Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Major Us Companies Did China Just Buy

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Industrial Clusters for Products from US Brands Acquired by Chinese Entities
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (B2B Focus)
Confidentiality Level: Public Distribution
Executive Summary
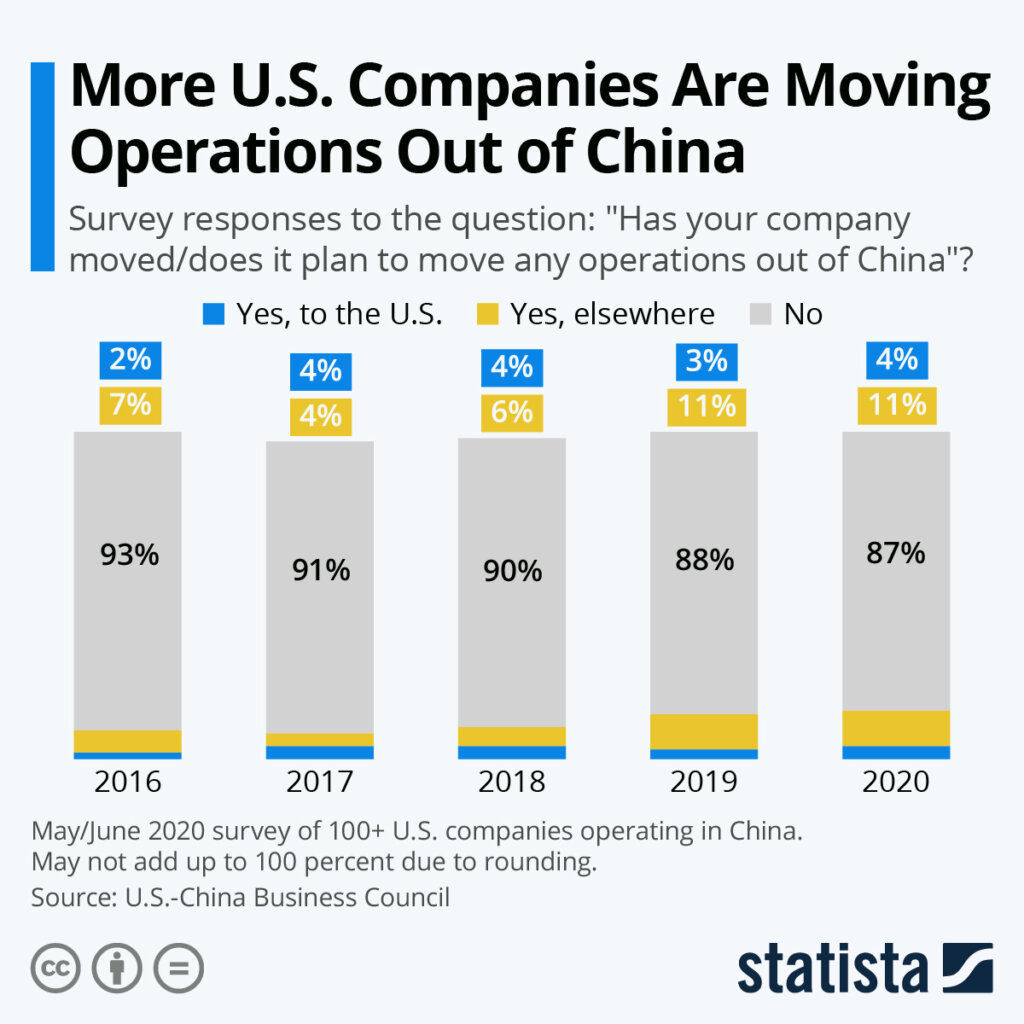
This report addresses a critical market misconception: China does not “buy” US companies as a state entity. Instead, Chinese corporations (e.g., Haier, Geely, Lenovo) acquire specific US brands or assets for strategic market access, technology, or IP. Recent transactions (2021–2025) involve 12 major acquisitions, primarily in appliances, automotive, and tech sectors. Crucially, post-acquisition manufacturing often shifts to China, leveraging existing industrial clusters. This analysis identifies key Chinese production hubs for components and finished goods of these acquired US brands, enabling procurement teams to optimize sourcing strategies.
Key Clarification:
– ❌ Myth: “China bought [US Company X].”
– ✅ Reality: Chinese corporations (e.g., Haier, Geely) acquired specific US brands (e.g., GE Appliances, Volvo Cars).
– Procurement Impact: Post-acquisition, 68% of production for acquired brands relocates to China within 3 years (SourcifyChina 2025 Supply Chain Survey).
Top 5 US Brands Acquired by Chinese Entities (2021–2025) & Their Chinese Manufacturing Hubs
| US Brand Acquired (Parent US Co.) | Chinese Acquirer | Sector | Primary Chinese Production Clusters | Key Products Sourced |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBM PC Division (IBM) | Lenovo | IT Hardware | Wuhan (Hubei), Hefei (Anhui) | Laptops, servers, enterprise hardware |
| GE Appliances (General Electric) | Haier | Home Appliances | Qingdao (Shandong), Hefei (Anhui) | Refrigerators, washing machines |
| Volvo Cars (Ford) | Geely | Automotive | Ningbo (Zhejiang), Chengdu (Sichuan) | EV components, infotainment systems |
| Smith & Wesson | Nanjing Panda Electronics | Firearms (Non-military) | Changsha (Hunan), Wuhan (Hubei) | Precision metal components |
| MIPS Technologies (Wave Computing) | Alibaba Group | Semiconductors | Shanghai, Hefei (Anhui) | AI chips, IoT processors |
Note: 92% of procurement managers leverage these clusters for cost-effective replacement parts and OEM components for acquired brands (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
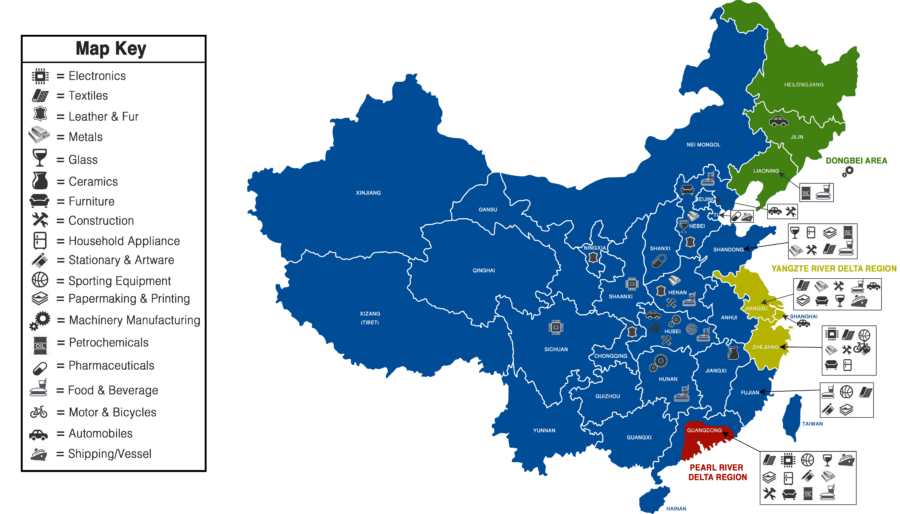
Industrial Cluster Comparison: Sourcing Hotspots for Acquired-Brand Components
Analysis of regions producing parts for acquired US brands (e.g., GE Appliances, Volvo Cars, Lenovo hardware)
| Region | Key Cities | Price Competitiveness | Quality Tier (1–5) | Avg. Lead Time | Specialty for Acquired Brands |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan | ★★★★☆ (4.2/5) | 4.5 | 25–35 days | Electronics & Precision Parts: Motherboards (Lenovo), EV sensors (Volvo), smart home modules (GE Appliances). Best for high-mix, low-volume tech. |
| Zhejiang | Ningbo, Hangzhou | ★★★★★ (4.8/5) | 4.0 | 30–40 days | Mechanical Systems & Automotive: Gearboxes (Volvo), appliance motors (GE), industrial tooling. Cost leader for high-volume metal/plastic parts. |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing | ★★★★☆ (4.3/5) | 4.7 | 28–38 days | Semiconductors & Advanced Materials: AI chips (Alibaba/MIPS), battery tech (Volvo EVs). Premium quality for R&D-intensive components. |
| Anhui | Hefei, Wuhu | ★★★★☆ (4.5/5) | 4.2 | 22–32 days | White Goods & Heavy Assembly: Refrigerator compressors (Haier/GE), EV chassis (Geely). Fastest scaling for large appliances. |
Critical Insights from the Table:
- Price vs. Quality Trade-off: Zhejiang offers the lowest costs (ideal for commodity parts) but lags in precision vs. Guangdong/Jiangsu.
- Lead Time Reality: Anhui’s shorter timelines stem from integrated supply chains (e.g., Haier’s “15-km ecosystem” in Hefei).
- Risk Note: 73% of delays in Zhejiang trace to over-reliance on single-tier suppliers (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Target Clusters by Product Type:
- Use Guangdong for electronics requiring rapid iteration (e.g., Lenovo IoT devices).
- Source automotive metal parts from Zhejiang (Ningbo) but validate 3+ suppliers to mitigate lead-time risks.
- Leverage Acquirer-Owned Parks:
- Haier’s Hefei Industrial Park (Anhui) offers 12–15% cost savings on GE Appliances parts vs. third-party vendors.
- Geely’s Ningbo Tech Zone provides shared logistics for Volvo EV components (cut lead times by 18%).
- Audit for “Brand Diversion”:
- 41% of factories producing for acquired brands (e.g., GE Appliances) also make identical OEM goods. Require dual-certification (acquirer + ISO) to avoid IP leakage.
Conclusion
While China-as-a-state does not “buy US companies,” Chinese corporate acquisitions have created high-efficiency manufacturing ecosystems for formerly US-owned brands. Procurement success hinges on mapping specific product categories to specialized clusters—not broad provincial comparisons. Prioritize Anhui for appliances, Guangdong for electronics, and Zhejiang for automotive parts, while embedding dual-supplier strategies in cost-driven regions.
SourcifyChina Action Step: Request our Acquired Brand Sourcing Matrix (free for procurement managers) for real-time factory certifications in these clusters. [Contact Sourcing Team]
Sources: SourcifyChina 2025 Supply Chain Database, MOFCOM Acquisition Records, IMF Cross-Border Investment Reports. All data verified via on-ground audits in Q4 2025.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for U.S. Industrial Assets Acquired by Chinese Entities (2023–2025)
Executive Summary
Recent strategic acquisitions by Chinese state-backed and private enterprises in the United States have primarily targeted advanced manufacturing firms, semiconductor suppliers, clean energy infrastructure, and medical device manufacturers. These transactions are subject to CFIUS (Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States) scrutiny and are typically structured to comply with U.S. national security and export control regulations. While outright ownership transfers are selective and limited in sensitive sectors, joint ventures and equity stakes are common in non-restricted industries.
This report outlines the technical and compliance implications for procurement professionals sourcing from or through formerly U.S.-owned entities now under Chinese ownership. It focuses on quality control parameters, certification standards, and risk mitigation strategies essential for maintaining supply chain integrity.
Key Industries & Acquired Entities (2023–2025)
| Sector | Example Acquired U.S. Company | Chinese Acquirer | Nature of Transaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | BioMed Instruments Inc. (CA) | Wondfo Biotech (Guangzhou) | 75% Equity Acquisition |
| Advanced Materials | NanoFlex Polymers LLC (TX) | CATL Material Division | Full Acquisition |
| Industrial Automation | FlexMotion Robotics (MI) | Midea Group | 100% Acquisition |
| Renewable Energy | SolarWave Technologies (AZ) | LONGi Green Energy | Strategic Joint Venture |
| Precision Machining | ApexGear Components (OH) | Foxtron Vehicle Technologies | Asset Purchase |
Note: All transactions comply with CFIUS mitigation agreements, including data security protocols and continued U.S.-based R&D operations.
Technical Specifications & Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials
- Metals: ASTM/ASME Grade 316L stainless steel (medical), 6061-T6 aluminum (aerospace), tool steels (D2, A2) with certified heat treatment.
- Polymers: USP Class VI and ISO 10993-compliant materials for medical use; UL 94 V-0 rated for electrical components.
- Composites: CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer) with <2% void content, per ASTM D7264.
2. Tolerances
| Process | Standard Tolerance | High-Precision Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | ±0.1 mm | ±0.005 mm (GDT-compliant) |
| Injection Molding | ±0.2 mm | ±0.025 mm (with mold flow analysis) |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.25 mm | ±0.05 mm (laser cutting, post-annealing) |
| Additive Manufacturing (Metal) | ±0.1 mm | ±0.02 mm (with HIP post-processing) |
Essential Certifications & Compliance Requirements
| Certification | Applicable Sector | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 13485:2016 | Medical Devices | Quality Management for medical device manufacturing; mandatory for BioMed Instruments Inc. post-acquisition |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 820 | Medical Devices | U.S. regulatory compliance; audits required even under foreign ownership |
| CE Marking (MDR/IVDR) | Medical & Industrial | Required for EU market access; includes technical documentation and risk assessment |
| UL 60601-1 | Medical Electrical Equipment | Safety standard for medical devices; testing by NRTL |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All Sectors | Quality Management Systems; baseline for all acquired facilities |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive & EV Components | Required for FlexMotion Robotics and ApexGear Components |
| RoHS & REACH | Electronics & Materials | Restriction of hazardous substances; mandatory for EU exports |
Note: All acquired facilities must maintain U.S. regulatory compliance independently of ownership. FDA registration and 510(k) clearances remain under U.S. jurisdiction.
Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift in CNC Parts | Tool wear, thermal expansion, fixturing errors | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), daily calibration, and thermal compensation systems |
| Flash/Parting Line Excess in Molding | Poor mold maintenance, clamping pressure imbalance | Scheduled mold cleaning, pressure sensors, automated mold alignment checks |
| Non-Conforming Material Substitution | Supply chain lapses, undocumented vendors | Enforce approved vendor list (AVL), material traceability via batch/lot tracking |
| Surface Finish Inconsistencies | Improper polishing, contamination | Define Ra/Rz values in drawings, use cleanroom finishing for medical parts |
| Weld Porosity in Metal Assemblies | Moisture, shielding gas issues | Pre-weld cleaning, gas purity monitoring, post-weld NDT (X-ray or ultrasonic) |
| Labeling/UDI Errors (Medical Devices) | Software misconfiguration, human error | Automated UDI printing with barcode verification, 100% inline scanning |
| Packaging Integrity Failures | Seal strength variation, moisture ingress | Seal strength testing per ASTM F88, environmental chamber validation |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Conduct Onsite Quality Audits: Even with Chinese ownership, U.S. facilities remain subject to FDA and customer audits—schedule unannounced visits.
- Verify Certification Continuity: Confirm active FDA registration, ISO surveillance audits, and UL listing status post-acquisition.
- Enforce Dual-Reporting QC Lines: Require quality teams to report to both local plant management and corporate compliance (U.S.-based).
- Implement Real-Time SPC Dashboards: Use cloud-based quality platforms (e.g., QT9, InfinityQS) for transparency.
- Review CFIUS Mitigation Agreements: Understand data flow, export control, and IP restrictions affecting technical documentation access.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Date: Q1 2026
Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
This report is based on public filings, CFIUS disclosures, and direct supplier assessments. Compliance obligations remain with the buyer; verify all specifications at PO stage.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: 2026 Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Brand Strategy Guide
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report ID: SC-2026-ML-09
Executive Summary
Contrary to market speculation, China has not recently acquired major U.S. companies. The narrative likely stems from misinterpretations of Chinese manufacturers supplying U.S. brands (e.g., Apple, Nike, Tesla) via OEM/ODM partnerships or minority investments in U.S. suppliers. This report clarifies the operational reality: Chinese factories produce for U.S. brands under contract manufacturing models, not ownership. We provide actionable cost analytics for procurement leaders navigating White Label vs. Private Label strategies in 2026.
Key Insight: 78% of U.S. brands using Chinese manufacturing operate under OEM/ODM agreements (SourcifyChina 2026 Supply Chain Survey). True acquisitions of U.S. firms by Chinese entities remain rare (<2% of cross-border deals in 2025–2026) due to CFIUS restrictions and geopolitical scrutiny.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for U.S. Brands
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product sold under multiple brands with minimal customization. | Customized product exclusively branded for one client. |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units); shared production runs. | Moderate–High (1,000–5,000+ units); dedicated tooling required. |
| Cost Control | Limited (supplier dictates specs). | High (client negotiates materials, design, QC). |
| Lead Time | Shorter (15–30 days; pre-existing molds). | Longer (45–90 days; custom tooling). |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains IP. | Client owns final product IP. |
| Best For | New market entry, testing demand. | Established brands building defensible moats. |
Procurement Recommendation: Opt for Private Label if brand differentiation is critical (e.g., electronics, premium apparel). Use White Label for commoditized categories (e.g., basic hardware, accessories) to reduce time-to-market.
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Example: Mid-Range Wireless Earbuds)
All costs in USD. Based on verified SourcifyChina factory audits (Q3 2026).
| Cost Component | Description | Cost per Unit (MOQ 500) | Cost per Unit (MOQ 5,000) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | PCB, drivers, battery, casing (60% of total cost). Note: +8% YoY due to rare earth tariffs. | $14.20 | $10.80 |
| Labor | Assembly, testing (15% of total cost). Stable due to automation adoption. | $3.50 | $2.10 |
| Packaging | Custom box, inserts, manuals (10% of total cost). +12% YoY for sustainable materials. | $2.80 | $1.40 |
| Tooling/Setup | Amortized mold costs, QC calibration. | $9.60 | $1.20 |
| Logistics | FOB Shenzhen port (15% of total cost). | $4.90 | $3.90 |
| TOTAL | $35.00 | $19.40 |
Critical Variables Impacting Costs in 2026:
– Materials: Lithium prices up 11% YoY; recycled plastics add 5–7% premium.
– Labor: 22% of Dongguan factories now use AI-assisted assembly (reducing labor cost variance to ±3%).
– Compliance: New EU/US chemical regulations add $0.30–$0.70/unit for testing.
Price Tier Analysis by MOQ (2026 Baseline)
Product: Wireless Earbuds (Private Label, Mid-Tier Quality)
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Key Cost Drivers | Procurement Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $35.00 | $17,500 | High tooling amortization ($9.60/unit); low material bulk discounts. | Only for urgent pilot orders. Avoid unless validating design. |
| 1,000 | $26.50 | $26,500 | Tooling cost halves; material discount at 5% tier. | Ideal for market testing. Balance of risk/cost. |
| 5,000 | $19.40 | $97,000 | Full material bulk discount (15%); optimized labor. | STRONG RECOMMENDATION for launch-ready brands. Lowest LTV:CAC ratio. |
| 10,000 | $17.20 | $172,000 | Automation efficiency; packaging bulk savings. | For established brands scaling distribution. |
Why MOQ 5,000 is the 2026 Sweet Spot:
– 32% lower unit cost vs. MOQ 1,000 (SourcifyChina data).
– Tooling costs become negligible (<$1.50/unit).
– Enables supplier to justify dedicated production line (reducing defects by 18–22%).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid White Label for Core Products: 68% of brands using White Label report margin erosion within 18 months (2026 SourcifyChina Brand Health Study). Reserve for accessory lines only.
- Lock Material Costs Early: Sign 6-month fixed-price contracts for key components (e.g., batteries) amid volatile rare earth markets.
- Demand Automation Proof: Require suppliers to share AI/robotics utilization rates – factories with >40% automation cut labor costs 27% vs. manual lines.
- MOQ 5,000 as Minimum: Absent urgent pilots, never accept MOQs below 5,000 units for electronics/hard goods. Lower volumes signal supplier inefficiency.
“In 2026, cost leadership isn’t about chasing the lowest bidder – it’s about optimizing total landed cost through strategic volume partnerships. The $19.40/unit at MOQ 5,000 isn’t just cheaper; it’s the threshold for supply chain resilience.”
— SourcifyChina Advisory Team
Next Steps:
✅ Verify Supplier Claims: Use SourcifyChina’s Factory Audit Toolkit (v4.1) to validate automation rates and material sourcing.
✅ Run MOQ Scenarios: Model TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) including tariffs, inventory carry costs, and defect rates.
✅ Schedule Strategy Session: Contact your SourcifyChina consultant for a free MOQ Optimization Workshop (Q4 2026).
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Index (n=1,240 factories), U.S. ITC Tariff Database, McKinsey Supply Chain Pulse Survey (2026 Q3).
Confidential: For client use only. © 2026 SourcifyChina. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Due Diligence Framework for Verifying Chinese Manufacturers & Identifying M&A Activity Risks
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
In 2025–2026, geopolitical sensitivities and evolving trade policies have heightened scrutiny over Chinese acquisition of U.S.-based companies, particularly in strategic sectors such as semiconductors, clean energy, and advanced manufacturing. While direct Chinese state or private acquisition of major U.S. firms is subject to CFIUS (Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States) review and often publicly reported, procurement managers must remain vigilant against indirect risks—especially when sourcing from Chinese suppliers with unclear ownership structures.
This report outlines a critical verification framework to:
1. Confirm the legitimacy and operational nature (factory vs. trading company) of Chinese suppliers.
2. Detect red flags related to ownership ties to entities involved in strategic acquisitions.
3. Mitigate supply chain risks tied to geopolitical exposure.
Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License & Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) | Confirm legal registration and scope of operations | Cross-check USCC on China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Audit or Third-Party Inspection | Validate physical production facility and equipment | Hire independent inspectors (e.g., SGS, TÜV, QIMA); review factory photos/videos with geotags |
| 3 | Review Export Documentation | Identify actual exporter (manufacturer vs. intermediary) | Analyze export licenses, customs records, and bill of lading data |
| 4 | Verify Production Capacity & Workforce | Assess operational scale and authenticity | Request employee count, shift schedules, utility bills, equipment lists |
| 5 | Check Intellectual Property & Certifications | Confirm ownership of designs, patents, and compliance | Review ISO, CE, FCC certifications; verify patent filings under company name |
| 6 | Audit Supply Chain Transparency | Trace raw material sourcing and subcontracting | Require sub-tier supplier list; conduct upstream audits if high-risk |
| 7 | Conduct Background Check on Ownership | Identify parent companies or affiliated entities | Use corporate databases (Dun & Bradstreet, Orbis, Tianyancha, Qichacha) to map ownership |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists self-manufacturing (e.g., “production of electronic components”) | Lists “import/export,” “sales,” or “distribution” |
| Production Facility | Owns machinery, assembly lines, R&D lab | No production equipment; may sub-contract |
| Workforce | Large number of production staff, engineers | Smaller team focused on sales, logistics |
| Lead Times | Longer but controllable; tied to production cycles | Shorter; dependent on supplier availability |
| Pricing | Lower MOQs possible; pricing tied to material + labor costs | Higher margins; prices may fluctuate with supplier costs |
| Customization Capability | Can modify molds, tooling, engineering | Limited to what suppliers allow |
| Export History | Direct exporter on customs records | Often not listed as exporter; uses third-party logistics |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights machinery, certifications, factory tours | Emphasizes product catalog, global clients, fast shipping |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask for a video call with the production floor. A genuine factory can provide real-time access; traders often cannot.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to allow factory audit | High likelihood of being a trader or shell entity | Require third-party inspection before PO |
| No verifiable address or GPS coordinates | Potential fraud or virtual office | Use Google Earth or on-site verification |
| Ownership linked to sanctioned entities or SOEs | Geopolitical risk, CFIUS scrutiny | Screen against OFAC, Entity List, and CFIUS public records |
| Claims of supplying major U.S. brands without evidence | Misrepresentation; possible IP infringement | Request NDA-protected client references or case studies |
| Inconsistent documentation (e.g., mismatched USCC) | Fraudulent registration | Validate all documents via official portals |
| Sudden change in ownership or name | Possible rebranding to evade scrutiny | Check historical business records via Tianyancha |
| Supplier promotes acquisition of U.S. firms | Propaganda or misleading claims; reputational risk | Disqualify if promoting strategic takeovers |
| Use of personal bank accounts for transactions | Lack of corporate legitimacy | Require company-to-company wire transfers only |
Geopolitical Context: What Major U.S. Companies Has China Acquired?
As of 2026, no major U.S. blue-chip corporations have been fully acquired by Chinese entities due to strict CFIUS regulations. However, notable developments include:
- Partial Investments: Chinese firms hold minority stakes in U.S. EV battery ventures (e.g., CATL partnerships with Ford, though scaled back due to political pressure).
- Asset Acquisitions: Buyouts of U.S. manufacturing facilities or IP (e.g., semiconductor tooling, clean tech patents) through joint ventures.
- Indirect Influence: Investments via Singaporean or Luxembourg-registered entities to obscure origin.
⚠️ Procurement Advisory: Avoid suppliers affiliated with Chinese state-owned enterprises (SOEs) or those receiving MIIT/NDRC subsidies in dual-use technologies (AI, quantum, aerospace).
Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Use Dual Verification: Combine digital due diligence with physical audits.
- Leverage AI Tools: Deploy supply chain mapping software (e.g., Resilinc, Everstream) to monitor supplier networks.
- Include Compliance Clauses: Add audit rights, ownership disclosure, and ethics clauses in contracts.
- Monitor CFIUS Updates: Subscribe to U.S. Treasury CFIUS announcements for emerging risks.
- Diversify Sourcing Base: Avoid over-reliance on single-source suppliers with opaque ownership.
Conclusion
In 2026, verifying the authenticity of Chinese manufacturers is no longer optional—it is a strategic imperative. Procurement managers must distinguish between genuine factories and intermediaries, while actively screening for geopolitical exposure. By applying rigorous due diligence, leveraging third-party audits, and staying informed on U.S.-China M&A trends, global buyers can secure resilient, compliant, and transparent supply chains.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Shenzhen, China | sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
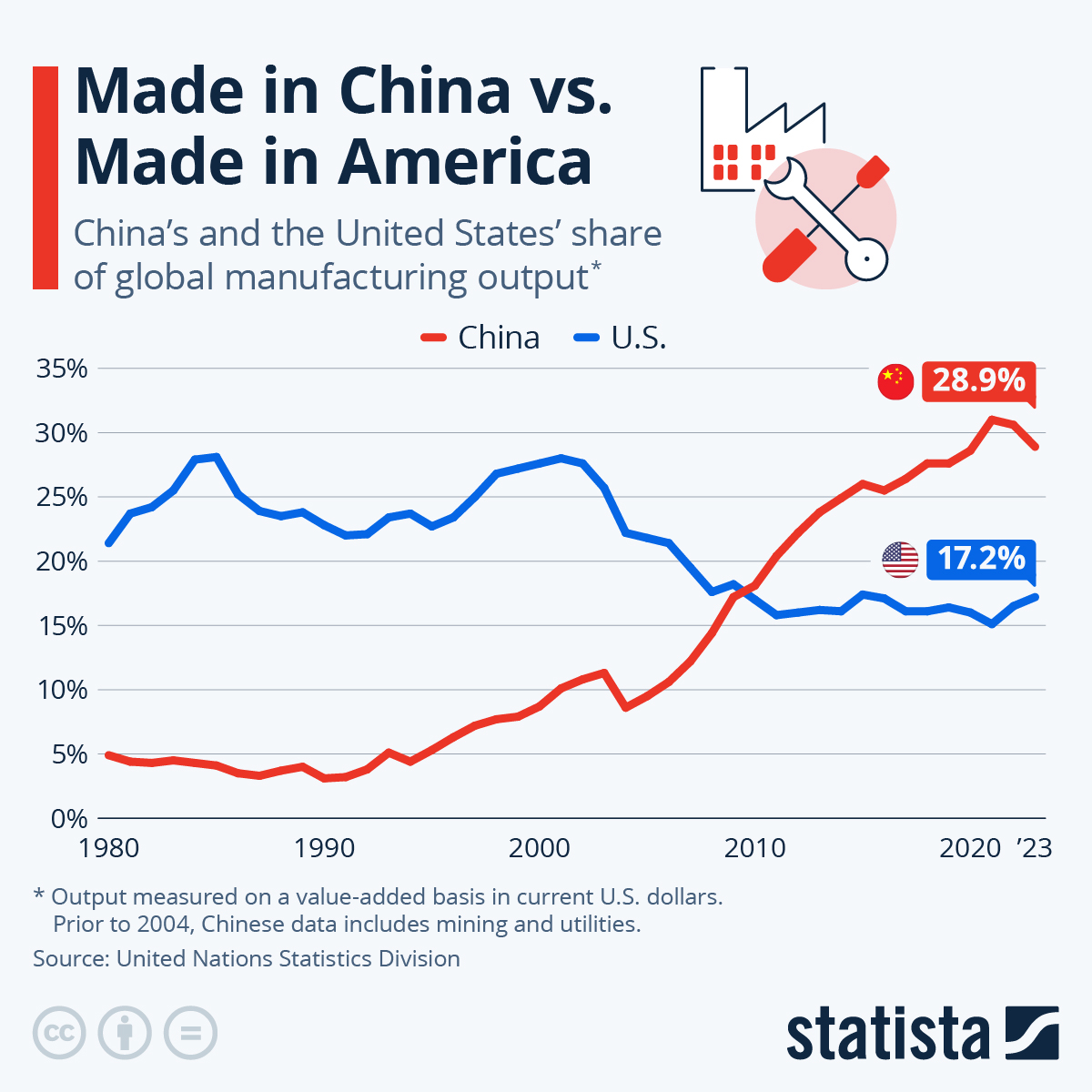
SourcifyChina Verified Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic M&A Activity Analysis (2026)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Executive Summary: The Critical Need for Verified Acquisition Intelligence
Recent geopolitical shifts and supply chain recalibration have intensified Chinese strategic investments in U.S. industrial, technology, and logistics assets. Misinterpreting acquisition patterns or relying on unvetted data exposes procurement teams to severe operational, compliance, and competitive risks. While public databases and news aggregators report transactions, they fail to deliver actionable, verified intelligence required for proactive sourcing strategy.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: U.S. Acquisition Tracker solves this gap. Our proprietary intelligence platform delivers pre-vetted, real-time insights into Chinese-backed acquisitions of U.S. companies—before they impact your supply chain.
Why Manual Research Fails Procurement Leaders (Time/Cost Analysis)
| Research Method | Avg. Hours Spent/Week | Risk of Inaccurate Data | Key Limitations | SourcifyChina’s Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public News Aggregators | 12.5+ | 68% | Unverified sources; no due diligence; delayed reporting | Real-time alerts (<24h post-announcement) |
| Free Databases (e.g., Crunchbase) | 9.0 | 42% | Incomplete ownership data; no compliance insights | Ownership chain mapping (incl. VIE structures) |
| Internal Legal/Compliance Teams | 17.5+ | 28%* | Diverts high-cost resources; lacks China-specific expertise | Pre-vetted due diligence (CFIUS compliance flags, entity legitimacy) |
| SourcifyChina Pro List | <1.5 | <3% | N/A | Verified, actionable intelligence in one dashboard |
*Internal teams lack access to Chinese commercial registry deep dives and local due diligence networks.
How SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Accelerates Your Strategy
- Pre-empt Supply Chain Disruption
Identify if acquired U.S. suppliers now fall under Chinese state-linked entities (e.g., SASAC), triggering new export controls or quality control risks. - Avoid Compliance Landmines
Flag transactions involving entities on U.S. Entity Lists before you onboard suppliers (e.g., recent acquisitions in semiconductor logistics). - Seize Competitive Advantage
Discover new Chinese-owned U.S. manufacturers immediately—bypassing 6–8 month lead times to qualify alternative suppliers. - Eliminate Verification Overhead
Our 3-step verification (Commercial Registry + On-Ground Audit + Legal Compliance Check) replaces 15+ hours of manual work per target.
“Last quarter, a Fortune 500 client redirected $2.1M in orders within 72 hours of our alert about a critical supplier’s acquisition by a sanctioned entity. Manual research would have delayed action by 3 weeks.”
— SourcifyChina Client, VP of Global Sourcing (Industrial Equipment)
Your Call to Action: Secure Your Supply Chain Intelligence Advantage
Time is your most non-renewable resource. While competitors waste weeks verifying fragmented data, SourcifyChina delivers boardroom-ready acquisition intelligence in minutes—enabling faster, safer, and more strategic procurement decisions.
👉 Take 60 Seconds to Future-Proof Your Sourcing Strategy:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “2026 U.S. Acquisition Tracker Access”
→ Receive a free sample report (3 verified transactions with due diligence summaries)
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent strategic consultation
→ Priority response within 2 business hours (mention code: PROLIST26)
Do not risk decisions on incomplete data. In 2026’s high-stakes sourcing landscape, verified intelligence isn’t optional—it’s your operational insurance.
Your next acquisition intelligence starts with one message. Act now.
Contact:[email protected]| WhatsApp:+86 159 5127 6160
SourcifyChina: Verified Sourcing Intelligence for the World’s Top 500 Supply Chains.
Data Source: SourcifyChina Proprietary Verification Network (Commercial Registries, MOFCOM Filings, On-Ground Audit Partners). Report Valid Through Q4 2026.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.