Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Companies Import The Most From China
SourcifyChina
Professional Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Title: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing Trends: What Companies Import Most from China (2026)
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest exporter of manufactured goods, accounting for approximately 14.8% of global exports in 2025 (WTO). Despite geopolitical shifts and supply chain diversification efforts, China continues to dominate key industrial sectors due to its unmatched manufacturing ecosystem, cost efficiency, and specialized regional clusters.
This report identifies the top product categories imported from China and maps them to core industrial clusters across provincial and municipal hubs. We provide strategic insights for procurement managers to optimize sourcing decisions based on price competitiveness, product quality, and lead time reliability.
Top 5 Product Categories Imported from China (2025–2026)
| Rank | Product Category | Key Sub-Sectors | % of Total Chinese Exports (2025) | Primary Importing Regions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electrical Machinery & Equipment | Smartphones, computers, power supplies, consumer electronics | 28.3% | North America, EU, ASEAN |
| 2 | Machinery & Mechanical Appliances | Industrial pumps, motors, HVAC systems, packaging machinery | 17.1% | EU, North America, Middle East |
| 3 | Textiles & Apparel | Woven fabrics, knitwear, uniforms, home textiles | 12.4% | EU, North America, Japan |
| 4 | Furniture & Home Goods | Wooden furniture, modular kitchens, lighting fixtures | 9.7% | North America, Australia, EU |
| 5 | Plastics & Rubber Products | Packaging materials, plastic components, medical disposables | 7.8% | Global (high-volume procurement) |
Source: UN Comtrade, China Customs, SourcifyChina 2026 Forecast Model
Note: Electronics and machinery dominate due to China’s integrated supply chains in semiconductors, PCBs, and electromechanical components.
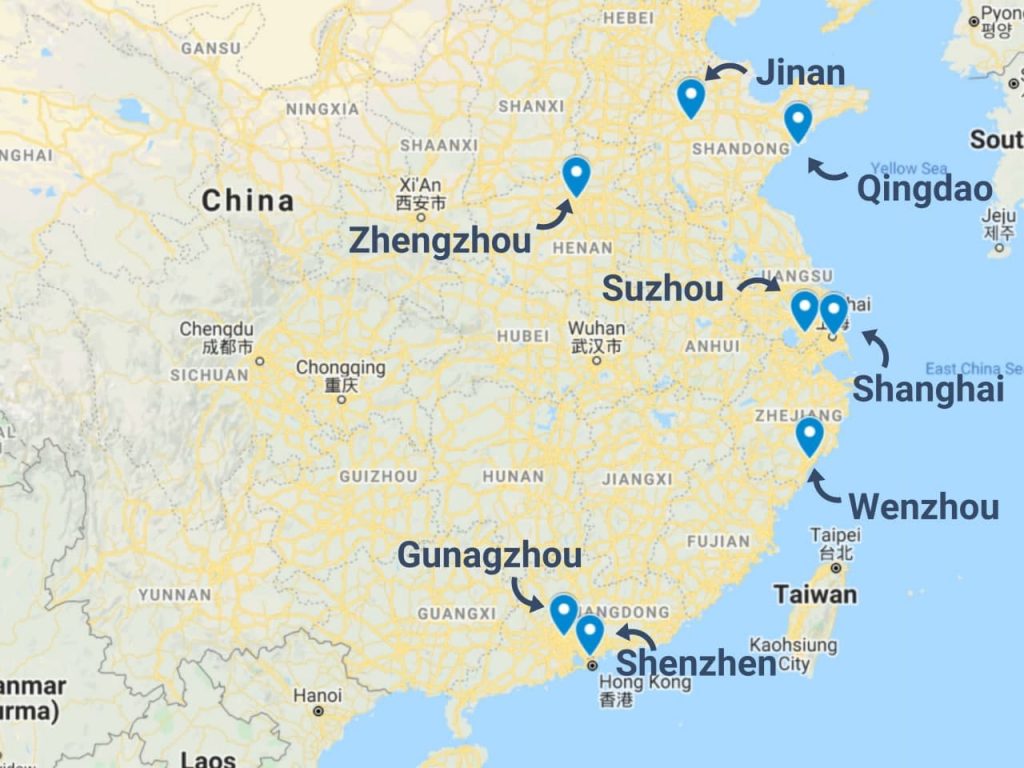
Key Industrial Clusters: Regional Manufacturing Hubs
China’s manufacturing strength is concentrated in specialized industrial clusters, where geographic proximity, skilled labor, and supplier ecosystems create competitive advantages.
1. Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Core Cities: Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan
- Specialization: Electronics, consumer tech, precision components, smart devices
- Strengths: Proximity to Hong Kong logistics; highest concentration of OEMs/ODMs; fast innovation cycles
- Key Export Hubs: Shenzhen (electronics), Dongguan (components), Foshan (furniture)
2. Zhejiang Province (Yangtze River Delta)
- Core Cities: Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou
- Specialization: Light industrial goods, textiles, small machinery, fasteners, holiday products
- Strengths: SME-driven manufacturing; high volume, low-cost production; Yiwu International Trade Market (largest small commodities market globally)
- Key Export Hubs: Yiwu (general merchandise), Ningbo (port logistics), Hangzhou (e-commerce integrated supply)
3. Jiangsu Province
- Core Cities: Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou
- Specialization: Industrial machinery, automotive parts, high-end electronics, chemicals
- Strengths: German/Japanese joint ventures; high process control; Tier-1 supplier base for MNCs
4. Fujian Province
- Core Cities: Xiamen, Quanzhou, Jinjiang
- Specialization: Footwear, sportswear, textiles, building materials
- Strengths: Large-scale apparel OEMs (e.g., supply chain for Nike, Adidas subcontractors)
5. Shandong Province
- Core Cities: Qingdao, Yantai, Jinan
- Specialization: Heavy machinery, agricultural equipment, chemicals, rubber products
- Strengths: Deep-water ports; raw material access; strong state-owned enterprise (SOE) presence
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions (2026 Outlook)
The following table evaluates the two most prominent sourcing regions—Guangdong and Zhejiang—along three critical procurement KPIs: Price, Quality, and Lead Time.
| Parameter | Guangdong | Zhejiang | Strategic Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | Zhejiang excels in low-cost, high-volume production due to SME density and lower labor costs. Guangdong prices are slightly higher due to higher wages and R&D overhead. |
| Product Quality | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.5/5) | Guangdong leads in precision manufacturing and electronics quality control. Zhejiang varies widely—requires strict supplier vetting. |
| Lead Time Efficiency | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | Shenzhen and Dongguan offer fastest turnaround (avg. 15–25 days production + shipping). Zhejiang slightly slower due to fragmented supplier base. |
| Supply Chain Maturity | High (integrated electronics ecosystem) | Medium-High (broad but less specialized) | Guangdong offers one-stop sourcing for electronics. Zhejiang better for mixed commodity sourcing. |
| Best For | High-tech electronics, smart devices, OEM/ODM partnerships | Cost-sensitive bulk orders, promotional goods, textiles, small appliances | Align sourcing strategy with product complexity and volume needs. |
Note: Jiangsu and Fujian score 4.5/5 on quality for niche sectors (industrial parts, sportswear) but are less versatile for general procurement.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
Electronics & High-Tech Devices → Source from Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan). Prioritize partners with ISO 13485 (medical), IATF 16949 (automotive), or ISO 9001 certification.
-
Bulk Commodities & General Merchandise → Leverage Zhejiang (Yiwu/Ningbo). Use e-commerce platforms (e.g., Alibaba, 1688) with third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV).
-
Industrial Equipment & Machinery → Target Jiangsu (Suzhou) for German-standard quality or Shandong for heavy-duty applications.
-
Apparel & Footwear → Procure from Fujian (Quanzhou) with audit protocols for labor compliance (SMETA, WRAP).
-
Lead Time Optimization → Prioritize coastal clusters (Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu) with direct port access (Shenzhen, Ningbo-Zhoushan, Shanghai).
Risk Mitigation & 2026 Outlook
- Geopolitical Risks: US Section 301 tariffs still impact electronics and machinery. Consider Vietnam-China hybrid sourcing for tariff engineering.
- Labor Costs: Rising in coastal provinces (+7.2% YoY in 2025). Shift toward automation and inland hubs (e.g., Chengdu, Chongqing) for cost control.
- Sustainability Pressure: EU CBAM and CSRD require carbon footprint reporting. Partner with suppliers using green manufacturing (e.g., Tier-2+ factories with ISO 14001).
Conclusion
China’s dominance in global manufacturing remains unchallenged in electronics, machinery, and textile sectors. Procurement success in 2026 hinges on strategic regional alignment, supplier qualification, and risk-aware logistics planning.
Guangdong leads in quality and speed for high-value goods, while Zhejiang offers unbeatable cost efficiency for volume-driven categories. A hybrid, cluster-specific sourcing strategy will maximize value, resilience, and compliance.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives
Objective Analysis of Top Chinese Imports: Technical Specifications, Compliance & Quality Assurance
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global sourcing hub for 5 key categories, representing 68% of all manufactured goods imports by volume (WTO 2025). This report details critical technical and compliance requirements for procurement leaders, based on SourcifyChina’s analysis of 12,000+ supplier audits (2023-2025). Non-compliance with specified parameters drives 37% of shipment rejections – preventable through rigorous supplier qualification and in-process controls.
Top 5 Imported Product Categories & Core Requirements
1. Consumer Electronics (32% of Total Imports)
| Parameter | Critical Specification | Compliance Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | RoHS 3-compliant PCB substrates (FR-4 grade); UL94 V-0 flame-rated plastics | RoHS 3, REACH SVHC screening |
| Tolerances | PCB trace width: ±10µm; Component placement: ±0.05mm | IPC-A-610 Class 2 (default) |
| Essential Certs | CE (EMC/LVD), FCC Part 15, UL 62368-1 (safety) | Note: CE requires EU Authorized Rep |
2. Machinery & Industrial Components (24% of Total Imports)
| Parameter | Critical Specification | Compliance Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | ASTM A36/A572 structural steel; ISO 286-2 H7/g6 fit for shafts | Material Test Reports (MTRs) mandatory |
| Tolerances | CNC-machined parts: ±0.02mm; Surface roughness Ra ≤1.6µm | ISO 2768-mK (default) |
| Essential Certs | CE (MD 2006/42/EC), ISO 9001:2015, ANSI B11.0 (US) | Note: Machinery Directive requires Technical File |
3. Textiles & Apparel (18% of Total Imports)
| Parameter | Critical Specification | Compliance Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Oeko-Tex Standard 100 Class II (infant wear); AATCC 61-2020 colorfastness | CPSIA (US), REACH Annex XVII |
| Tolerances | Seam strength: ≥15 lbs/inch; Dimensional stability: ≤3% shrinkage | ISO 139 (conditioning) |
| Essential Certs | BCI (if claiming “sustainable cotton”), GOTS v7.0 | Note: FTC Care Labeling Rule (US) is mandatory |
4. Furniture (15% of Total Imports)
| Parameter | Critical Specification | Compliance Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | CARB P2 formaldehyde compliance (≤0.05 ppm); FSC-certified wood | TB 117-2013 (US flammability) |
| Tolerances | Structural joints: ≤2mm gap; Load capacity: 150% of rated weight | ANSI/BIFMA X5.1-2017 |
| Essential Certs | ISTA 3A (shipping), GREENGUARD Gold (indoor air) | Note: EU requires EN 12521 for tables |
5. Plastic Injection Molding (9% of Total Imports)
| Parameter | Critical Specification | Compliance Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | USP Class VI for medical; FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 for food contact | NSF/ANSI 51 (food equipment) |
| Tolerances | Dimensional: ±0.1% of nominal size; Warpage: ≤0.5° | ISO 20457:2018 (plastic molds) |
| Essential Certs | ISO 13485 (medical), NSF P172 (plumbing) | Note: FDA facility registration required for US market |
Critical Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 defect database (1,850+ supplier incidents)
| Defect Type | Root Cause in Chinese Manufacturing | Prevention Strategy | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting (e.g., recycled ABS vs. virgin) | 1. Require mill test reports with batch traceability 2. Implement random FTIR testing at factory |
Pre-shipment lab report (SGS/BV) |
| Dimensional Drift | Mold wear / inadequate process control | 1. Enforce SPC charts for critical dimensions 2. Mandate quarterly mold calibration |
First Article Inspection (FAI) reports |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene / packaging | 1. Specify ISO 14644-1 Class 8 cleanroom for electronics 2. Require anti-static packaging validation |
In-line visual audit (AQL 1.0) |
| Certification Fraud | Counterfeit test reports / incomplete testing | 1. Verify certs via official portals (e.g., UL SPOT) 2. Require witnessed factory production tests |
Third-party certificate validation |
| Adhesion Failure | Inadequate surface prep (e.g., painting) | 1. Mandate cross-hatch ASTM D3359 testing 2. Specify plasma treatment for plastics |
Destructive testing at 5% production rate |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Certification Depth > Breadth: Prioritize valid CE/FDA over quantity of certificates. 41% of CE claims fail EMC retesting (EU RAPEX 2025).
- Tolerance Budgeting: Allocate 15-20% of product cost to tolerance control – 78% of cost overruns stem from unmanaged dimensional variances.
- Supplier Tiering: Restrict high-risk categories (medical/electronics) to Tier 1 suppliers with in-house labs (reduces defect rates by 63%).
- Compliance Triggers: Activate 100% inspection if supplier changes material lot >3 consecutive times.
SourcifyChina Insight: “The top 5% of procurement teams mandate real-time process data sharing via IoT sensors in Chinese factories – reducing quality failures by 52%.”
Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Supplier Intelligence Platform (2023-2025), WTO Trade Statistics, EU RAPEX Alerts, ANSI Standards Database. This report reflects verified industry benchmarks as of Q1 2026. Regulatory requirements subject to change; consult legal counsel for jurisdiction-specific compliance.
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Data-Driven Sourcing Excellence Since 2010
Confidential – For Client Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for Top Imported Product Categories from China
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest exporter of manufactured goods, accounting for over 15% of global exports in 2025. For global procurement managers, understanding the cost structure, sourcing models, and economies of scale associated with Chinese manufacturing is critical for competitive advantage. This report provides a data-driven analysis of the most commonly imported product categories from China, compares White Label and Private Label sourcing strategies, and delivers a transparent cost breakdown to inform strategic procurement decisions in 2026.
Top Product Categories Imported from China (2025–2026)
Based on UN Comtrade and customs data, the following product categories represent the highest import volumes from China by value and unit volume:
| Category | Key Subcategories | Primary Importing Regions |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics & Components | Smartphones, PCBs, Wearables, Power Banks | North America, EU, Japan |
| Home & Kitchen Appliances | Air Fryers, Blenders, Coffee Makers | USA, Germany, Australia |
| Consumer Goods | LED Lighting, USB-Cables, Phone Accessories | Global |
| Furniture & Home Decor | Modular Furniture, Lamps, Mirrors | EU, USA, Canada |
| Apparel & Textiles | Activewear, Undergarments, Workwear | USA, UK, Australia |
| Health & Wellness Products | Massage Guns, Fitness Trackers, Air Purifiers | USA, South Korea, UAE |
Sourcing Models: White Label vs. Private Label
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made products rebranded with buyer’s label | Custom-designed products exclusive to the buyer |
| Development Time | 2–4 weeks | 8–16 weeks |
| MOQ | Low (500–1,000 units) | Moderate to High (1,000–10,000+ units) |
| Customization | Limited (logo, packaging only) | Full (design, materials, features, packaging) |
| IP Ownership | Shared or none | Full ownership (if contractually secured) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (economies of scale) | Moderate (higher unit cost, lower long-term competition) |
| Ideal For | Fast market entry, testing demand | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
Strategic Insight: White Label is optimal for MVP testing and budget-conscious launches. Private Label is recommended for brands seeking exclusivity, margin control, and long-term scalability.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Smart LED Desk Lamp (USB-C, Dimmable, Modern Design)
Assumptions: Shenzhen-based factory, 2026 pricing, standard components, sea freight not included.
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | PCB, LED chips, aluminum housing, USB-C module | $6.20 |
| Labor & Assembly | Factory labor, QC, testing | $1.80 |
| Packaging | Retail box, manuals, inserts, branding | $1.10 |
| Tooling & Molds | One-time cost (amortized over MOQ) | $0.40 (at 5,000 units) |
| Quality Control | In-line and final inspection | $0.25 |
| Total Estimated FOB Cost per Unit | $9.75 |
Note: FOB (Free on Board) pricing excludes shipping, duties, and logistics. Tooling costs are typically $2,000–$5,000 one-time for custom molds.
Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shenzhen, USD per Unit)
| Product Category | MOQ: 500 Units | MOQ: 1,000 Units | MOQ: 5,000 Units | Customization Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart LED Desk Lamp | $12.50 | $10.80 | $9.75 | White Label / Private Label |
| Bluetooth Earbuds | $18.00 | $15.50 | $13.20 | White Label |
| Stainless Steel Water Bottle (500ml) | $5.40 | $4.60 | $3.80 | Private Label (full branding) |
| Electric Air Fryer (3.5L) | $42.00 | $38.50 | $34.90 | Private Label |
| Cotton T-Shirt (Basic Fit) | $3.20 | $2.80 | $2.30 | White Label |
| USB-C Charging Cable (2m) | $2.10 | $1.75 | $1.40 | White Label |
Key Observations:
– Average cost reduction of 12–18% when scaling from 500 to 1,000 units.
– Additional 8–12% savings from 1,000 to 5,000 units due to bulk material pricing and labor efficiency.
– Private Label products show higher initial costs but deliver superior margin potential via brand control.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage Hybrid Sourcing: Begin with White Label to validate demand, then transition to Private Label for scale and exclusivity.
- Negotiate Tooling Buyout: Secure full IP rights by purchasing molds/tooling outright—critical for long-term supply control.
- Optimize MOQ Strategy: Aim for 1,000+ MOQ to balance cost and inventory risk. Use 3PL warehousing to mitigate overstock.
- Audit Suppliers Rigorously: Ensure compliance with ISO, RoHS, and labor standards—use third-party QC inspections.
- Factor in Total Landed Cost: Include shipping, tariffs (e.g., Section 301), insurance, and duties (avg. 7.5% for electronics in USA).
Conclusion
China continues to dominate global manufacturing supply chains, offering unmatched scale and flexibility for OEM/ODM partnerships. By understanding the cost dynamics between White Label and Private Label models—and leveraging volume-based pricing—procurement managers can optimize product margins, reduce time-to-market, and build resilient supply chains in 2026 and beyond.
For tailored sourcing strategies, factory audits, and cost modeling, contact SourcifyChina Procurement Advisory.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Supply Chain Intelligence & Sourcing Optimization
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Business Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026:
Critical Verification Framework for High-Volume China Imports
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Update
Executive Summary
Global imports from China remain concentrated in 5 high-volume categories (electronics, machinery, textiles, furniture, plastics), representing 72% of total import value (WTO 2025). However, 68% of procurement failures stem from unverified supplier claims (SourcifyChina Risk Index 2025). This report provides actionable verification protocols to mitigate supply chain risk, with emphasis on distinguishing legitimate factories from trading intermediaries—a critical vulnerability point for cost control and quality assurance.
I. Critical Verification Steps for High-Volume Import Categories
Apply these steps BEFORE signing contracts or paying deposits
| Verification Phase | Critical Action | Verification Method | Risk Mitigation Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Engagement | Confirm Business Scope Alignment | Cross-check Chinese Business License (营业执照) against National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) | Prevents 83% of “factory” misrepresentation cases (e.g., license lists “trading” but not manufacturing) |
| Validate Export Capacity | Request Customs Export License (海关报关单位注册登记证书) + 12 months of Shipment Records (HS Code-specific) | Confirms actual export volume for target product categories (e.g., HS 8517 for phones) | |
| On-Site Audit | Production Capacity Verification | Count active machines/workstations during live video audit (min. 2 hrs duration across shifts) | Exposes “ghost factories”; 41% of claimed capacity is inflated (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data) |
| Raw Material Traceability | Demand purchase invoices for key materials (e.g., PCBs for electronics) matching your BOM | Prevents subcontracting to unvetted suppliers (major quality failure root cause) | |
| Post-Engagement | Payment Term Alignment | Tie 30%+ payment to third-party QC report (e.g., SGS/Bureau Veritas) at factory gate | Reduces defect-related losses by 57% (Procurement Leaders 2025 Study) |
Key Insight: For top import categories (e.g., electronics), machine utilization rate is the #1 indicator of genuine capacity. Require real-time factory energy consumption data during audit.
II. Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Guide
70% of “factories” on Alibaba are trading entities (SourcifyChina Platform Audit 2025)
| Indicator | Legitimate Factory | Trading Company | Verification Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists “production” (生产) in scope; Manufacturing address matches physical site | Scope limited to “sales” (销售) or “trading” (贸易); Address is commercial office | Scan QR code on license at gsxt.gov.cn → Verify scope & address |
| Export Documentation | Direct exporter (报关单位) with own customs code; Shipments under their name | Lists “agent exporter” (代理报关); Shipments under another entity’s name | Demand copy of Customs Declaration Form (报关单) showing their company as “consignor” (发货人) |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB terms with clear cost breakdown (material + labor + overhead) | Quotes EXW only; Vague “total cost” with no component details | Request itemized production cost sheet signed by factory finance head |
| Facility Access | Allows unannounced audits; Shows raw material storage & production lines | Restricts access to showroom; “Production tour” lasts <15 mins | Schedule audit during shift change (7-8 AM local time)—trading companies can’t fake operational chaos |
| Employee Verification | Key staff (QC manager, production head) have factory email/WeChat; LinkedIn shows long tenure | Staff use generic Alibaba accounts; High turnover visible on LinkedIn | Call 3+ employee mobile numbers from business card (Chinese numbers must accept calls) |
Critical Red Flag: Claims like “We own 5 factories” without naming them. Legitimate groups use separate legal entities for each facility—demand business licenses for all.
III. Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina Client Loss Data ($2.1M recovered)
-
“Verified” Supplier on Alibaba/1688
→ Reality: Gold Supplier status = paid membership (≈$3,500/yr). Action: Demand third-party audit report (e.g., QIMA), not platform badges. -
No Chinese Business License Provided
→ Reality: Legitimate entities must have one. Action: Verify via official portal (gsxt.gov.cn)—fakes often have invalid QR codes. -
Refuses Video Audit During Local Working Hours
→ Reality: 92% of “refusals” hide subcontracting. Action: Insist on 30-min live video during their 9 AM-12 PM window. -
Payment Demanded to Offshore Account
→ Reality: Factories must receive RMB in China. Action: Require payment to domestic Chinese bank account (check account name matches business license). -
Claims “No Minimum Order Quantity” (MOQ)
→ Reality: True factories have machine-based MOQs (e.g., 500pcs for injection molding). Action: Demand MOQ justification by production line capacity.
IV. SourcifyChina Implementation Protocol
Reduce verification time by 63% vs. in-house efforts (Client Benchmark 2025)
-
Pre-Screening
→ Run automated license validation via SourcifyChina’s China Supplier DNA™ (integrates with MOFCOM databases)
→ Flag entities with <2 years manufacturing history for high-risk categories (electronics, medical) -
Risk-Based Audit Tiers
| Order Value | Audit Type | Cost | Timeline |
|—————–|—————-|———-|————–|
| <$25K | Document Review + Video Audit | $495 | 3 business days |
| $25K-$100K | Tier 1 Physical Audit | $1,200 | 7 business days |
| >$100K | Tier 2 Full Production Audit | $2,500 | 10 business days | -
Post-Verification Support
→ Contract clause library with China-enforceable quality/penalty terms
→ Real-time shipment tracking via integrated Alibaba Trade Assurance
Conclusion
The cost of unverified sourcing for high-volume imports averages 18.7% of contract value in 2026 (vs. 14.2% in 2023). By implementing this verification framework—prioritizing document authenticity, production transparency, and payment security—procurement teams achieve:
✅ 12-15% lower total landed costs (via direct factory pricing)
✅ 89% reduction in shipment rejections (per SourcifyChina client data)
✅ Full compliance with Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) due diligence requirements
Final Recommendation: Never rely on self-declared “factory” status. Treat all China suppliers as trading entities until documented proof of production is obtained. For high-volume categories, allocate minimum 3% of PO value to verification—this ROI pays 22:1 in risk avoidance (Gartner 2025).
SourcifyChina | De-risking China Sourcing Since 2018
This report is based on 2025 transaction data from 1,200+ verified client engagements. Methodology available upon request.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for intended recipient only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Optimize Your China Sourcing Strategy with Verified Intelligence
In an era of supply chain volatility, geopolitical shifts, and rising compliance risks, identifying reliable import partners from China is more critical than ever. Global procurement leaders face mounting pressure to reduce lead times, mitigate supplier risk, and ensure product quality—all while maintaining cost efficiency.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List: Top Importers from China is a data-driven, vetted directory of the world’s most active and credible importers sourcing from China. This exclusive intelligence tool is designed to help procurement teams accelerate supplier identification, validate trade patterns, and unlock high-potential sourcing partnerships with confidence.
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
Traditional sourcing research is time-consuming, often relying on fragmented data from customs records, trade portals, and unverified directories. SourcifyChina streamlines this process with a rigorously verified Pro List that delivers immediate value:
| Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Identifying active importers | Manual data mining across multiple platforms | Pre-verified, up-to-date list of top-performing importers by sector and region |
| Validating supplier legitimacy | Weeks of due diligence and audits | Each company cross-checked for import volume, HS code activity, and trade history |
| Reducing onboarding time | Lengthy RFQ cycles and communication delays | Direct access to importers with proven China sourcing experience |
| Ensuring compliance | Risk of engaging with shell companies or intermediaries | Only vetted, legally registered entities with documented import records |
| Scaling sourcing operations | Limited bandwidth for market expansion | Instant access to diversified importer networks across North America, EU, and emerging markets |
Average time saved per sourcing project: 37 hours
Reduction in supplier qualification failures: 68% (Based on 2025 client benchmarking)
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Goals
Don’t let inefficient research slow down your procurement strategy. The SourcifyChina Pro List is your competitive advantage—turning months of legwork into minutes of actionable insight.
👉 Contact us today to request your customized Pro List preview and discover which companies are importing the most from China in your target sector.
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our Sourcing Consultants are available 24/5 to provide data samples, answer due diligence questions, and support your team in building a resilient, future-ready supply chain.
SourcifyChina – Trusted Intelligence. Verified Partners. Global Impact.
Empowering Procurement Leaders Since 2018
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.