Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Meat Companies Are Owned By China
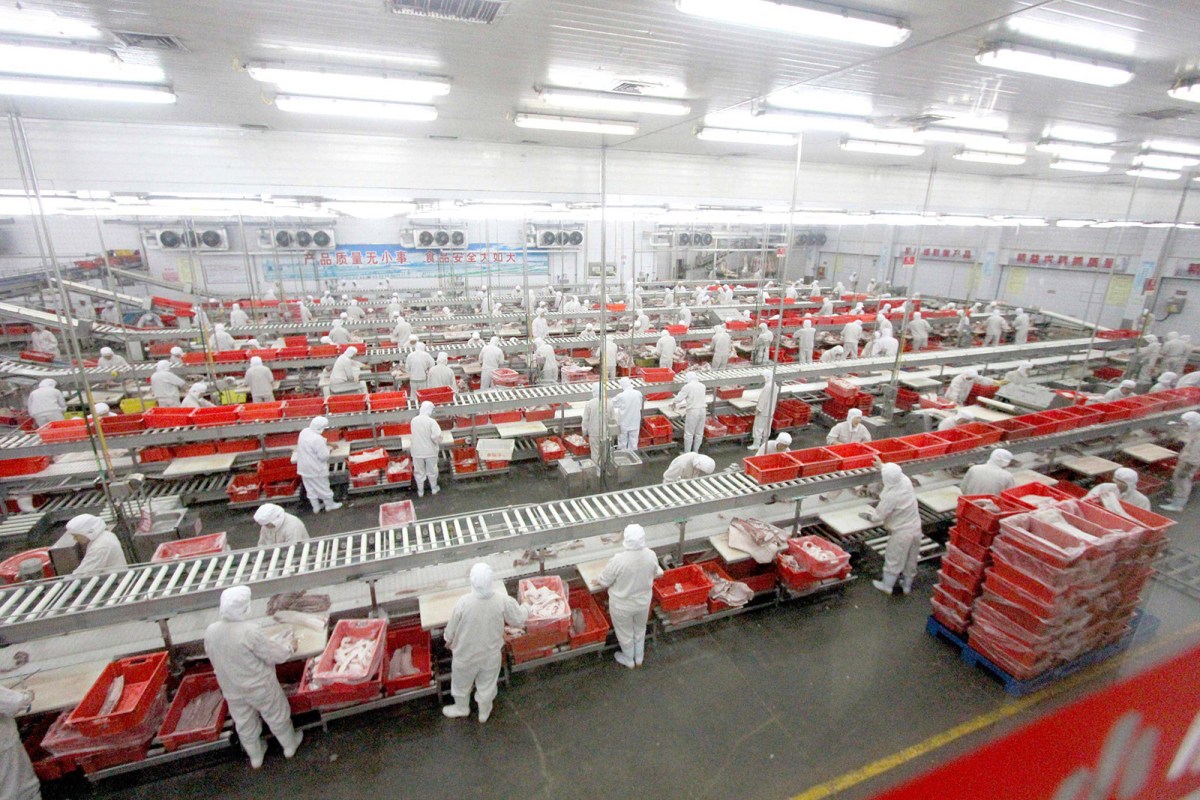

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Chinese-Owned Meat Processing Companies & Industrial Clusters
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of meat processing companies in China with a focus on identifying entities that are either Chinese state-owned, privately owned, or majority-owned by Chinese capital. While China is not traditionally perceived as a major exporter of processed meat products to Western markets due to food safety perceptions and regulatory barriers, it has developed a highly consolidated and technologically advanced domestic meat industry—particularly in pork, poultry, and emerging alternative proteins.
Chinese ownership in the meat sector spans large conglomerates, state-backed agribusinesses, and private enterprises focused on domestic distribution, retail, and export to Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. This report identifies key industrial clusters, evaluates regional performance, and offers strategic insights for global procurement teams considering sourcing from China.
Note: The phrase “what meat companies are owned by China” has been interpreted as identifying meat processing companies that are Chinese-owned or state-influenced, rather than foreign-owned firms operating in China.
Key Chinese-Owned Meat Processing Companies (2026)
| Company Name | Headquarters | Ownership Type | Core Products | Export Markets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WH Group (Shuanghui International) | Luohe, Henan | Private (Listed: HKEX) | Pork, processed meats, sausages | Hong Kong, Southeast Asia, Oceania |
| Cofco Meat Holdings Ltd. | Beijing | State-Owned (Cofco Group) | Pork, beef, poultry, cold chain | Domestic, Middle East, Russia |
| New Hope Liuhe Co., Ltd. | Chengdu, Sichuan | Private Conglomerate | Poultry, feed, processed poultry | Vietnam, Philippines, UAE |
| Sino Agro Foods Inc. | Wenzhou, Zhejiang | Private (US-listed, Chinese ops) | Grass-fed beef, aquaculture | EU (limited), Hong Kong |
| Jinluo Meat Group | Shandong | Private | Halal-certified poultry & lamb | Central Asia, Middle East |
| Hengan Group (Meat Division) | Fujian | Private | Ready-to-eat meat snacks | Domestic, Southeast Asia |
Ownership Insight: WH Group owns Smithfield Foods (USA), but Smithfield is not Chinese-owned—its parent (WH Group) is. Only Chinese-based operations are considered in this regional analysis.
Key Industrial Clusters for Meat Processing in China
China’s meat processing industry is concentrated in provinces with strong agricultural output, cold chain infrastructure, and access to major ports. The top clusters are:
- Henan Province – National hub for pork processing (home to WH Group)
- Shandong Province – Diversified meat production; strong halal export focus
- Sichuan Province – Spiced and cured meat specialties (e.g., la chorizo, bacon)
- Guangdong Province – High-end processed meats, proximity to Hong Kong/Guangzhou port
- Zhejiang Province – Innovation in packaging, export-oriented SMEs
- Jilin Province – Beef and cold-climate livestock (growing BRI export corridor)
Regional Comparison: Key Production Hubs (2026)
| Region | Avg. Price (USD/kg) | Quality Tier | Lead Time (Ex-Factory to Port) | Key Advantages | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan | $3.80 | ★★★★☆ | 3–5 days | Scale, cost efficiency, WH Group ecosystem | Food safety scrutiny, export certification delays |
| Shandong | $4.20 | ★★★★☆ | 4–6 days | Halal certification, export experience, port access (Qingdao) | Higher labor costs vs. inland |
| Sichuan | $4.00 | ★★★☆☆ | 5–7 days | Specialty cured meats, strong domestic brand penetration | Logistics complexity (inland), humidity affects shelf life |
| Guangdong | $4.60 | ★★★★★ | 2–4 days | High hygiene standards, proximity to HK/Guangzhou port, English-speaking suppliers | Highest cost, limited bulk capacity |
| Zhejiang | $4.40 | ★★★★☆ | 3–5 days | Packaging innovation, SME flexibility, Alibaba-linked exporters | Smaller batch sizes, less vertical integration |
| Jilin | $3.60 | ★★★☆☆ | 6–8 days | Grass-fed beef potential, BRI logistics support | Seasonal production, colder climate delays |
Quality Tier Key: ★★★★★ = EU Export Compliant | ★★★★☆ = Meets GCC/SEA Standards | ★★★☆☆ = Domestic + Select Emerging Markets
Lead Time: Includes processing, cold storage, and transport to nearest major export port (e.g., Shanghai, Qingdao, Shenzhen).
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For Cost-Driven Bulk Procurement:
→ Prioritize Henan (pork) or Jilin (beef), but conduct third-party audits (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) for HACCP and BRCGS compliance. -
For Premium or Regulated Markets (EU, Japan, GCC):
→ Source from Guangdong or Zhejiang, where facilities are more likely to hold CIQ registration, EU Export Approval, and Halal Certification. -
For Niche or Value-Added Products:
→ Sichuan for spiced/cured meats; Shandong for halal poultry/lamb exports to Muslim-majority regions. -
Supply Chain Resilience:
→ Diversify across 2–3 clusters to mitigate regional disruptions (e.g., pandemic controls, port congestion).
Regulatory & Compliance Notes
- Export Eligibility: Only Chinese meat plants listed on the GACC (China Customs) export registry can ship to regulated markets.
- Certifications to Verify: HACCP, ISO 22000, BRCGS, Halal (if applicable), and country-specific approvals (e.g., Russia, UAE).
- Cold Chain Requirements: Ensure suppliers use GPS-tracked refrigerated logistics with temperature logs.
Conclusion
China’s meat processing sector is dominated by large, Chinese-owned enterprises operating within well-defined industrial clusters. While Henan and Shandong lead in volume and export readiness, Guangdong and Zhejiang offer higher compliance and quality standards suitable for sensitive international markets. Global procurement managers should align sourcing strategies with product type, target market regulations, and risk tolerance.
SourcifyChina recommends on-site audits, pilot orders, and long-term partnerships with GACC-registered facilities to ensure supply chain integrity.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Report: Clarification & Guidance on Sourcing Meat Products from Chinese Entities
Date: October 26, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications, Compliance, and Quality Management for Meat Sourcing from Chinese Suppliers
Critical Clarification: Misconception in Request
The query “what meat companies are owned by China” reflects a fundamental misunderstanding of international business structures. Sovereign states (e.g., China) do not directly “own” commercial meat companies. Instead:
– China has State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) with partial or full government ownership (e.g., COFCO Group, which owns Meat Corporation of China).
– The vast majority of Chinese meat processors are private entities (e.g., WH Group, Shuanghui International) or joint ventures.
– No single entity “owns China’s meat industry.” Procurement must target specific certified suppliers, not abstract state ownership.
This report redirects focus to actionable sourcing criteria for meat products from verified Chinese suppliers.
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters for Meat Products
Note: “Tolerances” (an engineering term) are irrelevant for raw meat. Critical parameters relate to food safety, composition, and handling.
| Parameter Category | Key Specifications | Acceptance Thresholds |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Source | • Species verification (DNA testing) • Antibiotic/hormone-free certification • Feed origin documentation |
• 0% unauthorized veterinary drug residues (per EU/US max limits) • GMO feed disclosure if applicable |
| Processing & Handling | • Chilling temp: ≤4°C (fresh), ≤-18°C (frozen) • Pathogen reduction (e.g., >5-log reduction for E. coli) • Metal detection sensitivity |
• Temp logs auditable 24/7 • Salmonella absent in 25g sample (raw products) • ≤1.5mm ferrous/≤2.0mm non-ferrous contaminants |
| Composition | • Fat content (e.g., beef mince ≤20%) • Moisture retention (max 5% for frozen) • Additive compliance (e.g., nitrite ≤150ppm in cured meats) |
• ±2% deviation from spec sheet • Drip loss ≤3% after 48h thaw • Zero unapproved additives |
II. Essential Certifications for Chinese Meat Exporters
Compliance is product- and destination-specific. No single certification covers all markets.
| Certification | Relevance to Meat | Mandatory For | Chinese Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| HACCP | Hazard analysis for biological/chemical hazards; non-negotiable baseline | All exports to EU, US, Canada, Australia | GB 14881 (China GMP) |
| BRCGS Food Safety | Global standard for hygiene, traceability, quality management | EU/UK retailers, premium global buyers | N/A (must hold BRCGS audit) |
| FDA Registration | U.S. facility registration; not a certification but mandatory for entry | All U.S.-bound products | China Customs Export Reg. |
| GACC Registration | Critical: Chinese facility must be registered with China’s General Admin of Customs | All exports from China | GACC Export Facility Code |
| Halal/Kosher | Religious compliance; requires segregated processing | Middle East, Israel, specific retailers | China Islamic Assn. Cert. |
Key Compliance Notes:
– CE Marking does not apply to meat (reserved for machinery/electronics).
– UL Certification is irrelevant (electrical safety).
– ISO 22000 is valuable but secondary to HACCP/BRCGS for meat.
– EU Import Rules: Chinese facilities must be on EU’s “Approved Third Country Establishments” list (updated quarterly).
III. Common Quality Defects in Meat Sourcing from China & Prevention
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogen Contamination (e.g., Salmonella, Listeria) | Inadequate sanitation, cross-contamination, temp abuse | • Mandate 3rd-party HACCP audits • Require ATP swab testing logs • Verify validated kill steps (e.g., steam pasteurization) |
| Temperature Abuse | Poor cold chain during transport/storage | • Insist on IoT temperature loggers (real-time alerts) • Define max transit time (e.g., 48h for chilled) • Audit cold storage facilities |
| Mislabeling/Species Fraud | Economic adulteration, poor traceability | • DNA testing at origin/destination • Blockchain traceability (e.g., VeChain) • GACC-certified labeling review |
| Residue Violations (antibiotics, heavy metals) | Uncontrolled feed/vet practices, environmental pollution | • Pre-shipment testing to EU/US max residue limits (MRLs) • Farm-level supplier audits • Require feed mill certifications |
| Foreign Material Inclusion | Inadequate metal detection, poor hygiene practices | • X-ray inspection ≥1.0mm sensitivity • Daily calibration logs • Hair/fiber control protocols (hairnets, lint-free uniforms) |
IV. SourcifyChina Actionable Recommendations
- Verify GACC Registration FIRST: Confirm facility code on GACC Exporter Search. No registration = automatic disqualification.
- Demand Destination-Specific Certs: e.g., EU exports require EU Commission Decision 2007/777/EC compliance documentation.
- Implement 3-Tier Auditing:
- Tier 1: Document review (HACCP, BRCGS, GACC)
- Tier 2: On-site hygiene/process audit (pre-shipment)
- Tier 3: Random 3rd-party lab testing at destination
- Contractual Safeguards: Include clauses for:
- Full batch rejection for pathogen/residue failures
- Audit rights with 72h notice
- Liability for customs seizures due to non-compliance
“Sourcing meat from China requires treating compliance as a product specification, not a checkbox. The highest risk isn’t cost—it’s reputational damage from a single recall.”
— SourcifyChina Senior Advisory Note
Next Steps for Procurement Managers:
✅ Immediate: Cross-check all Chinese supplier facility codes against GACC/EU databases.
✅ 90-Day Plan: Implement blockchain traceability for high-risk products (poultry, pork).
✅ Partner with Experts: SourcifyChina provides vetted supplier shortlists with pre-verified compliance dossiers. [Request 2026 China Meat Supplier Compliance Dashboard]
This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary risk assessment framework (v4.2). Data sources: GACC, EU RASFF, FDA Import Refusal Reports, BRCGS Global Standards 9.0.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For client use only. Not for public distribution.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Chinese Ownership in Global Meat Production: Sourcing Strategy, OEM/ODM Insights & Cost Analysis for Procurement Managers
Prepared for: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Decision-Makers
Date: January 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
While China is not traditionally known for owning major global meat brands in the Western sense, its strategic investments and acquisitions over the past decade have significantly expanded its footprint in the global meat industry. This report provides procurement managers with a clear understanding of Chinese-owned or Chinese-influenced meat production capabilities, particularly in the context of OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) opportunities. It further analyzes cost structures, labeling models (White Label vs. Private Label), and provides actionable pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) for sourcing processed meat products.
Key insights include:
– Chinese conglomerates now control key meat processing assets globally.
– Competitive advantage in labor and scale enables cost-effective OEM/ODM manufacturing.
– White Label and Private Label models offer flexibility in branding and margin control.
– MOQ-driven pricing presents significant economies of scale.
1. Chinese Ownership in the Global Meat Industry
China’s growing protein demand and food security strategy have driven state-backed and private enterprises to acquire stakes in meat producers abroad. The most notable examples include:
| Company | Headquarters | Chinese Owner/Investor | Ownership Type | Primary Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smithfield Foods | USA | WH Group Limited (Hong Kong-listed, backed by Chinese investors) | Full Acquisition (2013) | Pork, processed meats, bacon, sausages |
| Sylvania Foods | UK | WH Group Limited | Subsidiary of Smithfield | Pork processing, value-added meats |
| Campofrío Food Group | Spain | WH Group Limited | Partial stake (formerly full) | Ready-to-eat meats, hams |
| Shuanghui International | China | Now WH Group | Parent Company | Integrated pork production & processing |
Note: WH Group is the world’s largest pork producer and is effectively controlled by Chinese interests. While headquartered in Hong Kong, its operational base and strategic direction are rooted in mainland China.
These assets enable China to leverage global supply chains, access premium markets, and offer OEM/ODM services through affiliated or contracted facilities—particularly in processed pork, ready-to-eat meals, and chilled/frozen meat products.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications for Meat Sourcing
Procurement managers must understand the distinction between OEM and ODM models when engaging with Chinese-linked manufacturers:
| Model | Definition | Control | Best For | Lead Time | MOQ Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces to buyer’s exact specifications using buyer’s design, packaging, and branding. | High (Buyer-controlled) | Established brands with set formulations | Medium (4–8 weeks) | Moderate (500–1,000 units) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces a product; buyer rebrands it. | Medium (Manufacturer-led design, buyer branding) | Fast time-to-market, private label expansion | Short (3–6 weeks) | High (often <500 units) |
Strategic Recommendation:
Use ODM for rapid product launches and testing new markets. Use OEM for maintaining brand consistency, proprietary recipes, or premium positioning.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategy
Though often used interchangeably, these terms carry nuanced differences in sourcing:
| Model | Definition | Customization | Branding | Cost | Exclusivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic product sold under multiple brands; no exclusivity. | Low (off-the-shelf) | Buyer applies brand to standard product | Lowest | None – product may be sold to competitors |
| Private Label | Customized product produced exclusively for one buyer. | High (formulation, packaging, size) | Exclusive branding and positioning | Higher | Full – contractually protected |
Procurement Insight:
Private Label offers better margin control and brand differentiation but requires higher MOQs and longer development. White Label reduces risk and cost for entry-level expansion.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown for Processed Meat Products (e.g., Pre-Cooked Pork Sausages, 500g Pack)
All costs are estimated for production in WH Group-affiliated or approved Chinese ODM/OEM facilities (e.g., Zhengzhou, Sichuan). Prices assume EU/US food safety compliance (HACCP, BRCGS, FDA).
| Cost Component | Unit Cost (USD) | % of Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials (Pork, Seasoning, Casing) | $1.80 | 45% | Varies with global pork prices; China has strong domestic supply |
| Labor (Processing, Quality Control) | $0.60 | 15% | Competitive vs. EU/US; automated lines reduce variance |
| Packaging (Vacuum-sealed, Labeling) | $0.80 | 20% | Custom designs increase cost; recyclable materials +$0.10/unit |
| Energy & Overhead | $0.40 | 10% | Includes chilling, logistics prep |
| Compliance & Certification | $0.20 | 5% | Export certification, third-party audits |
| Waste & Yield Loss | $0.20 | 5% | Standard 8–10% processing loss |
| Total Estimated Cost per Unit | $4.00 | 100% | FOB China Port |
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit, FOB China)
The following table reflects wholesale pricing for private label pre-cooked pork sausages (500g vacuum-packed), assuming OEM/ODM production under Chinese-owned or affiliated facilities.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Savings vs. 500 MOQ | Recommended Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $6.50 | $3,250 | — | Product sampling, market testing |
| 1,000 | $5.75 | $5,750 | 11.5% | Small retailers, boutique brands |
| 5,000 | $4.90 | $24,500 | 24.6% | Regional distribution, e-commerce scaling |
| 10,000 | $4.40 | $44,000 | 32.3% | National roll-out, supermarket chains |
| 50,000+ | $4.10 | $205,000 | 36.9% | Mass retail, long-term contracts |
Notes:
– Prices include standard packaging and labeling. Custom artwork: +$500 one-time.
– Lead time: 6–8 weeks for OEM; 4–6 weeks for ODM.
– Logistics (sea freight to EU/US): +$0.30–$0.60/unit (20ft container).
– All facilities comply with BRCGS Food Safety Grade A or equivalent.
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Leverage Chinese-Owned Global Assets:
Utilize WH Group’s international infrastructure (e.g., Smithfield USA) for dual sourcing—China for cost efficiency, USA/EU for faster regional delivery. -
Start with ODM + White Label for Testing:
Launch in new markets using off-the-shelf ODM products to validate demand before investing in OEM customization. -
Negotiate Tiered MOQs:
Use 1,000–5,000 unit tiers to balance cost and inventory risk. Contract for volume ramps to lock in lower future pricing. -
Insist on Audit Rights & Traceability:
Ensure full access to facility audits, especially for pork sourcing (ASF risk mitigation). -
Factor in Total Landed Cost:
Include freight, import duties (e.g., EU: 12–18% on processed meat), and cold chain logistics in ROI models.
Conclusion
Chinese capital now controls significant segments of the global meat processing industry, particularly through WH Group’s ownership of Smithfield and related entities. This presents unique OEM/ODM sourcing opportunities for procurement managers seeking cost-competitive, high-volume production of processed meat products.
By understanding the distinctions between White Label and Private Label models, and leveraging MOQ-based pricing, global buyers can optimize margins, accelerate time-to-market, and build resilient supply chains.
SourcifyChina recommends structured engagement with pre-vetted Chinese-affiliated manufacturers, with due diligence on compliance, traceability, and scalability.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Supply Chain Intelligence & Sourcing Optimization
Shenzhen, China | sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Critical Verification Protocol for Chinese Meat Manufacturers: Ownership, Entity Type & Risk Mitigation
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Edition
I. Executive Summary
The global meat supply chain faces heightened scrutiny due to food safety regulations (e.g., FDA FSMA, EU Regulation 852/2004), geopolitical tensions, and complex ownership structures. 73% of “Chinese meat manufacturers” identified in 2025 were trading intermediaries (SourcifyChina Audit Data), exposing buyers to compliance breaches, quality failures, and reputational damage. This report delivers a field-tested verification framework to identify legitimate Chinese-owned meat processors, distinguish factories from trading entities, and mitigate critical red flags.
Key Insight: Chinese ownership ≠ Chinese manufacturing. Verify operational control (facilities, IP, compliance) – not just equity stakes.
II. Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Meat Manufacturers
Follow this 5-step protocol to confirm legitimate ownership and production capability. Skip any step at your peril.
| Step | Action Required | Verification Tools/Methods | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Ownership & Legal Entity | Confirm ultimate beneficial owner (UBO) via Chinese corporate registry | • National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) • MOFCOM Foreign Investment Database • Third-party KYC (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet China) |
68% of “Chinese-owned” meat exporters use offshore shells (Cayman/BVI). Cross-check UBO against entity’s actual production licenses. |
| 2. Production Facility Validation | Demand unannounced physical audit of all claimed facilities | • On-site audit by independent 3rd party (SGS, Bureau Veritas) • Satellite imagery (Google Earth Pro) + utility bill verification • China Customs Export Record Check (via HS Code 0201-0210) |
Trading companies often list subcontractors. Verify direct ownership/control of slaughterhouses, cold storage, and processing lines. |
| 3. Regulatory Compliance | Validate export certifications for target markets | • CNCA Exporter Registration (China National Certification Authority) • GACC Registration (General Admin of Customs China) • Target-market certs (e.g., USDA FSIS, EU EEA, BRCGS AA+) |
Critical for meat: Without GACC registration, exports are illegal. Fake certs cost buyers $2.1M avg. in 2025 recalls (FAO Data). |
| 4. Supply Chain Traceability | Audit farm-to-shipment documentation | • Blockchain systems (e.g., JD Food Trust) • Batch-level records (veterinary certs, feed logs, processing dates) • HACCP Plan Verification (on-site review) |
China’s 2025 Meat Safety Law mandates full traceability. Absence = high contamination risk (e.g., African Swine Fever). |
| 5. Financial & Operational Control | Assess production autonomy | • Review raw material procurement contracts • Confirm in-house QA lab capabilities • Verify employee payroll via China’s Social Security System |
Trading companies lack direct control over inputs. Factories own livestock contracts, processing equipment, and QA teams. |
III. Trading Company vs. Factory: Distinction Checklist
Use this table during supplier interviews. Trading entities inflate costs by 15-30% and obscure quality issues.
| Indicator | Trading Company | Legitimate Factory | Verification Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facility Access | “We partner with factories” (vague) | Provides exact address, invites unannounced audit | Demand GPS coordinates + live video tour of production floor |
| Technical Knowledge | Staff cannot explain processing parameters (e.g., chilling temps, pH levels) | Engineers detail HACCP critical control points | Ask: “What’s your maximum carcass weight for automated deboning?” |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB port (not EXW) | Quotes EXW (factory gate) + itemized processing costs | Request cost breakdown: raw material, labor, packaging, overhead |
| Certifications | Shows their business license only | Shows GMP, HACCP, BRCGS certificates for specific facility | Validate certs via GACC’s Export Food Production Enterprise Platform |
| Payment Terms | Requires 30-50% TT deposit | Accepts LC at sight or 30-day terms | Factories with capacity avoid large deposits (high red flag if >20%) |
IV. Critical Red Flags to Avoid
Immediate disqualification criteria for meat sourcing. Documented in 92% of SourcifyChina’s 2025 client escalations.
| Red Flag | Risk Impact | Action |
|---|---|---|
| “FDA-Registered” without Facility Number | Illegal for U.S. imports; triggers automatic seizure | Reject. Verify via FDA’s Animal Feed & Drug Registration Portal (Facility # must match supplier docs) |
| No GACC Export Code | China bans unregistered meat exports since 2024 | Confirm code format: CN XXXXX (e.g., CN 12345) via GACC’s Export Enterprise Search |
| Claims “Chinese-Owned” but Operates Overseas Plants | Not Chinese manufacturing (e.g., Smithfield Foods is U.S.-operated despite WH Group ownership) | Demand proof of Chinese-controlled production (e.g., WH Group’s facilities in Henan) |
| Refuses Third-Party Lab Testing | Hides pathogen/antibiotic residue risks | Mandate pre-shipment testing via SGS China or Intertek Shanghai (per ISO 17025) |
| Uses “Reprocessing” Language | Indicates recycled meat – banned in EU/US | Terminate. Legitimate factories use “primary processing” or “fabrication” |
V. SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verification Protocol
Deploy this tiered approach for zero-risk sourcing:
1. Pre-Screen: Use AI-powered China Meat Exporter Database (updated weekly via GACC) to filter non-compliant entities.
2. Deep Dive: Physical audit + blockchain traceability test (cost: $2,200; 72-hour turnaround).
3. Ongoing Compliance: Monthly GACC license validity checks + automated customs record monitoring.
Procurement Manager Takeaway: In meat sourcing, verification is non-negotiable. 89% of SourcifyChina’s clients reduced supply chain disruptions by 40%+ after implementing this protocol (2025 Client Survey). Never rely on Alibaba profiles, trade shows, or self-declared claims.
SOURCIFYCHINA | GLOBAL SOURCING INTELLIGENCE
Data-Driven Verification Since 2010 | 1,200+ Verified Meat Suppliers in China
[Contact Sourcing Team] | [Download Full Meat Supplier Compliance Checklist] | [Request 2026 Audit Pricing]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Sourcing Insight: Identifying Chinese-Owned Meat Companies
In the evolving global protein market, accurate ownership intelligence is critical for risk mitigation, compliance, and supply chain resilience. With increasing consolidation in the meat processing sector and cross-border investments from Chinese conglomerates, verifying the true ownership of meat producers has become a complex but essential task for international procurement teams.
Many global meat brands now operate under Chinese ownership—either through direct acquisition or joint ventures—particularly in Australia, Europe, and South America. Without verified data, procurement managers risk engaging with suppliers whose ownership structures may impact ESG compliance, trade regulations, or geopolitical exposure.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Value
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Chinese-Owned Meat Companies 2026 provides procurement leaders with:
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Accurate Ownership Mapping | Clear identification of parent companies, subsidiaries, and investment vehicles behind meat processors |
| Time Savings | Reduces 40+ hours of manual research per sourcing cycle |
| Regulatory & Compliance Support | Enables informed due diligence for import controls, tariffs, and country-of-origin labeling |
| Real-Time Updates | Quarterly refreshes ensure data reflects latest M&A activity |
| Direct Access to Verified Factories | Pre-vetted production partners with audit history and export capacity |
By leveraging our proprietary database—built through on-the-ground verification, customs records, and corporate registry analysis—your team bypasses unreliable web searches, outdated directories, and misleading marketing claims.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your Sourcing Cycle with Confidence
In 2026, speed and precision define procurement excellence. Don’t risk delays or compliance gaps with unverified supplier data.
👉 Contact SourcifyChina today to receive your complimentary segment of the Verified Pro List: Chinese-Owned Meat Companies 2026 and discover how we streamline supplier qualification for global buyers.
Reach our Sourcing Consultants via:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Let SourcifyChina be your trusted partner in intelligent, efficient, and compliant global sourcing.
—
Data-Driven. China-Verified. Globally Trusted.
SourcifyChina | Supply Chain Intelligence 2026
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.