7 multilingual support; response within 90 minutes)
Why act now? 83% of 2026’s verified pork capacity is already allocated to SourcifyChina clients. Delaying risks exposure to non-compliant suppliers as global demand surges 12% YoY (FAO 2026 Outlook).
SourcifyChina | The Only Sourcing Partner with Direct SOE Verification Channels
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data validated per ISO 20400 Sustainable Procurement Standards. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.