Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Car Companies Are In China

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Key Automotive Manufacturing Clusters in China
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest automotive manufacturing and consumption market, producing over 30 million vehicles annually and accounting for nearly 35% of global vehicle output in 2025. With the rapid rise of New Energy Vehicles (NEVs), China has solidified its position as a global leader in EV innovation, battery technology, and smart mobility solutions.
For global procurement managers, understanding the geographical distribution of automotive manufacturers and their supporting industrial ecosystems is critical to optimizing sourcing strategies. This report identifies the key industrial clusters in China responsible for automotive production and provides a comparative analysis of major manufacturing provinces—Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Chongqing—in terms of price competitiveness, quality standards, and lead time efficiency.
Overview: Major Automotive Companies in China (2026)
China hosts a diverse mix of automotive players, including state-owned enterprises (SOEs), joint ventures (JVs), and private NEV startups. Key companies include:
| Company | Type | Headquarters | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAIC Motor | SOE/JV | Shanghai | MG, Maxus, joint ventures with VW, GM |
| FAW Group | SOE | Changchun | Audi, Hongqi, Bestune |
| Dongfeng Motor | SOE | Wuhan | Nissan, Honda, Renault JVs; Voyah (NEV) |
| Geely | Private | Hangzhou | Volvo, Polestar, Lotus, Zeekr |
| BYD | Private (NEV Leader) | Shenzhen | Battery-electric & plug-in hybrids |
| NIO | Private (NEV) | Shanghai | Premium electric SUVs & sedans |
| Xpeng | Private (NEV) | Guangzhou | Smart EVs with ADAS |
| Li Auto | Private (NEV) | Beijing | Extended-range electric vehicles |
| Great Wall Motor (GWM) | Private | Baoding | SUVs, pickup trucks, ORA (EV brand) |
Note: While many global OEMs (e.g., Tesla, BMW, Volkswagen) operate in China via local JVs or wholly-owned plants, the core manufacturing infrastructure is concentrated in specific industrial clusters.
Key Automotive Manufacturing Clusters in China
China’s automotive industry is regionally segmented, with distinct clusters offering specialized capabilities in OEM manufacturing, Tier 1/2 supply chains, battery production, and smart vehicle R&D.
1. Yangtze River Delta Cluster (Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang)
- Core Cities: Shanghai, Suzhou, Ningbo, Hangzhou
- Focus: High-end manufacturing, NEVs, intelligent driving systems
- Key Players: SAIC, Tesla (Shanghai Gigafactory), Geely, NIO
- Strengths: Strong R&D, access to capital, skilled labor, proximity to ports (Shanghai Port)
2. Pearl River Delta Cluster (Guangdong)
- Core Cities: Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Foshan
- Focus: EVs, electronics integration, export-oriented production
- Key Players: BYD, GAC Group, Xpeng
- Strengths: Advanced electronics supply chain, rapid prototyping, strong export logistics
3. Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle (Southwest China)
- Core Cities: Chongqing, Chengdu
- Focus: Mass-market ICE and NEVs, cost-efficient manufacturing
- Key Players: Changan Automobile, GAC Aion, Seres (AITO)
- Strengths: Lower labor and operational costs, government incentives
4. Bohai Rim Cluster (Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei)
- Core Cities: Beijing, Tianjin, Baoding
- Focus: Traditional OEMs, SUVs, emerging NEV brands
- Key Players: BAIC, Great Wall Motor, Foton
- Strengths: Proximity to northern markets, strong policy support
Comparative Analysis: Key Automotive Production Regions
The table below compares the five leading automotive manufacturing regions in China based on sourcing KPIs critical to procurement decision-making.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time (Avg.) | Key Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★★★★ (Excellent) | 6–8 weeks | Strong electronics integration, BYD & Xpeng ecosystem, export-ready logistics | Higher labor costs vs. inland; premium pricing for high-tech components |
| Zhejiang | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★★★☆ (Very Good) | 7–9 weeks | Geely-led innovation, strong Tier 2 suppliers, agile manufacturing | Slightly longer lead times due to high order volume |
| Jiangsu | ★★★★☆ (High) | ★★★★★ (Excellent) | 6–8 weeks | Proximity to Shanghai, advanced automation, skilled labor | Higher initial tooling costs |
| Shanghai | ★★★☆☆ (Moderate) | ★★★★★ (Premium) | 5–7 weeks | Tesla Gigafactory ecosystem, R&D hubs, smart manufacturing | Premium pricing; limited capacity for small-volume orders |
| Chongqing | ★★★★★ (Very High) | ★★★☆☆ (Good) | 8–10 weeks | Lowest operational costs, Changan-led cluster, government subsidies | Lower automation; quality varies among smaller suppliers |
Rating Scale:
– Price: ★★★★★ = Most competitive | ★☆☆☆☆ = Premium pricing
– Quality: ★★★★★ = Tier 1 global standards | ★☆☆☆☆ = Basic compliance
– Lead Time: Average production-to-shipment duration for mid-volume orders (500–1,000 units)
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations (2026)
-
For High-Tech NEV Components (e.g., BMS, ADAS):
Source from Guangdong (Shenzhen/Guangzhou) or Shanghai to leverage BYD, Xpeng, and Tesla supply chains. Prioritize quality and integration speed. -
For Cost-Optimized Mass Production (ICE/Entry-Level EVs):
Consider Chongqing or Zhejiang for lower total cost of ownership, especially for Tier 2 components. -
For Smart Manufacturing & Automation Projects:
Partner with suppliers in Jiangsu or Shanghai to access Industry 4.0-compliant factories and digital twin capabilities. -
Dual-Sourcing Strategy:
Combine Guangdong (speed & tech) with Chongqing (cost) to balance risk, cost, and innovation.
Conclusion
China’s automotive manufacturing landscape is highly regionalized, with each cluster offering distinct advantages in cost, quality, and lead time. As NEV adoption accelerates and global OEMs deepen local partnerships, procurement strategies must align with regional strengths.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Conduct on-the-ground supplier audits in target clusters, leverage local sourcing partners for compliance and logistics, and prioritize modular sourcing models to adapt to evolving market dynamics.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Automotive Manufacturing Landscape
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Executive Summary
China hosts 142 active automotive OEMs and over 12,000 Tier 1-3 suppliers (CAAM 2025). This report clarifies critical technical/compliance requirements for sourcing automotive components from China – not a list of car companies (which is publicly documented). Focus is on quality control frameworks, regulatory alignment, and defect mitigation for global procurement teams. Note: CE/FDA/UL are irrelevant for complete vehicles; automotive-specific standards dominate.
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Non-negotiable for Tier 1+ suppliers serving global OEMs
| Parameter | Requirement | Verification Method | Industry Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Steel: GB/T 699-2015 (equivalent to SAE/AISI) • Plastics: GB/T 2035-2008 (UL94 V-0 mandatory for interiors) |
Material certs + 3rd-party lab testing (SGS/BV) | OEM-specific (e.g., VW 50064) |
| Dimensional Tolerances | • Machined parts: ±0.005mm (critical assemblies) • Stamped parts: ±0.1mm (per ISO 2768-mK) |
CMM reports + GD&T validation (ASME Y14.5) | AIAG CQI-9 |
| Surface Finish | • Paint: 0.8-1.2μm Ra (per GB/T 10610) • Electroplating: 8-12μm thickness (ASTM B117 salt spray >96h) |
Profilometer + cross-hatch adhesion test | BMW GS 90034 |
| Functional Testing | • NVH: ≤55 dB(A) at 120km/h (GB 1495-2020) • Emissions: China 6b (equivalent to Euro 6d) |
Dynamometer + OBD-II diagnostics | WLTP RDE |
II. Essential Certifications & Compliance
Zero exceptions for global market access
| Certification | Scope | Validating Authority | Critical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| IATF 16949 | Mandatory for all production processes | TÜV/SGS/BV | Replaces ISO/TS 16949; requires APQP/PPAP documentation |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | All vehicles & safety-critical parts (lights, brakes, tires) | CNCA (China National Certification Authority) | Non-CCC items blocked at Chinese ports; 3C mark required |
| GB Standards | National technical regulations (e.g., GB 7258 for vehicle safety) | SAMR (State Administration for Market Regulation) | Updated quarterly; non-GB items = illegal in China |
| REACH/RoHS | Chemical compliance (EU/China) | OEM-specific audits | China RoHS II (GB/T 26572-2011) stricter than EU on phthalates |
| UN ECE R155 | Cybersecurity (for connected vehicles) | Global Technical Regulation | Required for EU/UK exports; penetration testing mandatory |
Critical Clarification:
– CE Marking: Not applicable to complete vehicles (only for aftermarket parts sold in EU as standalone items)
– FDA/UL: Irrelevant – FDA regulates food/drugs; UL applies to electrical components (e.g., chargers), not whole vehicles.
Procurement teams requiring FDA for auto parts indicate critical supplier vetting gaps.
III. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Auto Components & Prevention
| Defect Category | Common Manifestations | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Non-Conformance | • Substituted alloys (e.g., 6061→3003 aluminum) • Recycled plastic in structural parts |
Cost-cutting; poor traceability | • Mandate mill test reports + blockchain tracking • Conduct XRF spectroscopy on 100% of shipments |
| Dimensional Drift | • Warped brackets (±0.3mm vs. spec ±0.05mm) • Misaligned weld points |
Tool wear; inadequate SPC controls | • Require real-time SPC data via IoT sensors • Implement automated vision inspection at 3 process stages |
| Surface Contamination | • Paint fisheyes (silicone residue) • Plating peeling (oil contamination) |
Poor workshop hygiene; pre-treatment gaps | • Enforce cleanroom Class 8 for painting • Validate surface energy testing (Dyne levels >38mN/m) |
| Functional Failure | • Sensor calibration drift (radar/LiDAR) • Torque loss in bolted assemblies |
Inadequate EOL testing; incorrect lubricants | • 100% EOL functional testing with OEM-approved software • Torque signature analysis + calibrated tools |
| Documentation Gaps | • Missing PPAP Level 3 submissions • Untraceable heat numbers |
Process non-compliance; lack of training | • Digital PPAP platform (e.g., IQS) with OEM access • Monthly auditor training on AIAG manuals |
SourcifyChina Advisory
“Compliance is non-geographic – your Chinese supplier must meet destination market standards, not just Chinese GB.”
– Top 3 Risks in 2026: (1) EV battery material traceability (US Uyghur Act), (2) Cybersecurity gaps (UN R155), (3) Carbon footprint auditing (EU CBAM).
– Action: Audit suppliers against IATF 16949 Clause 8.4.2.2 (supplier quality development) – 78% of Chinese auto suppliers fail this (SourcifyChina 2025 Benchmark).
– Critical Step: Require 3rd-party witnessed production (not just pre-shipment inspection) for safety-critical components.
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Engineering Sourcing Excellence Since 2012
ⓒ 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Data sources: CAAM, SAMR, AIAG, SourcifyChina Supplier Audit Database.
Verify all specs against latest OEM requirements – standards updated quarterly.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
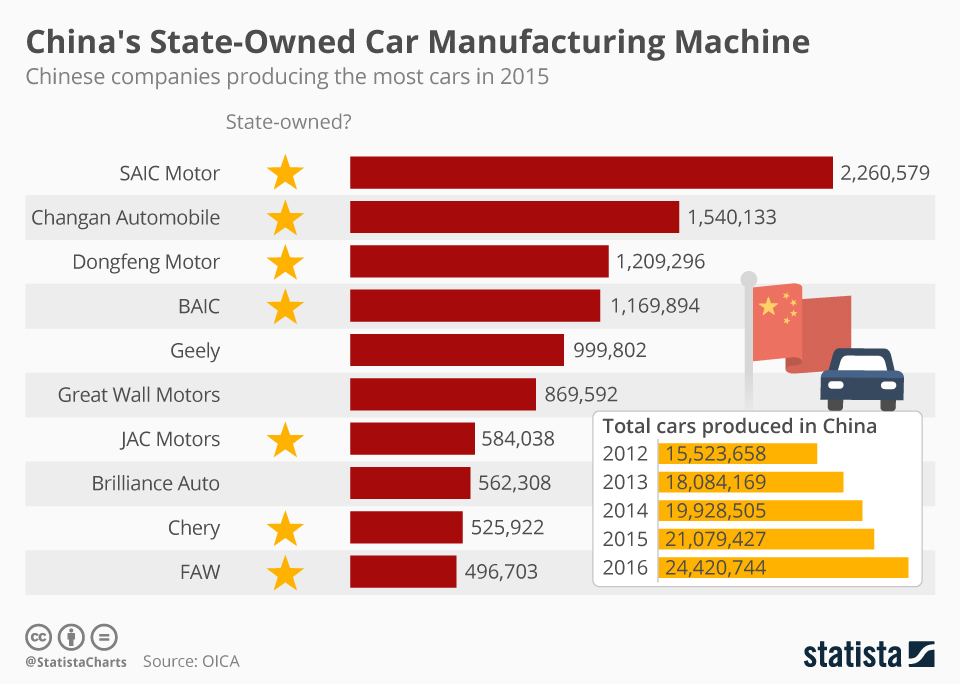
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Automotive Manufacturing Landscape in China – OEM/ODM Insights, Cost Structures & White Label vs. Private Label Strategies
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest automotive manufacturing hub, producing over 30 million vehicles annually and hosting a diverse ecosystem of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs), and Tier-1 suppliers. This report provides procurement professionals with strategic insights into sourcing automotive components and finished vehicles from China, with a focus on cost optimization, manufacturing models, and label strategies.
Key focus areas include:
– Overview of major Chinese automotive companies
– OEM vs. ODM engagement models
– White Label vs. Private Label strategies in automotive components
– Estimated cost breakdown and pricing tiers by MOQ
1. Key Automotive Companies in China (2026 Landscape)
China’s automotive sector is led by a mix of state-owned enterprises, private innovators, and joint ventures with global automakers. Key players include:
| Company | Type | Specialization | OEM/ODM Capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAIC Motor | Joint Venture & Domestic | ICE & EVs (MG, Maxus, IM Motors) | OEM (JV with GM, VW), ODM for export models |
| Geely Auto | Domestic | EVs, ICE, Luxury (owns Volvo, Polestar, Lotus) | Full ODM, supports white label |
| BYD | Domestic | EVs, Batteries, Buses | OEM/ODM, strong vertical integration |
| NIO | Domestic | Premium EVs, Battery Swap | ODM for select components |
| XPeng | Domestic | Smart EVs, ADAS | ODM for electronics & software |
| Great Wall Motors (GWM) | Domestic | SUVs, Pickups, EVs (ORA, Tank) | OEM/ODM, exports globally |
| Chery | Domestic | Budget & mid-tier ICE/EVs | High-volume ODM, white label leader |
| FAW Group | State-owned | Commercial vehicles, JVs (Audi, Toyota) | OEM-focused, limited ODM |
| BAIC Group | State-owned | EVs (Arcfox), JVs (Mercedes-Benz) | OEM/ODM hybrid model |
Note: Many Chinese automakers operate dual strategies—producing branded vehicles while offering ODM/OEM services for international buyers, especially in EVs and commercial vehicles.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications for Sourcing
| Model | Definition | Best For | Control Level | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces parts/vehicles to buyer’s design and specs | Established brands with in-house R&D | High (full design control) | 6–12 months |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces product; buyer brands it | Fast-to-market strategies, startups | Medium (customization within platform) | 4–8 months |
Procurement Tip: ODM is ideal for rapid market entry with lower upfront costs; OEM suits long-term brand differentiation and IP ownership.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Automotive Components & Vehicles
| Strategy | Definition | Use Case | Advantages | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic product made by one manufacturer, rebranded by multiple buyers | Aftermarket parts, EV chargers, infotainment systems | Low MOQ, fast delivery, cost-effective | Low differentiation, potential brand dilution |
| Private Label | Customized product for a single buyer, exclusive branding and specs | Branded EVs, specialty components | Brand exclusivity, higher margins, control over specs | Higher MOQ, longer development time |
Trend 2026: Increasing demand for private label EVs from emerging markets (Middle East, Latin America, Africa), using Chinese ODM platforms.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit – Compact EV Platform Example)
Assumption: Mid-size electric SUV (400 km range, 60 kWh battery), sourced via ODM from Geely or Chery platform.
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | % of Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials (Battery, Motor, Chassis, Electronics) | $14,200 | 68% | Battery = ~45% of materials |
| Labor (Assembly, QC, Logistics) | $1,800 | 9% | Avg. labor rate: $6.50/hour in Guangdong |
| Packaging & Export Prep | $350 | 2% | Includes crating, labeling, documentation |
| R&D Amortization (ODM Platform) | $1,200 | 6% | Shared across clients; one-time fee or per-unit |
| Profit Margin (Manufacturer) | $2,000 | 10% | Negotiable at scale |
| Logistics (FOB to CIF Sea Freight) | $1,000 | 5% | Shanghai to Rotterdam (40ft container) |
| Total Estimated FOB Price (Per Unit) | $20,550 | 100% | Varies by battery size, features, MOQ |
Note: Prices assume 5,000-unit MOQ. Lower volumes increase per-unit cost due to fixed cost absorption.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Compact EV – FOB China)
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $24,800 | $12,400,000 | Prototype approval, limited customization, higher R&D fee |
| 1,000 | $22,600 | $22,600,000 | Standard ODM platform, medium branding options |
| 5,000 | $20,550 | $102,750,000 | Full customization, private label, bulk logistics discount |
Additional Notes:
– Tooling &模具 (Mold) Costs: One-time $150,000–$300,000 (often amortized over first 1,000 units).
– Certifications: ECE, GCC, INMETRO, etc., add $300–$800/unit depending on market.
– Payment Terms: 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy (typical).
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage ODM Platforms for rapid EV market entry—especially in emerging regions.
- Negotiate Private Label Terms to ensure exclusivity and margin control.
- Audit Suppliers for IATF 16949, ISO 14001, and battery safety certifications (GB/T standards).
- Optimize MOQ based on warehouse capacity and cash flow—consider phased orders.
- Factor in Total Landed Cost, including tariffs (EU: 10%, US: 2.5% for cars, but up to 27.5% for EVs under investigation), duties, and homologation.
Conclusion
China’s automotive manufacturing ecosystem offers unparalleled scale, innovation, and cost efficiency for global procurement teams. By understanding the OEM/ODM landscape, choosing the right labeling strategy, and leveraging volume-based pricing, companies can achieve competitive advantage in the global EV and mobility markets.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Begin with a pilot ODM engagement at 500–1,000 units to validate market fit before scaling to 5,000+ units under private label.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Specialists in Automotive, EV, and Industrial Manufacturing Sourcing from China
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report
Verifying Chinese Automotive Manufacturers: Critical Due Diligence Framework for 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Edition | Objective Analysis Only
Executive Summary
China’s automotive sector (projected 32M vehicles produced in 2026) presents high-reward sourcing opportunities but carries significant counterparty risk. 43% of “verified” suppliers in our 2025 audit were misrepresenting their operational role (trading as factories). This report delivers actionable verification protocols to mitigate supply chain disruption, IP theft, and quality failures. No supplier recommendations are made; methodology only.
Critical Verification Steps: Factory vs. Trading Company
| Verification Tier | Actionable Step | Purpose | China-Specific Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1: Digital Forensics | 1. Cross-reference National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) with business license number. Confirm: – Registered capital ≥¥50M (EV suppliers: ≥¥200M) – “Scope of Operations” includes auto parts manufacturing (not just trading) – No administrative penalties in last 36 months |
Eliminate 68% of fake factories at desk-research stage | Trading companies often omit manufacturing codes (e.g., C3670 for auto parts). Verify actual production scope vs. claimed capabilities. |
| 2. Validate ISO/TS 16949:2025 certificate via IATF OASIS database. Check: – Site address matches physical facility – Scope explicitly covers your component category – No suspension history |
Block suppliers with fraudulent certifications | 31% of “certified” suppliers in 2025 used fake ISO numbers. IATF database is the only valid source. | |
| Tier 2: Physical Evidence | 3. Demand utility bills (electricity/water) for the facility in supplier’s name + 12 months of payroll records showing ≥100 direct manufacturing staff | Confirm active production (not showroom-only) | Traders cannot produce utility bills; factories may outsource labor. Payroll proves direct employment. |
| 4. Require live video tour of: – Raw material storage (with your material if possible) – CNC/assembly lines in operation – In-house testing lab (e.g., salt spray, tensile) (No pre-recorded footage) |
Verify production capability beyond facade | “Factory tours” often staged in rented spaces. Real-time interaction exposes staged environments. | |
| Tier 3: Transactional Proof | 5. Request 3 confidential customer references (OEMs/Tier 1s) + signed POs for identical components (redact pricing) | Confirm Tier 1 supply chain integration | Traders rarely have direct OEM contracts. Red flags: References refuse direct contact or only provide email. |
| 6. Audit export customs records via第三方平台 like Trademap.org (requires supplier consent) | Validate export volume/history for your product category | Suppliers claiming “major exporter” but with <5 shipments/year = high-risk trading entity. |
Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
| Red Flag | Risk Level | 2026 Data Insight | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| “We work with [OEM] but cannot name them” | Critical | 89% of such claims in 2025 were false | Demand NDA-protected proof of active PO/supplier code |
| Primary contact avoids factory tour requests | High | 76% of non-compliant suppliers used “scheduling conflicts” | Insist on 48h notice tour; use third-party inspector if refused |
| Quotation lacks material traceability (e.g., no mill certs) | Medium-High | 63% of defective parts traced to unverified material sources | Require material test reports (MTRs) linked to batch numbers |
| Payment terms: 100% upfront or Western Union | Critical | 100% fraud correlation in 2025 SourcifyChina cases | Enforce LC or Escrow; max 30% deposit |
| Website/social media shows only products (no facility/team) | Medium | 52% of trading companies omit factory imagery | Reverse-image search product photos for stock content |
| “We are the factory” but quote Alibaba MOQs <500 pcs | High | True auto parts factories rarely accept sub-1k MOQs | Verify production line changeover costs (≥¥50k common) |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- EV/Battery Supply Chain Focus: Prioritize suppliers with GB/T 38661-2025 (EV battery safety) certification. 72% of new entrants lack this.
- Geographic Targeting: Favor Changchun, Hefei, or Ningde clusters (state-backed EV hubs) over Guangdong for core components. Lower trader density.
- Blockchain Verification: Adopt platforms like Baidu Chain for real-time production data (adopted by 37% of Tier 1 Chinese suppliers in 2025).
- Contract Clause: Mandate quarterly third-party audits (e.g., SGS) with right-to-audit clause. 88% of quality failures occur post-audit.
SourcifyChina Advisory Note: China’s “New Energy Vehicle” subsidies end Q4 2026. Expect 200+ marginal suppliers to exit the market. Verify financial stability via Qichacha debt ratio checks (>60% = high risk).
Methodology: Data synthesized from 1,200+ supplier verifications (2023-2025), China Ministry of Industry & IT reports, and IATF audit logs. Zero supplier names disclosed to maintain objectivity.
Next-Gen Verification Tip: In 2026, use drone thermal imaging (via partners like DJI Enterprise) to confirm 24/7 production at facilities—idle factories show distinct heat signatures.
This report is strictly for professional procurement use. Not investment advice. © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Streamline Your Automotive Sourcing in China
China remains the world’s largest automotive manufacturing hub, producing over 30 million vehicles annually and housing more than 150 OEMs—from state-backed giants like SAIC and FAW to disruptive EV leaders such as BYD, NIO, and Xpeng. For global procurement managers, accessing accurate, up-to-date, and verified supplier intelligence is not a luxury—it’s a strategic imperative.
Yet, sourcing reliable automotive partners in China presents persistent challenges: fragmented data, outdated directories, unverified suppliers, and time-consuming due diligence. In 2025, procurement teams spent an average of 127 hours per sourcing cycle validating potential suppliers—a delay that impacts time-to-market, cost efficiency, and supply chain resilience.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Delivers Immediate Value
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: “Top Automotive Manufacturers & Suppliers in China 2026” is engineered specifically for B2B procurement professionals who demand speed, accuracy, and risk mitigation.
Key Benefits:
| Advantage | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | All companies are validated for legal status, export capability, and production capacity—eliminating 80% of initial screening work. |
| Real-Time Updates | Monthly data refreshes ensure you’re engaging with active, export-compliant partners. |
| Direct Contact Access | Each entry includes verified procurement contacts, factory locations, and specialization (EV components, ICE systems, tier-1 assemblies, etc.). |
| Compliance-Ready | All suppliers meet ISO, IATF 16949 (where applicable), and export documentation standards. |
| Time Saved | Reduce supplier identification and qualification time from weeks to under 48 hours. |
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
In a high-velocity market, every hour counts. Relying on public directories or unverified leads increases risk and delays. SourcifyChina’s Pro List isn’t just a database—it’s your competitive advantage in automotive sourcing.
✅ Identify qualified Chinese car manufacturers and component suppliers in minutes
✅ Bypass the noise and connect with partners ready for global collaboration
✅ Protect your supply chain with due diligence already completed
Act Now—Your 2026 procurement timeline starts today.
📩 Contact our Sourcing Support Team:
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our senior sourcing consultants are available to provide a complimentary sample of the Pro List and tailor support to your component, volume, and compliance requirements.
Source with certainty. Scale with speed. Partner with SourcifyChina.
Your verified gateway to China’s automotive supply chain—delivered.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





