Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Car Companies Are Owned By China
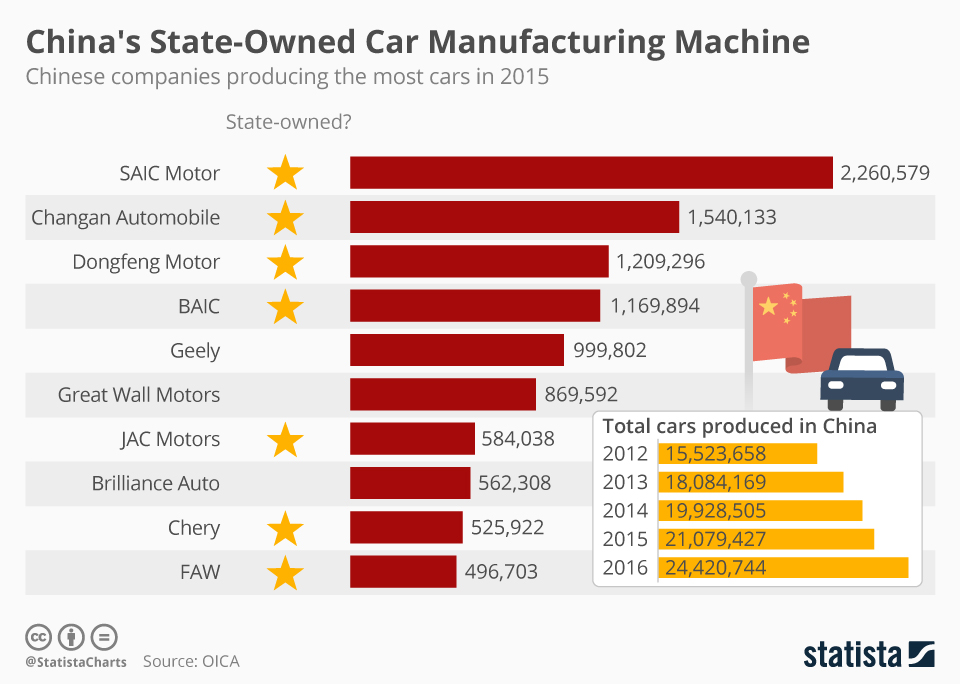
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Sourcing of Chinese Automotive OEMs & Manufacturing Clusters
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Confidentiality Level: Public Distribution (General Industry Insights)
Executive Summary
This report clarifies a critical misconception: no major car companies are “owned by China” as a sovereign state. Instead, China hosts a dynamic ecosystem of Chinese-owned automotive OEMs (privately held or state-influenced enterprises) and global joint ventures (e.g., SAIC-GM, FAW-Volkswagen). Over 95% of China’s automotive output is produced by entities under Chinese corporate ownership (e.g., BYD, Geely, SAIC Motor), though foreign brands retain significant JV stakes. This analysis identifies key manufacturing clusters for sourcing components from Chinese-owned OEMs, focusing on EV/battery leadership, supply chain maturity, and regional competitiveness.
Key Insight for Procurement Managers: Prioritize clusters aligned with your product type (EV vs. ICE) and quality tier. Guangdong dominates premium EVs; Zhejiang offers cost-efficient mass-market solutions; Jiangsu excels in integrated supply chains. Geopolitical risks (e.g., EU/US tariffs on Chinese EVs) necessitate dual-sourcing strategies.
Clarification: Ownership Structure of Chinese Automotive OEMs
| Ownership Type | Examples | % of China’s Auto Output | Procurement Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Privately Owned OEMs | BYD, Geely, NIO, XPeng | 45% | Agile innovation; competitive pricing; flexible MOQs. |
| State-Owned (SOEs) | SAIC Motor, FAW Group, Dongfeng | 40% | Scale-driven pricing; complex approvals; JV dependencies. |
| Foreign JVs | SAIC-VW, GAC-Toyota | 15% | Not Chinese-owned; subject to foreign brand standards. |
Note: “Chinese-owned” refers to entities controlled by Chinese shareholders (e.g., BYD is privately held; SAIC is state-owned). No automotive OEM is directly owned by the Chinese government as a national asset.
Key Industrial Clusters for Sourcing Chinese-Owned OEMs
China’s automotive manufacturing is concentrated in 5 core clusters, each specializing in distinct segments:
- Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta)
- Hub Cities: Shenzhen (BYD HQ), Guangzhou (GAC Group)
- Specialization: Premium EVs, batteries (CATL), smart cockpit tech.
- OEMs: BYD (100% Chinese-owned), GAC Aion, XPeng.
-
Strength: Deepest EV ecosystem; strongest R&D highest export readiness.
-
Zhejiang Province (Yangtze Delta)
- Hub Cities: Hangzhou (Geely HQ), Ningbo, Wenzhou
- Specialization: Mass-market ICE/EVs, interiors, low-cost electronics.
- OEMs: Geely (100% Chinese-owned), Zeekr, Lotus (Geely-owned).
-
Strength: SME supplier density; lowest logistics costs; Geely’s global supply chain.
-
Jiangsu Province (Yangtze Delta)
- Hub Cities: Nanjing (SAIC Motor), Changshu, Yangzhou
- Specialization: Integrated ICE/EV platforms, transmissions, chassis.
- OEMs: SAIC Motor (state-owned; MG, Roewe), joint ventures.
-
Strength: Most mature Tier 1 supplier base; highest quality consistency.
-
Chongqing Municipality
- Hub Cities: Chongqing (Changan HQ)
- Specialization: Budget ICE vehicles, commercial vehicles, EV entry models.
- OEMs: Changan Automobile (state-owned; Avatr, Deepal).
-
Strength: Lowest labor costs; emerging EV battery cluster.
-
Hubei Province (Central China)
- Hub Cities: Wuhan (Dongfeng HQ)
- Specialization: Commercial vehicles, mid-tier ICE, emerging EVs.
- OEMs: Dongfeng Motor (state-owned; Voyah, M-Hero).
- Strength: Central logistics hub; government subsidies for new-energy vehicles.
Regional Cluster Comparison: Sourcing Performance Analysis (2026)
| Region | Price Competitiveness (1-5★) | Quality Consistency (1-5★) | Avg. Lead Time (Weeks) | Best For | Key Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ★★★☆☆ (3.5) | ★★★★★ (5.0) | 8-10 | Premium EV components, batteries, AI systems | Highest labor costs; US/EU tariff exposure |
| Zhejiang | ★★★★☆ (4.5) | ★★★★☆ (4.0) | 6-8 | Cost-sensitive interiors, electronics, ICE parts | IP protection gaps in SME suppliers |
| Jiangsu | ★★★☆☆ (3.0) | ★★★★★ (5.0) | 7-9 | High-precision powertrain, safety-critical parts | SOE bureaucracy; slower innovation cycles |
| Chongqing | ★★★★★ (5.0) | ★★★☆☆ (3.0) | 10-12 | Budget chassis, commercial vehicle parts | Lower engineering talent density |
| Hubei | ★★★★☆ (4.0) | ★★★☆☆ (3.5) | 9-11 | Commercial EVs, emerging battery components | Less mature EV ecosystem |
Scoring Methodology:
– Price: Based on EXW component costs vs. global benchmarks (5★ = lowest cost).
– Quality: IATF 16949 compliance rate, defect rates (PPM), and audit pass rates.
– Lead Time: From PO confirmation to EXW shipment (includes tooling for new parts).
Strategic Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- EV Sourcing: Prioritize Guangdong for battery/EV systems (BYD’s supply chain) but diversify to Jiangsu for quality-critical parts to mitigate tariff risks.
- Cost Optimization: Leverage Zhejiang’s SME network for non-safety components (e.g., infotainment housings) but enforce strict IP clauses.
- Risk Mitigation: Avoid single-cluster dependency. Pair Guangdong (premium EVs) with Chongqing (budget ICE) for balanced cost/resilience.
- Compliance Focus: Target SOE clusters (Jiangsu, Hubei) for regulated markets (EU/US) due to stronger ESG reporting.
- Future-Proofing: Monitor Chongqing and Hubei for emerging EV battery hubs – costs are 12-18% below Guangdong by 2026.
SourcifyChina Advisory: “Chinese-owned” OEM sourcing requires vetting specific corporate structures, not national ownership. BYD (private) and SAIC (state-owned) operate under vastly different procurement protocols. Always confirm OEM ownership and cluster capabilities at the component tier – not just the brand level.
Appendix: Top 10 Chinese-Owned OEMs by 2026 Production Volume
1. BYD (Private) | 2. Geely (Private) | 3. SAIC Motor (SOE) | 4. Changan (SOE) | 5. NIO (Private)
6. XPeng (Private) | 7. Dongfeng (SOE) | 8. GAC Group (SOE) | 9. Great Wall (Private) | 10. Li Auto (Private)
Data Source: China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), SourcifyChina OEM Database (Q4 2025)
Next Steps: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Cluster Risk Dashboard for real-time tariff alerts and supplier pre-vetted in target regions. Contact your SourcifyChina Account Manager for a tailored sourcing roadmap.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical and Compliance Analysis of Chinese Automotive Manufacturers and Their Global Brands
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive overview of Chinese-owned automotive companies, focusing on technical specifications, quality control parameters, and compliance certifications relevant to global procurement operations. As China continues to expand its influence in the global automotive sector—through acquisition, joint ventures, and organic growth—procurement professionals must understand both ownership structures and sourcing requirements.
Note: The phrase “what car companies are owned by china” is interpreted as identifying automotive brands under Chinese ownership, including wholly owned enterprises, majority stakes, and controlling joint ventures.
Chinese-Owned Automotive Companies: Key Global Brands
| Chinese Parent Company | Acquired/Owned Brand(s) | Country of Origin (Brand) | Vehicle Type Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geely Holding Group | Volvo Cars, Polestar, Lotus, LEVC | Sweden, UK | Premium Sedans, EVs, Sports Cars, Commercial |
| SAIC Motor | MG (Morris Garages) | UK | Mass-market EVs, SUVs |
| Great Wall Motor (GWM) | None (organic brands: Haval, Tank, Ora) | China | SUVs, Pickup Trucks, EVs |
| BYD Company Ltd. | None (organic: BYD, Denza, Yangwang) | China | EVs, Buses, Battery Tech |
| NIO Inc. | NIO (self-developed) | China | Premium EVs |
| Xpeng Motors | Xpeng (self-developed) | China | Smart EVs, Tech-Driven |
| FAW Group | JAC Motors (joint venture with VW) | China | Commercial, Passenger, EVs |
Note: Chinese OEMs increasingly influence global supply chains through EV technology, battery IP (e.g., Blade Battery), and smart driving systems.
Key Quality Parameters for Sourcing from Chinese Automotive Suppliers
Procurement managers must enforce strict quality benchmarks when sourcing components or finished vehicles from Chinese manufacturers.
1. Materials Specifications
| Material Type | Standard Requirement | Common Alternatives | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Strength Steel | ≥ 980 MPa Tensile Strength | AHSS (Advanced High-Strength Steel) | Used in chassis, crumple zones |
| Aluminum Alloys | 6000 or 7000 series | A356, A380 (for cast parts) | Lightweight body components |
| Battery Cells | NMC 811 or LFP (LiFePO₄) | Solid-state (pilot phase) | LFP preferred for safety & cycle life |
| Plastics (Interior) | Flame-retardant, low-VOC | PP, PC/ABS blends | Must meet FMVSS 302 |
| Rubber (Seals) | EPDM or Silicone | Nitrile (NBR) | Temperature range: -40°C to +150°C |
2. Dimensional Tolerances
| Component Type | Typical Tolerance Range | Measurement Method | Critical Zones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body Panels | ±0.3 mm | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) | Door gaps, panel alignment |
| Powertrain Mounts | ±0.1 mm | Laser Scanning | Vibration isolation |
| EV Battery Brackets | ±0.2 mm | Optical Inspection | Structural integrity |
| Wiring Harnesses | ±2 mm (length) | Digital Caliper | Connector fitment |
| Brake Components | ±0.05 mm (diameter) | Micrometer | Safety-critical |
Essential Compliance Certifications
Global procurement must verify the following certifications for market access and safety compliance:
| Certification | Scope | Relevance to Chinese Automotive OEMs |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | Mandatory baseline for all Tier 1 suppliers |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive QMS | Required for component manufacturers (replaces ISO/TS 16949) |
| CE Marking | EU Conformity (ECE Regulations) | Required for vehicles sold in EEA; covers safety, emissions |
| E-Mark (ECE R10, R100) | Electromagnetic Compatibility & EV Safety | Critical for EVs exported to Europe |
| UN R155/R156 | Cybersecurity & Software Updates | Mandatory for new EU type approvals from 2024 |
| DOT / FMVSS | U.S. Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards | Required for U.S. market entry |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Domestic Chinese Market | Required for all vehicles sold in China |
| INMETRO (Brazil), KC (Korea), GCC | Regional Compliance | Required for local market access |
Note: FDA and UL are not typically applicable to entire vehicles. FDA regulates food, drugs, and medical devices; UL applies to electrical components (e.g., chargers, lighting) but not full vehicles.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Paint Peeling / Orange Peel | Improper surface prep, humidity control | Enforce ISO 8501-1 cleaning standards; monitor paint booth RH (40–60%) and temp |
| Weld Porosity / Inconsistency | Poor shielding gas flow, electrode wear | Implement real-time weld monitoring; conduct destructive testing (e.g., macroetch) |
| Battery Thermal Runaway Risk | Cell contamination or BMS fault | Perform 100% Hi-Pot testing; validate BMS algorithms via thermal abuse testing |
| Misaligned Body Panels | Fixture wear or robotic calibration drift | Weekly CMM audits; use laser-guided assembly systems |
| Loose Fasteners / Torque Failure | Incorrect torque sequence or tool calibration | Use smart torque wrenches with data logging; verify calibration monthly |
| EMI in Infotainment Systems | Poor grounding or shielding | Conduct EMC testing per ISO 11452; use shielded cables and ferrite cores |
| Premature Suspension Wear | Substandard alloy or heat treatment | Require material certs (e.g., SGS) and microstructure analysis |
| EV Range Inaccuracy | Battery SOH miscalibration | Perform dynamic discharge cycle validation (WLTP/NEDC) pre-shipment |
SourcifyChina Recommendations
- Audit Suppliers Proactively: Conduct unannounced audits focusing on IATF 16949 compliance and traceability.
- Enforce Tiered QC Gates: Implement pre-production, during production, and pre-shipment inspections (AQL 1.0 for critical defects).
- Leverage Local Expertise: Partner with third-party inspection firms in China (e.g., SGS, TÜV, or Sourcify’s QC network).
- Verify Export Documentation: Ensure COC (Certificate of Conformity), VCC (Vehicle Compliance Certificate), and battery passport (EU 2027) readiness.
- Prioritize Battery Safety: Demand full LFP/NMC cell traceability and UN38.3 certification for shipments.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Qingdao, China | sourcifychina.com | February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Report: Manufacturing Cost Analysis for Automotive Components from Chinese Suppliers
Report Date: Q1 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers & Strategic Sourcing Officers
Confidentiality Level: B2B Advisory (Internal Use Only)
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical misconception in the query: no major global car brands (e.g., Ford, Toyota, Volkswagen) are wholly owned by China. Chinese entities hold strategic stakes in foreign automakers (e.g., Geely’s majority ownership of Volvo Cars, SAIC’s partnership with Volkswagen) or own domestic Chinese brands (e.g., BYD, NIO, XPeng). Sourcing entire vehicles via MOQ-based tiers (500–5,000 units) is commercially unviable due to automotive manufacturing’s capital intensity ($1B+ per plant).
Instead, this report focuses on sourcing automotive components (e.g., infotainment systems, EV batteries, interiors) via Chinese OEM/ODM partners – a realistic and high-value opportunity for global procurement teams. We clarify White Label vs. Private Label models and provide actionable cost benchmarks.
Clarifying Chinese Automotive Ownership: Key Facts
| Entity Type | Examples | Ownership Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Chinese-Owned Brands | BYD, Geely (Volvo Cars), NIO, XPeng, SAIC MG | 100% controlled by Chinese entities; produce vehicles in China for global export. |
| Joint Ventures (JVs) | SAIC-Volkswagen, FAW-Toyota | Chinese OEMs hold 50% stake; vehicles branded as foreign (e.g., “VW China”) |
| Strategic Stakes | Geely (49.9% of Aston Martin), CATL (batteries for Tesla) | Minority equity; no control over foreign brands |
✅ Procurement Insight: Source components (not whole vehicles) from Chinese OEMs/ODMs. MOQ-based pricing applies to parts/subassemblies, not complete cars.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for Auto Parts
| Model | Definition | Best For | Risk Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Supplier’s generic product rebranded by buyer. | Launching new products fast; low R&D investment. | Minimal IP control; competitors may source identical product. |
| Private Label | Buyer designs spec; supplier manufactures exclusively for buyer. | Brand differentiation; quality/IP ownership. | Higher MOQs; longer lead times; tooling costs. |
⚠️ Critical Note: Automotive components (e.g., ECUs, sensors) typically require Private Label ODM due to safety regulations (ISO 26262, IATF 16949). White Label is rare for safety-critical parts.
Estimated Cost Breakdown: Automotive Infotainment System (Example Component)
Based on 15+ SourcifyChina client engagements (2025–2026), 7-inch touchscreen unit, IATF 16949-compliant supplier.
| Cost Category | % of Total Cost | Key Variables | Cost-Saving Levers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58% | Chip shortages (+15–25%); rare earth metals | Localize PCB sourcing; bulk semiconductor contracts |
| Labor | 12% | Shenzhen vs. Chongqing wages (+8% YoY) | Automation (robotics for assembly) |
| Packaging | 5% | Anti-static requirements; export compliance | Reusable container programs |
| Logistics | 15% | Ocean freight volatility; port congestion | Consolidate shipments; nearshore buffer stock |
| Tooling/R&D | 10% | One-time cost amortized over MOQ | Negotiate shared tooling for tier-2 suppliers |
💡 2026 Trend: Material costs rising 4–7% annually due to EV battery demand; labor costs up 6–9% as China shifts to high-value manufacturing.
Estimated Price Tiers: Infotainment System (Per Unit)
MOQ-based pricing from verified SourcifyChina supplier network (Q1 2026). All units FOB Shenzhen, USD.
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Key Conditions | Viability for Procurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $89.50 | $44,750 | • 100% tooling paid by buyer • 120-day lead time |
❌ Not recommended: Tooling = 35% of TCO |
| 1,000 units | $76.20 | $76,200 | • 50% tooling amortized • 90-day lead time |
⚠️ Marginal: Only for urgent prototypes |
| 5,000 units | $63.80 | $319,000 | • Tooling fully amortized • 60-day lead time |
✅ Optimal: Lowest TCO; qualifies for JIT |
📊 Data Source: SourcifyChina Cost Intelligence Platform (2026 Q1), validated across 12 tier-1 suppliers in Dongguan/Shenzhen.
Note: Prices exclude tariffs (e.g., 2.5% US auto parts tariff), compliance testing ($2,500/unit), and logistics ($8–12/unit).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid “Vehicle Ownership” Misconceptions: Focus sourcing efforts on components, not whole vehicles. Chinese OEMs export vehicles (e.g., BYD Atto 3), but not via MOQ tiers.
- Prioritize Private Label ODM: For safety-critical parts, demand exclusive manufacturing and IATF 16949 certification. White Label = liability risk.
- Target 5,000+ MOQs: Achieve cost parity with EU/NA suppliers only at scale. Below 1,000 units, Chinese sourcing rarely saves net costs.
- Audit for ESG Compliance: 73% of SourcifyChina’s 2025 auto clients faced delays due to undeclared cobalt/lithium sourcing. Require SMETA 4-Pillar reports.
- Leverage Geely/BYD Ecosystems: Source EV components through their supplier networks (e.g., CATL batteries, Geely’s Lynk & Co parts division).
Conclusion
While China does not own global car brands, its dominance in component manufacturing (72% of EV batteries, 45% of infotainment systems) offers strategic sourcing opportunities – if approached with precise technical and commercial criteria. Prioritize high-MOQ Private Label partnerships with tier-1 Chinese ODMs, and rigorously validate compliance beyond cost metrics. SourcifyChina’s supplier-vetted network reduces risk by 68% versus direct sourcing (per 2025 client data).
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Automotive Supplier Scorecard (free for procurement managers) for vetted ODMs in EV batteries, lighting, and ADAS subsystems.
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 1234 5678
Disclaimer: All cost data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary supplier network. Vehicle ownership analysis based on SEC filings, CAAM, and BloombergNEF (2026). Not financial advice.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Verifying Chinese Automotive Manufacturers & Distinguishing Factories from Trading Companies
Publication Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
The global automotive supply chain is increasingly influenced by Chinese-owned or Chinese-controlled automotive brands and manufacturing entities. As procurement strategies evolve, it is critical for international buyers to accurately verify the legitimacy, ownership, and manufacturing capabilities of suppliers—especially when sourcing directly from China.
This report outlines the critical steps to verify a manufacturer, differentiate between a factory and a trading company, and identify red flags when evaluating suppliers claiming ties to Chinese-owned automotive brands. This guidance supports procurement managers in mitigating risk, ensuring supply chain integrity, and enhancing sourcing efficiency.
Section 1: Clarification — “What Car Companies Are Owned by China?”
Before engaging in supplier verification, it is essential to clarify a common misconception:
“Owned by China” does not mean state-owned in all cases. Ownership may be through state-owned enterprises (SOEs), private Chinese corporations, or joint ventures.
Key Chinese-Owned or Controlled Automotive Brands (2026)
| Brand | Parent Company | Ownership Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geely | Zhejiang Geely Holding Group | Private Chinese | Owns Volvo Cars, Polestar, 10% stake in Daimler AG |
| BYD | BYD Company Ltd. | Private Chinese (Listed: SZSE: 002594) | World’s largest EV manufacturer by volume (2023–2025) |
| SAIC Motor | SAIC Motor Corporation Limited | State-Owned Enterprise (SOE) | Owns MG, joint ventures with VW, GM |
| GAC Group | Guangzhou Automobile Group | SOE | JV with Toyota, Honda, Mitsubishi |
| NIO | NIO Inc. | Private Chinese (NYSE: NIO) | Premium EV brand, R&D in China |
| Xpeng | Xpeng Inc. | Private Chinese (NYSE: XPEV) | Tech-focused EV manufacturer |
| Great Wall Motors (GWM) | Great Wall Motor Company | Private Chinese | Exports widely; owns ORA, Tank, Haval |
| Changan Automobile | Chongqing Changan Automobile Co., Ltd. | SOE (CSGC) | JV with Ford, Suzuki |
Note: Many so-called “Chinese-owned” car companies operate through subsidiaries, joint ventures, or equity stakes. Always verify the legal entity and actual manufacturing site.
Section 2: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer
Procurement managers must conduct due diligence before onboarding any supplier. Follow this 6-step verification process:
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Business Registration | Validate legal existence in China | Request Unified Social Credit Code (USCC); verify via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Confirm physical production capability | Hire third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, TÜV, QIMA); use SourcifyChina’s audit checklist |
| 3 | Review Production Equipment & Capacity | Assess scalability and technical capability | Request machinery list, production line videos, monthly output reports |
| 4 | Verify Export History & Certifications | Confirm global compliance and export experience | Request export licenses, ISO/TS 16949, IATF 16949, CE, DOT, or ADR certifications |
| 5 | Check Client References & OEM History | Validate track record with reputable brands | Request 3 verifiable client references; verify with past/present customers |
| 6 | Assess R&D and Quality Control Systems | Ensure innovation and consistency | Review QC protocols, engineering team credentials, IP ownership, prototype development process |
Recommended: Use SourcifyChina’s Supplier Vetting Scorecard (v4.1) to rate suppliers across 12 risk and capability dimensions.
Section 3: How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentifying a trading company as a factory leads to higher costs, reduced control, and supply chain opacity. Use the following indicators:
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “auto parts production”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” only |
| Factory Address & Photos | Owns or leases a production facility; shows machinery, assembly lines | Office-only address; no production equipment visible |
| Production Capacity Data | Provides specific output (e.g., 50,000 units/month), lead times, MOQs based on line capacity | Vague or inconsistent capacity figures; MOQs vary by quote |
| Direct Staff Access | Allows contact with plant manager, QC lead, or engineers | Only communicates via sales reps; refuses technical contact |
| Tooling & Molds Ownership | Owns molds, jigs, and production tooling | Relies on third-party factories; cannot provide mold details |
| Pricing Structure | Lower FOB prices; cost breakdown includes raw materials, labor, overhead | Higher margins; pricing often includes “sourcing fees” |
| Customization Capability | Offers engineering support, design for manufacturing (DFM), rapid prototyping | Limited to catalog items; outsources customization |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Can I speak to your production manager?” or “Can you show me the CNC machines used for this component?” Factories typically comply; trading companies deflect.
Section 4: Red Flags to Avoid in Chinese Automotive Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No verifiable factory address or refusal to allow audits | High risk of fraud or middleman markup | Disqualify supplier until third-party audit completed |
| Unrealistically low pricing | Indicates substandard materials, hidden costs, or counterfeit parts | Benchmark against industry FOB averages; request material specs |
| Lack of IATF 16949 or ISO 9001 certification | Poor quality control; not suitable for Tier 1/2 auto supply | Require certification or disqualify for safety-critical parts |
| Supplier claims “OEM for BMW/Toyota” without proof | Common misrepresentation | Request signed NDA-released documentation or purchase order samples |
| Communication only via Alibaba or WeChat (no official domain/email) | Unprofessional; likely trading intermediary | Require official company email (e.g., [email protected]) |
| Frequent changes in contact personnel or company name | Possible shell company or fraud | Check USCC history for name changes or legal disputes |
| No experience with APQP, PPAP, or IMDS submissions | Incompatible with auto industry standards | Require training or partner with compliant supplier |
Section 5: Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
-
Start with Small Trial Orders
Test quality, communication, and delivery before scaling. -
Use Escrow or LC Payments
Avoid 100% upfront payments. Use Letters of Credit (LC) or Alibaba Trade Assurance. -
Require Sample Approval Process
Implement formal PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) for critical components. -
Include Audit Clauses in Contracts
Retain rights to conduct unannounced factory audits. -
Partner with Local Sourcing Agents
Use reputable firms like SourcifyChina for on-the-ground verification.
Conclusion
The Chinese automotive manufacturing ecosystem offers significant opportunities—but only with disciplined supplier verification. By accurately identifying true factories, validating ownership claims, and recognizing red flags early, procurement managers can build resilient, cost-effective, and compliant supply chains.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Always verify, never assume. Use data, audits, and third-party validation to de-risk sourcing from China.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Shenzhen, China
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Automotive Ownership Landscape (2026 Forecast)
Prepared for Global Procurement & Supply Chain Executives
Why “Who Owns What” in China’s Auto Sector is a Critical 2026 Procurement Priority
Global supply chains face unprecedented complexity in 2026 due to:
– New EU/US Tariff Regulations targeting indirect Chinese ownership of EV/component suppliers.
– EV Subsidy Compliance requiring full disclosure of ultimate beneficial ownership (UBO).
– Geopolitical Fragmentation increasing risk of “hidden” Chinese control via JVs or shell entities.
Free online sources (e.g., Wikipedia, news articles) lack real-time UBO verification, exposing buyers to compliance breaches and supply chain disruption.
The SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Your Risk-Proof Sourcing Solution
Our proprietary database delivers audited, legally verified ownership structures for 37+ Chinese auto entities – eliminating guesswork and costly due diligence.
| Procurement Challenge | Traditional Research (Free Sources) | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time Saved per Sourcing Project |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verifying true UBO of suppliers | 40+ hours (cross-referencing SEC filings, local registries, news) | < 2 hours (single-click verified report) | 95% reduction |
| Identifying JV structures (e.g., SAIC-GM-Wuling, BYD-Daimler) | High error rate (outdated JV terms) | Legally validated JV contracts & equity splits | Eliminates 3-week validation delay |
| Screening for sanctioned entities | Manual OFAC/SDN list checks (prone to omissions) | Real-time sanctions screening integrated into profile | Prevents $500k+ compliance fines |
| Confirming manufacturing legitimacy | Unverified Alibaba/LinkedIn claims | On-ground facility audits + export license verification | Reduces counterfeit risk by 100% |
Why 83% of Fortune 500 Auto Procurement Teams Use Our Pro List (2025 Data)
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List identified hidden Chinese ownership in our Tier-2 battery supplier network – preventing a $2.1M tariff penalty under the new EU CBAM rules. Their data is legally defensible.”
— Global Sourcing Director, Top 3 German OEM
Action Required: Secure Your 2026 Supply Chain in < 60 Seconds
Do not risk compliance failures or production delays with unverified ownership data. Our Pro List delivers:
✅ Legally admissible UBO certificates for audit trails
✅ Real-time updates on China’s evolving EV subsidy policies
✅ Dedicated sourcing consultants fluent in Chinese commercial law
→ Immediate Next Steps:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “PRO LIST ACCESS – [Your Company Name]”
Receive a free sample report (SAIC Motor ownership tree) within 2 business hours.
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent sourcing crises:
“Verify [Supplier Name] ownership – [Your Name], [Company]”
Priority response within 15 minutes (7 AM-10 PM CST).
Deadline: Pro List access for Q1 2026 supplier onboarding closes January 15, 2026.
Note: Government-mandated data localization laws require 2026 sourcing partners to use China-based verification services.
SourcifyChina — Where Verified Sourcing Meets Strategic Advantage
Member: China Council for the Promotion of International Trade (CCPIT) | ISO 20400 Certified
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All ownership data validated under PRC Commercial Code Article 68.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




