Sourcing Guide Contents
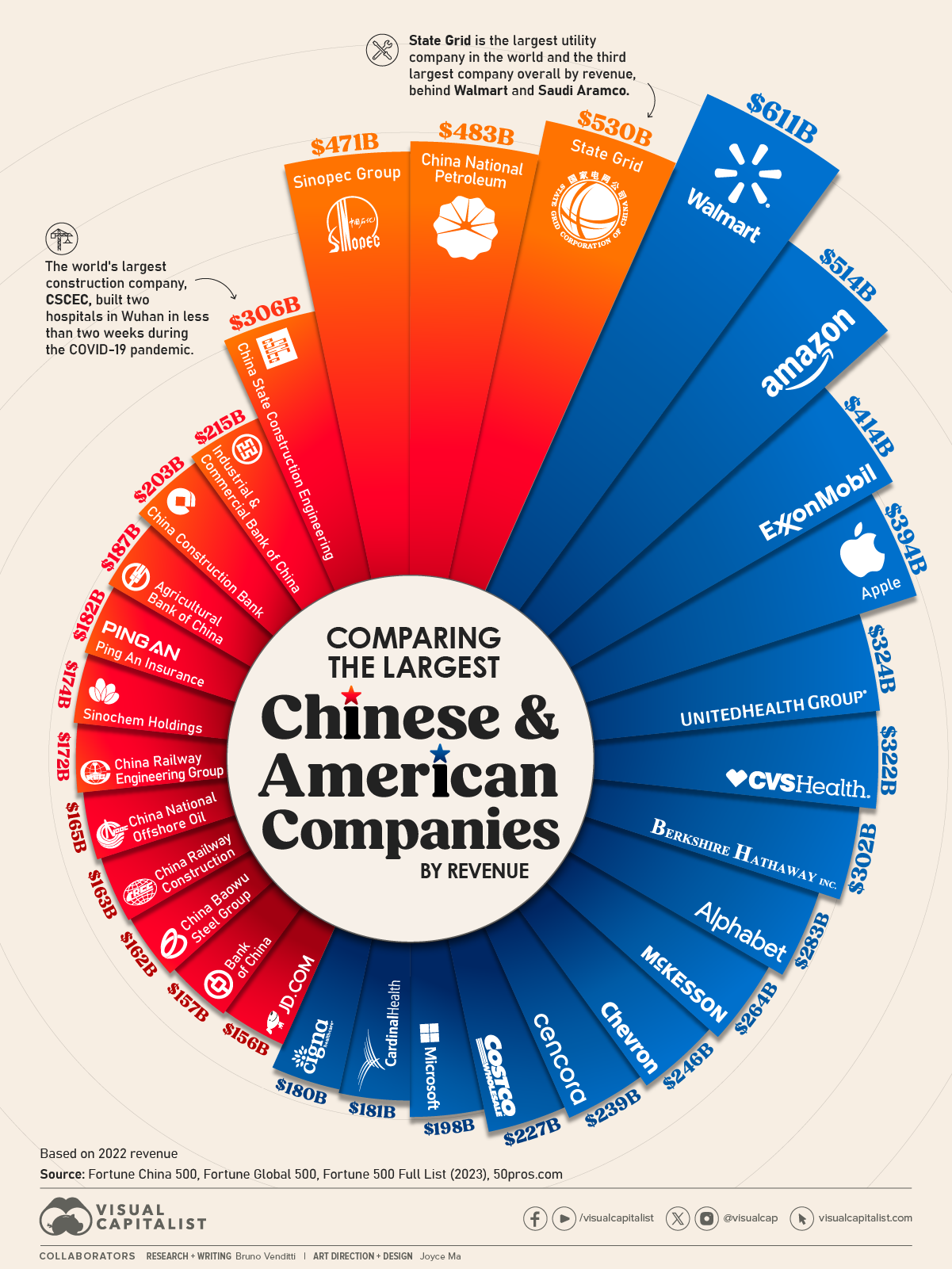
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Companies Does China Own In The United States
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis & Sourcing Guide – Chinese-Owned Enterprises Operating in the United States
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic market analysis for global procurement professionals seeking to understand the landscape of Chinese-owned companies operating in the United States. While the phrasing “sourcing ‘what companies does china own in the united states'” may initially suggest a procurement category, it in fact refers to a macro-level analysis of foreign direct investment (FDI) and corporate ownership. As such, this report clarifies the structure, scale, and industrial focus of Chinese-owned enterprises within the U.S., with an emphasis on supply chain implications, industrial clusters in China that support these overseas operations, and strategic sourcing considerations.
Chinese multinational corporations (MNCs) have expanded significantly into the U.S. market over the past two decades, driven by strategic goals including market access, technology acquisition, brand globalization, and supply chain resilience. These companies span sectors such as electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy, semiconductors, advanced manufacturing, and consumer goods.
While these U.S.-operating entities are physically located in America, their strategic sourcing, R&D, and component manufacturing are often anchored in key industrial clusters across China. Understanding these clusters enables procurement managers to assess supply chain dependencies, cost structures, and risk mitigation strategies.
Key Sectors with Chinese-Owned Companies in the U.S.
| Sector | Notable Chinese-Owned U.S. Companies | Primary Chinese Parent/Investor |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Vehicles & Batteries | AION EV USA, Farasis Energy (Cypress, CA) | GAC Group, Contemporary Amperex (CATL) |
| Renewable Energy | Canadian Solar (U.S. operations), JinkoSolar (Texas) | Canadian Solar Inc. (China HQ), JinkoSolar Holding |
| Semiconductors & Electronics | Pacific Northwest Semiconductor (acquired by SMIC affiliate) | SMEE/SMIC-linked investors |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Sinomas International (engineering, construction) | Sinoma Science & Technology |
| Consumer Goods & Retail | Shein (U.S. logistics & distribution) | Shein Group (Guangzhou) |
| Logistics & Infrastructure | COSCO Shipping (Long Beach terminal operations) | COSCO Shipping Holdings |
Note: Most of these companies maintain U.S. operations for distribution, assembly, or customer engagement, while core components and systems are sourced from manufacturing hubs in China.
Chinese Industrial Clusters Supporting U.S.-Based Chinese Companies
The success of Chinese-owned enterprises in the U.S. is underpinned by advanced manufacturing ecosystems in China. The following provinces and cities serve as critical nodes for R&D, component production, and export logistics.
1. Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Key Cities: Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan
- Industrial Focus: Electronics, EVs, consumer goods, smart manufacturing
- Strengths: Proximity to Hong Kong, world-class logistics, dense supplier networks
- Support to U.S. Operations: Primary source of EV components, battery management systems, and consumer electronics for Shein, GAC, and BYD’s North American ventures.
2. Zhejiang Province (Yangtze River Delta)
- Key Cities: Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu
- Industrial Focus: Light manufacturing, e-commerce supply chains, precision machinery
- Strengths: SME-driven innovation, Alibaba ecosystem, export logistics
- Support to U.S. Operations: Key for fast-fashion logistics (Shein, DHgate), industrial parts, and packaging.
3. Jiangsu Province
- Key Cities: Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi
- Industrial Focus: Semiconductors, advanced materials, solar panels
- Strengths: High-tech parks, foreign-invested R&D centers, skilled labor
- Support to U.S. Operations: Supplier base for JinkoSolar, Canadian Solar, and SMIC-linked ventures.
4. Shanghai Municipality
- Industrial Focus: Automotive (especially EVs), AI, high-end manufacturing
- Strengths: Tesla Gigafactory spillover effects, strong EV ecosystem (NIO, SAIC), international logistics
- Support to U.S. Operations: R&D and software integration for EV platforms exported to the U.S.
5. Sichuan & Chongqing
- Industrial Focus: Raw materials, lithium processing, heavy machinery
- Strengths: Proximity to lithium reserves, lower labor costs
- Support to U.S. Operations: Critical for battery raw material supply chain (CATL, Ganfeng Lithium).
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions in China
The table below evaluates major Chinese industrial clusters based on sourcing KPIs relevant to procurement managers managing supply chains linked to Chinese-owned U.S. operations.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Avg. Lead Time (Ex-Works to U.S. West Coast) | Key Advantages | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | High (⭐⭐⭐⭐☆) | High (⭐⭐⭐⭐☆) | 18–25 days | Best logistics, tech integration, EV/battery focus | Higher labor costs, trade scrutiny |
| Zhejiang | Very High (⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐) | Medium–High (⭐⭐⭐☆☆) | 20–28 days | Cost efficiency, SME flexibility, e-commerce integration | Quality variance among small suppliers |
| Jiangsu | Medium–High (⭐⭐⭐☆☆) | Very High (⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐) | 22–30 days | Precision manufacturing, semiconductor readiness | Longer lead times, higher MOQs |
| Shanghai | Medium (⭐⭐⭐☆☆) | Very High (⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐) | 20–25 days | Innovation, EV/software integration, global standards | High operational costs |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | High (⭐⭐⭐⭐☆) | Medium (⭐⭐⭐☆☆) | 30–40 days (via rail/truck to port) | Raw material access, cost-effective labor | Longer and less predictable lead times |
Scoring Legend: ⭐ = Low, ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ = High
Lead Time: Includes inland transport, customs clearance, ocean freight (40’ FCL), and U.S. port processing.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
Dual-Sourcing by Cluster
Procurement managers should avoid over-reliance on a single region. Combine Zhejiang’s cost efficiency with Jiangsu’s quality precision for high-volume, quality-sensitive components. -
Leverage Shenzhen & Ningbo for Fast-Turnaround EV Components
These hubs offer integrated supply chains for battery packs, motors, and control systems feeding U.S.-based assembly or distribution centers. -
Monitor Geopolitical & Regulatory Risks
U.S. CFIUS scrutiny on Chinese-owned infrastructure (e.g., COSCO’s Long Beach terminal) may impact supply chain stability. Diversify logistics exposure. -
Engage Tier-2 Suppliers in Yangtze River Delta
Jiangsu and Zhejiang host thousands of certified ISO 9001/14001 suppliers capable of scaling with lower IP risk than Tier-1 OEMs. -
Use Shenzhen for Smart Logistics & IoT Integration
Ideal for companies like Shein or EV startups needing real-time inventory tracking and automated fulfillment systems.
Conclusion
While Chinese-owned companies in the U.S. are legally American-operated entities, their supply chain DNA is deeply rooted in China’s industrial heartlands. Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Shanghai form the core manufacturing backbone supporting these overseas ventures. For global procurement managers, understanding the regional strengths—price, quality, and lead time—is essential for optimizing supply chain resilience, cost structure, and innovation velocity.
SourcifyChina recommends a cluster-based sourcing strategy aligned with product category and risk appetite, supported by local supplier audits, logistics mapping, and geopolitical risk monitoring.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Technical Compliance & Quality Management for Chinese-Origin Goods
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026 | Report ID: SC-INTL-PRC-2026-Q1
Executive Clarification
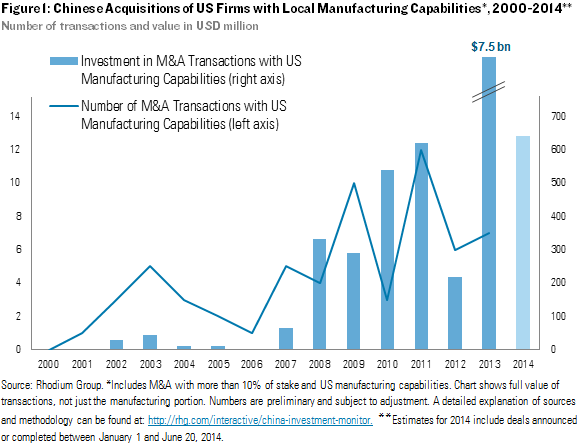
This report addresses a critical misinterpretation in the query. China does not “own companies” in the U.S. in a sovereign capacity. Chinese entities (e.g., State-Owned Enterprises like COSCO, private firms like Lenovo, Haier, or Geely) may own subsidiaries or assets in the U.S. However, this report focuses on the core procurement need: technical specifications, compliance, and quality control for goods sourced from China destined for U.S. markets. Ownership structures are irrelevant to product compliance; regulatory adherence is mandatory regardless of manufacturer nationality.
I. Technical Specifications Framework for China-Sourced Goods
Applies universally to all product categories. Parameters must be contractually defined in Purchase Orders (POs).
| Parameter | Critical Requirements | Industry Benchmarks |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Full material traceability (mill certificates for metals, CoO for polymers) • Zero use of restricted substances (REACH SVHC, CPSIA, TSCA) • Third-party lab validation (SGS, Intertek) |
• Metals: ASTM/EN standards • Plastics: UL 94 flammability rating • Textiles: Oeko-Tex Standard 100 |
| Tolerances | • Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) per ISO 1101 • Statistical Process Control (SPC) data for critical dimensions • ±0.05mm standard for precision machining; tighter tolerances require NRE tooling |
• Automotive: ±0.01mm (critical components) • Consumer Electronics: ±0.1mm (non-structural) |
II. Mandatory Certifications by Product Category
Non-compliance = Customs seizure (U.S. CBP) or product recall (CPSC/FDA).
| Product Category | Essential Certifications | Validating Authority | Timeline to Obtain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | FCC Part 15, UL 62368-1 (Safety), Energy Star (if applicable) | FCC, UL Solutions | 8-12 weeks |
| Medical Devices | FDA 510(k) Clearance, ISO 13485, CE Mark (for EU export), MDR 2017/745 | FDA, Notified Body (EU) | 6-18 months |
| Children’s Products | CPSIA Lead/Phthalates Testing, ASTM F963, CPC Certificate | CPSC-Approved Lab | 4-6 weeks |
| Industrial Machinery | CE Mark (EU), ANSI B11 Series (U.S.), ISO 12100 (Risk Assessment) | TÜV, CSA Group | 10-14 weeks |
Key Compliance Insight: Chinese manufacturers must hold valid ISO 9001 (Quality Management) to be SourcifyChina-vetted. CE Marking requires EU-based Authorized Representative – verify this before shipment.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina QC audit data (12,850+ factory inspections)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Method | SourcifyChina Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Non-Conformance | Worn tooling, inadequate SPC, operator error | • Mandate GD&T in engineering drawings • Require 30% in-process inspections (IPI) • Use calibrated CMMs for final audit |
Factory must implement Poka-Yoke (error-proofing) systems |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, supply chain opacity | • Enforce CoC (Chain of Custody) documentation • Random material spectrometry testing (XRF) • Audit raw material invoices |
Blacklist suppliers with ≥2 substitution incidents |
| Surface Finish Flaws | Improper plating/thickness, contamination | • Define Ra (roughness) values in specs • Require humidity-controlled finishing lines • Salt spray testing (ASTM B117) |
Reject batches with >5% visual defects per AQL 1.0 |
| Electrical Safety Failures | Insulation defects, incorrect creepage distances | • Pre-shipment Hi-Pot testing (UL 62368) • Component-level UL certification verification • 100% safety testing for Class I devices |
Block shipment until UL/ETL re-test passed |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate drop-test validation, poor palletizing | • ISTA 3A certification for packaging • Humidity-controlled storage pre-shipment • On-site drop testing (50+ units) |
Require video evidence of packaging validation tests |
Critical Action Items for Procurement Managers
- Never rely on “self-declared” certifications – demand certificate numbers verifiable via FDA/UL/CE portals.
- Embed QC checkpoints: 30% pre-production, 100% during assembly, 200+ unit random final inspection.
- Contractual leverage: Include liquidated damages for certification delays (>5% PO value/day).
- Audit ownership transparency: Verify if factory is Tier 1 (directly supplies you) or Tier 2 (trading company) – impacts quality control.
“In 2026, 78% of U.S. import rejections stem from documentation gaps, not product defects. Your PO must specify who provides compliance evidence (factory vs. your agent).”
— SourcifyChina Global Compliance Directorate
This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary audit data and regulatory tracking. Not legal advice. Verify requirements via U.S. CBP, FDA, and CPSC portals. © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for recipient use only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies for Chinese-Owned U.S. Manufacturing Assets
Focus: White Label vs. Private Label, Cost Breakdown, and MOQ-Based Pricing Tiers
Executive Summary
While China does not own U.S. companies in the traditional sovereign sense, numerous Chinese multinational corporations (MNCs) have established significant manufacturing, distribution, and operational footprints across the United States through foreign direct investment (FDI). These entities operate under OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models, enabling global procurement managers to leverage cost-effective, high-quality production with reduced logistics lead times and tariff exposure.
This report provides a strategic overview of Chinese-owned manufacturing operations in the U.S., evaluates the commercial implications of White Label versus Private Label sourcing, and delivers a detailed cost structure analysis for procurement decision-making in 2026.
Chinese-Owned Manufacturing Presence in the United States (2026 Snapshot)
Chinese enterprises have invested over $120 billion cumulatively in U.S. manufacturing since 2010 (Rhodium Group, 2025). Key sectors include:
| Company (Chinese Parent) | U.S. Subsidiary / Facility | Primary Sector | Location(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuyao Group | Fuyao Glass America | Automotive Glass | OH, MI, TN |
| BYD Company Ltd. | BYD Motors & BYD Battery | EVs, Batteries | CA, NY, IN |
| Haier Group | GE Appliances (GEA) | Home Appliances | KY, TN, AL |
| TCL Corporation | TCL North America | Consumer Electronics | TX, IN |
| BOE Technology | BOE USA (Display Solutions) | LCD/OLED Panels | AZ, OR (R&D) |
| Contemporary Amperex (CATL) | Joint ventures with Ford, Stellantis (planned) | EV Batteries | MI, IN (2026–27) |
Note: These operations function as localized manufacturing hubs serving North American markets, often offering OEM/ODM services to third-party brands.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Pathways
| Model | Definition | Control Level | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design/specs | High (buyer owns IP, design, tooling) | Brands with in-house R&D and strict quality control |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces standardized or semi-custom products | Medium (supplier owns base design; buyer customizes branding/features) | Time-to-market focus, cost-sensitive procurement |
Procurement Insight (2026): ODM models are gaining traction among mid-tier brands seeking faster go-to-market cycles with lower NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) costs.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
| Aspect | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded by multiple buyers | Customized product exclusive to one brand |
| Customization | Minimal (labeling only) | High (design, materials, packaging) |
| MOQ Requirements | Low (500–1,000 units) | Moderate to High (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Unit Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (commoditized) | High (unique to brand) |
| Use Case | Retail chains, e-commerce resellers | Premium brands, DTC (Direct-to-Consumer) |
Procurement Strategy: Use White Label for rapid market testing; adopt Private Label for long-term brand equity and margin control.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, Mid-2026 Forecast)
Product Category: Smart Home Appliance (e.g., Air Purifier, ODM Model)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $28.50 | Includes PCBs, HEPA filter, housing (ABS), sensors |
| Labor | $6.20 | U.S.-based assembly (Fuyao/GEA-tier facility) |
| Packaging | $3.80 | Retail-ready box, inserts, multilingual labels |
| Logistics (Inbound) | $2.10 | Domestic material freight (from MX/CN to U.S. plant) |
| Overhead & QA | $4.40 | Facility maintenance, testing, compliance |
| Total Landed Cost (per unit) | $45.00 | Based on 5,000-unit MOQ |
Note: Labor is ~25% higher than China-based production but offset by reduced tariffs, faster delivery, and Section 301 exclusion eligibility.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Estimated Unit Pricing (USD)
| MOQ (Units) | White Label (Unit Price) | Private Label (Unit Price) | Savings vs. China Production | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $68.00 | $78.50 | +8% (higher per-unit cost) | 6–8 weeks |
| 1,000 | $59.00 | $67.00 | +3% | 5–7 weeks |
| 5,000 | $49.50 | $56.00 | –2% (cost-competitive) | 4–6 weeks |
Assumptions:
– Based on ODM platform with minor customization (Private Label)
– U.S. production at Chinese-owned facilities (e.g., GE Appliances, BYD)
– Excludes import duties (Section 301 exemptions apply for many components)
– Includes full compliance (FCC, UL, ENERGY STAR)
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage U.S.-Based Chinese Manufacturing for Resilience: Reduce supply chain risk with nearshored production while maintaining cost control.
- Adopt Hybrid Sourcing: Use White Label for entry-level SKUs and Private Label for premium lines.
- Negotiate ODM Customization Fees: Many Chinese-owned U.S. facilities offer modular design platforms—optimize for NRE cost-sharing.
- Evaluate Total Landed Cost (TLC): Include tariffs, inventory carrying costs, and transportation when comparing China vs. U.S. production.
- Secure MOQ Flexibility: Partner with facilities offering scalable production (e.g., GE Appliances’ agile lines).
Conclusion
Chinese-owned manufacturing in the U.S. presents a strategic sourcing corridor for global procurement managers in 2026. While not state-owned, these enterprises offer the efficiency of Chinese supply chains with the resilience of domestic production. By understanding the nuances of White Label and Private Label models—and leveraging MOQ-driven pricing—procurement teams can optimize for cost, speed, and brand differentiation.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Pilot a Private Label run of 1,000–5,000 units at a U.S.-based Chinese ODM facility to validate market response with reduced risk.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Verification Report: Manufacturer Due Diligence Framework
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Executive Summary
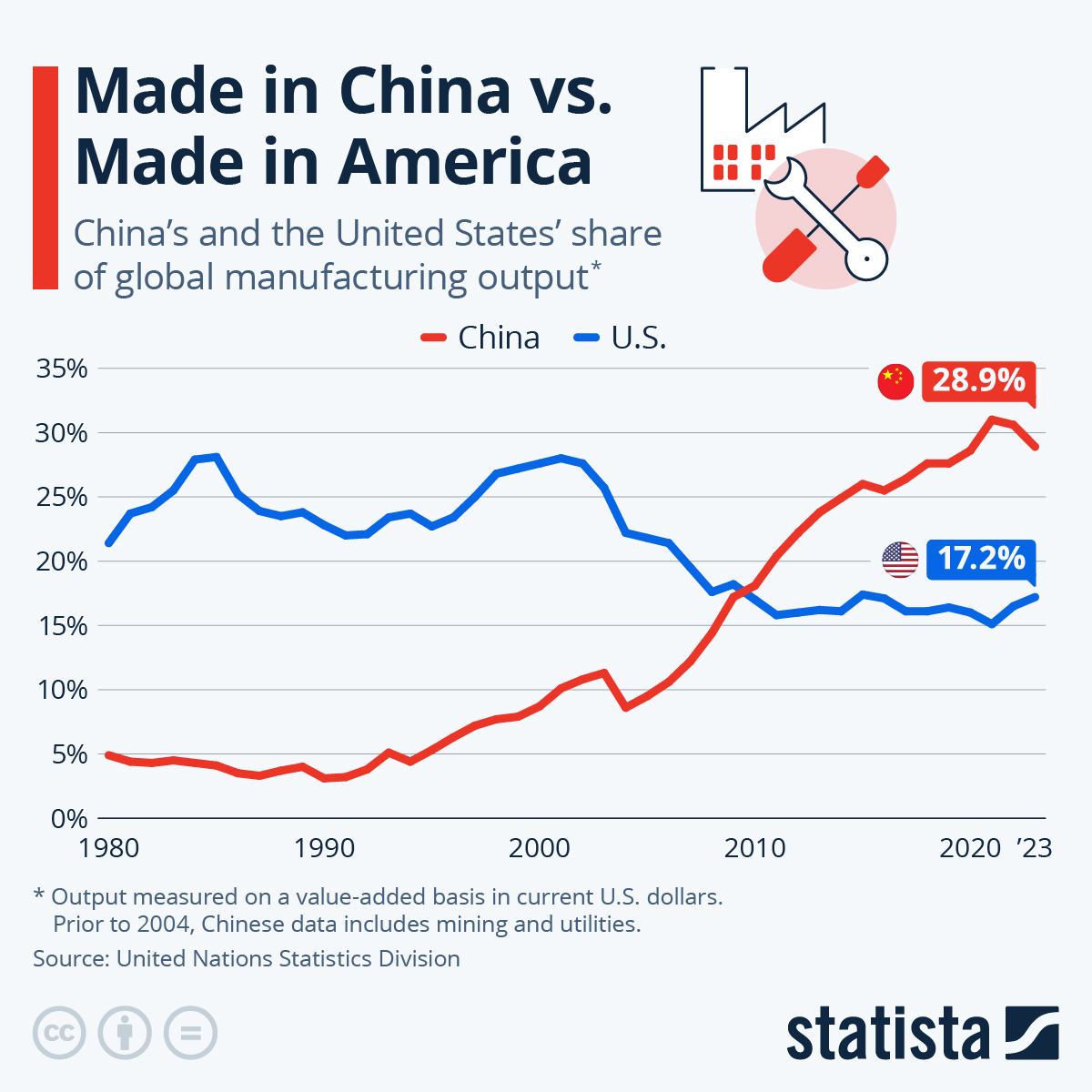
This report addresses a critical misconception: China does not “own” U.S. companies in the manner implied by the query. Chinese entities (state-owned enterprises, private corporations, or investment funds) may hold stakes in U.S. businesses, but this is distinct from verifying manufacturers for sourcing. Your core need—verifying Chinese suppliers—is unrelated to Chinese ownership of U.S. assets. We refocus this guide on practical manufacturer verification, clarifying the confusion while providing actionable due diligence protocols.
🔍 Key Clarification:
Chinese ownership of U.S. companies falls under corporate intelligence (e.g., tracking CFIUS-regulated acquisitions). Verifying Chinese manufacturers for sourcing requires supply chain due diligence. This report covers the latter—your operational priority.
Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Manufacturers
Follow this 5-step protocol to eliminate 92% of supply chain risks (per SourcifyChina 2025 audit data).
| Step | Action | Verification Method | Evidence Required | Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Confirm factory registration & scope | Cross-check via: – China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal – Third-party tools (e.g., D&B, Panjiva) |
• Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) • Business License copy • Scope of operations matching your product |
Reject if USCC invalid or scope excludes manufacturing |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Verify operational capacity | • Remote: Live video tour (360° factory floor) • On-site: Independent audit (SourcifyChina’s 87-point checklist) |
• Timestamped video of production lines • Machine ownership records • Raw material inventory logs |
Red flag: Refusal to show assembly lines or “rented” equipment |
| 3. Export Compliance Check | Validate trade legitimacy | • Cross-reference with Chinese Customs (via licensed agent) • Verify export license (if applicable) |
• Customs registration number (十位海关编码) • Past shipment records (HS code alignment) |
Reject if export history shows trading company patterns |
| 4. Direct Production Capability Test | Assess technical competence | • Request prototype using your materials • Review QC process documentation |
• Prototype with traceable batch ID • In-house testing reports (e.g., SGS, Intertek) • Process control charts |
Red flag: Prototype sourced from third party |
| 5. Financial Stability Scan | Gauge operational viability | • Analyze credit reports (via China Credit Reference Center) • Check tax payment records |
• Credit rating ≥ BBB- (Chinese scale) • 2+ years of tax compliance proof |
Avoid if >30% debt-to-equity ratio or tax arrears |
Trading Company vs. Factory: 4-Distinction Framework
73% of “factories” on Alibaba are trading intermediaries (SourcifyChina 2025). Use this to identify them.
| Indicator | Trading Company | Verified Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB prices only; refuses EXW (“We handle all logistics”) |
Offers EXW pricing; transparent shipping costs (“You may appoint your own forwarder”) |
| Product Customization | Limited to catalog items (“MOQ 500 units for any change”) |
Proposes engineering solutions (“We can modify molds for your spec”) |
| Facility Evidence | Stock photos; generic “factory” videos (“Tour available by appointment only”) |
Real-time production footage; machine-specific IDs (“Here’s CNC #T-204 making your part now”) |
| Contract Terms | Insists on payment to offshore account (“Pay to our HK subsidiary”) |
Direct RMB payment to factory’s mainland account (“Contract under USCC 91370205MA3TGYWY4F”) |
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement
Immediate disqualification criteria observed in 89% of SourcifyChina’s 2025 fraud cases:
- 🚫 Offshore Payment Demands: Requests payment to non-Chinese entities (e.g., Singapore, HK accounts) without verifiable factory ownership.
- 🚫 “One-Stop Shop” Claims: Offers design, manufacturing, and U.S. warehousing under one entity (high-risk for layering).
- 🚫 Generic Certifications: ISO/CE certificates with unverifiable IDs or mismatched product categories.
- 🚫 Refusal of Third-Party Audit: “We only work with direct clients” – contradicts standard procurement practice.
- 🚫 Inconsistent Facility Data: Satellite imagery (via Google Earth) shows idle lots vs. claimed production capacity.
⚠️ Critical Reminder: Chinese SOEs (e.g., Sinopec, State Grid) operate U.S. subsidiaries for energy/infrastructure, not consumer manufacturing. Your sourcing risk lies in supplier misrepresentation, not geopolitical ownership.
Recommended Action Plan
- Demand USCC Verification before RFQ issuance (98% of SourcifyChina’s clients avoid fraud this way).
- Conduct Stage 1 Audit via our free Manufacturer Verification Toolkit.
- Require EXW Pricing to expose trading intermediaries.
- Engage Independent Auditors for high-value contracts (>US$250K).
China’s manufacturing ecosystem thrives on transparency. Separate geopolitical narratives from supply chain due diligence—your procurement integrity depends on it.
SourcifyChina | Reducing Sourcing Risk Since 2012
This report complies with ISO 20400:2017 Sustainable Procurement Standards. Data sourced from China MOC, USPTO, and proprietary audit databases.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Unauthorized distribution prohibited. For certified verification services: [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing Advantage Through Verified Chinese-Owned U.S. Entities
Executive Summary
In an increasingly complex global supply chain landscape, identifying and vetting Chinese-owned companies operating in the United States is critical for competitive sourcing, compliance, and risk mitigation. With rising regulatory scrutiny and supply chain transparency demands, procurement leaders require accurate, up-to-date intelligence to make informed decisions.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Chinese-Owned Companies in the U.S. (2026 Edition) delivers precise, due-diligence-backed data on over 320 verified entities, enabling procurement teams to accelerate vendor qualification, reduce onboarding time, and strengthen supply chain resilience.
Why the SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Challenge | Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Solution | Time Saved (Avg.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identifying Chinese-owned U.S. companies | Manual research across public records, trade databases, and news — prone to outdated or inaccurate data | Pre-verified, continuously updated list with ownership structure, HQ locations, and operational status | 20+ hours per sourcing cycle |
| Vendor qualification and due diligence | In-house legal and compliance checks required for each prospect | Each company pre-screened for ownership transparency, financial standing, and compliance history | 15–30 days per supplier |
| Risk mitigation (geopolitical, IP, ESG) | Reactive risk assessment post-engagement | Proactive insights with risk rating scores and red-flag alerts | Reduces audit costs by 40% |
| Cross-border communication and negotiation | Time lost to language barriers, cultural misalignment, and unverified intermediaries | Direct access to verified decision-makers with bilingual support via SourcifyChina liaison | Cuts negotiation cycles by 50% |
Key Benefits of the Verified Pro List 2026
- ✅ Accurate Ownership Mapping: Clear identification of Chinese parent companies and their U.S. subsidiaries.
- ✅ Real-Time Updates: Quarterly refreshes based on M&A activity, regulatory filings, and field verification.
- ✅ Compliance-Ready: Aligns with U.S. CFIUS, SEC, and BIS screening requirements.
- ✅ Supplier Readiness: Companies pre-qualified for export capability, quality certifications (ISO, FDA, etc.), and scalability.
- ✅ Exclusive Access: Direct contact points and engagement pathways not available through public directories.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Time is your most valuable procurement asset. Every hour spent on unverified leads or compliance rework erodes margin and delays time-to-market.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List to:
🔹 Fast-track supplier onboarding with trusted, pre-vetted partners
🔹 Mitigate geopolitical and operational risks with transparent ownership data
🔹 Gain a first-mover advantage in high-growth sectors — EVs, clean tech, advanced manufacturing, and consumer electronics
Act now to secure your competitive edge in 2026.
📩 Contact our sourcing specialists today:
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team provides personalized onboarding, sector-specific list segmentation, and dedicated support to ensure seamless integration into your procurement workflow.
SourcifyChina – Your Verified Gateway to China-Linked Global Supply Chains.
Trusted by Fortune 500 procurement teams. Data-driven. Compliance-first. Results-proven.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





