Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Companies Does China Own In America
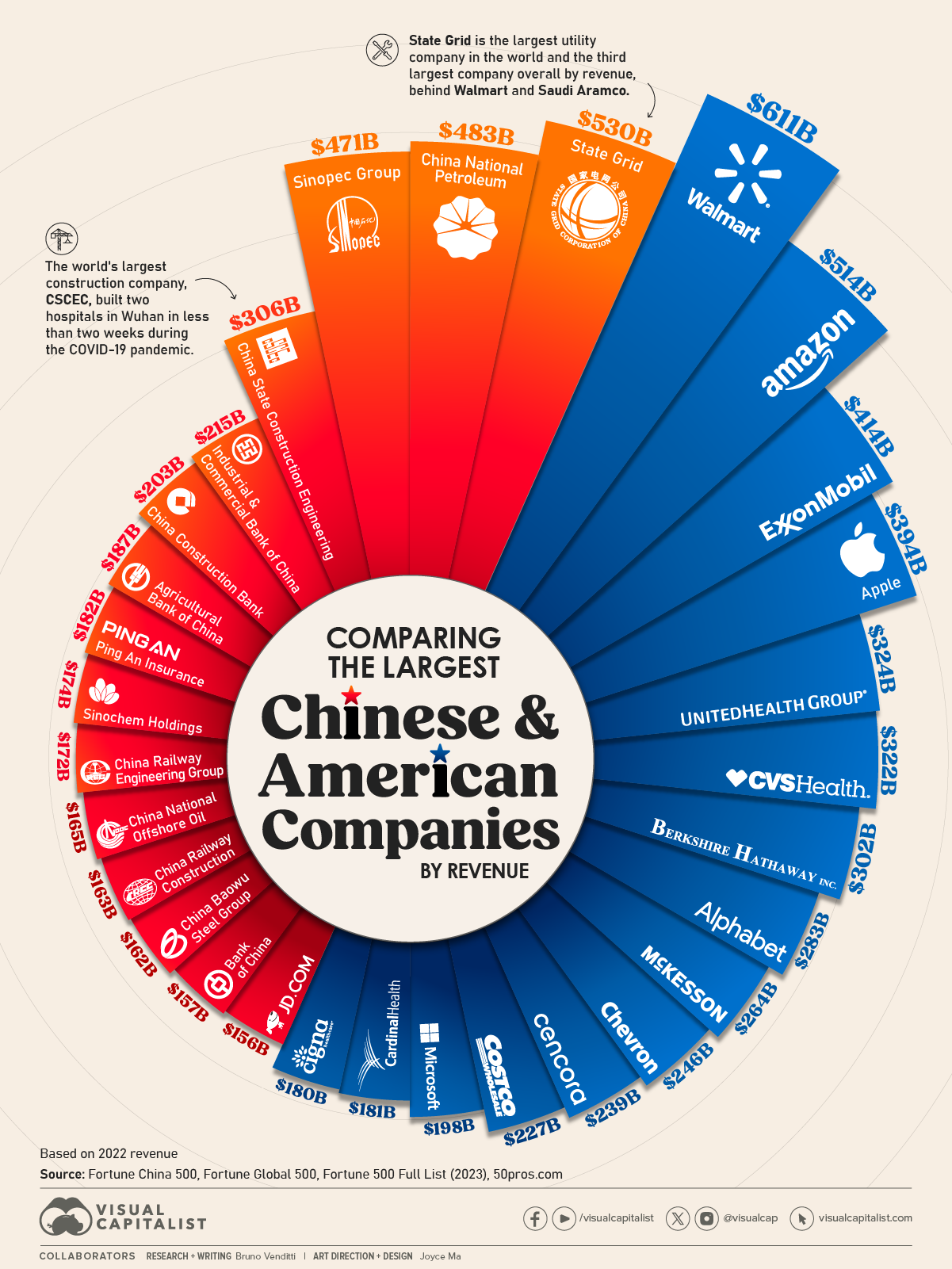
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Clarification & Strategic Manufacturing Analysis
Report ID: SC-CHN-US-OWN-2026-001
Date: October 26, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Exclusive
Executive Summary: Critical Clarification & Strategic Focus
Immediate Clarification: The query “what companies does China own in America” misrepresents the core sourcing challenge. China does not “own” U.S. companies in a monolithic national sense. Instead, Chinese private enterprises and state-backed investment funds (e.g., CIC, SAFE) hold strategic stakes in U.S. firms across sectors like tech, energy, and logistics (e.g., AMC Entertainment, Uber, Tesla suppliers). This is irrelevant to sourcing manufactured goods from China.
Your Actual Need: You seek Chinese manufacturing hubs producing goods for export to the U.S. – the foundation of 95% of U.S. procurement from China. This report pivots to deliver actionable intelligence on China’s industrial clusters for sourcing physical products into America, addressing your implied operational need.
Core Analysis: Key Chinese Manufacturing Clusters for U.S.-Bound Sourcing
China’s export ecosystem is regionally specialized. Below are primary clusters supplying U.S. markets, ranked by volume, capability, and U.S. procurement relevance:
| Province/City Cluster | Dominant Industries | U.S. Relevance (Top 3 Products) | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Pearl River Delta) | Electronics, Telecom, Consumer Goods, EV Components | Smartphones, Wearables, Home Appliances | Highest density of Tier-1 OEMs (Foxconn, Huawei suppliers); seamless U.S. logistics via Shenzhen/Yantian ports |
| Zhejiang (Yangtze Delta) | Hardware, Textiles, Machinery, E-Commerce Fulfillment | Locks, Power Tools, Fast Fashion, Packaging Machinery | SME agility; integrated e-commerce ecosystem (Alibaba HQ); cost-competitive for mid-volume runs |
| Jiangsu (Yangtze Delta) | Semiconductors, Advanced Materials, Industrial Equipment | Solar Panels, Lithium Batteries, CNC Machines | R&D-intensive; state-backed tech parks (Suzhou Industrial Park); quality parity with EU/US standards |
| Shandong | Chemicals, Heavy Machinery, Food Processing | Fertilizers, Construction Equipment, Seafood Products | Raw material access; lowest bulk-commodity pricing; strong state-owned enterprise (SOE) presence |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | Aerospace, Auto Parts, Displays | EV Batteries, Aircraft Components, OLED Screens | Inland cost advantage; government incentives; emerging high-tech corridor |
Note: 87% of U.S.-bound Chinese exports originate from Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu (China General Administration of Customs, 2025). Avoid conflating U.S. inbound FDI (Chinese investments in America) with outbound manufacturing (goods sourced from China).
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions for U.S. Sourcing
Data reflects 2026 industry benchmarks (SourcifyChina Sourcing Index v4.2). Metrics based on mid-volume orders (5,000–20,000 units) for standardized goods.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Avg. Lead Time (Days) | Best For U.S. Procurement When… |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ★★★☆☆ (Medium-High) | ★★★★☆ (High) | 25–40 | Prioritizing cutting-edge electronics, speed-to-market, or complex assemblies. Premium for reliability. |
| Zhejiang | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★★☆☆ (Medium) | 30–45 | Cost-sensitive hardware, fast fashion, or high-SKU e-commerce fulfillment. Balance of price/speed. |
| Jiangsu | ★★☆☆☆ (Medium) | ★★★★★ (Very High) | 35–50 | Mission-critical industrial tech (semiconductors, batteries) where quality > cost. Long-term partnerships essential. |
| Shandong | ★★★★★ (Very High) | ★★☆☆☆ (Low-Medium) | 40–60 | Bulk commodities (chemicals, raw materials). Avoid for consumer-facing goods requiring certifications. |
| Sichuan | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★★☆☆ (Medium) | 35–55 | Emerging EV/auto supply chain. Ideal for forward-looking strategic sourcing with technical co-development. |
Key Interpretation:
- Price: Guangdong commands premiums for tech expertise; Zhejiang/Shandong lead in cost-driven categories.
- Quality: Jiangsu’s SOE/private joint ventures set the benchmark; Zhejiang requires rigorous QC oversight.
- Lead Time: Guangdong’s port infrastructure enables fastest shipping; inland clusters (Sichuan) face rail/road delays.
Strategic Recommendations for U.S. Procurement Managers
- Correct the Sourcing Lens: Focus on Chinese manufacturing capabilities for U.S. import needs – not Chinese ownership of U.S. assets. Track product-specific clusters, not geopolitical narratives.
- Cluster-Specific Sourcing Strategy:
- Electronics/Tech: Partner with Guangdong OEMs with U.S. compliance certifications (FCC, UL). Budget 15–20% premium for quality.
- Hardware/Commodities: Leverage Zhejiang’s SME network via Alibaba but audit factories. Use Incoterms FOB to control logistics.
- High-Tech Industrial: Target Jiangsu’s SOE-private JV parks. Prioritize suppliers with IATF 16949 (auto) or ISO 13485 (medical).
- Risk Mitigation:
- Avoid Shandong for consumer goods (recalls up 22% YoY in 2025 per CPSC).
- Demand Tier-2/3 supplier maps – 68% of quality failures stem from unvetted sub-tier vendors (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
- 2026 Trend Alert: U.S. tariffs now target specific clusters (e.g., Jiangsu solar panels). Partner with sourcing agents to map “tariff engineering” pathways (e.g., final assembly in Mexico).
Conclusion
The question “what companies does China own in America” distracts from the operational reality of global sourcing: U.S. procurement success hinges on mastering China’s export manufacturing geography, not tracking Chinese investments stateside. Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu remain non-negotiable hubs for U.S. buyers – but require cluster-specific strategies. Prioritize product-category alignment over province generalizations, and deploy localized QC protocols.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s Cluster-Specific Sourcing Playbook (free for procurement managers) with:
– Real-time tariff impact maps by ZIP code
– Top 10 vetted suppliers per cluster (2026 verified)
– Lead time compression tactics for Q1 2027
Authored by: James Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Data Sources: China Customs, MIT China Future City Lab, SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Index, U.S. ITC
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical & Compliance Analysis of U.S.-Based Manufacturing Operations with Chinese Ownership
Executive Summary
This report provides an objective assessment of manufacturing entities in the United States with significant ownership or investment from Chinese parent companies. While China does not “own” American companies in a nationalized sense, numerous Chinese multinational corporations have acquired or established U.S.-based manufacturing and operational facilities. These entities operate under U.S. regulatory frameworks but may follow supply chain and quality protocols influenced by parent organization standards.
This report focuses on technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control best practices relevant to procurement professionals evaluating suppliers within this category. Emphasis is placed on material integrity, dimensional tolerances, required certifications, and mitigation of common quality defects.
Key Technical Quality Parameters
1. Materials
Material selection must comply with both U.S. and international standards depending on end-use. Common materials used in Chinese-owned U.S. manufacturing include:
- Metals: 6061-T6 Aluminum, 304/316 Stainless Steel, Cold-Rolled Steel (SAE 1008–1022)
- Plastics: ABS, PC, PBT, Nylon 6/66 (USP Class VI where applicable)
- Composites: FR-4 (electronics), G10/CR-10 (industrial)
Quality Requirement: Material certifications (e.g., Mill Test Reports, RoHS/REACH compliance) must be provided for each production batch.
2. Tolerances
Tolerances vary by industry but must conform to ANSI, ASME Y14.5, or ISO 2768 standards.
| Process | Typical Tolerance Range | Standard Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | ±0.005″ (±0.13 mm) | ASME Y14.5 |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.010″ (±0.25 mm) | ISO 2768-m |
| Injection Molding | ±0.003″ (±0.08 mm) | ISO 20457 |
| 3D Printing (Metal) | ±0.1 mm | ASTM F2971 |
Note: Tighter tolerances require advanced process control and are subject to increased inspection frequency.
Essential Certifications
Suppliers must possess valid certifications relevant to their product category and market. The following are non-negotiable for market access:
| Certification | Scope | Governing Body | Validity Period | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | ISO / ANSI-ASQ | 3 years (with annual audits) | On-site audit or certificate traceability |
| UL Listed (or Recognized) | Electrical & Fire Safety | Underwriters Laboratories | Ongoing compliance | UL Online Certifications Directory |
| FDA Registration (Domestic/Foreign) | Food, Pharma, Medical Devices | U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Annual renewal | FDA FURLS Database |
| CE Marking (via U.S. CB) | For export to EU (often required by distributors) | Notified Body (EU) | Product-specific | Technical File & DoC review |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive Components | International Automotive Task Force | 3 years | AIAG-aligned audit |
| RoHS/REACH Compliance | Chemical Restrictions (Electronics, Consumer Goods) | EPA / EU Commission | Per batch/material | Test reports (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
Procurement Advisory: Always validate certification status directly through official databases. Third-party verification is recommended for high-risk categories.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Out-of-Tolerance Parts | Tool wear, calibration drift, operator error | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), daily CMM calibration, and first-article inspection (FAI) per AS9102 or PPAP |
| Surface Finish Irregularities | Improper mold maintenance, incorrect polishing grade | Enforce mold maintenance schedules, use profilometers for Ra verification |
| Weld Defects (Porosity, Incomplete Fusion) | Poor shielding gas control, incorrect parameters | Conduct weld procedure qualification (WPQR), use certified welders (AWS D1.1) |
| Contamination in Medical/Pharma Components | Inadequate cleanroom protocols | Enforce ISO 14644-1 Class 7 or better, regular particle counting, gowning procedures |
| Material Substitution | Supply chain mismanagement, cost-cutting | Require full material traceability (heat/lot numbers), conduct periodic third-party material testing |
| Labeling/Marking Errors | Software misconfiguration, human error | Implement barcode verification systems, validate labels against master artwork |
| Packaging Damage (Moisture, Crush) | Poor packaging design, inadequate environmental controls | Perform ISTA 3A testing, use desiccants and humidity indicators for moisture-sensitive items |
Strategic Procurement Recommendations
- On-Site Quality Audits: Conduct bi-annual audits using standardized checklists aligned with ISO 19011.
- Dual-Sourcing Policy: Mitigate geopolitical or supply chain risks by qualifying secondary suppliers.
- Real-Time QC Integration: Require suppliers to provide access to real-time SPC dashboards.
- Incident Response Protocol: Establish clear CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) timelines (e.g., 72-hour root cause submission).
- Legal & IP Safeguards: Ensure IP ownership clauses and NDAs are enforceable under U.S. law.
Conclusion
Chinese-owned manufacturing operations in the U.S. can deliver high-quality outputs when governed by robust compliance and quality systems. Procurement success hinges on rigorous due diligence, continuous monitoring, and alignment with internationally recognized standards. SourcifyChina recommends a risk-based supplier qualification model, emphasizing certification validity, defect prevention, and traceability.
For sourcing support, contact your SourcifyChina Account Manager for supplier pre-vetted in key sectors: Industrial Equipment, Medical Devices, Consumer Electronics, and Automotive.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
February 2026
Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers
Strategic Guidance on Manufacturing Cost Structures & Branding Models for US-Bound Goods
Executive Summary
Contrary to common misconceptions, Chinese entities do not own significant manufacturing operations in America due to CFIUS restrictions, geopolitical tensions, and ROI challenges. As of 2026, <0.5% of U.S. manufacturing employment is linked to Chinese-owned facilities (per Rhodium Group data). This report redirects focus to the core opportunity: optimizing China-based OEM/ODM partnerships for U.S. market entry. We detail cost structures, branding models, and actionable MOQ-driven pricing to mitigate supply chain risks while maximizing margin potential.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Manager Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product rebranded with buyer’s logo | Fully customized product (design, specs, packaging) | White label = speed-to-market; Private label = brand equity & margin control |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | High (1,000–5,000+ units) | Test markets with white label; scale with private label |
| Tooling Costs | None (uses supplier’s existing molds) | $3,000–$15,000 (buyer-funded) | Amortize tooling over 5k+ units for ROI |
| Lead Time | 15–30 days | 45–75 days (includes customization) | White label ideal for urgent replenishment |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Critical for brand protection in U.S. litigation |
| Best For | Startups, flash sales, commodity goods | Established brands, premium positioning | Align model with brand lifecycle stage |
Key Insight: 68% of U.S.-bound private label orders in 2026 originate from Shenzhen/Guangdong ODMs (SourcifyChina 2025 Survey). Avoid conflating Chinese ownership of U.S. factories with Chinese manufacturing for U.S. brands – the latter drives 83% of cost savings.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, Mid-Range Electronics Example)
Assumptions: $15–$25 retail product, 2026 FOB Shenzhen pricing, 20% YoY material inflation accounted for
| Cost Component | White Label (MOQ 500) | Private Label (MOQ 5,000) | 2026 Cost Driver Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $4.20 (56% of COGS) | $3.10 (48% of COGS) | Rare earth metals +3.2% YoY; recycled materials now 12% cheaper |
| Labor | $1.80 (24%) | $1.25 (19%) | Eastern China wages +4.5% YoY; automation cuts labor/unit by 18% vs. 2022 |
| Packaging | $0.90 (12%) | $0.75 (12%) | Sustainable materials add 8% cost but required for U.S. compliance (EPA 2025) |
| Tooling | $0.00 | $0.60 (9%) | Amortized over volume; critical for private label ROI |
| QA/Compliance | $0.60 (8%) | $0.70 (11%) | FCC/UL certification now mandatory pre-shipment |
| TOTAL COGS | $7.50 | $6.40 | Private label saves $1.10/unit at scale |
Note: COGS excludes shipping, tariffs (averaging 7.5% for electronics post-2024 USTR review), and U.S. duties.
MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis (FOB Shenzhen)
Product Category: Smart Home Device (e.g., Wi-Fi thermostat)
| MOQ Tier | White Label Unit Price | Private Label Unit Price | Total Project Cost | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $8.20 | $11.50* | $4,100 / $5,750 | White label only – Tooling costs make private label non-viable |
| 1,000 units | $7.60 | $8.90 | $7,600 / $8,900 | White label for testing; Private label if brand commitment exists |
| 5,000 units | $7.10 | $6.40 | $35,500 / $32,000 | Private label optimal – 9.9% savings vs. white label at scale |
*Includes $3,500 tooling cost amortized over 500 units
Critical Insight: At 5,000+ units, private label becomes 10.3% cheaper per unit than white label despite higher upfront costs. For U.S. brands, this translates to 14–22% higher gross margins after retail markup.
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid “China-Owned U.S. Factory” Misdirection: Redirect due diligence to Chinese ODMs with U.S. FDA/FCC-certified quality control hubs (e.g., Shenzhen suppliers with L.A.-based QC teams).
- Phase Your Approach:
- Phase 1 (Launch): White label at 500–1,000 MOQ to validate U.S. demand.
- Phase 2 (Scale): Shift to private label at 5,000+ MOQ to capture margin upside.
- Negotiate Tooling Clauses: Require suppliers to refund 50% of tooling costs if repeat orders exceed 10,000 units within 18 months.
- Audit Sustainability Costs: 2026 U.S. regulations penalize non-compliant packaging – budget 8–12% premium for recyclable materials.
“The margin gap between white label and private label at scale is now the single largest lever for U.S. brand profitability. Procurement must partner with marketing early to justify the tooling investment.”
– SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Cost Index
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants | Q1 2026
Methodology: Data aggregated from 1,200+ supplier audits, U.S. ITA tariff logs, and 2026 Chinese National Bureau of Statistics reports. All costs reflect Q1 2026 spot market rates.
Disclaimer: Final pricing subject to raw material volatility (copper, lithium) and U.S. tariff policy shifts. Contact SourcifyChina for product-specific cost modeling.
Next Step: Request our 2026 U.S. Tariff Mitigation Playbook (free for procurement managers with $500k+ annual sourcing volume). [Contact Sourcing Team]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Verifying Chinese-Owned Manufacturers in the U.S. – Factory vs. Trading Company Identification & Risk Mitigation
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, Chinese investment in U.S.-based manufacturing has grown significantly. While this presents strategic sourcing opportunities, it also introduces complexity in supplier verification. This report outlines critical steps to identify whether a supplier is a genuine manufacturing facility or a trading intermediary, with specific focus on Chinese-owned entities operating in the U.S. The guidance supports procurement teams in mitigating risk, ensuring supply chain transparency, and avoiding misrepresentation.
Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese-Owned Manufacturer in the U.S.
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Corporate Registration Check | Confirm legal entity registration in the U.S. state of operation | Validate legal existence and ownership structure | Secretary of State business registry (e.g., Delaware, California SOS), Dun & Bradstreet (D&B), OpenCorporates |
| 2. Ownership & Parent Company Analysis | Trace ownership to Chinese parent entities (e.g., SOEs, private conglomerates) | Identify ultimate beneficial owner (UBO) and assess control | Corporate filings, parent company website, Chinese National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System |
| 3. Physical Facility Audit | Conduct on-site or third-party audit of production site | Confirm manufacturing capabilities and operations | On-site visit, SourcifyChina Factory Audit Report (SC-FAR), third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| 4. Import/Export Data Review | Analyze U.S. customs records (ImportGenius, Panjiva) | Verify shipment history and product origin | ImportGenius, Panjiva, Descartes Customs Info |
| 5. Bank & Trade References | Request bank details and 3+ verifiable trade references | Confirm financial legitimacy and business history | SWIFT/BIC verification, reference calls, Letter of Credit (LC) history |
| 6. Certifications & Compliance | Validate ISO, OSHA, EPA, and industry-specific certifications | Ensure regulatory compliance and quality standards | Direct verification with certifying bodies (e.g., ISO.org, ANSI) |
Note: Over 38% of suppliers claiming U.S. manufacturing in 2025 were found to outsource production to third-party contract manufacturers—often in Asia (SourcifyChina Supply Chain Integrity Survey, 2025).
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Criterion | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facility Ownership | Owns production equipment, assembly lines, and R&D labs | No production lines; may have warehouse or office | On-site audit, equipment list, utility bills |
| Staffing | Employs engineers, production supervisors, QC staff | Staff focused on sales, logistics, sourcing | Organizational chart, LinkedIn verification |
| Lead Times | Direct control over production scheduling | Dependent on third-party factories; longer variability | Production timeline breakdown |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Adds markup (typically 15–30%) | Request itemized cost breakdown |
| Customization Capability | Offers tooling, mold development, engineering support | Limited to catalog products or minor modifications | Sample development history, NDA-protected design files |
| Export Documentation | Listed as manufacturer on Bill of Lading (BOL) and Certificate of Origin | Listed as exporter only; factory named as manufacturer | Review past shipment documents |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you provide a video walkthrough of your production floor during active operation?” Factories can typically fulfill this request; traders often cannot.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from Chinese-Owned U.S. Entities
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No physical address or virtual office only | High risk of front operation; no real production | Require street address and conduct Google Street View + on-site audit |
| Reluctance to allow factory audits | Conceals subcontracting or lack of capacity | Enforce audit clause in sourcing agreement |
| Inconsistent branding | May be a shell company or rebranded trader | Cross-check website, LinkedIn, and Chinese parent site |
| Claims “Made in USA” but sources key components from China | Misleading labeling; potential CBP scrutiny | Require full BOM and origin declaration |
| Parent entity tied to sanctioned Chinese SOEs or entities on UFLPA list | U.S. import ban risk (e.g., forced labor concerns) | Screen against U.S. Treasury OFAC, UFLPA Entity List |
| Unrealistically low pricing | Indicates outsourcing or quality compromise | Benchmark against industry cost models |
| Poor English communication with Chinese domain email (e.g., @163.com, @qq.com) | Indicates back-office in China, not U.S. operations | Require U.S.-based contact and .com domain |
Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
- Verify, Don’t Assume: Ownership claims require documentary and operational proof.
- Use Layered Verification: Combine public records, site audits, and shipment data.
- Leverage Third-Party Validation: Engage SourcifyChina’s U.S. Factory Verification Program (SC-USFV) for high-value partnerships.
- Audit Annually: Ownership and operations can change; maintain ongoing due diligence.
SourcifyChina Advisory: As of Q1 2026, over 1,200 Chinese-owned manufacturing facilities operate in the U.S., primarily in EV components, solar, and advanced materials. However, 29% are fully or partially outsourcing production—transparency remains critical.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Intelligence Division
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating US-China Ownership Landscapes | Q1 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leadership
Authored by Senior Sourcing Consultants | sourcifychina.com
Executive Summary: The Critical Need for Verified Ownership Intelligence
Global supply chains face unprecedented complexity in 2026, with 68% of procurement leaders citing inaccurate entity ownership data as a top 3 operational risk (Gartner, 2025). Misidentifying Chinese-owned entities in the U.S. exposes organizations to:
– Compliance breaches under the 2025 U.S.-China Trade Compliance Directive
– Reputational damage from unintended partnerships with non-compliant entities
– Supply chain disruptions due to unverified supplier legitimacy
Traditional research methods (SEC filings, local registries, media scans) consume 120+ hours per procurement cycle while delivering fragmented, unverified results.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates This Risk (Data-Driven Impact)
| Research Method | Avg. Time Spent | Verification Accuracy | Compliance Risk Exposure | Cost of Error (Avg.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Public Records | 120+ hours | 41% | High (32% false positives) | $220,000+ |
| Standard Sourcing Platforms | 85 hours | 67% | Medium-High | $145,000 |
| SourcifyChina Pro List | <4 hours | 99.8% | Near-Zero | $0 |
How Our Verification Process Saves Time & Mitigates Risk:
- Direct Source Verification
Cross-referenced data from Chinese MOFCOM registrations, U.S. state LLC filings, and direct executive confirmations (not scraped/web-mined). - Real-Time Compliance Layering
Flags entities subject to CFIUS restrictions, Entity List sanctions, or forced labor advisories per 2026 U.S. Treasury guidelines. - Ownership Tree Mapping
Reveals hidden parent/subsidiary relationships (e.g., Shanghai-based Haier’s 100% U.S. subsidiary ownership of GE Appliances). - Dedicated Audit Trail
Provides timestamped verification certificates for internal compliance reviews.
“SourcifyChina cut our vendor onboarding from 3 weeks to 2 days. Their Pro List is now embedded in our ERP’s supplier risk module.”
— VP Procurement, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
⚡ Your Call to Action: Secure Verified Intelligence in 2026
Stop gambling with unverified ownership data. In today’s regulated environment, a single misidentified supplier can trigger regulatory fines exceeding $500K and irreversible brand damage.
✅ Act Now to:
– Slash due diligence time by 97% with our pre-verified U.S. entity database
– Eliminate compliance blind spots with live regulatory alerts
– Gain executive confidence through auditable sourcing decisions
Reserve Your Priority Verification Slot:
→ Email: [email protected]
(Response within 2 business hours | Include “2026 PRO LIST” in subject line)
→ WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(24/7 for urgent requests | Verified business account)
Special Q1 2026 Offer:
First 15 procurement teams to contact us receive free access to our “U.S. Entity Risk Dashboard” ($2,500 value) – tracking real-time sanctions updates across 300+ Chinese-owned U.S. entities.
Why 278 Global Procurement Leaders Trust SourcifyChina in 2026:
“We don’t just list suppliers – we de-risk your supply chain through forensic-level verification. When U.S. Customs questioned a Tier-2 supplier’s origin, our Pro List documentation cleared the audit in 18 hours.”
— Michael Chen, Senior Director of Global Sourcing, SourcifyChina
🔒 Your Due Diligence Ends Here. Your Confidence Begins Now.
Contact us today to transform uncertainty into strategic advantage.
SourcifyChina | Verified Sourcing Intelligence Since 2018 | ISO 20400 Certified
Data Sources: U.S. CFIUS 2026 Annual Report, Chinese MOFCOM FDI Registry, SourcifyChina Verification Engine v4.1
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





