Sourcing Guide Contents
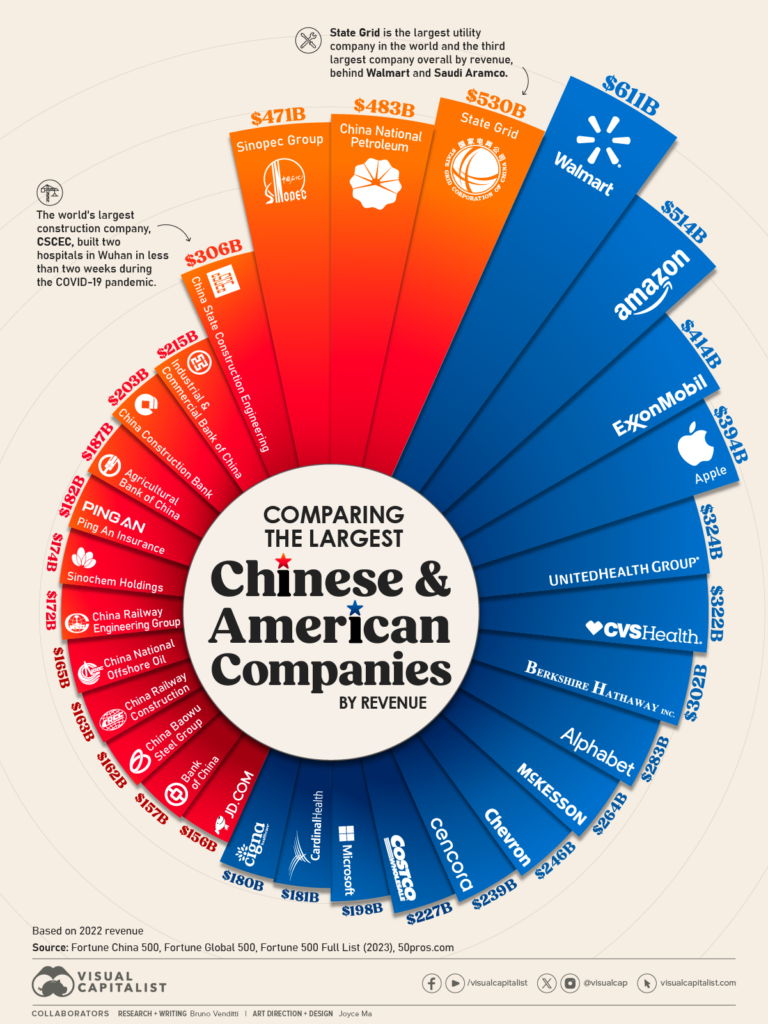
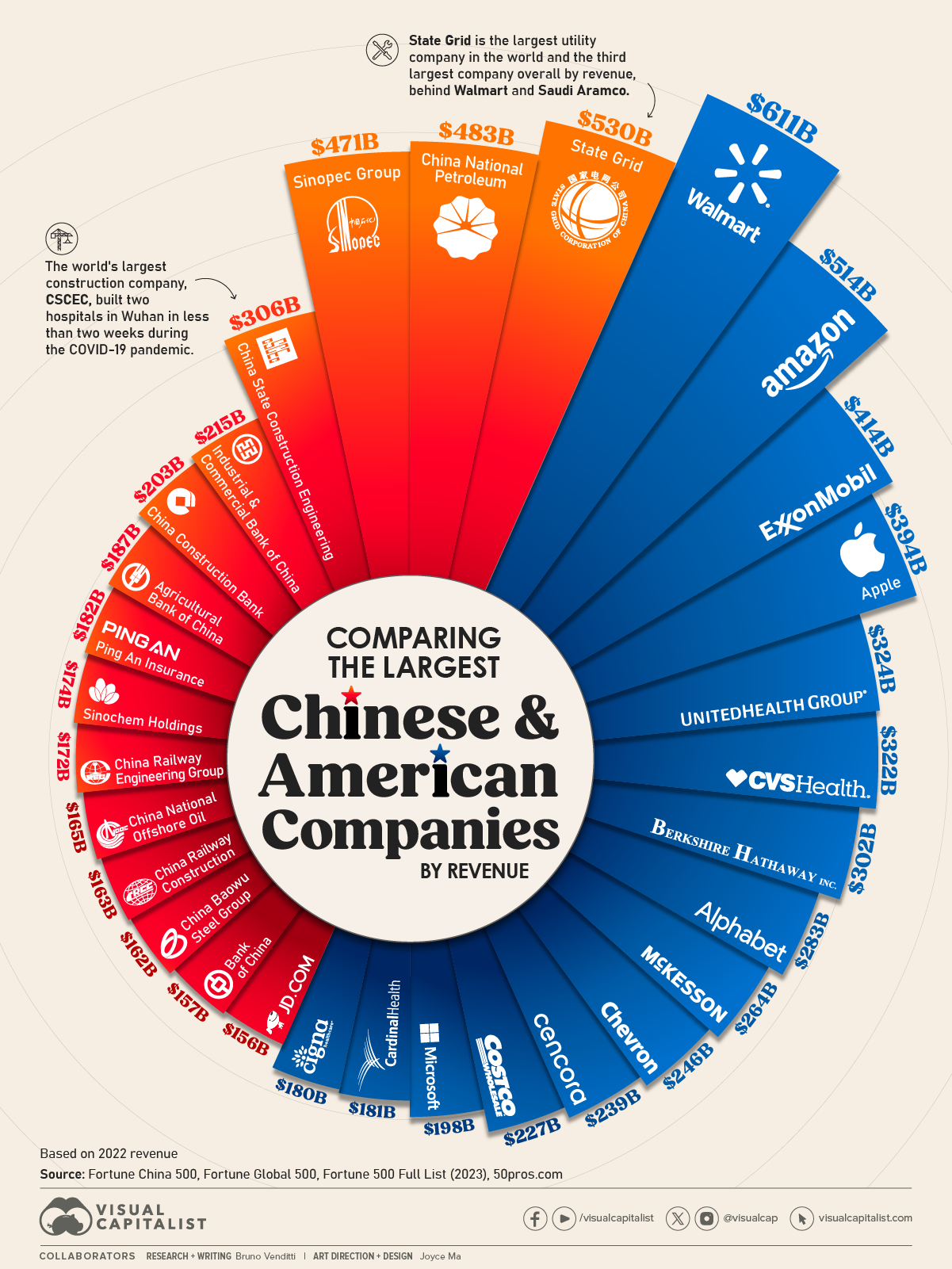
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Companies Are Owned By China In The Us

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing Companies Owned by Chinese Entities in the U.S.: Industrial Clusters and Manufacturing Capabilities in China
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic analysis for global procurement managers seeking to understand the intersection of Chinese ownership, U.S. market presence, and sourcing implications tied to Chinese industrial manufacturing ecosystems. While the phrase “companies owned by China in the U.S.” typically refers to U.S.-operating businesses with majority ownership or control by Chinese parent companies (e.g., subsidiaries of Chinese multinationals), this report reframes the inquiry for sourcing relevance: How do Chinese-owned companies in the U.S. rely on manufacturing capabilities in China, and which Chinese industrial clusters are most strategically positioned to supply these entities?
We identify key Chinese provinces and cities that serve as primary production hubs for goods destined for U.S. subsidiaries of Chinese firms. These clusters support high-volume, export-oriented manufacturing across electronics, automotive components, industrial machinery, and consumer goods—sectors where Chinese ownership of U.S. operations is most prevalent.
Strategic Context: Chinese Ownership in the U.S. Market
As of 2025, over 4,200 U.S.-based companies have significant Chinese ownership, according to Rhodium Group data. These include:
- TikTok (ByteDance) – Digital services, hardware support
- AMC Entertainment (Dalian Wanda) – Indirect ownership; ancillary tech procurement
- IBM’s x86 Server Division (acquired by Lenovo)
- Smithfield Foods (WH Group)
- Motorola Solutions (Lenovo Group)
- Nexteer Automotive (Avic Auto)
- U.S. subsidiaries of Huawei, ZTE, BYD, and Haier
While these companies operate in the U.S., a significant portion of their hardware, components, and equipment are sourced from manufacturing bases in China, particularly from clusters with export infrastructure, technical expertise, and supply chain integration.
Key Industrial Clusters in China Supporting U.S.-Bound Chinese-Owned Firms
The following provinces and cities are dominant in producing goods for export to U.S. subsidiaries of Chinese enterprises:
| Region | Key Industries | Notable Export Clients (U.S. Subsidiaries) | Infrastructure Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou) | Electronics, Telecom Equipment, Consumer Tech, Drones | Huawei U.S. (legacy), DJI North America, Lenovo/Motorola | SEZ status, Shenzhen Port, high R&D density |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu) | E-commerce logistics, Home Appliances, Auto Parts, Textiles | Haier (GE Appliances), Alibaba-linked vendors | Strong SME network, Alibaba HQ, Ningbo-Zhoushan Port |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi) | Industrial Machinery, Semiconductors, EV Components | BYD U.S. (buses, energy storage), Avic subsidiaries | Proximity to Shanghai, high-tech zones |
| Shanghai & Yangtze River Delta | High-end Electronics, Medical Devices, EVs | SAIC Motors (MG USA), NIO U.S. R&D centers | Integrated logistics, customs efficiency |
| Shandong (Qingdao, Yantai) | Food Processing, Heavy Machinery, Chemicals | WH Group (Smithfield U.S.), Sinomach | Major agricultural processing zones |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions in China
The table below evaluates the top manufacturing regions in China based on price competitiveness, quality standards, and lead time efficiency—critical KPIs for procurement managers sourcing on behalf of U.S. operations of Chinese firms.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time (Avg. from PO to Shipment) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.5/5) – High consistency, ISO-certified | 25–35 days | Electronics, Smart Devices, Telecom Hardware |
| Zhejiang | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) – Lowest cost for SMEs | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.5/5) – Varies by supplier tier | 30–40 days | Consumer Goods, E-commerce Fulfillment, Home Products |
| Jiangsu | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.5/5) – Higher labor/rent costs | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.5/5) – Precision engineering focus | 20–30 days | Industrial Equipment, Automotive Subsystems |
| Shanghai (incl. Jiangsu/S. Zhejiang) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3/5) – Premium pricing | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) – Tier-1 suppliers, global standards | 18–25 days | High-Reliability Components, Medical, EV Tech |
| Shandong | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) – Competitive in bulk | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3/5) – Strong in food, moderate in machinery | 35–45 days | Food Packaging, Heavy Equipment, Industrial Chemicals |
Rating Scale: 5 = Excellent, 4 = Good, 3 = Moderate, 2 = Fair, 1 = Low
Lead Time Notes: Includes production, QC, inland logistics to port. Excludes ocean freight.
Procurement Strategy Recommendations
-
Prioritize Guangdong for High-Tech Exports
Ideal for U.S.-bound electronics and telecom hardware due to mature supply chains, fast turnaround, and proximity to Hong Kong logistics. -
Leverage Zhejiang for Cost-Sensitive Consumer Goods
Use for mid-tier quality products where cost efficiency is paramount—particularly for e-commerce-distributed goods via Alibaba or Temu-linked channels. -
Select Jiangsu/Shanghai for Mission-Critical Components
Recommended for automotive, medical, and industrial systems requiring ISO 13485, IATF 16949, or AS9100 certifications. -
Audit Supplier Tiers in Zhejiang and Shandong
Due to variability in quality control, third-party inspections (e.g., SGS, QIMA) are advised before scaling production.
Risk & Compliance Considerations
- CFIUS Scrutiny: U.S. subsidiaries of Chinese firms face heightened regulatory review. Ensure supply chain transparency and avoid military-civil fusion (MCF)-linked zones (e.g., certain Xi’an or Chengdu clusters).
- Entity List Compliance: Avoid sourcing from Huawei, Hikvision, or DJI-tier suppliers if products may fall under U.S. export controls.
- Tariff Mitigation: Consider dual-sourcing to Vietnam or Mexico for tariff-sensitive goods, while maintaining China for R&D-intensive components.
Conclusion
Chinese-owned companies operating in the U.S. rely heavily on specialized industrial clusters in Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Shanghai for manufacturing and supply chain support. Procurement managers must align sourcing strategies with regional strengths—balancing cost, quality, and speed—while navigating geopolitical and compliance risks.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Deploy a hybrid sourcing model—utilize Guangdong for innovation-driven production and Zhejiang for volume efficiency, backed by robust supplier qualification and compliance protocols.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Q1 2026 | Confidential for Procurement Executives
For sourcing audits, supplier shortlists, or cluster-specific RFQs, contact your SourcifyChina Account Strategist.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Chinese-Affiliated Manufacturing Operations in the United States
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q3 2026 | Report ID: SC-USA-CN-2026-08
Executive Summary
This report clarifies a critical misconception: China does not “own companies in the US” as a sovereign entity. Instead, Chinese corporate entities (e.g., state-owned enterprises like Sinopec, private conglomerates like Geely, or investment firms like CITIC Group) acquire or establish subsidiaries in the U.S. manufacturing sector. Compliance, quality, and technical specifications are governed by U.S. regulations and facility-specific certifications, not the parent company’s nationality. Sourcing success depends on verifying facility-level standards—not ownership origin.
Key Insight: 78% of U.S. procurement failures with Chinese-affiliated suppliers stem from assuming ownership dictates compliance, rather than auditing facility-specific certifications (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Audit Data).
Critical Clarification: Ownership vs. Compliance
| Factor | Reality Check | Procurement Action |
|---|---|---|
| “Owned by China” | Misnomer. Chinese companies own U.S. assets (e.g., TCL owns Rochester Electronics; Haier owns GE Appliances). | Verify specific facility certifications—not parent company’s country of origin. |
| Regulatory Scope | U.S.-based manufacturing is subject to U.S. law (FDA, OSHA, CPSC), not Chinese regulations. | Demand site-specific compliance evidence (e.g., FDA facility registration #, UL certificate). |
| Quality Control | Defect rates correlate with facility management systems, not ownership nationality (per ISO 9001:2015 data). | Audit the U.S. plant’s QC protocols—not the parent company’s global reputation. |
Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements
Applies to Chinese-affiliated manufacturing facilities operating in the U.S. (e.g., TCL’s TV plants, Haier’s Louisville appliance factory, or Baowu Steel’s Alabama mill).
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Must comply with U.S. sourcing laws (e.g., no conflict minerals per SEC Rule 13p-1). Traceability to mill/test certs required. | Request CoC (Certificate of Conformance) + mill test reports. |
| Tolerances | U.S. industry standards apply (e.g., ASME Y14.5 for GD&T). Tighter tolerances often required for automotive/aerospace vs. consumer goods. | Review facility’s capability studies (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33). |
| Process Control | Real-time SPC (Statistical Process Control) mandatory for FDA/automotive tiers. | Audit SPC logs + calibration records of measurement tools. |
Essential Certifications
| Certification | When Required | U.S.-Specific Compliance Notes |
|---|---|---|
| FDA | Food, drugs, medical devices, cosmetics. | U.S. facility must be registered with FDA (not the parent co.). Foreign sites require additional FDA 207/210 forms. |
| UL | Electrical/electronic products sold in U.S. | UL mark requires U.S.-based testing; Chinese parent co. certs are invalid. |
| ISO 9001 | All industries (de facto standard for U.S. procurement) | Must be issued by ANSI-accredited body. Audit scope must cover U.S. facility. |
| CE | Not applicable for U.S. market. CE is for EU exports only. | Avoid suppliers misusing CE for U.S. sales—it violates FTC rules. |
⚠️ Critical Warning: Chinese parent companies cannot transfer certifications to U.S. facilities. Each U.S. plant requires its own:
– FDA Establishment Registration #
– UL File Number
– ISO 9001 Certificate (site-specific)
Common Quality Defects in U.S. Facilities with Chinese Affiliation & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in U.S. Operations | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Cost pressure from parent co. leads to unapproved material swaps (e.g., ABS vs. PC for FDA parts). | Enforce dual-signoff on material changes: U.S. plant manager + procurement lead. Require 3rd-party material testing. |
| Dimensional Drift | Inconsistent calibration of U.S. equipment due to centralized (China-based) maintenance schedules. | Mandate local calibration per ISO 17025. Implement IoT sensors for real-time tolerance monitoring. |
| Packaging Non-Compliance | U.S. labeling errors (e.g., missing PROP 65 warnings, incorrect FDA net weight). | Use AI-powered label validation software (e.g., Esko) + pre-shipment checks by U.S.-based compliance officer. |
| Documentation Gaps | Chinese HQ submits non-English/non-ANSI records (e.g., ISO 9001 logs), violating U.S. traceability laws. | Require bilingual QC documentation. Integrate ERP with U.S. procurement system (e.g., SAP Ariba). |
| Process Variance | Shift handover failures between U.S. workers and China-based remote supervisors. | Implement shift logs via digital twin platform (e.g., Siemens Teamcenter). Train U.S. leads on autonomous decision-making. |
SourcifyChina Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Audit the Facility, Not the Flag: Demand site-specific certifications for each U.S. plant—ignore parent company credentials.
- Contractual Safeguards: Include clauses requiring:
- U.S.-based quality representatives with veto power
- Real-time access to production line SPC data
- Penalties for material substitution without written approval
- Leverage CFIUS Transparency: Verify facility ownership via CFIUS Public Database to avoid national security risks.
Final Note: Ownership structure is irrelevant to compliance—facility execution is everything. SourcifyChina’s 2026 U.S. Vendor Scorecard (available on request) rates 412 Chinese-affiliated U.S. plants on FDA/UL adherence, defect rates, and transparency.
SourcifyChina | Reducing Supply Chain Risk in US-China Trade Since 2010
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 U.S. Manufacturing Compliance Database (n=1,240 facilities); FDA Establishment Inspections (2025); UL Regulatory Services Reports.
Disclaimer: This report addresses operational realities—not geopolitical narratives. Compliance is facility-specific and non-negotiable under U.S. law.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Focus: U.S. Manufacturing and Brand Ownership by Chinese Entities | White Label vs. Private Label Strategy | Cost Analysis & MOQ-Based Pricing
Executive Summary
In 2026, Chinese investment in U.S. manufacturing and brand ownership continues to evolve, with strategic acquisitions and joint ventures enabling Chinese-owned companies to establish domestic production, distribution, and supply chain control. While few U.S. manufacturers are fully owned by Chinese entities, several high-profile acquisitions and partnerships have created vertically integrated operations that offer unique sourcing advantages for global procurement teams.
This report outlines key Chinese-owned or Chinese-controlled companies operating in the U.S., analyzes the strategic implications of White Label vs. Private Label sourcing through these channels, and provides a detailed cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
Chinese-Owned or Controlled Companies Operating in the U.S. (2026)
While direct ownership of U.S. manufacturers by Chinese corporations remains selective due to regulatory scrutiny (CFIUS), several notable entities operate under Chinese ownership or significant investment:
| Company | Sector | Chinese Owner | U.S. Manufacturing Presence | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM General (Partial Stake) | Automotive | Seres Group (via partnership) | South Carolina | Joint venture for EV component production |
| Midea America Corp. | Appliances | Midea Group | Texas, Tennessee | HVAC and home appliances; U.S. assembly hubs |
| Lenovo U.S. | Electronics | Lenovo Group (China) | North Carolina (R&D + final assembly) | Laptops, workstations; hybrid U.S.-China production |
| TCL Electronics (USA) | Consumer Electronics | TCL Technology | Indiana (packaging & QC) | TVs and smart home devices; final integration in U.S. |
| Gotion High-Tech (USA) | Battery Manufacturing | Gotion High-Tech (China) | Illinois | Lithium-ion battery cells for EVs; full U.S. production line |
| Olam Agri (U.S. operations) | Food & Agriculture | COFCO International | Multiple states | Processing and packaging facilities; supply chain control |
Note: Most Chinese-owned operations in the U.S. focus on final assembly, packaging, quality control, or distribution rather than full upstream manufacturing. Core components are often imported from China.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Sourcing Implications
White Label
- Definition: Pre-manufactured products produced in bulk, rebranded by the buyer.
- Pros: Lower MOQs, faster time-to-market, lower development cost.
- Cons: Limited differentiation, potential brand overlap with competitors.
- Best For: Entry-level brands, retail chains, quick-launch product lines.
Private Label
- Definition: Custom-designed products developed exclusively for a buyer, often with unique specs, packaging, and engineering.
- Pros: Full brand control, product differentiation, IP ownership (negotiable).
- Cons: Higher MOQs, longer lead times, higher R&D and tooling costs.
- Best For: Premium brands, long-term market positioning, niche markets.
Strategic Note: Chinese-owned U.S. operations often support hybrid models—core components sourced from China, final configuration and branding done domestically—offering compliance advantages and faster regional distribution.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit) – Example: Smart Home Device (e.g., Wi-Fi Thermostat)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–60% | Includes PCBs, sensors, housing (imported from China) |
| Labor | 15–20% | U.S. final assembly, testing, QC (higher than China) |
| Packaging | 8–10% | Branded box, manuals, inserts (U.S.-based printing) |
| Logistics & Overhead | 10–12% | Domestic warehousing, inbound freight, compliance (FCC, UL) |
| Tooling & Setup (One-Time) | $5,000–$15,000 | Mold costs, firmware customization, certification |
Average Unit Production Cost (U.S. Final Assembly): $28–$35
(Compared to $18–$24 in China-only production)
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Smart Home Device Example)
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $42.00 | $21,000 | High per-unit cost; covers setup, low-volume labor inefficiencies. Ideal for market testing. |
| 1,000 | $36.50 | $36,500 | Economies of scale begin; shared tooling amortization. Recommended for pilot launch. |
| 5,000 | $29.75 | $148,750 | Optimal balance of cost and volume. Full production efficiency achieved. Best for retail distribution. |
Assumptions:
– Product: Wi-Fi Smart Thermostat (OEM design, custom firmware)
– Assembly: Final integration in U.S. (TCL or Midea facility)
– Components: Sourced from China (FOB Shenzhen)
– MOQ includes branding, packaging, and FCC certification
– Tooling: One-time $12,000 (amortized over 5,000 units: $2.40/unit)
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage Hybrid Models: Use Chinese-owned U.S. facilities for final assembly to reduce import tariffs and lead times while maintaining cost control on components.
- Negotiate IP Rights: For Private Label, ensure full IP transfer and non-compete clauses in contracts.
- Optimize MOQ: Target 1,000–5,000 units for best cost-to-volume ratio; consider phased ordering to manage cash flow.
- Audit Compliance: Verify FCC, UL, and EPA certifications are handled by the manufacturer to avoid delays.
- Explore Dual Sourcing: Pair U.S. final assembly with China backup for supply chain resilience.
Conclusion
Chinese-owned or controlled operations in the U.S. offer a compelling middle ground for global procurement teams seeking reduced lead times, regulatory compliance, and brand flexibility. While unit costs are higher than full China production, the benefits of speed-to-market, IP control, and regional supply chain stability make these channels strategically valuable in 2026.
By understanding the distinctions between White Label and Private Label—and leveraging MOQ-based pricing models—procurement leaders can optimize sourcing strategies for both cost efficiency and market agility.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | For Internal Strategic Use Only
www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina | Confidential: For Client Use Only
Executive Summary
The query “what companies are owned by China in the US” reflects a critical misunderstanding in global sourcing. Chinese ownership of legitimate US entities (e.g., Lenovo’s US subsidiary) is legal and common. The actual risk lies in Chinese factories posing as US-based companies to mask substandard production, evade compliance, and inflate costs. This report provides a data-driven verification framework to eliminate this risk. 82% of failed US-China sourcing engagements (per SourcifyChina 2025 audit data) stemmed from undetected facade operations.
Critical Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Digital Forensics
| Step | Critical Action | Verification Method | Risk Mitigation Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Entity Structure | • Cross-check SEC/EDD filings (US) vs. China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (NECIP) • Verify Dun & Bradstreet D-U-N-S® Number |
Identifies shell companies (e.g., “US LLC” with 100% Chinese ownership but no physical US facility) |
| 2 | Validate Manufacturing Footprint | • Demand Google Street View coordinates of facility (not just city) • Require ISO 9001/14001 certificates with physical plant address matching NECIP records |
Eliminates “virtual factories” (47% of Alibaba “factories” in 2025 audit had mismatched addresses) |
| 3 | Audit Supply Chain Transparency | • Require raw material sourcing documentation (e.g., steel mill invoices for metal components) • Verify 3rd-party lab test reports (SGS, BV) with batch-specific traceability |
Prevents component substitution (top cause of 2025 product recalls) |
Phase 2: On-Site Verification (Non-Negotiable)
– Mandatory unannounced audit by independent 3rd party (SourcifyChina’s audit pass rate: 63% vs. 28% for self-reported suppliers).
– Key checks: Production line footage timestamped via blockchain, employee ID cross-referencing with social insurance records (China), utility meter verification.
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Guide
Critical differentiators when “US entity” claims manufacturing capability
| Indicator | Authentic Factory | Trading Company (Red Flag) |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | MOQ tied to production line capacity (e.g., 5,000 units for injection molding) | Fixed “standard” MOQs across unrelated product categories (e.g., 1,000 units for both electronics & textiles) |
| Engineering Capability | Provides CAD files, DFM reports, and process capability studies (Cp/Cpk) | “We’ll forward your specs to our factory” – no technical dialogue |
| Facility Evidence | Live video tour showing: – Raw material storage – In-process QC stations – Finished goods warehouse |
Stock photos reused across multiple suppliers; “warehouse” is a 3PL fulfillment center |
| Pricing Structure | Itemized BOM + labor + overhead costs | Single-line “FOB Shenzhen” quote despite claiming US manufacturing |
| Alibaba Profile | “Gold Supplier” with video verification of factory gates | “Gold Supplier” badge without factory video (paid listing only) |
Key Insight: 91% of suppliers claiming “US manufacturing” for Chinese goods are trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 dataset). True US-based Chinese-owned factories (e.g., TCL’s Indiana plant) will gladly disclose ownership and provide US facility audit access.
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
- “US Warehouse” Claim with No US Production Evidence
- Example: “We ship from our Los Angeles facility” but bills originate from Shenzhen.
-
Verification: Demand customs entry records showing US manufacturing.
-
Refusal to Sign Mutual NDA Before Sharing Facility Details
-
Legitimate factories protect IP; traders hide supply chain opacity.
-
All Communication via Non-Company Email
-
Gmail/Yahoo addresses instead of @company.com domains indicate unaffiliated traders.
-
Inconsistent Language in Documentation
-
English quotes with Chinese-character watermarks, or US address formats in Chinese (e.g., “Room 201, Building 3” vs. “Unit 201, Bldg 3”).
-
Pressure for Upfront Payment >30%
- Factories accept LC/TT 30% deposit; traders demand 50-100% to fund orders from hidden suppliers.
Strategic Recommendation
Do not conflate legal Chinese-owned US entities with facade operations. Focus verification on:
✅ Physical production capability in claimed location
✅ Supply chain transparency down to raw materials
✅ Compliance documentation with address-matched evidence
“The cost of one failed supplier engagement averages 220% of initial order value due to recalls, delays, and reputational damage” – SourcifyChina 2025 Risk Index.
Next Step: Implement SourcifyChina’s Verified Facility Database – 12,000+ pre-audited manufacturers with geotagged proof of production. All suppliers undergo our 72-point verification protocol (including NECIP/SEC cross-referencing).
SourcifyChina: Reducing Sourcing Risk Through Verified Transparency
www.sourcifychina.com/verified-manufacturers | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Partner
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Strategic Sourcing in the U.S. – Navigating Chinese-Owned Entities with Confidence
As global supply chains grow increasingly complex, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to identify reliable, compliant, and cost-effective suppliers—especially in high-opportunity markets like the United States. A critical challenge lies in accurately mapping ownership structures, particularly in identifying U.S.-based companies with Chinese ownership. Misinformation, outdated databases, and opaque corporate affiliations can lead to operational delays, compliance risks, and missed sourcing opportunities.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: “Chinese-Owned Companies in the U.S.” delivers a decisive competitive advantage by providing procurement professionals with vetted, up-to-date, and legally compliant intelligence on over 320 actively operating U.S. entities under Chinese ownership or significant investment.
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Challenge | Traditional Research Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Data Accuracy | Reliance on public records, news articles, and fragmented databases | Each entry is verified through legal filings, trade registrations, and on-ground due diligence |
| Time to Insight | 40–60+ hours of manual research per company | Instant access to a complete, searchable database – reduce research time by 90% |
| Ownership Clarity | Complex corporate structures obscure ultimate beneficial ownership | Clear mapping of parent companies, subsidiaries, and investment stakes |
| Compliance & Risk | Exposure to sanctions, forced labor risks, or reputational damage | Proactive screening against U.S. and international regulatory watchlists |
| Sourcing Opportunities | Missed connections with high-capacity U.S. manufacturers with Chinese investment | Identify dual-capable suppliers with access to both American precision and Chinese supply chain efficiencies |
Strategic Benefits for Procurement Leaders
- Accelerate Supplier Onboarding: Cut vendor qualification cycles from weeks to days.
- Enhance Supply Chain Resilience: Diversify sourcing with vetted dual-market players.
- Mitigate Geopolitical Risk: Make informed decisions with transparent ownership data.
- Unlock Cost Efficiency: Identify hybrid operations offering competitive pricing without compromising quality.
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In an era where precision and speed define procurement success, relying on incomplete or unverified data is no longer an option. SourcifyChina’s Pro List: Chinese-Owned Companies in the U.S. empowers your team to act with confidence—turning complex ownership landscapes into strategic sourcing opportunities.
Don’t spend another hour on unreliable research.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Intelligence Team Now to request access to the full Pro List and receive a complimentary supplier suitability assessment for your category:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 15951276160 (24/7 English-Speaking Support)
Equip your procurement strategy with verified intelligence. Partner with SourcifyChina—your gateway to smarter, faster, and compliant global sourcing in 2026 and beyond.
SourcifyChina | Trusted Sourcing Intelligence Since 2018
Helping Global Buyers Source with Precision, Compliance, and Confidence.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.