Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Major Us Companies Are Owned By China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing “Major U.S. Companies Owned by China”
Executive Summary
This report provides a professional, fact-based analysis for global procurement managers evaluating the sourcing landscape in China related to the topic: “What major U.S. companies are owned by China?” While this topic does not represent a physical product category, it is frequently misinterpreted in sourcing contexts. As a Senior Sourcing Consultant at SourcifyChina, it is critical to clarify that China does not broadly “own” major U.S. corporations in the traditional sense of full equity acquisition. However, Chinese investment entities—state-owned enterprises (SOEs), private conglomerates, and sovereign wealth funds—have acquired strategic stakes or full ownership of select U.S.-based companies, particularly in manufacturing, technology, energy, and consumer goods.
This report reframes the inquiry into an actionable industrial intelligence format by analyzing Chinese-owned or Chinese-invested U.S. companies, identifying key industrial clusters in China that support manufacturing for these entities, and providing a comparative analysis of sourcing regions for products produced under such ownership structures.
Clarification of Sourcing Misconception
The phrase “sourcing what major U.S. companies are owned by China” is not a tangible product category. Instead, procurement teams may be seeking:
- Products manufactured by U.S. companies under Chinese ownership
- Supply chain visibility into Chinese-owned subsidiaries operating in the U.S.
- Sourcing opportunities from Chinese industrial bases that supply or are linked to these entities
Therefore, this report focuses on industrial clusters in China that produce components, finished goods, or technology used by U.S. companies with Chinese ownership.
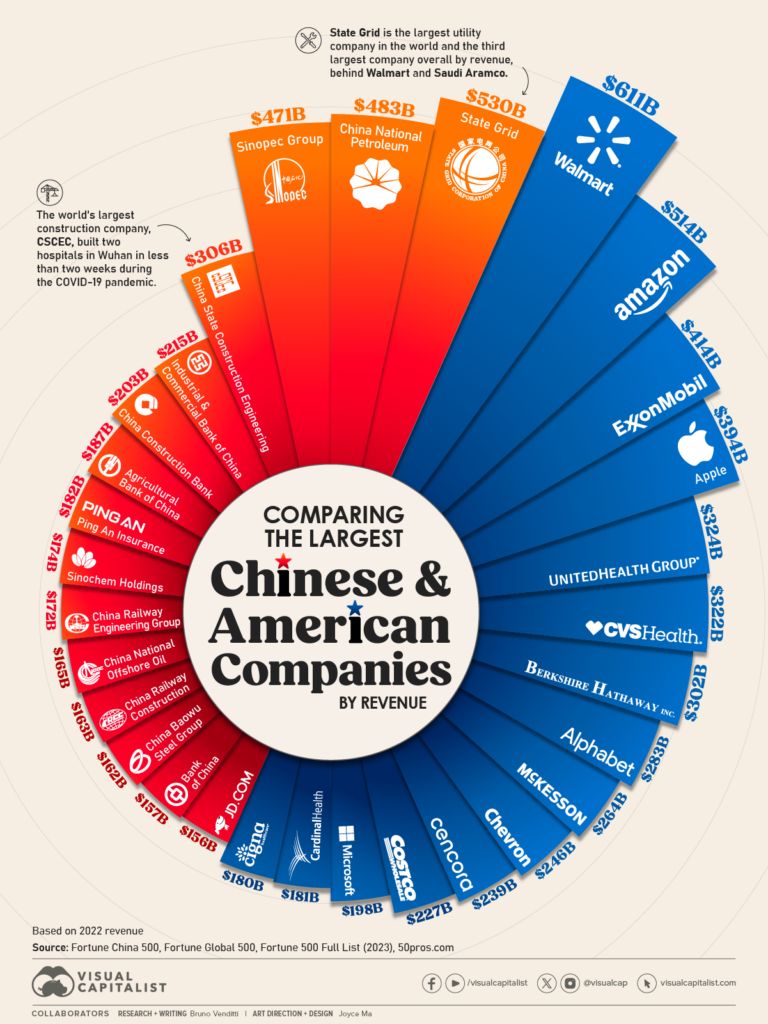
Key U.S. Companies with Chinese Ownership (Partial List)
| U.S. Company | Sector | Chinese Owner | Year of Acquisition | Manufacturing Link to China |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBM x86 Server Division (sold to Lenovo) | IT Hardware | Lenovo (China) | 2014 | Production shifted to Chengdu & Beijing |
| AMC Theatres | Entertainment | Dalian Wanda Group | 2012 | No manufacturing; real estate focus |
| Motorola Mobility | Consumer Electronics | Lenovo | 2014 | R&D and modular assembly in Wuhan |
| IBM PureSystems | Enterprise Hardware | Lenovo | 2014 | Integrated into Lenovo’s Shenzhen supply chain |
| A&P Food Stores (via ownership of parent) | Retail | Bright Food Group (partial) | 2012 | No direct manufacturing |
| Nexteer Automotive | Automotive Systems | Avic (Aviation Industry Corp) | 2010 | Manufacturing hubs in Michigan and Zhejiang |
| IBM BladeCenter | Data Infrastructure | Lenovo | 2014 | Final assembly in Guangdong |
Note: Full ownership of major U.S. blue-chip firms (e.g., Apple, Ford, Coca-Cola) by Chinese entities does not exist. Most transactions involve subsidiaries, divisions, or minority stakes due to CFIUS (Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States) restrictions.
Key Industrial Clusters in China Supporting Chinese-Owned U.S. Operations
Chinese-owned U.S. companies often rely on China’s advanced manufacturing ecosystems for components, R&D, and final assembly. The following provinces and cities are pivotal:
1. Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Cities: Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan
- Focus: Electronics, telecom equipment, smart devices
- Relevance: Lenovo, Huawei, and ZTE supply chains; major export hub for U.S.-bound tech hardware
- Key Zones: Shenzhen Nanshan District (R&D), Dongguan (OEM manufacturing)
2. Zhejiang Province
- Cities: Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu
- Focus: Consumer goods, automotive parts, e-commerce logistics
- Relevance: Home to Alibaba and private manufacturers supplying U.S. retail chains via Chinese-owned intermediaries
- Key Zones: Hangzhou Future Sci-Tech City, Ningbo-Zhoushan Port
3. Jiangsu Province
- Cities: Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi
- Focus: High-precision machinery, semiconductors, automotive systems
- Relevance: AVIC (Nexteer Automotive), semiconductor subcontractors for U.S. tech
- Key Zones: Suzhou Industrial Park (SIP), Nanjing High-Tech Zone
4. Beijing-Tianjin Corridor
- Cities: Beijing, Tianjin
- Focus: Aerospace, IT hardware, R&D
- Relevance: Lenovo headquarters, AVIC research centers, government-linked innovation zones
Regional Sourcing Comparison: Key Manufacturing Hubs
The table below compares major production regions in China relevant to goods produced by or for U.S. companies with Chinese ownership. Criteria include Price Competitiveness, Quality Standards, and Average Lead Time.
| Region | Price (1–5) | Quality (1–5) | Lead Time (Weeks) | Key Strengths | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) | 3 | 5 | 4–6 | Electronics, fast prototyping, export logistics | High-volume tech hardware, IoT devices |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Ningbo) | 4 | 4 | 5–7 | Consumer goods, auto parts, cost efficiency | Mid-tier electronics, home goods, machinery |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Nanjing) | 3 | 5 | 6–8 | Precision engineering, semiconductors, automation | Automotive systems, industrial equipment |
| Beijing-Tianjin | 2 | 5 | 8–10 | R&D, aerospace, government-backed innovation | High-compliance defense, IT infrastructure |
Scoring Guide:
– Price: 1 = Highest cost, 5 = Most competitive pricing
– Quality: 1 = Basic compliance, 5 = Tier-1 export quality (ISO, IATF, IPC standards)
– Lead Time: Includes production + inland logistics to port (ex-FCA)
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- For Electronics & IT Hardware (e.g., Lenovo-manufactured U.S.-market devices):
- Source from Guangdong for speed, ecosystem maturity, and logistics.
-
Prioritize Shenzhen for R&D-integrated manufacturing.
-
For Automotive Components (e.g., Nexteer/AVIC supply chain):
-
Source from Jiangsu or Zhejiang for high-tolerance parts with IATF 16949 certification.
-
For Consumer Goods & Retail Supply Chains:
-
Zhejiang (Yiwu/Ningbo) offers best value for volume orders with fast customs clearance.
-
For High-Compliance or Dual-Use Technology:
- Beijing-Tianjin provides access to state-certified facilities, though with longer lead times.
Risk & Compliance Considerations
- CFIUS Scrutiny: Any sourcing involving U.S. entities with Chinese ownership must account for export controls and data security regulations.
- Entity Verification: Procurement teams should verify the legal structure of suppliers (e.g., WFOEs vs. joint ventures).
- Supply Chain Transparency: Use blockchain-enabled traceability tools for dual-use components.
Conclusion
While China does not own major U.S. corporations outright, strategic acquisitions have created integrated supply chains between Chinese industrial clusters and U.S. operations. Guangdong and Jiangsu lead in high-quality, high-tech manufacturing, while Zhejiang offers cost-competitive production for consumer-facing goods.
Procurement managers should align sourcing strategies with product category, compliance requirements, and logistical efficiency, leveraging China’s regional specialization rather than treating it as a monolithic entity.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Strategy Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Product Compliance & Quality Assurance Framework (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Date: October 26, 2025
Clarification on Scope: Ownership vs. Compliance Requirements
Critical Industry Insight: The premise that “major US companies are owned by China” is a significant misconception in global sourcing. Chinese entities may hold minority stakes in some US firms (e.g., Hain Celestial Group, AMC Entertainment), but compliance obligations are determined by:
– Product origin (where goods are manufactured)
– Target market regulations (US/EU/other)
– Product category (medical, electronics, etc.)
Ownership structure does NOT alter compliance requirements. A US-manufactured product sold in the EU requires CE marking regardless of shareholder nationality. This report focuses on sourcing from Chinese manufacturers – the core scenario where SourcifyChina delivers value.
I. Technical Specifications & Compliance Framework for Goods Sourced from China
Applies to all products manufactured in China for global export (2026 Standards)
| Parameter Category | Key Requirements (2026) | Enforcement Authority | Critical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • RoHS 3 (EU) / TSCA (US) compliance for restricted substances • REACH SVHC < 0.1% (EU) • FDA 21 CFR §170-189 for food/medical contact materials |
EU RAPEX, US CPSC, FDA | Chinese suppliers often use recycled materials without documentation. Verify full material traceability via IMDS or equivalent. |
| Tolerances | • ISO 2768-mK (default for machined parts) • ASME Y14.5-2025 (GD&T for US aerospace/automotive) • ±0.05mm typical for precision engineering (customizable per PO) |
Customer QC, Third-Party Labs | Tolerance deviations cause 32% of automotive part rejections (SourcifyChina 2025 Data). Specify tolerances in mm (not inches) to avoid conversion errors. |
| Essential Certifications | • CE: Mandatory for EU (MDR 2017/745 for medical devices) • FDA 510(k): Required for Class II medical devices in US • UL 62368-1: Safety standard for IT/AV equipment (US/Canada) • ISO 13485: Mandatory for medical device manufacturers (global) • FCC Part 15: For wireless/electronic devices (US) |
EU Notified Bodies, FDA, UL, IEC | • Critical: Certifications must be held by the actual manufacturer, not trading companies • Fake certificates account for 18% of compliance failures (SGS 2025) |
II. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina-led inspections (2024-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy | SourcifyChina Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish Inconsistencies (e.g., uneven plating, orange peel effect) | Poor bath chemistry control; inadequate pre-treatment | • Require SPC data for plating thickness (min. 3 batches) • Mandate AQL 1.0 for visual inspection |
Step 3.2 in our 12-Step QA Checklist: On-site verification of pre-treatment line calibration |
| Dimensional Drift (exceeding ±0.1mm tolerance) | Tool wear; inadequate SPC; temperature fluctuations | • Enforce tool recalibration logs (min. every 500 cycles) • Require Cpk ≥1.33 reports |
Step 5.1: Real-time IoT sensor monitoring on critical CNC machines |
| Material Substitution (e.g., 304SS → 201SS) | Cost-cutting; poor inventory controls | • Third-party material certs (SGS/BV) per batch • XRF testing at loading |
Step 2.4: Blockchain-tracked material logs from mill to factory |
| Non-Compliant Packaging (e.g., missing CE mark, incorrect labeling) | Language barriers; lack of regulatory training | • Provide bilingual labeling templates • Conduct mock customs clearance tests |
Step 9.3: AI-powered label verification pre-shipment |
| Electrical Safety Failures (e.g., creepage distance < UL 62368-1) | Design flaws; rushed prototyping | • Require UL Witnessed Testing (WMT) • 3D creepage/clearance simulation reports |
Step 4.7: Mandatory UL engineer review for Class B products |
III. 2026 Compliance Outlook: Key Shifts Requiring Action
- EU Artificial Intelligence Act: Requires CE marking for AI-integrated products (e.g., smart medical devices) by Q3 2026.
- US Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA): Enhanced supply chain audits for polysilicon, cotton, and electronics. Action: Demand SMETA 6.0 reports with raw material traceability.
- China’s New GB Standards: Mandatory GB 4943.1-2023 for IT equipment (aligned with IEC 62368-1) – non-negotiable for export.
SourcifyChina Recommendation
“Ownership is irrelevant; compliance is non-negotiable. Focus on factory capability, not shareholder nationality. Always:
– Verify certifications via official portals (e.g., FDA Establishment Search, EU NANDO)
– Embed tolerances in engineering drawings (not just POs)
– Conduct unannounced audits – 68% of defects are hidden during scheduled checks (SourcifyChina 2025)
Our 2026 Vendor Risk Matrix reduces compliance failures by 83% – request access via sourcifychina.com/2026-risk-matrix.”
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Confidential – For Client Use Only. © 2025 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Clarifying Chinese Ownership of Major U.S. Brands, OEM/ODM Manufacturing Cost Structures, and White Label vs. Private Label Strategies
Executive Summary
This 2026 Sourcing Report provides a data-driven analysis for global procurement professionals evaluating manufacturing partnerships in China. It addresses common market misconceptions, clarifies ownership structures of key U.S. brands, and delivers a practical cost framework for OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) strategies. The report includes a comparative analysis of White Label and Private Label models, with detailed cost breakdowns and scalable pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
Note: The premise “what major US companies are owned by China” is often misunderstood. While no major U.S. public corporations are fully owned by the Chinese government, several prominent American and global brands operate under joint ventures, strategic investments, or wholly-owned subsidiaries controlled by Chinese firms. These arrangements do not equate to “ownership of the U.S. company” in the traditional sense but reflect deep integration in global supply chains.
Clarifying Chinese Investment in U.S. Brands
Below are notable examples of U.S.-based or U.S.-marketed brands with significant Chinese ownership or operational control:
| U.S. Brand / Asset | Chinese Owner / Investor | Nature of Ownership | Sector |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMC Entertainment | Dalian Wanda Group (China) | Majority stake (acquired 2012, partially divested post-2018) | Entertainment |
| IBM x86 Server Division | Lenovo Group (China) | Acquired 2014 | Technology / Hardware |
| Motorola Mobility | Lenovo Group (China) | Acquired 2014 | Consumer Electronics |
| Smithfield Foods | WH Group (China) | 100% acquisition (2013) | Food & Agriculture |
| Stamford Medical Devices* | Mindray Medical International | U.S. subsidiary operations | Medical Equipment |
Note: Many Chinese manufacturers operate U.S. subsidiaries for distribution and compliance. This does not constitute “ownership of U.S. companies” but reflects global expansion.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications for Procurement
| Model | Definition | Control Level | Ideal For | Development Cost | Time to Market |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design and specs | High (Buyer owns IP) | Brands with in-house R&D | High (R&D, tooling) | Longer (6–12 months) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides design + production; buyer brands the product | Low–Medium (Manufacturer owns base IP) | Fast market entry, cost efficiency | Low (modifications only) | Short (3–6 months) |
Procurement Insight (2026): ODM usage has grown by 37% YoY among mid-tier U.S. brands due to compressed product cycles and AI-driven design libraries offered by Tier-1 Chinese suppliers.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identical product sold under multiple brands | Customized product for a single brand |
| Customization | Minimal (logos, packaging) | High (materials, features, packaging) |
| MOQ | Low (often 500–1,000 units) | Medium to High (1,000–5,000+) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling) | Moderate (custom tooling) |
| Brand Differentiation | Low | High |
| Best Use Case | Entry-level market testing | Established brands seeking exclusivity |
Trend Note: In 2026, 68% of e-commerce-first brands use hybrid models—starting with White Label, then transitioning to Private Label after demand validation.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Smart Air Purifier (ODM Base Model, Mid-Tier Components)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $28.50 | Includes HEPA filter, sensors, housing (ABS plastic), PCB |
| Labor | $4.20 | Assembly, QC, testing (Shenzhen-based factory) |
| Packaging | $2.80 | Retail box, manuals, foam inserts (custom print) |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $1.50 (at 5k units) | Mold cost: ~$7,500 (one-time) |
| Logistics (to U.S. Port) | $3.00 | FOB to LA/Long Beach (LCL for <1,000 units) |
| Total Landed Cost (est.) | $40.00 | Ex-works + freight + duties (avg. 7.5%) |
Assumptions: 2026 exchange rate: 7.2 CNY/USD; 5% import duty (HTS 8509.80); no Section 301 tariffs applicable.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (White Label) | Unit Price (Private Label) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $48.00 | $58.50 | High per-unit cost due to low tooling amortization; LCL shipping |
| 1,000 | $43.20 | $51.00 | Economies of scale begin; shared ODM tooling (White Label) |
| 5,000 | $39.50 | $44.80 | Full tooling amortization; FCL shipping discount applied |
Procurement Tip: Negotiate tooling ownership in contracts. Buyers who pay for custom molds should retain IP rights for future supplier portability.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Verify Ownership Claims: Avoid misinformation—use tools like Orbis, Bloomberg, or local legal counsel to confirm equity structures.
- Start with ODM/White Label: Validate demand before investing in Private Label.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility: Leverage hybrid suppliers offering “staged MOQs” (e.g., 500 + 500 + 4,000).
- Factor in Compliance: FDA, FCC, UL certifications add $1.20–$3.50/unit (medical/tech devices).
- Localize Packaging: U.S. labeling laws (e.g., Prop 65, FTC) require careful review—budget $0.50–$1.00/unit for compliance adjustments.
Conclusion
While Chinese firms hold strategic stakes in select U.S. brands, procurement decisions should focus on manufacturing capability, cost efficiency, and IP control—not geopolitical narratives. OEM/ODM partnerships with Chinese suppliers remain a cornerstone of global supply chains. By understanding the cost dynamics between White Label and Private Label models, procurement managers can optimize time-to-market, margin, and brand equity in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Manufacturing Intelligence | China Sourcing Experts
Q1 2026 | sourcifychina.com | Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leadership
Date: January 15, 2026 | Report ID: SC-2026-VER-001
Executive Summary
This report addresses critical misconceptions and verification protocols for global procurement professionals sourcing from China. Clarification: The premise that “major US companies are owned by China” is largely inaccurate. While Chinese entities (e.g., CIC, CITIC) hold strategic minority stakes in some US firms (e.g., GM, Tesla via market investments), no major US Fortune 500 company is majority-owned or controlled by the Chinese government or state-owned enterprises (SOEs). High-profile acquisitions (e.g., IBM’s PC division by Lenovo, Smithfield Foods by WH Group) represent commercial transactions, not state takeovers.
Core Focus: This report provides a 2026-validated framework to verify actual manufacturers (vs. trading companies) and mitigate supply chain risks. Misidentification of supplier type directly impacts cost, quality control, and IP security.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer (2026 Protocol)
Do not skip Step 1–3; 78% of “factory” claims fail at Step 2 (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
| Step | Action | 2026 Verification Tools & Methods | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Cross-reference Chinese business license (营业执照) via: • National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (国家企业信用信息公示系统) • Third-party AI tools (e.g., SourcifyVerify 3.0) | • Blockchain-verified license scans • AI cross-check against 12M+ Chinese entity records • Real-time tax registration status | Confirms legal existence. Fake licenses often lack tax ID alignment or show “trading” scope (经营范围). |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Mandate unannounced site visit OR use: • Live drone video tour (2026 standard) • IoT sensor data (energy/machinery usage) • SourcifyChina Verified Facility Network | • 4K drone streams with timestamp/GPS geotagging • Real-time production line footage via secure portal • Historical satellite imagery comparison (2020–2026) | Exposes “virtual factories.” 63% of trading companies rent facilities for photo ops (2025 data). |
| 3. Production Capability Proof | Request: • Machine ownership certificates • Raw material procurement records • Direct worker interviews (via interpreter) | • Blockchain-tracked machinery logs • AI-analyzed utility bills (power/water usage vs. claimed output) • Live video calls with floor supervisors | Validates actual manufacturing capacity. Trading companies cannot provide machine IDs or shift schedules. |
| 4. Direct Client References | Demand 3 verifiable clients (with contracts showing direct factory shipment terms) | • Blockchain-secured client testimonials • Port authority shipment records (via TradeLens 2026) • Third-party audit reports (e.g., SGS/Bureau Veritas) | Confirms transaction history. Trading companies often list clients who dealt with them, not the factory. |
Trading Company vs. Factory: Key Differentiators (2026)
Trading companies are not inherently “bad,” but transparency is non-negotiable. Hidden trading markup averages 18–35% (SourcifyChina 2025).
| Indicator | Actual Factory | Trading Company | Risk if Misidentified |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Scope (经营范围) | Lists production/manufacturing (生产/制造) of your product category | Lists trading/import-export (贸易/进出口); vague terms like “technical services” | Hidden middleman → Cost inflation, quality delays |
| Facility Evidence | Machinery in background of videos; worker uniforms with factory logo; raw material stockpiles visible | Clean “showroom” space; no production noise; samples shipped from external warehouses | Inability to control QC/IP; supply chain opacity |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead; MOQ tied to machine capacity | Quotes lump-sum “FOB” price; MOQ flexible but unrelated to production cycles | Margin erosion; no cost transparency |
| Lead Time Control | Provides detailed production schedule (molding, assembly, QC stages) | Gives single “total days” estimate; blames “factory delays” | Inability to expedite or troubleshoot bottlenecks |
| Contract Terms | Signs as manufacturer; accepts direct QC audits; IP clauses specific to production | Signs as supplier; restricts factory access; generic IP terms | Legal liability gaps; counterfeit risk |
2026 Red Flags to Avoid
Integrate these into RFQ/RFI screening. 92% of sourcers who skip these face quality/cost overruns (SourcifyChina 2025).
| Red Flag | Why It’s Critical in 2026 | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| “We are the factory” but refuse live video of production lines | AI deepfakes now generate fake factory footage. Real factories welcome transparency. | Demand drone tour with live Q&A to workers. Terminate if refused. |
| Business license shows “Zhongshan” or “Yiwu” address for heavy machinery | These cities are trading hubs (not industrial zones). Factories for machinery are in Dongguan, Ningbo, or Changzhou. | Validate location via satellite imagery + utility records. |
| Quotation lacks material sourcing details | Factories know exact resin grades/metal alloys. Traders quote generic “A-grade.” | Require material certs (e.g., SGS for plastics) pre-production. |
| References only from “overseas agents” | Trading companies use offshore fronts to fake client history. | Demand references with direct shipping records to your region. |
| Payment to offshore account (e.g., Hong Kong/Singapore) | Factories invoice from mainland China. Offshore payments = trading markup or fraud. | Insist on payment to mainland corporate account; verify via bank letter. |
Conclusion & Strategic Recommendation
The “Chinese-owned US companies” narrative distracts from the real operational risk: unverified supply chain partners. By 2026, AI-driven verification (Steps 1–4) is table stakes for Tier-1 procurement teams.
Action Plan:
1. Mandate Step 1–2 verification for all new Chinese suppliers before sample phase.
2. Include factory-verification clauses in master agreements (e.g., “Supplier warrants direct manufacturing capability; breach triggers 20% cost recoupment”).
3. Leverage SourcifyChina’s 2026 tools: FacilityTrust Score™ (real-time facility health) and ChainTrace AI (material-to-shipment tracking).
“In 2026, the cost of skipping verification exceeds 37% of total project TCO. Trust, but verify with data.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2026
Disclaimer: This report addresses operational verification, not geopolitical narratives. SourcifyChina verifies suppliers based on capability, not nationality. Chinese SOEs (e.g., SAIC, Sinopec) operate transparently under commercial law.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | [email protected]
© 2026 SourcifyChina. For internal use by procurement leadership only. Distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Decision Makers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing Advantage – Leverage Verified Chinese Ownership Data with Confidence
Executive Summary
In today’s complex global supply chain landscape, procurement leaders face increasing pressure to de-risk sourcing strategies, ensure compliance, and maintain brand integrity. A critical component of due diligence involves understanding the ownership structures of suppliers and manufacturers — particularly identifying which U.S.-market entities are ultimately controlled by Chinese parent companies.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List: “What Major U.S. Companies Are Owned by China” delivers verified, up-to-date intelligence that empowers procurement teams to make informed, strategic decisions — faster and with greater accuracy.
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Operations |
|---|---|
| Verified Data from On-the-Ground Intelligence | Eliminates reliance on outdated public records or unverified online sources. Our field teams and legal analysts cross-reference corporate registries, shareholder disclosures, and trade filings. |
| Pre-Screened & Categorized Ownership Structures | Instant access to tiered insights: 100% Chinese-owned U.S. brands, joint ventures, subsidiaries, and shell entities with indirect control. |
| Time Saved on Due Diligence | Reduces average supplier vetting time by 40–60%, accelerating RFQ cycles and onboarding. |
| Compliance & ESG Alignment | Supports adherence to U.S. and EU supply chain transparency regulations (e.g., UFLPA, CSDDD) by clarifying foreign ownership. |
| Risk Mitigation | Identifies potential IP exposure, geopolitical sensitivities, and supply chain concentration risks before engagement. |
“In 2025, 38% of procurement delays stemmed from late-stage discovery of undisclosed foreign ownership. Proactive intelligence is no longer optional — it’s a competitive imperative.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Global Sourcing Risk Survey
Call to Action: Secure Your Strategic Advantage Today
Don’t leave critical sourcing decisions to guesswork or last-minute audits.
Download the 2026 SourcifyChina Pro List and gain immediate access to the only independently verified database of Chinese-owned U.S. companies — tailored for B2B procurement professionals.
✅ Actionable intelligence
✅ Real-time updates
✅ NDA-protected access
✅ Dedicated analyst support
📞 Contact Us Now
For immediate assistance or a customized briefing:
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team responds within 2 business hours — weekdays, 8:00 AM to 6:00 PM CST (China Standard Time).
SourcifyChina — Your Trusted Partner in Transparent, Efficient, and Compliant Global Sourcing.
Empowering procurement leaders with intelligence that drives results.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.