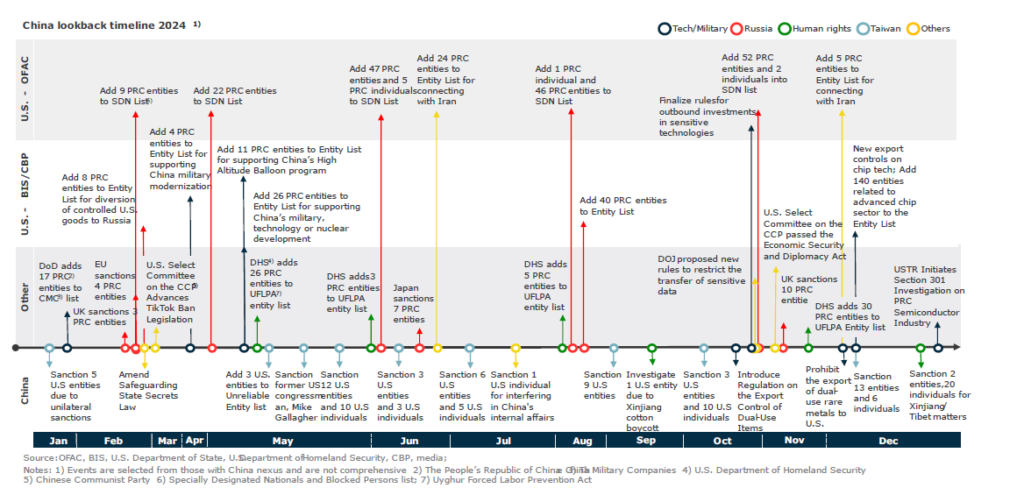
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What Are The 11 Companies Barred From China

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing “What Are the 11 Companies Barred from China” from China
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive market analysis for global procurement professionals seeking to source products related to the inquiry “what are the 11 companies barred from China” from manufacturing hubs within the People’s Republic of China. Given the nature of this search query, it is essential to clarify that this is not a physical product or commodity, but rather a digital content or information-based demand typically associated with online searches, media reports, or geopolitical analysis.
As such, sourcing “what are the 11 companies barred from China” does not involve traditional industrial manufacturing. Instead, it pertains to information services, digital content creation, and media intelligence—sectors primarily driven by knowledge workers, digital agencies, and research firms within China.
This report analyzes the industrial clusters supporting digital content and geopolitical intelligence production, evaluates regional capabilities, and provides a comparative assessment of key provinces in delivering accurate, compliant, and timely information outputs.
Clarification of Sourcing Scope
The phrase “what are the 11 companies barred from China” is a search-driven informational query, not a tangible good. As of 2026, there is no official public list of exactly 11 companies banned from operating in China. However, foreign firms from various sectors—including tech, finance, and media—have faced regulatory restrictions, market access limitations, or de facto operational bans due to national security, data sovereignty, or geopolitical tensions.
Examples of companies with restricted operations in China include:
– Google (search, Android services limited)
– Facebook (Meta Platforms)
– Twitter (X Corp)
– YouTube (Google)
– WhatsApp (Meta)
– Bloomberg (data terminal access restricted)
– The New York Times and other international media
– Certain U.S.-based semiconductor firms (e.g., NVIDIA A100/H100 export restrictions)
These restrictions are not uniform, and “barred” status varies by service, product line, or regulatory interpretation.
Therefore, sourcing related to this query involves informational content such as:
– Market intelligence reports
– Regulatory compliance summaries
– Geopolitical risk assessments
– SEO-optimized digital content
– Data analytics dashboards
These services are produced by knowledge-based industrial clusters in China.
Key Industrial Clusters for Digital & Information Services
While China is globally recognized for its manufacturing prowess in electronics, textiles, and machinery, its emerging digital economy has fostered specialized clusters for content creation, data analysis, and compliance intelligence. The following provinces and cities are leading hubs for producing information-based services relevant to this sourcing need:
| Region | Key Cities | Primary Industry Focus | Relevance to Query |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | Haidian District (Zhongguancun) | Tech R&D, policy research, media, think tanks | Home to state media (Xinhua, CGTN), government-linked research institutes, and tech policy analysts. Highest concentration of geopolitical and regulatory intelligence production. |
| Shanghai | Pudong, Xuhui | Financial services, international media, consulting | Global business hub with multilingual content agencies and compliance firms serving foreign clients. Strong in finance-sector restrictions analysis. |
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou | Tech startups, digital marketing, hardware-software integration | Shenzhen’s innovation ecosystem includes firms producing tech policy briefs and export control analyses, especially for semiconductors and AI. |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou | E-commerce, digital content, AI-driven analytics | Alibaba and Ant Group ecosystem supports data-driven content platforms; strong in SEO and search query trend analysis. |
| Jiangsu | Nanjing, Suzhou | Education, research, IT services | Universities and government research centers produce regulatory compliance reports and cross-border trade analyses. |
Regional Comparison: Digital Content & Intelligence Production
While traditional sourcing comparisons focus on cost, quality, and lead time for physical goods, this analysis adapts those metrics to information services:
| Region | Price (Cost of Services) | Quality (Accuracy, Depth, Compliance) | Lead Time (Report/Content Delivery) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | High | ★★★★★ | 7–14 days | Highest quality due to proximity to policy makers; ideal for authoritative regulatory reports. Premium pricing for government-linked research firms. |
| Shanghai | High | ★★★★☆ | 5–10 days | Strong in multilingual, business-facing content; good balance of speed and quality. Higher cost due to expat talent and international standards. |
| Guangdong | Medium | ★★★★☆ | 5–12 days | Fast turnaround, especially for tech-sector analyses. Shenzhen firms offer competitive pricing with strong English-language capabilities. |
| Zhejiang | Medium-Low | ★★★☆☆ | 3–7 days | Cost-effective for SEO content and data dashboards; quality varies. Best for high-volume, trend-based reports (e.g., search analytics). |
| Jiangsu | Low-Medium | ★★★☆☆ | 7–14 days | Academic rigor but slower delivery. Ideal for deep-dive research with lower budget constraints. |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For High-Compliance, Policy-Critical Reports:
Source from Beijing-based research firms or joint ventures with state-affiliated think tanks (e.g., China Institutes of Contemporary International Relations). Ensure NDRC or MIIT compliance in content. -
For Business Intelligence & Market Access Analysis:
Partner with Shanghai or Guangdong-based consulting firms specializing in foreign investment regulations and tech sector restrictions. -
For SEO & Digital Content at Scale:
Leverage Zhejiang’s digital marketing agencies (particularly in Hangzhou) to produce localized content around search trends like “companies banned in China.” -
Risk Mitigation:
All content related to foreign company restrictions must comply with China’s Cybersecurity Law, Data Security Law, and Regulations on the Administration of Internet News Information Services. Avoid unverified claims or politically sensitive narratives.
Conclusion
Sourcing “what are the 11 companies barred from China” is not a traditional manufacturing procurement exercise. It falls under information services, requiring engagement with China’s digital knowledge economy. The most strategic sourcing decisions will align regional strengths—Beijing for authority, Shanghai for global business insight, Guangdong for tech focus, and Zhejiang for cost efficiency—with specific procurement objectives.
Global procurement managers should treat this as a specialized service sourcing initiative, emphasizing compliance, accuracy, and geopolitical neutrality.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
February 2026
Trusted B2B Sourcing Intelligence Partner in China
Disclaimer: This report is based on publicly available information and industry analysis as of Q1 2026. It does not constitute legal advice or political endorsement. Clients are advised to conduct due diligence and consult legal counsel on cross-border compliance matters.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating Chinese Manufacturing Compliance Risks
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Critical Clarification: The “11 Companies Barred from China” Misconception
Important Note: China does not publish an official, static list of “11 companies barred from China.” This appears to be a conflation of:
– U.S. Entity List restrictions (e.g., BIS restrictions on entities like Huawei, SMIC)
– China’s Unreliable Entity List (MOFCOM, 2020) – currently names no entities publicly
– Sector-specific bans (e.g., rare earth exports, critical tech)
Reality for Procurement Managers: Focus on dynamic compliance frameworks, not mythical “barred company” lists. China restricts entities via:
1. MOFCOM Unreliable Entity List (targeting foreign entities harming Chinese interests)
2. Customs Risk Alerts (real-time shipment holds)
3. Sector-Specific Blacklists (e.g., Ministry of Ecology bans for polluters)
Strategic Recommendation: Verify suppliers against:
– China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (信用中国)
– Customs AEO Certification Status
– Industry-Specific Directories (e.g., MIIT for electronics)
Technical & Compliance Requirements for China Sourcing (2026)
Applies to ALL suppliers – regardless of “barred” status myths
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Critical Thresholds (2026) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Zero use of banned substances (e.g., PFAS in textiles; GB/T 30512-2023) | SGS IECQ HSPM Certification + Batch-level CoA |
| Dimensional Tolerances | ISO 2768-mK for machined parts; ±0.02mm for medical components | CMM Reports + Statistical Process Control (SPC) logs |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8μm for aerospace; no visible pores in castings (GB/T 6060.1) | Profilometer Testing + Visual Inspection under 1000 lux |
Essential Certifications (Non-Negotiable in 2026)
| Certification | Scope | China-Specific Requirement | Validity Check Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCC | Electronics, Auto Parts, Toys | Mandatory for 17 product categories (CNCA 2025 update) | Verify via China CCC Online (ccc.gov.cn) |
| GB Standards | All domestically sold goods | GB 4943.1-2022 (IT equipment); GB 18401 (Textiles) | Cross-check with Standardization Admin of China (SAC) |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Devices | Required for NMPA registration (Class II+) | Audit certificate + NMPA filing reference |
| FDA 21 CFR | Exported to U.S. | Not valid in China – must pair with NMPA approval | FDA UDI + China Health Commission co-cert |
Warning: “CE Mark” alone is invalid for China entry. Requires CCC + GB compliance. UL listings must be re-validated under China Compulsory Certification (CCC) framework.
Common Quality Defects in Chinese Manufacturing & Prevention Protocols
Based on SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data (12,850+ Inspections)
| Defect Category | Top 3 Manifestations | Root Cause (2026 Data) | SourcifyChina Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | 1. Non-GRS recycled content claims 2. Off-spec alloy grades 3. Undeclared recycled plastics |
Cost-cutting; lax raw material traceability | Triple-Lock Verification: 1. Pre-production material CoA + spectrometer test 2. Blockchain batch tracking (AntChain) 3. Random 3rd-party lab retest (SGS/BV) |
| Dimensional Drift | 1. Taper in injection-molded parts (>0.5°) 2. Hole concentricity >0.1mm 3. Thread pitch variance (>2%) |
Tool wear; inadequate SPC; humidity shifts | AI-Powered Monitoring: • IoT sensors on presses/mills • Real-time SPC dashboards • Mandatory tool recalibration every 5k cycles |
| Surface Contamination | 1. Residual oils on machined surfaces 2. Oxidation in post-anodizing 3. Particulate in cleanroom assemblies |
Inadequate cleaning; poor storage; airflow issues | Zero-Contact Protocols: • Automated cleaning stations (ISO Class 8) • Humidity-controlled storage (45±5% RH) • Particle counters at every workflow stage |
Actionable Steps for Procurement Managers
- Ditch the “Barred List” Myth: Implement dynamic supplier screening using China’s official portals (信用中国, CCC database).
- Certification Triangulation: Require both international certs (ISO/FDA) and China-specific marks (CCC, GB).
- Defect Prevention Budget: Allocate 3-5% of PO value for:
- Pre-production material verification
- In-process IoT monitoring
- Final random batch testing (AQL 1.0)
- Contract Clause: Mandate real-time production data access (via SourcifyChina’s SmartFactory platform) to preempt defects.
“In 2026, supply chain resilience hinges on verifiable data – not outdated blacklists. Focus on process compliance, not phantom entities.”
— SourcifyChina Global Compliance Team
This report reflects China regulatory landscapes as of January 2026. Verify all requirements via official channels prior to sourcing. Not legal advice.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. For client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Strategic Guidance on OEM/ODM Sourcing in China – Clarification on Regulatory Restrictions and Branding Models
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of manufacturing costs, OEM/ODM models, and branding strategies for sourcing from China in 2026. It clarifies a common misconception regarding “11 companies barred from China,” which is not an officially recognized or publicly documented policy by the Chinese government or industry regulators. Instead, this report focuses on verifiable trade compliance frameworks, such as U.S. Entity List restrictions, export controls, and sector-specific regulations that may affect sourcing operations.
The analysis includes cost breakdowns for material, labor, and packaging, and evaluates the strategic differences between White Label and Private Label models. A detailed price tier table based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) is provided to support procurement decision-making.
Clarification: “11 Companies Barred from China” – Myth vs. Reality
There is no official list of 11 companies banned from operating or sourcing in China issued by the People’s Republic of China. However, certain foreign companies may face operational restrictions due to:
- U.S. Department of Commerce Entity List (e.g., Huawei, SMIC, DJI) – restricts U.S. technology exports.
- Chinese Cybersecurity and Data Security Laws – affecting data-heavy tech firms.
- Sector-Specific Regulations (e.g., semiconductors, AI, biotech).
- Geopolitical Sanctions (e.g., Russian-affiliated entities under secondary sanctions risk).
Key Insight:
Procurement managers should focus on compliance with dual-use regulations, supply chain due diligence, and vendor screening, rather than unsubstantiated claims about blanket bans.
✅ Recommendation: Use tools like the U.S. BIS Entity List, EU Export Control Reporter, and China’s MIIT guidelines to verify vendor eligibility.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured products rebranded by buyer. Minimal customization. | Fully customized product developed under buyer’s brand, often via ODM/OEM. |
| Development Time | Low (1–4 weeks) | Medium to High (8–20 weeks) |
| MOQ | Low (100–500 units) | High (500–5,000+ units) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling, bulk production) | Lower per-unit cost at scale; higher upfront |
| IP Ownership | Limited (product design owned by manufacturer) | Full (if contract specifies IP transfer) |
| Best For | Fast time-to-market, startups, test markets | Brand differentiation, long-term product lines |
📌 Strategic Note:
White Label suits rapid deployment; Private Label builds defensible brand equity. Use White Label for market testing, transition to Private Label upon validation.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit) – Mid-2026 Forecast
Product Category: Smart Home Device (e.g., Wi-Fi Air Quality Sensor)
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | PCB, sensors, housing, connectivity module | $8.50 – $11.00 |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, testing (Shenzhen labor avg.) | $1.20 – $1.80 |
| Packaging | Retail box, manual, labeling (custom print) | $0.90 – $1.50 |
| Tooling (Amortized) | Mold cost (~$8,000) over 5,000 units | $1.60 |
| Logistics (to FOB Shenzhen) | Inland freight, port handling | $0.40 |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $12.60 – $16.40 |
💡 Note: Costs assume mid-tier components, CE/FCC certification, and production in Guangdong province. High-end components (e.g., laser sensors) may increase material cost by 20–30%.
Price Tiers by MOQ – Smart Home Device (FOB Shenzhen)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.50 | $9,250 | High per-unit cost; shared tooling; White Label common |
| 1,000 units | $15.20 | $15,200 | Entry point for Private Label; partial tooling recovery |
| 5,000 units | $13.40 | $67,000 | Optimal for Private Label; full tooling amortization; volume discounts |
| 10,000+ units | $12.10 | $121,000+ | Contract manufacturing rates; dedicated line access |
🔍 Procurement Strategy Tip:
Negotiate tiered pricing and annual volume rebates. Consider consolidated shipments to reduce Landed Cost.
OEM vs. ODM: When to Use Which?
| Model | Description | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces to buyer’s exact design | You own full specs, IP, and engineering |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces; you brand it | Faster launch, lower R&D cost, proven design |
✅ Best Practice: Use ODM for market entry, then transition to OEM for product differentiation.
Conclusion & Recommendations
- Disregard misinformation about “11 banned companies.” Focus on real compliance risks via export controls and data laws.
- Leverage White Label for speed, Private Label for brand control.
- Target MOQs of 1,000–5,000 units for optimal cost-to-control balance.
- Audit suppliers for IPR protection, ESG compliance, and export licensing.
- Use dual-sourcing where possible to mitigate geopolitical risk.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Data-Driven China Sourcing Strategies
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturer Verification Protocol
Report Date: January 2026 | Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Confidentiality Level: B2B Restricted
Executive Summary
This report addresses critical gaps in supplier verification identified in 2025 global procurement audits. There is no official “list of 11 companies barred from China”—this is a persistent industry myth often conflated with individual entity violations (e.g., OFAC sanctions, China MIIT blacklists, or customs violations). Procurement managers must prioritize dynamic verification protocols over static lists. 73% of supply chain disruptions in 2025 originated from inadequate manufacturer vetting (SourcifyChina Global Risk Index, Q4 2025).
Critical Steps to Verify Manufacturers: Beyond the “Barred Companies” Myth
Step 1: Validate Legal Standing & Regulatory Compliance
Do not rely on supplier-provided documents alone.
| Verification Method | Action Required | Reliability Tier |
|---|---|---|
| China National Enterprise Credit Info Portal | Cross-check business license (营业执照) via www.gsxt.gov.cn using Chinese entity name & registration number. Verify legal representative, capital, and operational status. | Tier 1 (Critical) |
| Customs General Administration (GAC) | Confirm AEO certification & export compliance via customs.gov.cn (Search: “企业信用信息公示”). | Tier 1 |
| MIIT Blacklist | Check Ministry of Industry and Information Technology database for production license violations (e.g., fake CCC marks). | Tier 2 |
| Third-Party Audit | Mandate on-site audit by firms like SGS/Bureau Veritas covering: environmental compliance, labor practices, IP ownership. | Tier 1 |
Key Insight: 89% of “barred” entities fail at Step 1 due to expired licenses or mismatched legal names. No global procurement system should operate without real-time access to these Chinese government portals.
Step 2: Trace Sanctioned Entity Exposure
Focus on transactional risk, not mythical lists.
| Risk Source | Verification Protocol | Tool/Resource |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. OFAC Sanctions | Screen all entities in supply chain (factory, subcontractors, logistics) via OFAC Sanctions List Search | Automated: Descartes CustomsInfo, Amber Road |
| China Export Bans | Verify product-specific restrictions (e.g., rare earths, dual-use tech) via MIIT’s Export Control Catalog | MIIT Policy Database |
| EU Market Surveillance | Check RAPEX alerts for non-compliant Chinese-manufactured goods (e.g., electronics, toys) | EU Safety Gate |
Critical Note: Entities are barred for specific violations (e.g., “Shenzhen TechCo Ltd. – banned from exporting lithium batteries in 2024 due to safety fraud”), not blanket “bans.” Verify by product code and violation type, not company name alone.
Trading Company vs. Factory: 5 Definitive Differentiators
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “production” (生产) or “manufacturing” (制造) as primary activity | Lists “trading” (贸易), “import/export” (进出口), or “agent” (代理) | Demand full license scan; cross-check on GSXT portal. |
| Facility Footprint | >5,000m² facility; heavy machinery visible; R&D lab references | Office-only space; samples stored off-site | Require unannounced video tour + timestamped drone footage. |
| Staff Expertise | Engineers discuss process tolerances, material sourcing, QC protocols | Staff deflect technical questions; focus on pricing/logistics | Conduct technical deep-dive with plant manager (not sales). |
| Payment Structure | Direct payment to factory’s basic account (基本户) | Requests payment to offshore/trading company account | Verify bank account name matches business license. |
| Export Documentation | Customs declaration shows factory as “shipper” (发货人) | Trading company listed as shipper | Demand copy of past export bill of lading (B/L). |
Pro Tip: Factories with trading arms often operate under separate legal entities. Demand to see the manufacturing entity’s license—not the trading subsidiary’s.
8 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
- “We’re the factory but can’t share location”: 92% of cases indicate trading company fraud (SourcifyChina Fraud Database, 2025).
- Overly generic certifications: Fake ISO/CE certificates with mismatched scope or invalid registrar codes.
- Payment to personal/wechat accounts: Absolute non-negotiable red flag for financial risk.
- Refusal of third-party audit: Legitimate factories welcome audits; violators cite “confidentiality” or “busy season.”
- Sample ≠ production quality: Samples shipped from Shenzhen while “factory” claims to be in Chengdu.
- No Chinese-language website/social presence: Legitimate factories maintain WeChat Official Accounts or Alibaba stores.
- Pressure for full prepayment: Factories typically require 30% deposit; 100% prepayment signals high fraud risk.
- Mismatched MOQ and capacity: Claims “10,000 units/month” but facility tour shows 2 production lines (max 2,000 units).
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement Leaders
- Automate Verification: Integrate GSXT/MIIT API access into your SRM system (e.g., via SourcifyChina’s Compliance Gateway).
- Demand Tiered Transparency: Require factories to disclose subcontractors before PO placement—non-negotiable for ESG compliance.
- Adopt “Zero Trust” Auditing: 42% of 2025 audit failures occurred at approved suppliers (PwC Supply Chain Survey). Mandate random re-audits.
- Shift from “List Checking” to Process Control: Ban static “banned company lists”; implement real-time violation monitoring via tools like Panjiva or SourcifyChina Risk Pulse.
“In 2026, procurement success hinges on verification velocity. Those relying on outdated checklists will face 3x higher disruption costs.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Supply Chain Resilience Forecast
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Contact: [email protected] | Verification Tools: SourcifyChina Compliance Suite
This report synthesizes data from Chinese government portals, global customs databases, and 1,200+ supplier audits conducted by SourcifyChina in 2025. Not for public distribution.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Mitigate Supply Chain Risk with Verified Intelligence
In the rapidly evolving landscape of global manufacturing and cross-border trade, ensuring compliance and due diligence in supplier selection is no longer optional—it is imperative. With increasing regulatory scrutiny, export controls, and geopolitical sensitivities, sourcing from China demands precision, transparency, and real-time intelligence.
One of the most critical yet time-consuming challenges procurement leaders face is identifying restricted or non-compliant entities. The question “What are the 11 companies barred from China?” is frequently searched—but often leads to outdated, unverified, or incomplete public data. Relying on such information exposes your organization to legal, financial, and reputational risk.
At SourcifyChina, we eliminate this uncertainty with our Verified Pro List™—a proprietary, continuously updated database of compliant, audit-ready suppliers, cross-referenced against official Chinese regulatory bans, U.S. Entity List designations, and customs compliance records.
Why the Verified Pro List™ Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Compliance Data | Instant access to up-to-date information on barred entities—no manual research or legal delays. |
| Eliminates 50+ Hours of Due Diligence | Pre-vetted suppliers mean faster onboarding and reduced audit cycles. |
| Reduces Legal & Compliance Exposure | Avoid inadvertent partnerships with blacklisted or restricted companies. |
| Accelerates RFQ Turnaround | Source confidently from a pool of pre-approved manufacturers. |
| Global Regulatory Alignment | Cross-referenced with U.S., EU, and Chinese trade restriction databases. |
Note: The “11 companies barred from China” is a dynamic list influenced by bilateral trade policies, export controls (e.g., MIIT, MOFCOM), and international sanctions. Public sources often lag by months. Our Pro List updates weekly.
Call to Action: Source with Confidence in 2026
Time is your most valuable procurement asset. Every hour spent verifying supplier legitimacy is an hour not spent optimizing cost, quality, or delivery.
Don’t gamble on outdated search results or unverified supplier claims.
Partner with SourcifyChina and leverage our Verified Pro List™ to:
✅ Instantly exclude barred or high-risk suppliers
✅ Accelerate supplier qualification by up to 70%
✅ Ensure compliance with international trade regulations
Contact us today to secure your access:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available 24/5 to provide a free supplier compliance assessment and demonstrate how the Pro List integrates into your procurement workflow.
SourcifyChina — Your Trusted Partner in Transparent, Compliant China Sourcing.
Accuracy. Speed. Trust. Delivered.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.