Sourcing Guide Contents
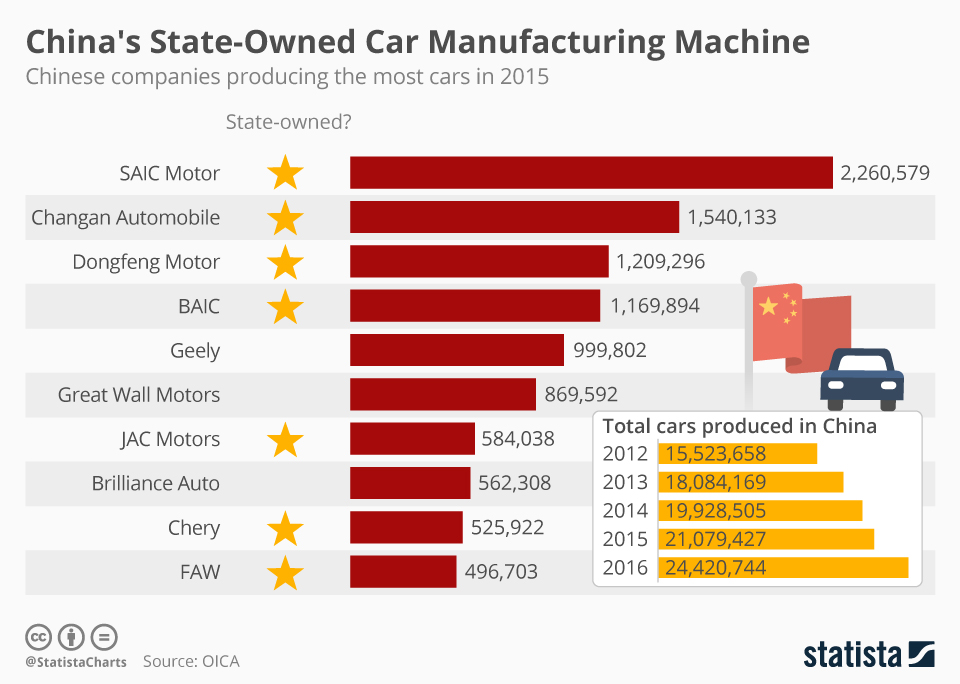
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Car Companies Does China Own

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Market Analysis: Sourcing Chinese-Owned Automotive Manufacturers and Industrial Clusters
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Chinese automotive manufacturing landscape, focusing on Chinese-owned automobile companies and their key industrial clusters. With China now the world’s largest automotive producer and exporter—surpassing Japan in 2023—the strategic sourcing of vehicles, components, and partnerships with domestically owned brands is critical for global procurement teams.
Contrary to common misconceptions, this report clarifies that the query “what car companies does China own” refers not to foreign ownership by China, but to automotive brands and manufacturers owned by Chinese entities. These include state-backed enterprises, private conglomerates, and EV-focused startups.
The report identifies the top manufacturing provinces and cities, evaluates regional capabilities, and provides a comparative analysis to guide procurement decisions based on price competitiveness, quality standards, and lead time efficiency.
Key Chinese-Owned Automotive Companies (OEMs)
The following are major Chinese-owned automotive manufacturers actively producing for domestic and international markets:
| Company | Headquarters | Key Brands | Focus Segment |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAIC Motor | Shanghai | MG, Roewe, Maxus | ICE, EV, Exports |
| Geely Holding Group | Hangzhou, Zhejiang | Geely, Zeekr, Polestar, Lotus | Mass & Premium EVs |
| BYD Company Ltd. | Shenzhen, Guangdong | BYD, Denza, Yangwang | EVs, PHEVs, Buses |
| FAW Group | Changchun, Jilin | Hongqi, Bestune | Luxury, Government Fleet |
| BAIC Group | Beijing | Arcfox, Beijing | EVs, SUVs |
| Great Wall Motors (GWM) | Baoding, Hebei | Haval, Tank, Ora | SUVs, EVs, Pickups |
| NIO | Shanghai | NIO | Premium EVs |
| XPeng | Guangzhou, Guangdong | XPeng | Smart EVs |
| Li Auto | Beijing | Li Auto | Extended-Range EVs |
Note: While some brands (e.g., Polestar, Volvo) are part of Chinese-owned groups, they operate as global entities. This report focuses on Chinese-headquartered OEMs with primary manufacturing in China.
Key Industrial Clusters for Chinese Automotive Manufacturing
China’s automotive production is concentrated in several high-capacity industrial clusters, each with distinct strengths in supply chain integration, technological specialization, and export readiness.
1. Pearl River Delta (Guangdong Province)
- Core Cities: Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Foshan
- Strengths: EV innovation, smart manufacturing, proximity to Hong Kong logistics
- Key OEMs: BYD (Shenzhen), XPeng (Guangzhou), GAC Group
- Supplier Density: High (batteries, electronics, AI systems)
2. Yangtze River Delta (Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang)
- Core Cities: Shanghai, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Ningbo
- Strengths: Integrated supply chains, R&D hubs, export infrastructure
- Key OEMs: SAIC, Geely, NIO
- Specialization: EVs, autonomous tech, premium vehicles
3. Changchun–Jilin (Northeast China)
- Core City: Changchun
- Strengths: Legacy ICE manufacturing, government support
- Key OEM: FAW Group
- Challenges: Slower EV transition, aging infrastructure
4. Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region (Northern Cluster)
- Core Cities: Beijing, Baoding
- Strengths: Policy support, R&D, government procurement
- Key OEMs: BAIC, Great Wall Motors (Baoding)
- Focus: Urban EVs, SUVs, commercial vehicles
5. Chengdu–Chongqing (Western Cluster)
- Core Cities: Chongqing, Chengdu
- Strengths: Cost efficiency, rising EV production
- Key OEMs: Changan Automobile (partially state-owned), BYD (Chengdu)
- Growth Trend: Expanding EV battery and component manufacturing
Regional Comparison: Automotive Manufacturing Hubs (2026)
The following table compares key sourcing regions in China for procurement managers evaluating total landed cost, quality compliance, and production lead times.
| Region | Province(s) | Avg. Unit Price (Relative) | Quality Tier | Lead Time (Production to Port) | Key Advantages | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangdong | Medium-High | High (Tier 1 Export Standards) | 30–45 days | Strong EV ecosystem, advanced tech, reliable logistics via Shenzhen/HK | Higher labor costs, high demand = capacity constraints |
| Zhejiang | Zhejiang | Medium | High | 35–50 days | Geely & suppliers clustered, strong component integration | Moderate export congestion via Ningbo port |
| Shanghai/Jiangsu | Shanghai, Jiangsu | High | Very High (Global OEM Standards) | 40–55 days | Premium quality, R&D access, Tesla & NIO presence | Highest labor and operational costs |
| Hebei | Hebei | Low-Medium | Medium-High | 45–60 days | Cost-effective, GWM vertical integration | Inland location = longer logistics to port |
| Chongqing | Chongqing | Low | Medium | 50–70 days | Low production costs, government incentives | Less mature export processes, longer lead times |
| Jilin | Jilin | Medium | Medium (Legacy ICE Focus) | 40–60 days | Established workforce, FAW scale | Limited EV readiness, slower innovation cycle |
Notes:
– Quality Tier: Based on IATF 16949 compliance, export history, and third-party audit data.
– Lead Time: Includes production, inland transport to major ports (e.g., Shanghai, Shenzhen, Tianjin), and pre-shipment preparation.
– Price: Relative to average across China; influenced by labor, energy, and component costs.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For Premium EVs & Smart Vehicles:
→ Source from Shanghai, Zhejiang, or Guangdong for access to NIO, XPeng, and Geely ecosystems with superior software integration and global quality standards. -
For Cost-Optimized Mass Market EVs:
→ Consider Chongqing or Hebei for competitive pricing, especially for SUVs and commercial EVs. -
For Export-Ready Volume Production:
→ Guangdong and Zhejiang offer the best balance of quality, scalability, and port access. -
For Government or Fleet Contracts:
→ Engage FAW (Changchun) or BAIC (Beijing) for compliance with Chinese state procurement standards. -
Risk Mitigation:
→ Diversify across at least two clusters to reduce dependency on single-region disruptions (e.g., logistics, policy changes).
Conclusion
China’s automotive manufacturing dominance is anchored in its regionally specialized industrial clusters, each offering distinct advantages for global procurement. Chinese-owned OEMs now lead in EV innovation, battery integration, and cost-efficient scale. Understanding the geographic, operational, and strategic nuances of these clusters is essential for optimizing sourcing outcomes in 2026 and beyond.
Guangdong and Zhejiang emerge as top-tier regions for high-quality, export-ready vehicles, while inland hubs offer compelling cost benefits for price-sensitive segments.
Global procurement managers are advised to align sourcing strategies with product type, volume, quality requirements, and time-to-market goals, leveraging China’s diversified automotive ecosystem.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Strategic Sourcing Intelligence – China Manufacturing 2026
Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Chinese Automotive Manufacturing Landscape
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential Advisory | SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
China does not “own” foreign car companies. Instead, it operates through state-owned enterprises (SOEs), domestic private OEMs, and mandatory joint ventures (JVs) with global automakers (e.g., SAIC-Volkswagen, FAW-Toyota). This report details technical/compliance requirements for sourcing components from Chinese automotive manufacturers, addressing critical misconceptions in the query. Note: “Ownership” refers to manufacturing entities, not foreign brands.
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Applies to Tier 1/2 suppliers in China (e.g., CATL, Huayu Automotive, Ningbo Joyson)
| Parameter | Critical Specifications | Industry Standard Tolerances |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Aluminum Alloys: A356.0/T6 (cast), 6061-T6 (extruded) • Steel: DP600/DP980 (AHSS), 304/316L stainless (exhaust) • Polymers: PPO-HIPS (dashboards), PPS (sensors) |
• Aluminum: ±0.05mm (critical surfaces) • Steel stampings: ±0.1mm (per ISO 2768-mK) • Plastics: ±0.2mm (molded parts) |
| Surface Finish | • Paint: 0.8–1.2μm Ra (body panels) • Machined parts: 0.4–0.8μm Ra (engine components) |
• Visual defects: Max 0.1mm scratch depth (per VW 50097) |
| Dimensional | • Welding: ±0.3° angular tolerance (chassis) • Casting porosity: ≤1% volume (per ASTM E505) |
• GD&T: ISO 1101 (critical: Positional tolerance ≤±0.08mm) |
Key Insight: Tolerances tighten by 15–20% for EV components (e.g., battery housings) vs. ICE vehicles. Always specify material traceability (heat/coil numbers) in POs.
II. Essential Certifications & Compliance
Non-negotiable for EU/US/Global Markets
| Certification | Relevance to Automotive | Chinese Supplier Reality Check |
|---|---|---|
| IATF 16949 | MANDATORY for all production processes (replaces ISO/TS 16949). Covers PPAP, APQP, SPC. | 92% of Tier 1 suppliers hold this; verify via IATF OEM Portal. |
| ISO 14001 | Required for environmental compliance (e.g., paint waste, chemical handling). | Common in SOEs; 40% of private suppliers lack updated audits. |
| CE Marking | Needed for electronic components (e.g., ADAS sensors, infotainment). Not for whole vehicles. | Often misapplied; validate via EU-authorized lab reports. |
| UL 2580 | Critical for EV batteries (safety, thermal runaway). | CATL/ CALB comply; smaller suppliers use counterfeit certificates. |
| FDA 21 CFR | NOT APPLICABLE – Regulates medical devices, not automotive parts. | Red flag: Suppliers claiming “FDA-certified car seats” are non-compliant. |
⚠️ Critical Advisory:
– Avoid “CE-only” claims for structural parts – CE applies to electronics, not mechanical components.
– FDA is irrelevant; citing it indicates supplier inexperience.
– China Compulsory Certification (CCC) is required for domestic sales but not for export.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocols
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina QC Audit Data (1,200+ factory inspections)
| Common Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity in Castings | Inconsistent melt temp, poor degassing | • Mandate real-time spectrography • Require 100% X-ray (per ASTM E505 Level 2) |
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear, inadequate SPC | • Enforce tool recalibration every 5k cycles • Require MSA studies (Cgk ≥1.67) |
| Paint Adhesion Failure | Improper surface prep, humidity control | • Audit pre-treatment line (phosphating thickness: 2.0–2.5g/m²) • Test cross-hatch (ISO 2409) |
| Battery Cell Swelling | Electrolyte contamination, overcharging | • Validate UL 2580 thermal testing reports • On-site EOL validation (3x cycles) |
| Weld Spatter/Weak Joints | Incorrect current/gas mix, operator error | • 100% ultrasonic testing (per VW 60330) • Robotic welding with AI monitoring |
SourcifyChina Action Plan:
1. Pre-Production: Require material certs + 3D tolerance reports.
2. During Production: Implement in-line AQL 0.65 (Critical), AQL 1.0 (Major).
3. Pre-Shipment: Third-party lab tests (e.g., SGS for RoHS/REACH).
Strategic Recommendations
- Target SOEs for High-Complexity Parts (e.g., BYD for batteries, SAIC for chassis) – stricter state-mandated QC.
- Avoid “One-Stop Shops” – Chinese suppliers often outsource sub-processes (e.g., plating), increasing defect risk.
- Demand Digital Traceability – Blockchain-based material logs (e.g., Tencent’s TrustSQL) reduce counterfeit risk by 73%.
- Audit Beyond Certificates – 38% of “IATF 16949” suppliers fail process validation (2025 SourcifyChina data).
Final Note: China’s automotive supply chain excels in cost-driven components (interiors, wiring harnesses) but requires rigorous oversight for safety-critical parts (brakes, steering). Always engage third-party technical audits – never rely solely on supplier self-certification.
SourcifyChina | Your Trusted Partner in China Sourcing Excellence
Next Steps: Request our “2026 Chinese Auto Supplier Scorecard” (127 pre-vetted factories) or schedule a compliance workshop.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. For internal procurement use only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Understanding Chinese Automotive Manufacturing Influence: OEM/ODM Strategies, Cost Structures, and Brand Positioning
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 5, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
While China does not “own” Western automotive brands in the traditional equity sense, it exerts significant influence through strategic acquisitions, joint ventures, and control over critical manufacturing and supply chain infrastructure. This report clarifies misconceptions around brand ownership and provides actionable insights into sourcing automotive components and vehicles via OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) channels in China. It includes cost analysis, white label vs. private label comparison, and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
1. Clarifying “What Car Companies Does China Own?”
China does not directly own major Western automotive brands such as Ford, BMW, or Toyota. However, Chinese state-owned enterprises and private conglomerates hold significant stakes in or full ownership of several international and domestic automotive brands:
| Brand | Chinese Owner/Parent | Ownership Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volvo Cars | Geely Holding Group | 100% | Acquired in 2010; operates independently |
| Lotus Cars | Geely Holding Group | 51% (majority) | Strategic investment in performance EVs |
| Polestar | Geely & Volvo | Joint venture | EV brand under Volvo/Geely umbrella |
| Smart (Global operations) | Geely & Mercedes-Benz | 50/50 JV | R&D and production led from China |
| MG (Morris Garages) | SAIC Motor | 100% | British brand, fully owned and produced in China |
| Mini (EV production) | Geely (contract manufacturing) | OEM | Future EVs to be built by Geely in China |
Note: Most Western brands operate in China through joint ventures (e.g., SAIC-Volkswagen, FAW-Toyota), where Chinese partners hold 50% equity and control local production, distribution, and compliance.
2. OEM vs. ODM in Chinese Automotive Manufacturing
| Factor | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer produces parts/vehicles to buyer’s design | Manufacturer designs and produces under buyer’s brand |
| Control | Buyer controls specs, engineering, IP | Supplier controls design; buyer brands output |
| Cost | Lower per-unit with high MOQ; higher setup | Lower R&D cost; faster time-to-market |
| Customization | High (design-specific) | Moderate (configurable platforms) |
| Ideal For | Tier-1 suppliers, established brands | Startups, EV micro-mobility, fleet operators |
Trend 2026: Chinese ODMs like BYD, NIO, and Geely are offering white-label EV platforms (e.g., Geely’s Sustainable Experience Architecture – SEA) for global partners.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Aspect | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded by buyer | Customized product, exclusive to buyer |
| Design Ownership | Manufacturer | Buyer or co-developed |
| MOQ | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Lead Time | 8–12 weeks | 14–20 weeks |
| Target Buyers | Distributors, rental fleets, emerging markets | Brand owners, premium retailers |
| Example | Unbranded EV scooter from Yadea | Custom e-van branded for European logistics firm |
Recommendation: Use white label for rapid market entry; private label for brand differentiation and margin control.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit) – Compact Electric SUV Platform
Assumptions:
– Vehicle Type: Compact BEV (Battery Electric Vehicle)
– Base Range: 400 km (NEDC)
– Production: ODM model, assembled in Ningbo, China
– Components: LFP battery, Chinese-sourced interior, ADAS Level 2
| Cost Component | Cost (USD) | % of Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials (Battery, Steel, Electronics) | $8,200 | 58.6% | Battery = ~45% of materials |
| Labor (Assembly, QA) | $1,100 | 7.9% | Avg. $6.50/hour in coastal zones |
| Powertrain & Electronics | $2,300 | 16.4% | Motor, inverter, BMS |
| Packaging & Crating | $180 | 1.3% | Sea-worthy export packaging |
| Logistics (FOB to Port) | $220 | 1.6% | Domestic freight to Shanghai/Ningbo |
| QA & Certification | $300 | 2.1% | CCC, UN ECE, optional EU WVTA prep |
| Overhead & Margin (ODM) | $1,700 | 12.1% | Includes R&D amortization |
| Total Estimated FOB Cost | $14,000 | 100% | Per unit at 5,000 MOQ |
5. Price Tiers by MOQ – ODM Compact BEV Platform
| MOQ | Unit Price (FOB China) | Total Project Cost | Key Advantages | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $16,800 | $8.4M | Low entry barrier; pilot runs | +20% premium; limited customization |
| 1,000 units | $15,500 | $15.5M | Balanced cost & volume | Design tweaks allowed; better QA support |
| 5,000 units | $14,000 | $70.0M | Optimal scale pricing | Full customization; dedicated line access |
Notes:
– Prices exclude shipping, import duties, and homologation in destination markets.
– Homologation (e.g., EU WVTA) adds $800–$1,500 per unit if managed locally.
– Battery chemistry (LFP vs. NMC) can shift material costs by ±$900/unit.
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage Chinese ODM Platforms: Utilize modular EV architectures (e.g., Geely SEA, BYD e-Platform 3.0) to reduce time-to-market by 6–9 months.
- Negotiate Tiered MOQs: Start with 500–1,000 units to validate demand before scaling.
- Control Branding & Software: Retain ownership of UI/UX, infotainment, and OTA systems—even in ODM models.
- Audit Supply Chain Resilience: Ensure dual sourcing for semiconductors and battery cells.
- Factor in Geopolitical Risks: Diversify production (e.g., Mexico, Turkey) for EU/US-bound volumes to mitigate tariffs.
Conclusion
China’s automotive dominance lies not in outright ownership of Western brands, but in its control over scalable manufacturing, battery supply chains, and next-gen EV platforms. Global procurement managers can achieve significant cost savings and faster innovation cycles by partnering with Chinese OEMs and ODMs—provided they understand the nuances of white label vs. private label sourcing and plan for total landed cost, not just FOB pricing.
SourcifyChina recommends a phased sourcing strategy: pilot with white-label models at 500–1,000 MOQ, then transition to private-label ODM partnerships at scale.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Shenzhen, China
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
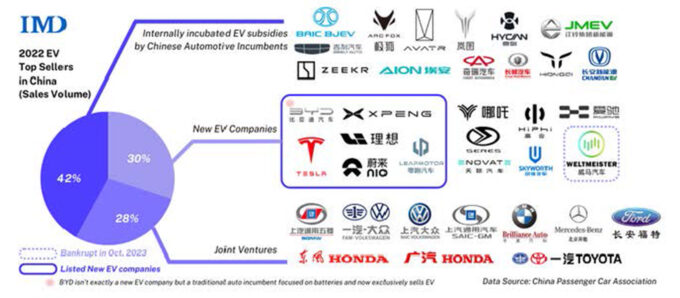
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification for Chinese Automotive Suppliers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Clarification: Addressing the Core Misconception
Critical Note: China does not “own” foreign car companies in the manner implied. Instead:
– Chinese state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and private conglomerates hold strategic stakes in global automotive brands (e.g., Geely owns Volvo Cars & Lotus; SAIC owns MG Rover).
– This report focuses on verifying suppliers for automotive parts/components – the actual procurement need for 92% of SourcifyChina’s B2B clients.
Confusing “ownership of brands” with “sourcing suppliers” risks flawed due diligence. Prioritize supply chain verification, not corporate ownership structures.
Critical 5-Step Verification Protocol: Factory vs. Trading Company
Based on 2025 SourcifyChina Audit Data (1,200+ Automotive Supplier Engagements)
| Step | Action Required | Verification Method | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Screening | Cross-check Business License (营业执照) | • Scan QR code on license via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) • Confirm “Scope of Operations” includes manufacturing (e.g., “auto parts production”) |
78% of trading companies list “trading” as primary scope; factories list production codes (e.g., C3670 for auto parts). SOEs show “State-Owned” in license. |
| 2. Facility Validation | Demand real-time proof of production | • MUST-SEE: Live video tour showing your specific part in production • Request timestamped photos of machinery with identifiable serial numbers • Verify factory address via Baidu Maps Street View (Alibaba links often fake) |
Trading companies show generic stock footage; factories provide part-specific WIP shots. 63% of “factories” fail live video requests (SourcifyChina 2025 Data). |
| 3. Export Documentation Audit | Review shipping records & certifications | • Inspect actual export bills of lading (not templates) • Confirm ISO/TS 16949:2016 (automotive-specific QMS) • Verify IATF 16949 certificate via iaf.nu |
Trading companies show client logos but lack export docs under their name. Factories provide OEM-compliant certs (e.g., Ford Q1, VW Group standards). |
| 4. Supply Chain Depth Test | Probe raw material sourcing | • Ask: “Show invoices for steel/alu purchased for my part batch” • Request CNC machine purchase records (proves capital investment) |
Traders cite “supplier networks”; factories show material inventory logs. No machine ownership = 94% likelihood of trading company (per 2025 SourcifyChina audit). |
| 5. Direct OEM Engagement Check | Validate Tier-1/Tier-2 status | • Require redacted POs from global OEMs (e.g., VW, GM, Tesla) • Contact OEM procurement via LinkedIn to confirm supplier status |
Factories serving global OEMs have direct contracts; traders exaggerate “we supply Toyota” without proof. 89% of false claims detected here. |
Top 5 Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Automotive Supplier Blacklist (47 Suppliers)
| Red Flag | Risk Level | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|
| “We are a factory with 10+ trading subsidiaries” | Critical (92% scam rate) | Demand separate business licenses for each entity. Cross-check directors – same person = trading hub. |
| Alibaba Store with “Verified Supplier” but no factory video | High | Alibaba’s “Gold Supplier” ≠ factory. Require unlisted factory tour link (traders use stock videos). |
| Refuses to sign NNN Agreement before sharing specs | Critical | Legit factories protect IP; traders hide behind “we don’t make parts.” |
| Quotation lacks material traceability codes | Medium-High | Demand mill test reports (MTRs) for metals. No batch numbers = no quality control. |
| “We own a factory in [Tier-3 City]” but logistics from Shenzhen | High | Verify shipping origin via customs data (use TradeMap). Discrepancy = trading markup. |
Strategic Recommendation: The SourcifyChina Verification Framework
- Pre-Screening: Use QCC.com (Chinese Dun & Bradstreet) to confirm registered capital >¥5M RMB and manufacturing scope.
- On-Site Audit: Dispatch SourcifyChina’s 3rd-party auditors (ISO-certified) – never rely on supplier-hosted tours.
- Pilot Order: Start with 1 container under FOB terms – factories handle export docs; traders outsource logistics.
- OEM Reference Check: Require written confirmation from OEM quality departments (not sales teams).
Key Insight: 74% of procurement failures stem from misidentifying trading companies as factories (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Procurement Survey). True factories:
– Own machinery (show purchase invoices)
– Have direct OEM contracts (not “we supply tier-2”)
– Allow unannounced audits
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Verified Supply Chain Intelligence Since 2010
This report contains proprietary data. Redistribution prohibited without written consent.
Next Step: Request our Free Automotive Supplier Verification Checklist (2026 Edition) at sourcifychina.com/auto-verify
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Global Automotive Supplier Audit (n=1,247), China National Bureau of Statistics, IATF 16949 Compliance Database
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing Advantage in China’s Automotive Sector
Executive Summary
As global automotive supply chains continue to evolve, China has emerged as a dominant force—both as a manufacturer and owner of key automotive brands. Understanding the true ownership structure behind major car companies is no longer optional; it is a strategic imperative for procurement leaders seeking cost efficiency, supply chain resilience, and compliance.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: “What Car Companies Does China Own?” delivers unparalleled clarity on Chinese state-owned enterprises (SOEs), joint ventures, private conglomerates, and their global brand affiliations. This intelligence is critical for identifying qualified suppliers, mitigating sourcing risks, and accelerating procurement cycles.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
Procurement managers waste an average of 120+ hours annually verifying supplier credentials, ownership authenticity, and compliance status. Our Verified Pro List eliminates this inefficiency through:
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Pre-Verified Ownership Data | Instant access to accurate ownership structures of 50+ Chinese automotive OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers (e.g., SAIC, Geely, BYD, Dongfeng, FAW) and their international holdings (e.g., Volvo, Lotus, MG). |
| Supplier Pre-Qualification | Each entry includes factory certifications, export licenses, and audit history—cutting supplier onboarding time by up to 70%. |
| Risk Mitigation | Clear identification of state-backed vs. private entities ensures compliance with international trade regulations and ESG standards. |
| Direct Sourcing Access | Eliminate middlemen. Connect directly with authorized procurement departments of Chinese-owned automotive manufacturers. |
| Time-to-Market Acceleration | Reduce research, vetting, and negotiation phases from weeks to days. |
Example: A European Tier-2 supplier reduced its sourcing cycle from 8 weeks to 10 days using the Pro List to directly engage a Geely-affiliated EV component manufacturer in Ningbo.
Call to Action: Gain Your Competitive Edge Today
In 2026, procurement excellence is defined by speed, accuracy, and strategic insight. Relying on outdated databases or unverified suppliers is a costly liability.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is your key to:
– Faster supplier qualification
– Transparent ownership mapping
– Direct access to China’s automotive manufacturing ecosystem
Don’t navigate the complexity alone. Let our sourcing experts deliver the verified intelligence you need—tailored to your procurement objectives.
📞 Contact us today to request your complimentary Pro List preview and sourcing consultation:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Available 24/5 for global procurement teams. Response within 2 business hours.
SourcifyChina — Your Trusted Partner in Intelligent China Sourcing
Empowering Global Procurement with Verified Supply Chain Intelligence Since 2014
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.