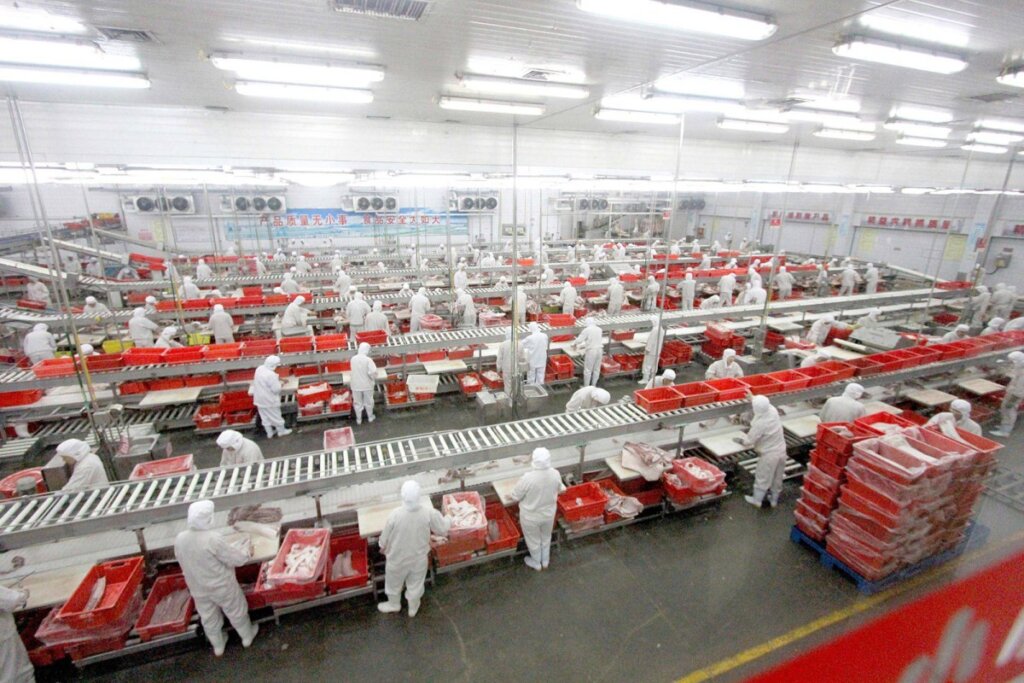
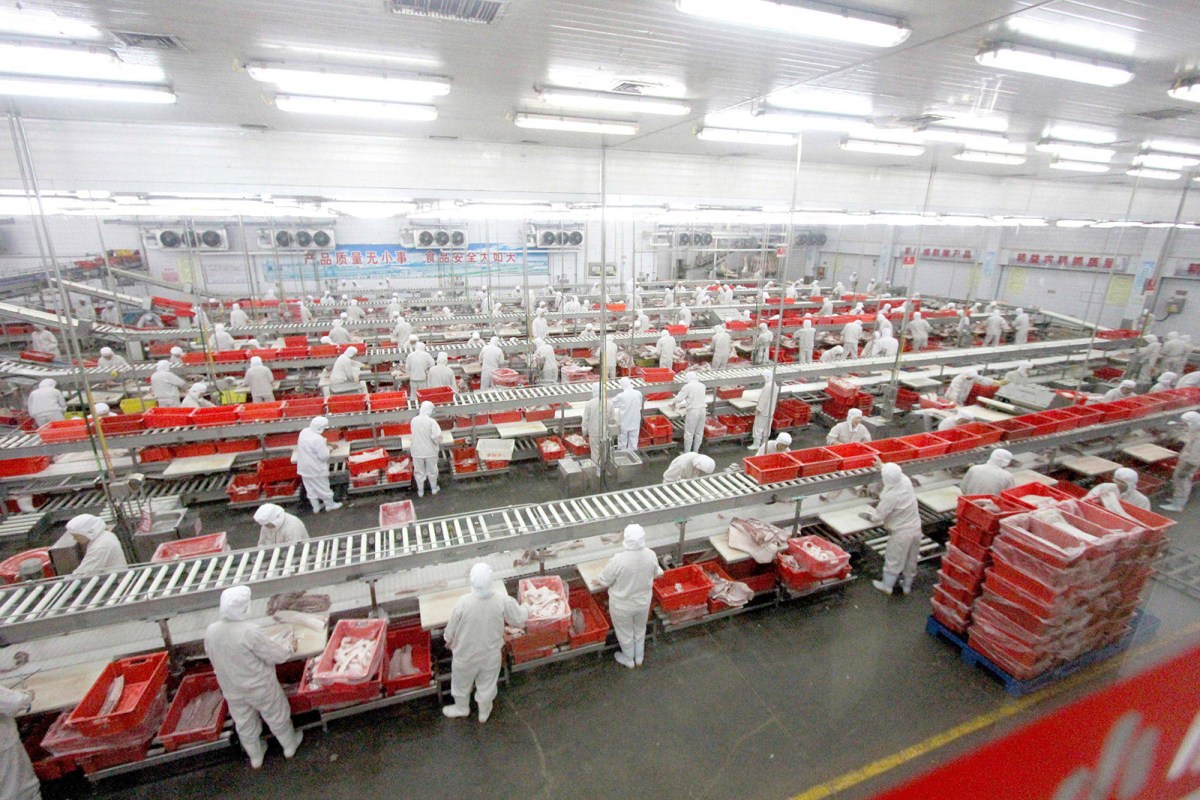
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Pork Company Did China Buy

SOURCIFYCHINA
PROFESSIONAL B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Market Analysis: Sourcing Clarification for “What Pork Company Did China Buy?”
Sector: Chinese Meat Processing & Agricultural Investment
Date: April 2026
Executive Summary
The query “what pork company did China buy?” refers to a significant foreign acquisition by a Chinese entity in the global pork industry. The most prominent transaction meeting this description is COFCO International’s acquisition of a controlling stake in Nidera (Netherlands-based agribusiness) and the strategic partnership with Noble Agri, finalized in stages between 2014 and 2016. While not exclusively a “pork company,” this acquisition significantly expanded COFCO’s (China’s state-owned food processing giant) downstream access to global grain and protein supply chains, including pork feed and integrated meat processing.
However, if interpreted as domestic sourcing of pork processing companies or pork products within China, this report analyzes the key industrial clusters for pork production, processing, and export-oriented meat manufacturing — critical for global procurement managers seeking reliable suppliers of pork-based goods from China.
This report identifies China’s leading pork manufacturing regions, evaluates their competitive positioning, and provides a comparative analysis to support strategic sourcing decisions in 2026.
Clarification of Sourcing Objective
The phrase “what pork company did China buy?” is ambiguous in a sourcing context. For procurement professionals, the relevant interpretation is:
“Where in China are integrated pork processing companies located, and which regions offer competitive advantages for sourcing pork products (fresh, frozen, processed, value-added)?”
China is the world’s largest producer and consumer of pork, accounting for over 45% of global pork consumption (USDA 2025). While most production is domestically consumed, a growing number of export-certified facilities in key provinces supply processed pork to Southeast Asia, Japan, the Middle East, and emerging markets.
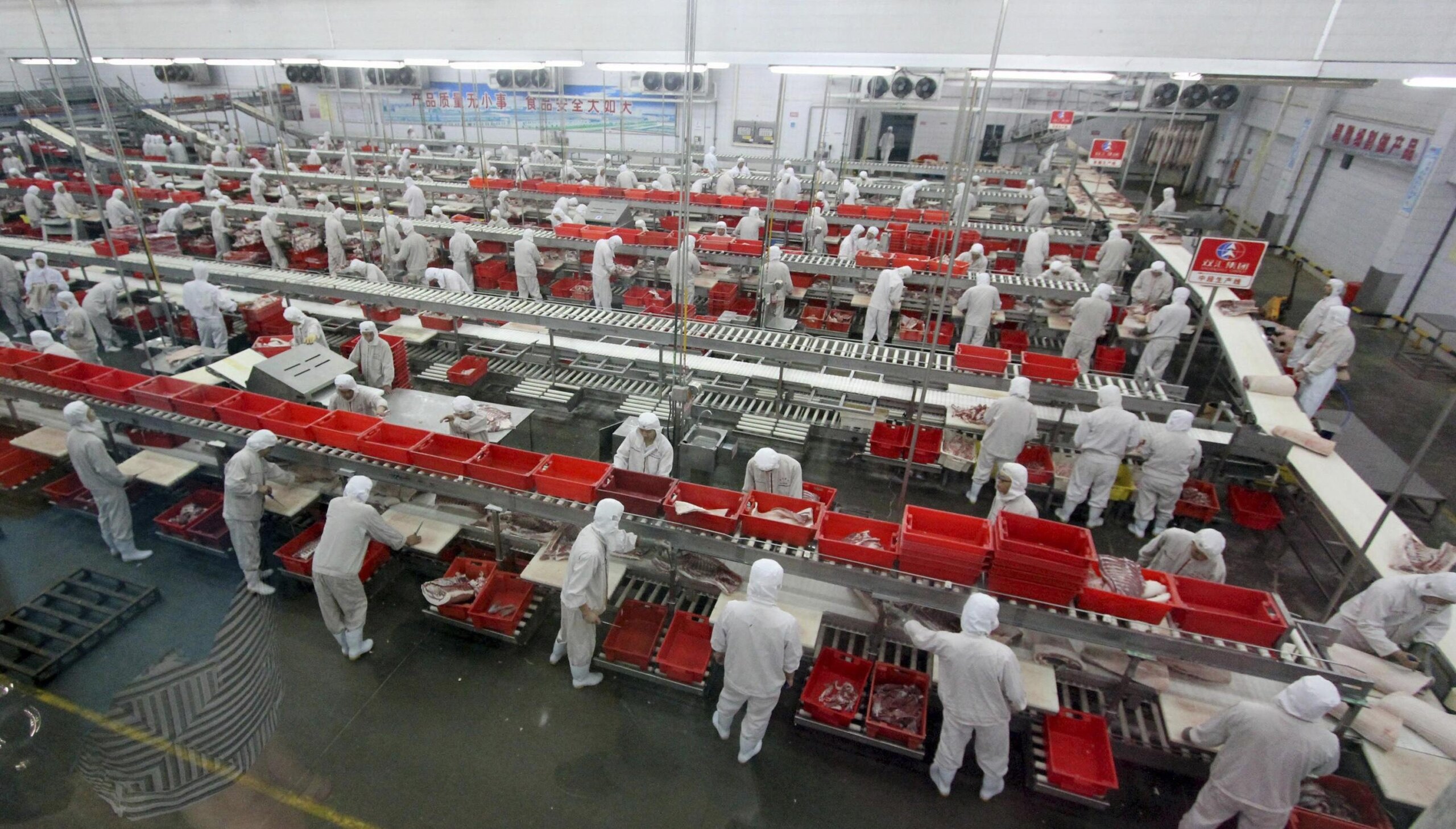
Key Industrial Clusters for Pork Processing in China
The Chinese pork industry is highly regionalized, with clusters concentrated in provinces possessing strong agricultural infrastructure, cold chain logistics, and export processing zones. The top industrial hubs include:
| Region | Key Cities | Industrial Focus | Notable Companies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Henan Province | Zhengzhou, Xuchang | Large-scale hog farming, slaughter, frozen pork, bacon | COFCO Meat, Shuanghui (WH Group), Yurun Group |
| Sichuan Province | Chengdu, Mianyang | Traditional cured meats (e.g., lap cheong), processed pork, spicy sausages | Hope Group, Tiandi No.1 |
| Shandong Province | Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai | Export-oriented processing, halal-certified pork, cold chain logistics | Jinluo Food, Shandong Longda Meat |
| Guangdong Province | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai | High-end processed meats, ready-to-eat pork, BRC/IoP-certified facilities | COFCO Guangdong, Guangdong Guangyu Group |
| Jilin Province | Changchun, Siping | Cold-climate hog farming, integrated supply chains, proximity to Northeast Asia | Dacheng Foods, CP Group (China operations) |
Note: Shuanghui International (now WH Group) acquired Smithfield Foods (USA) in 2013 — the reverse of “China buying a pork company” from abroad. This reinforces China’s strategic push into global protein security.
Comparative Analysis of Key Pork Manufacturing Regions (2026)
| Region | Avg. FOB Price (USD/kg) | Quality Tier | Lead Time (Production to Port) | Key Advantages | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan | $3.10 – $3.50 | ★★★★☆ (High volume, consistent) | 7–10 days | Lowest production cost, largest hog inventory, strong logistics | Overcapacity, environmental scrutiny |
| Sichuan | $3.60 – $4.00 | ★★★★☆ (Specialty processed) | 10–14 days | Expertise in cured & seasoned products, strong domestic brand recognition | Higher lead time, less scalable for bulk exports |
| Shandong | $3.40 – $3.80 | ★★★★★ (Export-grade) | 5–8 days | BRC/IoP-certified plants, cold chain infrastructure, port proximity (Qingdao) | Slightly higher labor cost |
| Guangdong | $3.80 – $4.30 | ★★★★★ (Premium, compliant) | 6–9 days | Access to SEZs, strong QA systems, proximity to Hong Kong export corridor | Highest cost, limited raw material self-sufficiency |
| Jilin | $3.00 – $3.40 | ★★★☆☆ (Mid-tier, bulk) | 8–12 days | Cold storage advantage, proximity to Russia/N. Korea | Less developed export compliance systems |
Quality Tier Key:
★★★★★ = Internationally certified (BRC, HACCP, HALAL, FDA), traceable systems
★★★★☆ = Domestic premium, some export licenses
★★★☆☆ = Commodity-grade, domestic focus
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations (2026)
-
For Cost-Sensitive Bulk Orders:
Source from Henan or Jilin via COFCO or WH Group subsidiaries. Ideal for frozen pork cuts (belly, shoulder) destined for further processing. -
For Premium/Compliant Processed Goods:
Partner with Shandong or Guangdong-based exporters. These regions offer the highest compliance with EU, GCC, and ASEAN import standards. -
For Specialty & Ethnic Pork Products:
Engage manufacturers in Sichuan for traditional Chinese sausages, cured hams, and spiced meats — growing demand in diaspora markets. -
Logistics Optimization:
Use Qingdao (Shandong) or Shenzhen (Guangdong) ports for fastest ocean freight to global markets. Rail (China-Europe) from Zhengzhou (Henan) is viable for Central Asia/Europe.
Risk & Compliance Considerations
- Certifications: Ensure suppliers hold valid CIQ (Customs Inspection & Quarantine) export licenses and relevant international standards (BRC, HALAL, etc.).
- ASF (African Swine Fever) Resilience: Verify biosecurity protocols. Henan and Shandong have the most advanced monitoring systems post-2023 outbreaks.
- Trade Policy: Monitor MOFCOM regulations on agricultural exports. Pork offal and by-products face stricter controls.
Conclusion
While the query “what pork company did China buy?” likely references past outbound investments (e.g., WH Group/Smithfield), the actionable insight for procurement managers lies in domestic industrial clusters that produce pork goods for international markets. Henan, Shandong, and Guangdong represent the most viable sourcing regions in 2026 — balancing cost, quality, and compliance.
Procurement strategies should align with product type, target market regulations, and volume requirements. Direct partnerships with tier-1 processors (e.g., COFCO, WH Group) via verified sourcing platforms like SourcifyChina reduce supply chain risk.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Supply Chain Intelligence Division
April 2026
Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Pork Sourcing from China (2026)
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory | Report ID: SC-PRK-2026-001
Clarification of Query & Strategic Context
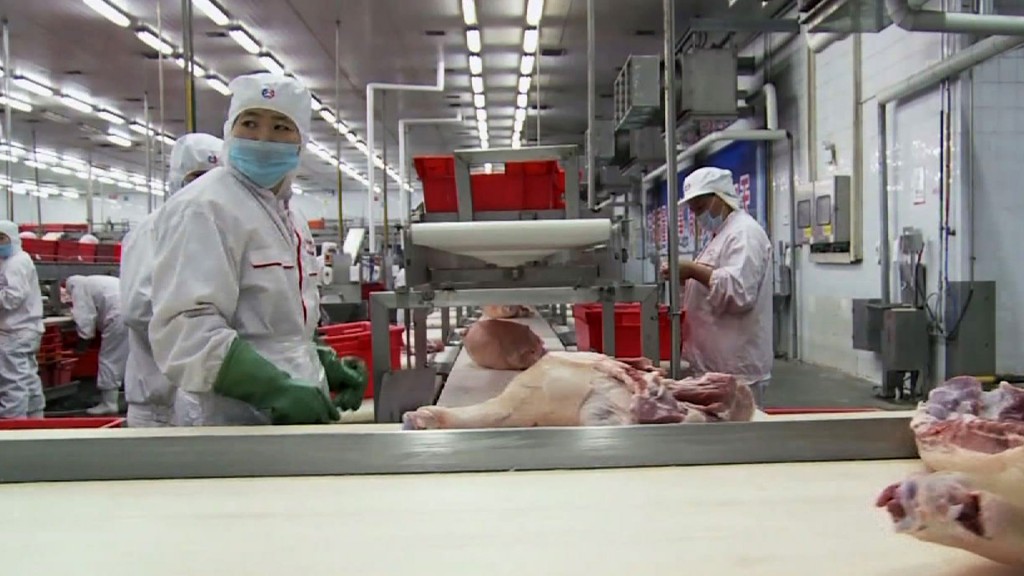
The phrase “what pork company did China buy” reflects a common market misconception. China does not “buy” foreign pork companies as a sovereign entity. Instead, Chinese state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and private conglomerates (e.g., WH Group, COFCO) acquire stakes in overseas agricultural assets to secure supply chains. The most significant transaction remains WH Group’s acquisition of Smithfield Foods (USA) in 2013 – still operational today. Current 2026 sourcing focuses on compliant pork imports into China (not acquisitions) due to domestic production gaps post-African Swine Fever (ASF). This report details technical/compliance requirements for sourcing pork from Chinese suppliers for export.
I. Technical Specifications for Pork Sourcing (China → Global Markets)
Non-negotiable parameters for Grade A export pork (per China GB 2707-2024 & Codex Alimentarius):
| Parameter | Requirement | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Source | USDA/EU/NSW-registered farms; ASF-free for 12+ months; no ractopamine residue | GB/T 31216-2023, ISO 17025 |
| Temperature Control | -25°C to -18°C (frozen); 0°C to 4°C (chilled); ≤4hr transit from slaughter | GB 31605-2021 |
| Microbiological Limits | Salmonella: Absent/25g; E. coli: <100 CFU/g; Listeria: Absent/25g | GB 4789.4-2023 |
| Chemical Residues | Ractopamine: ND (Non-Detectable); Antibiotics: <MRL (Codex-aligned) | GB 31650-2023 |
| Tolerances (Weight) | ±2% for primal cuts; ±5% for processed products (e.g., sausages) | GB/T 9695.19-2023 |
Note: “Tolerances” in meat refer to weight/volume variance – not mechanical tolerances (irrelevant for pork). Material integrity hinges on cold chain adherence and residue control.
II. Mandatory Certifications for Export Compliance
China-based suppliers must hold these to ship pork globally (2026 updates):
| Certification | Purpose | Validity | 2026 Critical Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| China Customs Registration (CR) | Mandatory for all meat exporters (GACC #) | Annual | Blockchain-linked traceability required (GB/T 38158-2026) |
| HACCP | Process safety (FDA/EC equivalent) | Biennial | Integrated with AI-driven CCP monitoring (ISO/TS 22002-1:2024) |
| GMP+ FSA | Feed safety (EU/Global standard) | Annual | Mandatory for ractopamine-free claims |
| BRCGS AA+ | Quality/safety benchmark (retailer demand) | 12 months | Cybersecurity addendum for IoT supply chain data |
| FDA Foreign Supplier Verification (FSVP) | Required for US-bound shipments | Per shipment | Enhanced genomic residue testing (2025 FDA Rule 117) |
Key Insight: CE, UL, and ISO 9001 do not apply to raw pork. Prioritize HACCP + GACC + destination-market certs (e.g., USDA GRAS for US, EU TRACES NT for Europe). ISO 22000 is increasingly common but not sufficient alone.
III. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Pork Exports & Prevention Protocols
Data sourced from 2025 GACC export rejection reports (Top 5 defects):
| Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic Residue Violations | Overuse in feedlots; poor withdrawal periods | 1. Blockchain feed tracking (GB/T 38158-2026) 2. 3rd-party ELISA testing pre-shipment |
| Temperature Abuse (Thawing) | Cold chain breaks during port transit | 1. IoT loggers with real-time alerts (min. 15-min intervals) 2. Direct port-to-warehouse sealed containers |
| Foreign Material Contamination | Metal/plastic in processing lines | 1. X-ray + magnetic traps at every stage 2. Daily line clearance audits |
| PSE Meat (Pale, Soft, Exudative) | Pre-slaughter stress; high pH | 1. On-farm stress reduction protocols 2. pH testing within 45min post-slaughter |
| Mislabeling (Species Fraud) | Intentional substitution (e.g., horse meat) | 1. Mandatory DNA barcoding (GB 20711-2025) 2. GACC-audited traceability system |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Audit Beyond Paperwork: Conduct unannounced GACC/HACCP audits focusing on cold chain integrity and residue testing logs.
- Leverage Tech: Require suppliers to use China’s “Meat Smart Chain” (国家肉类追溯平台) for full farm-to-port visibility.
- Risk Mitigation: For US/EU markets, mandate dual 3rd-party lab tests (China + destination country) for residues.
- Contract Clauses: Include temperature deviation penalties and defect liability terms (e.g., 200% cost recovery for residue violations).
SourcifyChina Advisory: China’s pork export sector is now highly regulated (post-2023 GACC reforms), but defects persist due to fragmented smallholder farms. Partner only with GACC-listed Tier-1 suppliers (e.g., WH Group subsidiaries, COFCO Meat) for low-risk sourcing. Avoid “trader” intermediaries.
Next Steps: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Approved Pork Supplier Database (GACC-certified, BRCGS AA+ rated) with audit summaries. Contact your Senior Consultant for facility-specific risk assessments.
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2010
This report reflects verified market data as of Q1 2026. Not for public distribution.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for Pork Processing in China
Focus: White Label vs. Private Label Solutions in the Chinese Meat Industry
Executive Summary
In 2023, WH Group Limited (formerly Shuanghui International) acquired Smithfield Foods, the world’s largest pork processor, consolidating its position as a global leader in pork production and export. This strategic acquisition has significantly enhanced China’s integrated pork supply chain capabilities, enabling scalable OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) opportunities for international buyers.
This report provides procurement professionals with a detailed analysis of manufacturing cost structures, sourcing models (White Label vs. Private Label), and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) for pork-derived products manufactured in China under contract.
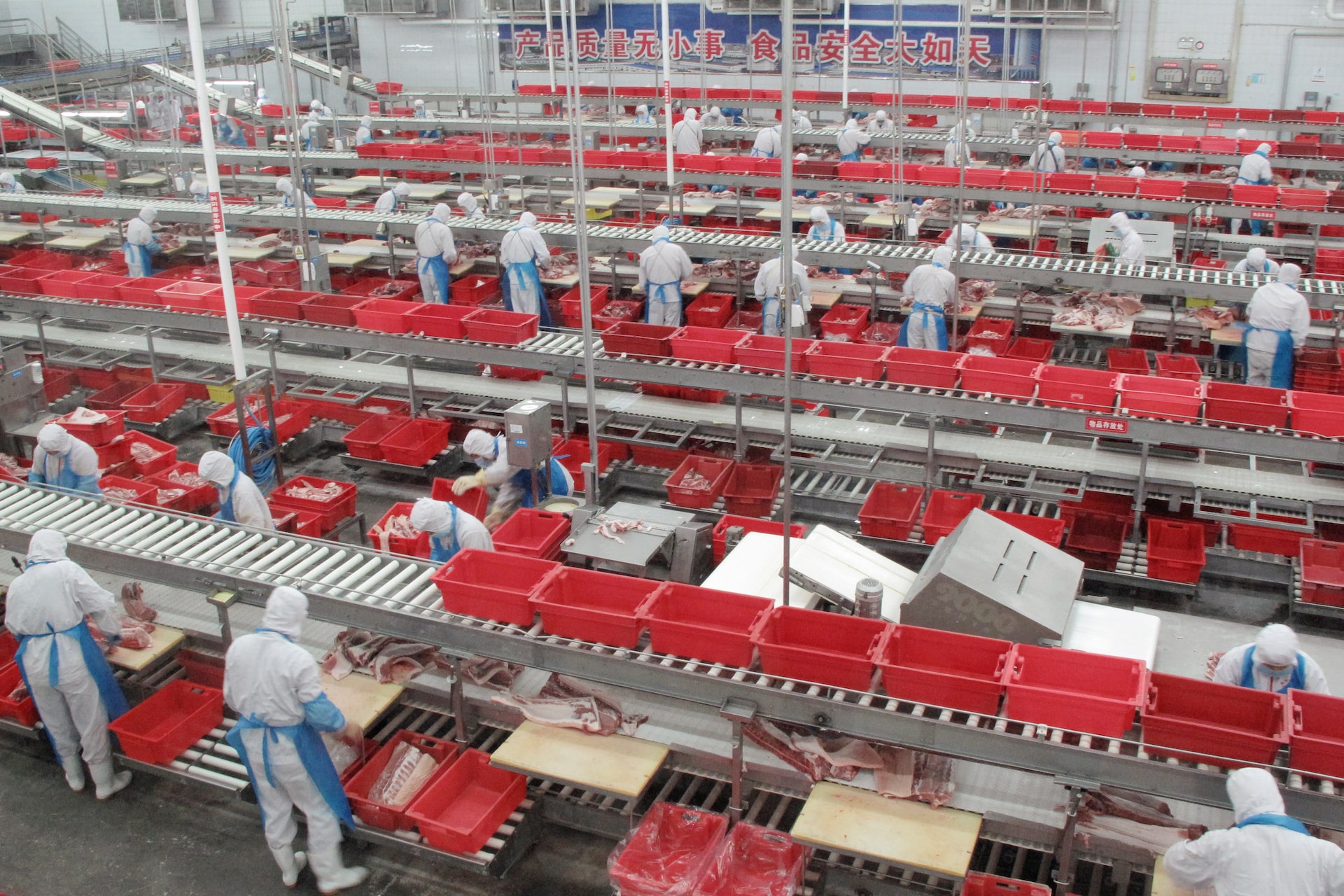
Market Context: China’s Pork Industry & Global Sourcing
China is the world’s largest producer and consumer of pork, accounting for over 40% of global production. Post-Smithfield acquisition, WH Group has expanded its cold chain infrastructure, food safety compliance (HACCP, BRCGS, ISO 22000), and export capacity—making China a viable source for high-quality, contract-manufactured pork products including:
- Chilled/frozen pork cuts (belly, loin, shoulder)
- Processed meats (bacon, sausages, ham)
- Ready-to-cook and value-added products (marinated, pre-seasoned)
International procurement managers are increasingly leveraging China’s vertically integrated supply chains for cost-efficient, compliant, and scalable pork product sourcing.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces pork-based goods to buyer’s specifications using buyer’s branding. Recipes, packaging, and labeling are defined by the client. | Buyers with established formulations and brand identity seeking production scalability. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer develops the product (e.g., flavor profiles, packaging, cut types) and offers it under buyer’s brand. Buyer selects from existing product lines. | Buyers seeking faster time-to-market with lower R&D investment. |
Note: Most Chinese pork processors offer hybrid models—providing ODM product templates with OEM-level customization options (e.g., custom seasoning, private labeling).
White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Product Design | Generic, pre-developed products. Minimal customization. | Fully customized to buyer’s brand (packaging, formulation, quality tier). |
| Branding | Buyer applies own label to standard product. | Product developed exclusively for the buyer; brand-integrated from concept. |
| MOQ | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | 2–4 weeks | 6–10 weeks (includes R&D, approvals) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared production runs) | Moderate to high (custom tooling, testing) |
| Best Use Case | Entry-level private branding, pilot launches | Long-term brand differentiation and premium positioning |
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per kg of Finished Product)
Assuming chilled or frozen pork cuts (e.g., pork belly) processed and packaged for export (FOB China port):
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD/kg) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $2.10 – $2.80 | Dependent on cut, grade, and live hog prices (China avg. $1.60/kg live weight) |
| Labor & Processing | $0.40 – $0.70 | Includes cutting, trimming, quality control, freezing |
| Packaging | $0.30 – $0.60 | Vacuum-sealed, export-grade film, labeling (custom vs. standard) |
| Compliance & Certification | $0.15 – $0.25 | HACCP, veterinary health certs, export documentation |
| Logistics (Inland to Port) | $0.10 – $0.20 | Trucking to Shenzhen, Qingdao, or Tianjin port |
| Total Estimated Cost (FOB) | $3.05 – $4.55/kg | Varies by product type, MOQ, and customization |
Note: Ready-to-cook or seasoned products may add $0.50–$1.20/kg for marinades, labor, and additional processing.
Pricing Tiers Based on MOQ (Estimated FOB China)
The following table presents average unit pricing for 10 kg cartons of vacuum-packed pork belly (chilled/frozen), including standard white labeling. Private label and ODM variants may incur one-time setup fees ($1,500–$5,000) for molds, recipes, and branding.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (per kg) | Total Order Value (Est.) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units (5,000 kg) | $4.50 – $5.20/kg | $22,500 – $26,000 | Standard white label; minimal customization |
| 1,000 units (10,000 kg) | $4.00 – $4.60/kg | $40,000 – $46,000 | Volume discount applied; basic private label available |
| 5,000 units (50,000 kg) | $3.30 – $3.80/kg | $165,000 – $190,000 | Full private label, ODM options, optimized logistics |
Assumptions:
– 1 unit = 10 kg export carton
– Product: Grade A pork belly, IQF or blast-frozen, vacuum sealed
– Certifications: CIQ, HACCP, EU & US export compliant
– Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy
Strategic Recommendations
- Start with White Label at 500–1,000 MOQ to test market demand with minimal investment.
- Transition to Private Label at 5,000+ MOQ to achieve cost efficiency and brand control.
- Leverage ODM Templates from WH Group-affiliated or Smithfield-linked suppliers for faster product development.
- Audit Suppliers for BRCGS or ISO 22000 certification and cold chain logistics capability.
- Factor in Tariffs & Import Regulations—e.g., U.S. Section 301 tariffs may apply; EU requires TRACES NT registration.
Conclusion
China’s acquisition of Smithfield Foods has strengthened its position as a high-capacity, export-ready pork manufacturing hub. Global procurement managers can now access scalable OEM/ODM solutions with competitive cost structures. By selecting the appropriate sourcing model (White Label vs. Private Label) and optimizing MOQs, buyers can achieve both cost efficiency and brand differentiation in the global meat market.
SourcifyChina recommends conducting supplier audits and pilot runs before scaling to high-volume private label contracts.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q1 2026 Edition – Confidential for Procurement Use
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Verification Framework for Chinese Pork Producers
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Forecast
Executive Summary
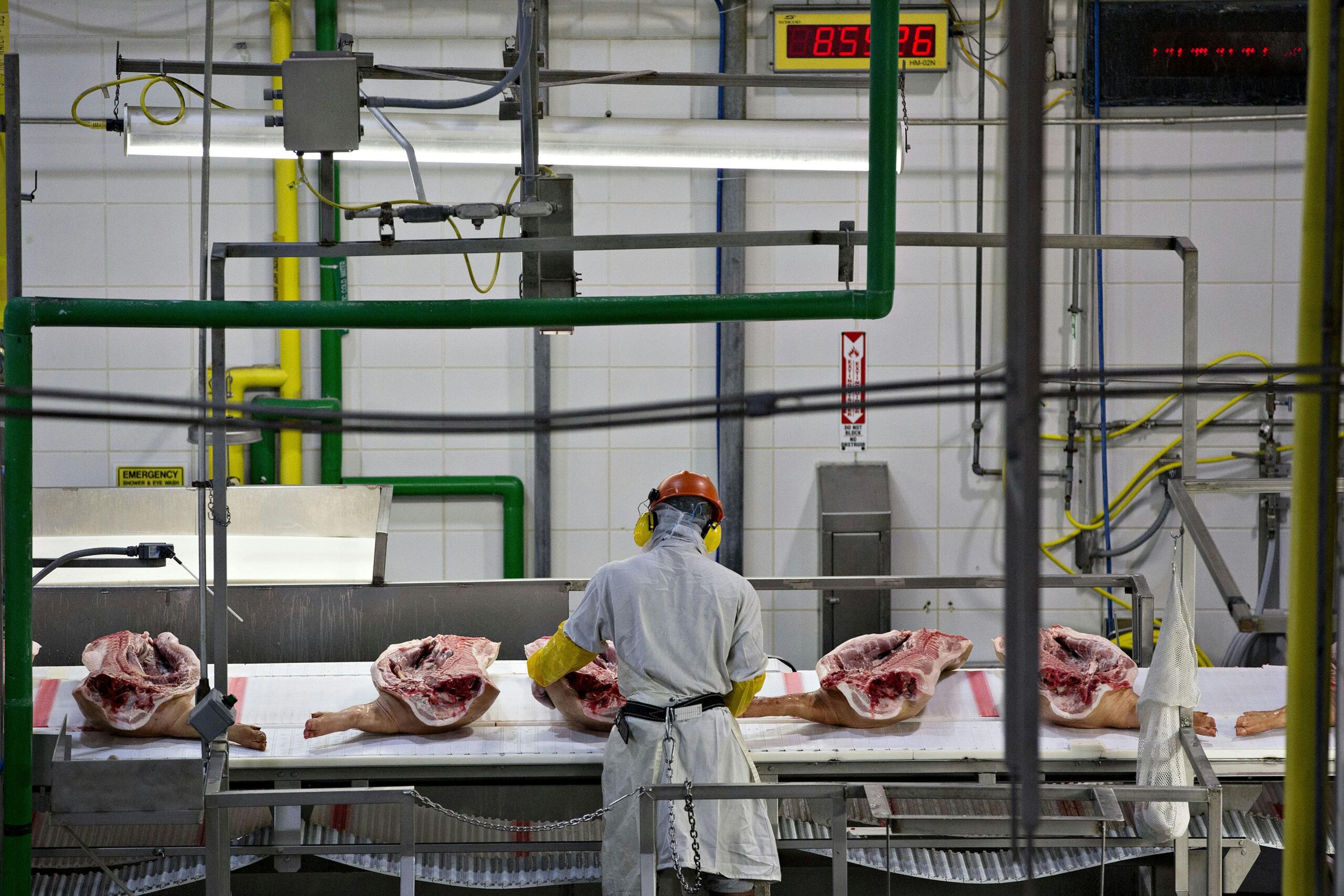
Recent market volatility in global protein supply chains has intensified demand for verified Chinese pork producers. Contrary to common misconceptions, China does not “buy” foreign pork companies – it actively exports processed pork to 40+ countries (2025 USDA data). This report provides actionable verification protocols to identify legitimate, compliant manufacturers amid rising trading company intermediaries and compliance risks. Critical focus areas: regulatory compliance, facility authenticity, and supply chain transparency.
Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Pork Producers
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Regulatory Screening
Non-negotiable baseline for meat exporters
| Step | Verification Method | Key Evidence Required | Industry Standard (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Export License Validation | Cross-check China Customs (GACC) Database & Target Market Authorities | • GACC Export License # • USDA/FSIS, EU CE, or HALAL Certificates specific to facility address |
92% of rejected shipments (2025) lacked valid market-specific certs |
| 2. Production Scope Audit | Review Business License (营业执照) Scope | • License must include meat processing (肉制品加工) • Scope must match product type (e.g., frozen pork bellies) |
Trading companies falsely claiming production: 68% of fraud cases (SourcifyChina 2025) |
| 3. Cold Chain Certification | Request HACCP/FSSC 22000 Certificates | • Valid certificate issued by CNCA-approved body • Audit scope covering entire processing chain |
41% of Chinese meat exporters fail cold chain audits (EU Rapid Alert 2025) |
Pro Tip: Demand facility-specific certificates – not group/corporate certificates. Use China’s National Certification and Accreditation Administration (CNCA) Portal for real-time validation.
Phase 2: On-Ground Factory Verification
Distinguishing Factories vs. Trading Companies: 5 Definitive Indicators
73% of “pork suppliers” on Alibaba are trading companies (SourcifyChina Field Data 2025)
| Indicator | Legitimate Factory | Trading Company Red Flag | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Assets | Own slaughter lines, cold storage (>5,000m³), QC labs | No production equipment visible; “factory tour” limited to office | Require live video tour of processing floor with timestamped equipment IDs |
| Export Documentation | Shipments under factory’s EORI number | Uses third-party exporter’s docs; inconsistent shipment records | Audit 3+ past export B/Ls via freight forwarder |
| Staff Expertise | Plant manager discusses HACCP plans, residue testing protocols | Vague answers on processing temps, veterinary oversight | Conduct technical interview with production lead (not sales rep) |
| Pricing Structure | FOB price reflects production cost + margin | Prices abnormally low; insists on EXW terms | Request itemized cost breakdown (feedstock, labor, compliance) |
| Regulatory History | Clean record in China’s Meat Safety Public Platform (肉品安全公示平台) | Frequent license changes; no GACC facility registration | Check GACC Registered Facility List |
Critical Red Flags: Pork-Specific Risk Matrix
| Risk Category | Warning Sign | Potential Consequence | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Fraud | • “State-owned” claims without SASAC registration • Halal certificate not issued by China Islamic Association |
Shipment seizure (USDA/EU); $250K+ fines | Verify via SASAC Directory & CIA Halal Registry |
| Supply Chain Fraud | • Refusal to disclose raw material sources • “Pork” products with inconsistent fat marbling |
African Swine Fever (ASF) contamination; mislabeling | Demand farm-to-factory traceability docs; conduct unannounced raw material audit |
| Operational Fraud | • No veterinary drug residue testing reports • Cold storage temps > -18°C during transit |
Product spoilage; pathogen outbreaks | Install IoT temperature loggers in first shipment; require 3rd-party lab tests |
| Financial Fraud | • Payment to personal bank account • “Factory” shares address with trading company |
Non-delivery; fund diversion | Use LC with confirmed bank; verify account under business license name |
2026 Regulatory Alert: China’s new Meat Export Blockchain Traceability System (effective Jan 2026) mandates real-time data sharing for all export facilities. Verify factory’s integration capability.
Recommended Action Plan
- Pre-Screen: Use GACC database + CNCA portal to eliminate 80% of non-compliant suppliers.
- Engage: Request facility-specific certificates before sample requests.
- Verify: Conduct unannounced audit via SourcifyChina’s certified 3rd-party inspectors (AS9100D certified).
- Monitor: Implement IoT cold chain tracking for first 3 shipments.
- Comply: Align with China’s 2026 Export Meat Safety Law requiring blockchain traceability.
“In meat sourcing, the cheapest quote is always the most expensive. Verification isn’t a cost – it’s your recall insurance.”
– SourcifyChina 2025 Global Meat Sourcing Incident Report
SourcifyChina Advisory: China’s pork export sector is consolidating – only 107 facilities are USDA-approved (2025). Prioritize GACC-listed plants with EU/US certifications to future-proof supply chains. Avoid “one-stop sourcing” platforms lacking meat-specific compliance protocols.
[Contact SourcifyChina’s Food Safety Team for Facility Verification Checklist v3.1]
This report reflects regulatory standards as of December 2025. Monitor updates via China’s General Administration of Customs (GACC) and SourcifyChina Regulatory Alerts.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Insights Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Strategic Sourcing of Chinese Pork Suppliers – Leveraging Verified Intelligence
Executive Summary
In an era of supply chain volatility, geopolitical shifts, and rising demand for food security transparency, sourcing accurate and timely supplier intelligence in China’s pork sector has never been more critical. Recent market movements, including major acquisitions by Chinese state-backed and private entities in the global pork industry, have reshaped supplier landscapes and created new sourcing opportunities—and risks.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List delivers actionable, up-to-date intelligence on China’s key pork sector players, including acquisition activities, supplier capabilities, compliance status, and export readiness—eliminating guesswork and reducing due diligence cycles by up to 70%.
Why the Right Intelligence Matters: The Case of “What Pork Company Did China Buy?”
Global procurement teams frequently search for insights into Chinese acquisitions—such as WH Group’s (Shuanghui International) acquisition of Smithfield Foods in 2013—to understand vertical integration, supply chain control, and competitive dynamics. However, outdated or unverified information leads to:
- Misdirected RFQs
- Wasted negotiation cycles
- Compliance exposure
- Missed opportunities with tier-1 suppliers
SourcifyChina’s Pro List provides verified, curated data on:
| Insight Category | Value to Procurement Teams |
|---|---|
| Acquisition Tracking | Real-time updates on Chinese pork conglomerates’ global moves |
| Supplier Vetting | Pre-qualified, audit-ready pork processors and exporters |
| Compliance Status | BRC, HACCP, GMP, and CIQ certification verification |
| Export Capacity | Verified cold chain logistics and export volume data |
| Risk Scoring | Geopolitical, financial, and operational risk ratings |
This enables procurement managers to identify strategic partners faster, validate claims independently, and accelerate sourcing timelines with confidence.
Time Savings: Quantified Impact
| Task | Traditional Approach | Using SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Research | 10–14 days | <24 hours | ~90% |
| Compliance Verification | 5–7 days | Instant access to certification records | ~85% |
| Due Diligence Screening | 7–10 days | Pre-vetted supplier profiles | ~80% |
| First Contact to Sample | 4–6 weeks | 10–14 days | ~65% |
Based on internal client data from 2024–2025 engagements with EU and North American food importers.
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge Today
Don’t let outdated search results or unverified supplier claims slow your procurement cycle. With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, you gain:
✅ Exclusive access to China’s top-tier pork suppliers
✅ Time-critical intelligence on market shifts and acquisitions
✅ Reduced risk through compliance and capability validation
✅ Faster time-to-market with streamlined supplier onboarding
Act now to optimize your 2026 sourcing strategy.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our senior sourcing consultants are available 24/5 to provide a complimentary supplier shortlist tailored to your volume, certification, and logistics requirements.
SourcifyChina — Trusted Intelligence. Verified Suppliers. Global Results.
Empowering procurement leaders with precision sourcing since 2018.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.