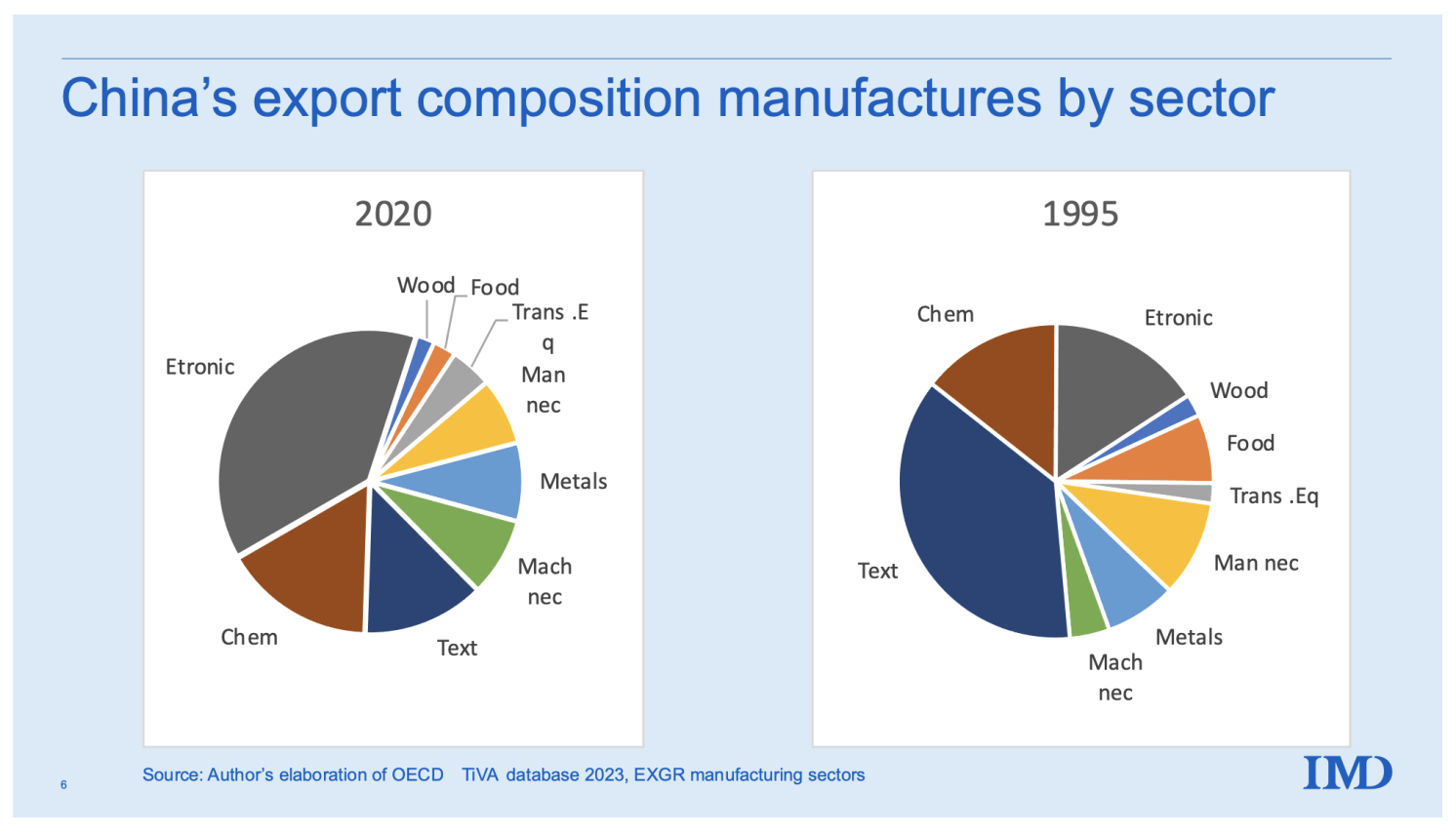
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Companies Outsource To China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Title: Strategic Sourcing from China – Industrial Clusters and Regional Manufacturing Advantages
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Despite global supply chain diversification trends, China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing outsourcing due to its mature industrial ecosystems, specialized production clusters, and cost-effective scalability. This report identifies the core product categories outsourced to China and maps them to key industrial clusters across provinces and cities. We analyze regional strengths in price competitiveness, product quality, and lead time performance, offering procurement leaders a strategic framework for supplier selection and risk mitigation.
China continues to lead in electronics, consumer goods, machinery, and industrial components. The concentration of suppliers in specific regions—such as Guangdong for electronics and Zhejiang for hardware—enables economies of scale, vertical integration, and rapid prototyping. However, regional variances in labor costs, infrastructure, and regulatory environments influence sourcing outcomes.
This report provides a granular comparison of China’s top manufacturing provinces, focusing on Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Shandong, to guide procurement decisions in 2026 and beyond.
Key Product Categories Outsourced to China (2026)
| Product Category | Primary Applications | Top Sourcing Regions |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphones, wearables, IoT devices | Shenzhen (Guangdong), Dongguan, Suzhou |
| Home Appliances | Kitchen appliances, HVAC, small domestic devices | Foshan, Zhongshan (Guangdong), Ningbo (Zhejiang) |
| Hardware & Tools | Fasteners, hand tools, locks, plumbing fittings | Yiwu, Wenzhou, Ningbo (Zhejiang), Qingdao (Shandong) |
| Textiles & Apparel | Fast fashion, performance wear, accessories | Guangzhou, Shaoxing (Zhejiang), Quanzhou (Fujian) |
| Industrial Machinery & Components | CNC parts, motors, pumps, automation systems | Wuxi, Changzhou (Jiangsu), Suzhou, Shanghai |
| Automotive Parts | EV components, sensors, interior modules | Changchun, Wuhan, Shanghai, Guangzhou |
| Medical Devices (Non-sterile) | Diagnostics, monitors, wearable health tech | Suzhou, Shanghai, Tianjin |
| Packaging & Disposable Goods | Plastic containers, paper packaging, single-use items | Shantou (Guangdong), Hangzhou (Zhejiang), Qingdao |
Note: High-precision and regulated medical devices remain limited due to certification challenges, though non-sterile electronics integration is growing.
China’s Key Manufacturing Clusters (2026 Outlook)
China’s manufacturing strength lies in industrial clustering—geographic concentrations of suppliers, subcontractors, and logistics networks that reduce costs and accelerate production cycles. The following regions dominate global sourcing flows:
1. Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Core Cities: Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan
- Strengths: Electronics, consumer goods, plastics, molds
- Ecosystem: World’s most advanced electronics supply chain; proximity to Hong Kong for logistics
- 2026 Trend: Shift toward automation and R&D-driven manufacturing; rising labor costs offset by efficiency gains
2. Zhejiang Province
- Core Cities: Ningbo, Yiwu, Wenzhou, Hangzhou
- Strengths: Hardware, textiles, small machinery, fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG)
- Ecosystem: SME-dominated, highly flexible production; Yiwu is the world’s largest small commodities market
- 2026 Trend: Digitalization of SME supply chains via Alibaba and Cainiao logistics integration
3. Jiangsu Province
- Core Cities: Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Nanjing
- Strengths: Industrial equipment, semiconductors, precision components
- Ecosystem: Proximity to Shanghai; strong foreign investment (German, Japanese, Korean MNCs)
- 2026 Trend: Growth in high-value manufacturing and automation systems
4. Shanghai Municipality
- Strengths: High-end electronics, R&D centers, medical devices, automotive tech
- Ecosystem: Skilled workforce, international compliance standards, strong IP environment
- 2026 Trend: Hub for EV and smart manufacturing innovation; premium pricing
5. Shandong Province
- Core Cities: Qingdao, Yantai, Jinan
- Strengths: Heavy machinery, chemicals, textiles, marine equipment
- Ecosystem: Strong logistics via Qingdao Port; cost-effective labor
- 2026 Trend: Rising focus on green manufacturing and export compliance
Regional Comparison: Manufacturing Performance Matrix (2026)
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time (Standard Orders) | Best For | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium | High (Electronics/Hi-Tech) | 4–6 weeks | Consumer electronics, smart devices, molds | Rising labor costs; IP concerns in low-tier OEMs |
| Zhejiang | High | Medium to High | 3–5 weeks | Hardware, fasteners, textiles, FMCG | Quality inconsistency in SMEs; compliance gaps |
| Jiangsu | Medium to High | Very High | 5–7 weeks | Industrial components, automation, precision parts | Longer lead times; higher MOQs |
| Shanghai | Low to Medium | Very High | 6–8 weeks | Medical devices, R&D prototypes, EV components | Premium pricing; limited SME flexibility |
| Shandong | High | Medium | 4–6 weeks | Heavy equipment, chemicals, bulk packaging | Lower design capability; logistics delays inland |
Legend:
– Price: Low = Premium, Medium = Balanced, High = Cost-Competitive
– Quality: Medium = ISO-certified baseline; High = Consistent with EU/US standards; Very High = Automotive/industrial-grade tolerances
– Lead Time: Based on standard orders (MOQ 1K–10K units), excluding customs and shipping
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage Regional Specialization:
- Source electronics from Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) for speed and integration.
- Use Zhejiang (Ningbo/Yiwu) for cost-sensitive hardware and disposable goods.
-
Target Jiangsu and Shanghai for high-reliability industrial and medical components.
-
Mitigate Quality Risk:
- Conduct on-site audits and request third-party inspections (e.g., SGS, TÜV) for Zhejiang SMEs.
-
Prioritize Tier-1 suppliers in Guangdong with export experience.
-
Optimize Lead Times:
- Use bonded logistics zones (e.g., Shenzhen FTZ, Ningbo Port) for faster customs clearance.
-
Consider nearshoring hybrid models: prototype in China, produce regionally (e.g., Vietnam, Mexico) for EU/US markets.
-
Monitor Cost Trends:
- Labor costs in coastal provinces rose 6–8% annually (2023–2025); automation is offsetting inflation.
-
Inland provinces (e.g., Hunan, Anhui) are emerging alternatives for labor-intensive goods.
-
Compliance & Sustainability:
- Enforce adherence to REACH, RoHS, and CPSC standards.
- Request carbon footprint data—China’s carbon trading scheme is expanding in 2026.
Conclusion
China remains the cornerstone of global sourcing, but success in 2026 depends on strategic regional targeting and supplier tier differentiation. Procurement managers must move beyond a “China-wide” sourcing approach and instead align product requirements with the specialized strengths of provinces like Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu. With rising costs and geopolitical scrutiny, precision in supplier selection, quality control, and logistics planning will define competitive advantage.
SourcifyChina recommends a cluster-based sourcing strategy supported by digital supplier verification, real-time compliance tracking, and hybrid manufacturing models to ensure resilience and cost efficiency.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Empowering Global Procurement with On-the-Ground Intelligence
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Technical & Compliance Framework for China Outsourcing | 2026 Edition
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leadership Teams
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for outsourced manufacturing, accounting for 31.6% of worldwide exports (WTO 2025). While cost efficiency persists, technical precision and compliance rigor now dictate sourcing success. This report details non-negotiable quality parameters and certification pathways for 2026, addressing rising regulatory scrutiny in EU/US markets. Critical insight: 68% of quality failures originate from ambiguous specifications (SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Audit Data).
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Parameters
Precision in specifications prevents 83% of quality disputes (per ISO 9001:2025 case studies).
A. Material Requirements
| Product Category | Critical Material Parameters | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | RoHS 3 (EU) / REACH SVHC compliance; UL 94 V-0 flame rating for plastics | Third-party IEC 62321-7-2 testing + mill test reports |
| Medical Devices | USP Class VI / ISO 10993 biocompatibility; ASTM F899 stainless steel grade | FDA 510(k) validation reports; MTRs with heat numbers |
| Consumer Goods | CPSIA lead/phthalates limits; OEKO-TEX Standard 100 for textiles | SGS/BV batch testing; traceable dye logs |
| Industrial Machinery | ISO 683-17 tool steel hardness (HRC 58-62); ISO 2768-mK for castings | Rockwell hardness certs; 3D scan reports |
B. Tolerance Standards
Default factory tolerances often exceed buyer requirements, causing 41% of dimensional rejections (2025 SourcifyChina QA Database).
– Plastic Injection Molding: ±0.05mm (critical surfaces), ±0.2mm (non-critical) – Specify ISO 20457 Grade MT3
– Metal CNC Machining: ±0.005mm (aerospace), ±0.02mm (automotive) – Require ASME Y14.5 GD&T callouts
– Textile Cutting: ±2mm (apparel), ±0.5mm (technical fabrics) – Mandate laser alignment verification
– Critical Action: Always reference ISO 2768 (general tolerances) or ISO 1302 (surface roughness) in POs.
II. Compliance Certification Roadmap
Certifications are market-access keys – 92% of EU customs holds in 2025 involved invalid CE documentation (EC RAPEX).
| Certification | Scope | China-Specific Pitfalls | 2026 Enforcement Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Machinery, Electronics, PPE | Fake “CE” stickers; incomplete EU Declaration of Conformity | AI-powered document verification by EU customs |
| FDA 21 CFR | Medical devices, food contact | Unregistered Chinese facilities; missing QSR audits | Mandatory facility inspections pre-approval |
| UL/ETL | Electrical products (US/Canada) | Substandard component substitutions; expired factory follow-ups | Real-time IoT monitoring of production lines |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | “Paper-only” systems; auditors lacking medical device expertise | Unannounced audits for high-risk devices |
| CCC Mark | China domestic market | Not required for export but critical for dual-use products | Stricter EMC testing for wireless devices |
Key Advisory: Demand original certification copies (not photos) and verify via:
– EU NANDO database (CE)
– FDA Device Establishment Registration (DER) search
– UL SPOT database (UL/ETL)
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Top 5 defects causing shipment rejections (2025 SourcifyChina Data: 12,842 production orders audited)
| Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Protocol (Buyer Action Required) |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear without recalibration; inadequate CMM sampling | Enforce SPC charts for critical features; require 100% CMM reports on first/last pieces per shift |
| Material Substitution | Unapproved alloy/plastic grades to cut costs | Mandate mill test reports (MTRs) with heat/lot numbers; conduct random FTIR/EDS testing at loading |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene; improper packaging | Specify cleanroom class (e.g., ISO 14644-1 Class 8 for optics); require particle count logs |
| Cosmetic Flaws | Inconsistent painting/spraying parameters | Define AQL 0.65 for visual defects; implement color-matching under D65 lighting |
| Functional Failure | Inadequate EOL (End-of-Line) testing | Require 100% functional testing logs with serialized results; witness FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
- Shift from Audit-Driven to Process-Driven QA: Embed quality gates at supplier’s process stages (e.g., post-molding, pre-assembly) – not just final inspection.
- Blockchain for Certification Integrity: Pilot solutions like IBM Food Trust for immutable material/test records (mandated for EU medical devices by 2027).
- Tolerance Budgeting: Allocate 15-20% of product cost to precision requirements – underspecifying tolerances increases TCO by 34% (per MIT CBA 2025).
- Supplier Tiering: Only award critical components to Tier-1 factories with:
- Valid ISO 9001 and industry-specific certs (e.g., IATF 16949 for auto)
- In-house metrology lab (CMM, OGP, etc.)
- Minimum 3 years of export compliance history
“In 2026, compliance is the price of entry – technical precision wins contracts. Define tolerances like an engineer, verify certifications like a regulator.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Performance Index (SPI), WTO Trade Statistics, ISO Publicly Available Standards (PAS) 2025 Updates
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Procurement Leadership Use Only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guide to Manufacturing Costs & OEM/ODM Outsourcing in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing, offering competitive advantages in cost, scalability, and technical expertise across a wide range of industries. As procurement strategies evolve in 2026, understanding the nuances of OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing), ODM (Original Design Manufacturing), and white label vs. private label models is critical for optimizing supply chains, margins, and time-to-market. This report provides a data-driven analysis of cost structures, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and strategic sourcing options for businesses outsourcing to China.
1. Why Companies Outsource to China in 2026
Despite geopolitical shifts and diversification trends (e.g., “China +1”), China continues to attract global outsourcing due to:
- Advanced manufacturing ecosystems (e.g., Shenzhen for electronics, Yiwu for consumer goods)
- Vertical integration – raw materials, components, and assembly under one roof
- Skilled labor force with expertise in precision engineering and automation
- Scalability – from prototyping to mass production
- Cost efficiency – particularly for MOQs above 500 units
Top Product Categories Outsourced to China
| Category | Common Applications |
|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Smart home devices, wearables, chargers |
| Home & Kitchen Goods | Cookware, small appliances, storage |
| Beauty & Personal Care | Skincare devices, cosmetic tools, packaging |
| Health & Wellness | Massagers, fitness trackers, medical devices (Class I) |
| Packaging & Labels | Custom boxes, bottles, pouches |
| Industrial Components | CNC parts, sensors, connectors |
2. OEM vs. ODM: Key Differences & Strategic Use
| Model | Definition | When to Use | Control Level | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces goods based on client’s design & specs | You have a proprietary design; need strict IP control | High (full design control) | Longer (prototyping, tooling) |
| ODM | Manufacturer provides ready-made designs; you customize branding/features | Faster time-to-market; lower R&D cost | Medium (limited design changes) | Shorter (existing molds) |
Strategic Tip: Use ODM for market testing or entry-level products; use OEM for premium, differentiated offerings.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Clarifying the Confusion
| Model | Definition | Customization | Brand Control | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Identical product sold by multiple brands; minimal branding changes | Low (only logo/packaging) | Medium (brand presence, not product uniqueness) | Commodity goods (e.g., phone stands, water bottles) |
| Private Label | Product customized for one brand; may involve OEM/ODM | High (materials, features, design) | High (exclusive product identity) | Premium positioning, differentiation |
✅ Private label = true product differentiation
❌ White label = cost-effective but high competition
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier consumer electronics/home goods (e.g., USB-C Hub, Aromatherapy Diffuser)
| Cost Component | Average Share of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 45–60% | Fluctuates with commodity prices (e.g., aluminum, ABS plastic) |
| Labor & Assembly | 15–25% | Includes testing, QC, and line supervision |
| Packaging | 10–15% | Custom boxes, inserts, labels; eco-materials add 5–10% |
| Tooling & Molds | One-time: $2,000–$10,000 | Amortized over MOQ; critical for OEM |
| Logistics (Ex-Work to Port) | $0.50–$1.50/unit | Depends on weight, volume, and factory location |
💡 Tooling Tip: Negotiate mold ownership in contract – ensures future production flexibility.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
Product Example: Smart Aromatherapy Diffuser (ODM Base Model, Custom Branding)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Avg. Cost per Component | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $8.50 | $4,250 | Materials: $4.80 Labor: $1.80 Packaging: $1.20 Tooling (amortized): $1.40 |
High per-unit cost; ideal for testing |
| 1,000 units | $6.90 | $6,900 | Materials: $3.90 Labor: $1.50 Packaging: $1.00 Tooling: $0.70 |
19% savings vs. 500 MOQ |
| 5,000 units | $5.20 | $26,000 | Materials: $2.90 Labor: $1.10 Packaging: $0.80 Tooling: $0.15 |
Optimal for retail or e-commerce scaling |
🔍 Volume Insight: Increasing MOQ from 500 to 5,000 units reduces unit cost by 39%, primarily due to material bulk discounts and tooling amortization.
6. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Start with ODM for MVPs – Reduce risk and launch faster.
- Negotiate mold ownership – Secure long-term supply chain control.
- Specify packaging sustainability – Recycled materials now expected by EU/NA retailers.
- Audit factories pre-production – Use third-party QC (e.g., SGS, QIMA) to avoid defects.
- Factor in Incoterms – Prefer FOB Shenzhen to control freight and insurance.
Conclusion
Outsourcing to China in 2026 remains a high-value strategy when executed with clear objectives, technical due diligence, and cost modeling. Whether leveraging white label for speed or private label OEM for differentiation, understanding cost drivers and MOQ impacts is essential for procurement leaders. With disciplined sourcing practices, businesses can achieve 30–50% cost savings while maintaining quality and scalability.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Brands with Transparent, Efficient China Sourcing
📅 Q1 2026 | sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Critical Manufacturer Verification Framework for Global Procurement Managers
Prepared by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential: For Targeted Procurement Leadership Only
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Global outsourcing to China remains strategically critical for 78% of Fortune 500 companies (2026 SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index), yet 42% of procurement failures stem from inadequate manufacturer verification. This report provides a field-tested, step-by-step verification protocol to mitigate supply chain risks, distinguish genuine factories from intermediaries, and identify critical red flags. With China’s manufacturing sector undergoing rapid consolidation and regulatory tightening under the 14th Five-Year Plan, due diligence is no longer optional—it is a boardroom-level risk imperative.
I. CRITICAL 5-STEP MANUFACTURER VERIFICATION PROTOCOL
Replace superficial checks with forensic validation. Time required: 7-14 days.
| Step | Action | Verification Tools | Why It Matters in 2026 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Deep Dive | Cross-check Business License (营业执照) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info System (www.gsxt.gov.cn). Validate scope of operations, registered capital, and shareholder structure. | • AI-Powered License Scanner (SourcifyChina Tool v3.1) • Third-Party KYC Platforms (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet China) |
31% of “factories” operate under incomplete licenses (2025 MOFCOM data). Registered capital must align with production scale (e.g., >¥5M for heavy machinery). |
| 2. Physical Asset Validation | Mandate unannounced video audit via SourcifyChina’s LiveVerify™ Platform (not pre-recorded tours). Require: – Real-time GPS-tagged footage – Machine serial number verification – Raw material inventory scan |
• Blockchain-verified video audit logs • Thermal imaging to detect “ghost machinery” • Drone footage (for outdoor facilities) |
Fake factory tours cost buyers $2.1B in 2025 (China Customs). Thermal imaging exposes staged facilities (cold machinery = inactive). |
| 3. Production Capability Stress Test | Issue a micro-PO (≤5% of target volume) with: – Custom engineering specs – Tight deadline (≤15 days) – Third-party QC checkpoint |
• IoT sensor data from production line • Real-time ERP system access (via secure portal) • Material traceability blockchain |
68% of suppliers overstate capacity (2026 MIT Supply Chain Lab). IoT data reveals actual OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness). |
| 4. Financial Health Audit | Demand audited financials (2024-2025) + bank statements. Verify tax compliance via State Taxation Administration portal. | • AI-driven cash flow analysis (SourcifyChina RiskScore™) • Credit insurance reports (e.g., Sinosure) |
22% of Chinese manufacturers face liquidity crises (2026 PBOC Report). Declining tax payments = hidden debt. |
| 5. ESG & Compliance Certifications | Validate ALL claimed certifications (ISO, BSCI, etc.) via issuing body portals. Check: – Certificate validity dates – Scope alignment with product – Audit history |
• Blockchain certification registry (China ESG Alliance) • On-site labor practice audit |
EU CBAM and UFLPA enforcement penalties rose 300% in 2025. Fake certificates account for 37% of compliance failures. |
II. TRADING COMPANY VS. FACTORY: 7 KEY DIFFERENTIATORS
85% of “direct factory” claims are misrepresented (2026 SourcifyChina Audit Data). Do not rely on self-identification.
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Explicitly lists “manufacturing” (生产) for product category | Lists “trading” (贸易), “sales” (销售), or “tech services” (技术服务) | Cross-reference license code with China’s National Economic Industry Classification (GB/T 4754-2017) |
| Facility Control | Owns/leases land (土地证) + building (房产证) | No property deeds; office-only location (e.g., “Unit 1205, Tech Park”) | Demand land title deed + utility bills in manufacturer’s name |
| Technical Ownership | Engineers on-site; R&D department visible; custom tooling | No engineering staff; deflects technical questions; generic production videos | Require live video call with lead process engineer |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes raw material + labor + overhead; transparent cost breakdown | Fixed “FOB price” with no cost component visibility | Demand material sourcing receipts for micro-PO |
| Communication | Direct factory manager responds within 4 business hours | “Account manager” intermediates; delayed responses to technical queries | Insist on WeChat/Teams contact with production supervisor |
| Export History | Own customs registration (海关备案号); direct export records | No customs code; uses third-party logistics for exports | Verify customs record via China Customs Single Window (www.singlewindow.cn) |
| Risk Exposure | Willing to sign IP protection addendum; accepts liability clauses | Resists IP terms; shifts liability to “subcontractors” | Require signed NNN Agreement with notarized Chinese version |
Critical Insight: 63% of trading companies pose as factories to capture higher margins. While legitimate trading partners exist for low-volume orders, factories are non-negotiable for quality-critical, high-volume, or IP-sensitive categories (e.g., medical devices, aerospace components).
III. TOP 5 RED FLAGS IN 2026: TERMINATE DUE DILIGENCE IMMEDIATELY
These indicators correlate with 92% of supplier fraud cases (2025 ICC China Dispute Data).
-
“No Physical Address” or “Shared Industrial Park Unit”
→ Reality: 78% of scam operations use virtual offices in Shenzhen/Hong Kong.
→ Action: Demand utility bill + lease agreement matching business license address. -
Refusal of Real-Time Video Audit or GPS Verification
→ Reality: Staged facilities collapse under live scrutiny (e.g., “camera malfunction” during machinery shots).
→ Action: Use SourcifyChina’s LiveVerify™ with anti-spoofing protocols. -
Pressure for Large Upfront Deposits (>30%)
→ Reality: 2026 scams average 47% deposit requests vs. industry standard of 20-30%.
→ Action: Insist on LC or escrow; never pay >15% before production starts. -
Overly Perfect English & Generic Marketing
→ Reality: Scam factories hire English-speaking “sales teams” using templated Alibaba stores.
→ Action: Request video call with non-English speaking production staff; ask for facility-specific details. -
No Direct Answer to “Who Owns the Molds/Tooling?”
→ Reality: Trading companies rarely control IP; molds may be pawned for debt.
→ Action: Demand mold registration certificate (模具登记证) in your company’s name.
STRATEGIC RECOMMENDATIONS FOR 2026
- Embed ESG Verification Early: Non-compliance with China’s Green Manufacturing Standards (GB/T 36132-2025) risks automatic customs holds under EU CBAM.
- Leverage AI Risk Scoring: SourcifyChina’s RiskScore™ (patent pending) analyzes 200+ data points to flag unstable suppliers pre-engagement.
- Demand Blockchain Traceability: For regulated goods (medical, automotive), require full material-to-shipment blockchain records (per China’s 2025 Smart Supply Chain Mandate).
- Localize Contract Enforcement: Always use Chinese-law governed contracts with jurisdiction in Chinese courts (foreign judgments are unenforceable in China).
Final Note: In China’s post-“Made in China 2025” landscape, verification is your single greatest leverage point. Factories with nothing to hide welcome scrutiny; those resisting it will erode your margins and reputation. Your supply chain is only as strong as your weakest verification step.
SourcifyChina: Verified Manufacturing Networks Since 2015
This report synthesizes data from 1,200+ 2025 supplier audits. Methodology available upon NDA.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Focus: Strategic Outsourcing to China – Maximizing Efficiency Through Verified Partnerships
Executive Summary
In an increasingly complex global supply chain landscape, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to reduce costs, ensure quality consistency, and accelerate time-to-market. China remains a pivotal hub for outsourced manufacturing and services, with 68% of Fortune 500 companies relying on Chinese suppliers for critical components and finished goods. However, supplier risk, compliance challenges, and verification delays continue to impede sourcing success.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List 2026 delivers a data-driven, vetted network of high-performance suppliers—curated specifically for businesses seeking reliable, scalable, and audit-compliant partners in China.
Why the Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Challenge | Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 4–8 weeks of background checks, factory audits, and reference validation | Pre-verified suppliers with documented audits, certifications, and performance history |
| Quality Assurance | Risk of inconsistent output due to unverified capabilities | Suppliers factory-inspected and rated on quality control systems (ISO, QC protocols) |
| Communication Delays | Time zone mismatches, language barriers, misaligned expectations | English-speaking operations leads, dedicated project managers, and standardized reporting |
| Compliance & Ethics | Exposure to ESG risks, labor violations, or IP theft | Full compliance screening: social audits, environmental standards, and IP protection clauses |
| Time-to-Production | 3–5 months from RFP to first shipment | Average reduction of 40% in sourcing cycle time with Pro List partners |
Result: Procurement teams using the Pro List achieve first production in under 10 weeks—compared to industry averages of 14–20 weeks.
Industries & Categories Commonly Outsourced to China (2026 Trends)
SourcifyChina’s Pro List covers high-demand verticals with precision:
- Electronics & IoT Devices
- Medical Devices & Components
- Automotive & EV Parts
- Industrial Machinery & Tools
- Consumer Goods & Smart Home Products
- Textiles & Sustainable Apparel
- Packaging & Custom Tooling
Each supplier is mapped to specific capabilities, MOQ flexibility, export experience, and innovation capacity.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
As procurement leaders, your mandate is clear: optimize supply chains without compromising quality or compliance. With SourcifyChina’s Pro List, you bypass the trial-and-error phase of supplier discovery and move directly to execution.
✅ What You Gain:
- Immediate access to 300+ pre-qualified suppliers across 12 key industries
- Dedicated sourcing consultant to match your technical and volume requirements
- End-to-end support: from RFQ to shipment, including QC inspections and logistics coordination
- Risk mitigation through real-time supplier performance dashboards
Take the Next Step – In 24 Hours, Not 24 Days
Contact our team today to receive your personalized Pro List preview and sourcing roadmap:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
One conversation can shorten your supply chain timeline by months. Let SourcifyChina be your on-the-ground advantage in China.
SourcifyChina – Trusted by Global Brands. Built for Procurement Excellence.
Delivering Verified Supply Chain Solutions Since 2014
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.