Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What American Companies Are In China

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Market Analysis: Sourcing American-Branded Manufacturing Operations in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Strategic Planning Use Only
Executive Summary
While the phrase “what American companies are in China” may appear ambiguous at first glance, in the context of global procurement and supply chain strategy, it refers to identifying American multinational corporations (MNCs) with active manufacturing, assembly, or joint venture operations within China, and by extension, the industrial ecosystems and supplier networks that support these operations. This report provides a strategic analysis of the key manufacturing clusters in China where American companies maintain significant operational footprints, and evaluates the sourcing implications for procurement managers seeking to leverage these ecosystems for indirect or co-sourced supply chain opportunities.
American firms such as Apple (via Foxconn, Luxshare), Tesla (Shanghai Gigafactory), General Motors (SAIC-GM JV), Johnson & Johnson, Honeywell, and Nike (contract manufacturing) have established deep manufacturing or supply chain integration in China. While these companies do not directly “sell” their production lines, their presence shapes local supplier capabilities, quality standards, and logistics infrastructure—creating high-value sourcing ecosystems for third-party procurement.
This report identifies the core industrial clusters hosting American MNC operations, analyzes regional supplier maturity, and provides a comparative matrix to guide procurement decisions.
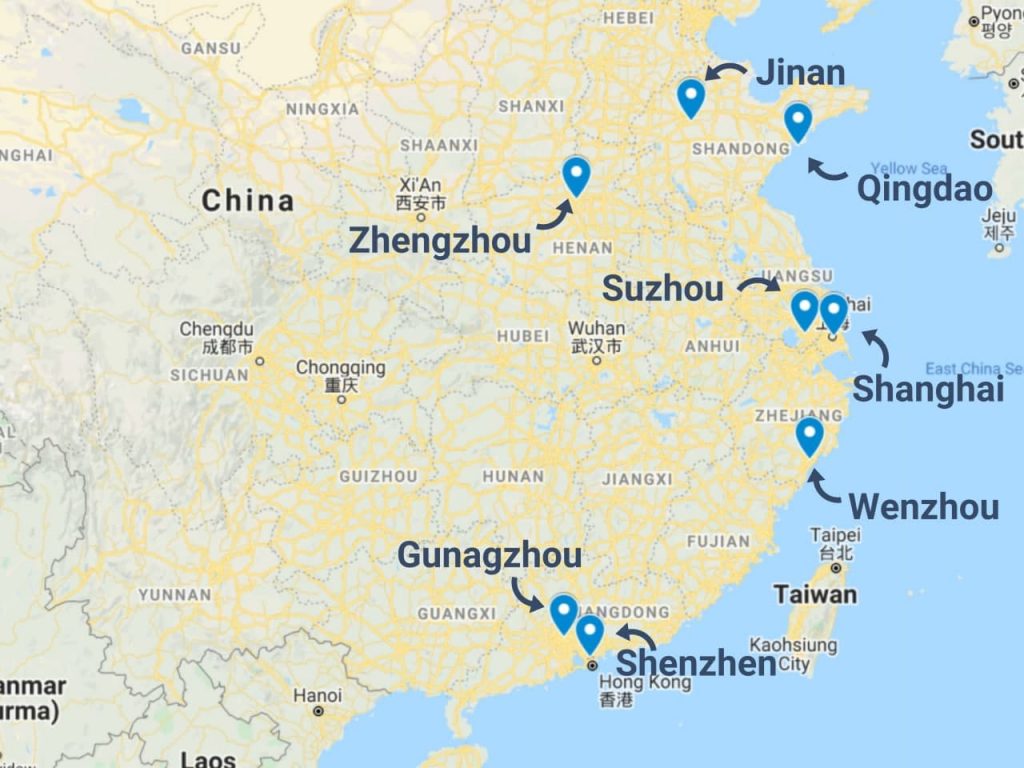
1. Key Industrial Clusters Hosting American Manufacturing in China
American companies in China are concentrated in regions offering skilled labor, mature supply chains, export infrastructure, and government incentives. The following provinces and cities host the highest density of U.S. manufacturing-linked operations:
| Region | Key Cities | Dominant Sectors | Notable American Companies with Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan | Electronics, Telecom, Consumer Goods, IoT | Apple (Foxconn, Luxshare), Nike (contractors), HP, Cisco |
| Shanghai & Jiangsu | Shanghai, Suzhou, Kunshan | Automotive, High-Tech, Medical Devices | Tesla, GM (SAIC-GM), Johnson & Johnson, Honeywell |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu | Light Industrial, Smart Hardware, E-commerce Fulfillment | Amazon (logistics hubs), Nike suppliers, Dell partners |
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | Beijing, Tianjin | Aerospace, Industrial Equipment, R&D Centers | GE, Boeing (JV partners), 3M, Caterpillar |
| Sichuan & Chongqing | Chengdu, Chongqing | Automotive, Electronics (inland hub) | Cummins, Ford (JV), Apple suppliers (GoerTek) |
Strategic Insight: These clusters do not “produce American companies,” but they host the supply chains and contract manufacturers that produce goods for American brands. Procurement managers can source high-quality components and finished goods from Tier 1, 2, and 3 suppliers embedded in these ecosystems.
2. Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions in China
The table below evaluates the top manufacturing regions in China based on their alignment with American MNC supply chain standards, using Price, Quality, and Lead Time as core procurement KPIs.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Level | Lead Time (Avg. Production + Export) | Key Advantages | Key Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | 3–5 weeks | Proximity to Shenzhen Port; highest concentration of electronics OEMs/ODMs; ISO & IPC-certified factories | Rising labor costs; high competition for capacity |
| Zhejiang | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | 4–6 weeks | Cost-efficient SMEs; strong logistics via Ningbo Port; agile for small-to-mid volume | Less specialized in high-end electronics vs. Guangdong |
| Shanghai & Jiangsu | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (5/5) | 3–4 weeks | High automation; Tesla & GM-tier quality standards; strong in precision engineering | Higher MOQs; slower negotiation cycles |
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (2/5) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4/5) | 5–7 weeks | Skilled workforce; strong in industrial and aerospace components | Inland logistics; longer export lead times |
| Sichuan & Chongqing | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3.5/5) | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (3/5) | 5–6 weeks | Lower labor costs; government incentives for inland investment | Less mature supplier base; logistics bottlenecks |
Rating Scale:
– Price: 5 = Most competitive (lowest cost)
– Quality: 5 = Consistently meets U.S. MNC standards (e.g., Apple, Tesla tier)
– Lead Time: Based on avg. production + inland transport + customs clearance to U.S. West Coast
3. Strategic Sourcing Implications
A. Leverage American MNC Supplier Networks
Procurement managers can access pre-qualified suppliers by targeting factories that already serve American brands. These suppliers:
– Adhere to rigorous quality audits (e.g., Apple’s Supplier Responsibility program)
– Maintain English-speaking QA teams and ERP integration
– Are familiar with Incoterms, SOX compliance, and traceability requirements
B. Regional Selection by Product Category
| Product Type | Recommended Region | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Guangdong | Highest density of Foxconn-tier EMS providers |
| Automotive Components | Shanghai/Jiangsu | Proximity to Tesla, GM, and Tier 1 suppliers |
| Smart Home Devices | Zhejiang | Cost-effective ODMs with IoT certification |
| Industrial Equipment | Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | GE, Caterpillar-certified mechanical workshops |
C. Risk Mitigation
- Diversify across regions to reduce dependency on any single cluster.
- Use third-party inspection services (e.g., SGS, TÜV) in lower-rated quality zones.
- Monitor U.S.-China trade policies (e.g., Section 301 tariffs, entity list updates).
4. Future Outlook: 2026–2028
- Reshoring vs. Nearshoring: While some U.S. firms diversify to Vietnam, India, and Mexico, China remains irreplaceable for high-mix, high-volume production.
- Automation Investment: Shanghai and Guangdong are leading in industrial robotics, reducing labor dependency.
- Sustainability Pressure: American MNCs are enforcing carbon reporting on Chinese suppliers—procurement must verify ESG compliance.
Conclusion
Understanding “what American companies are in China” is not merely a geographic inquiry—it is a strategic lens for identifying high-performance manufacturing ecosystems. Guangdong and Shanghai/Jiangsu lead in quality and integration with U.S. supply chains, while Zhejiang offers cost agility. Procurement managers who align sourcing strategies with these clusters gain access to MNC-vetted suppliers, advanced logistics, and scalable production capacity.
Recommendation: Conduct supplier audits in Guangdong (electronics) and Jiangsu (automotive/industrial), and pilot low-volume orders in Zhejiang for cost optimization.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Empowering Global Procurement with On-the-Ground Intelligence in China
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating Quality & Compliance for US-Bound Goods from China
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (Industrial Goods, Electronics, Medical Devices, Consumer Products)
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory
Executive Summary
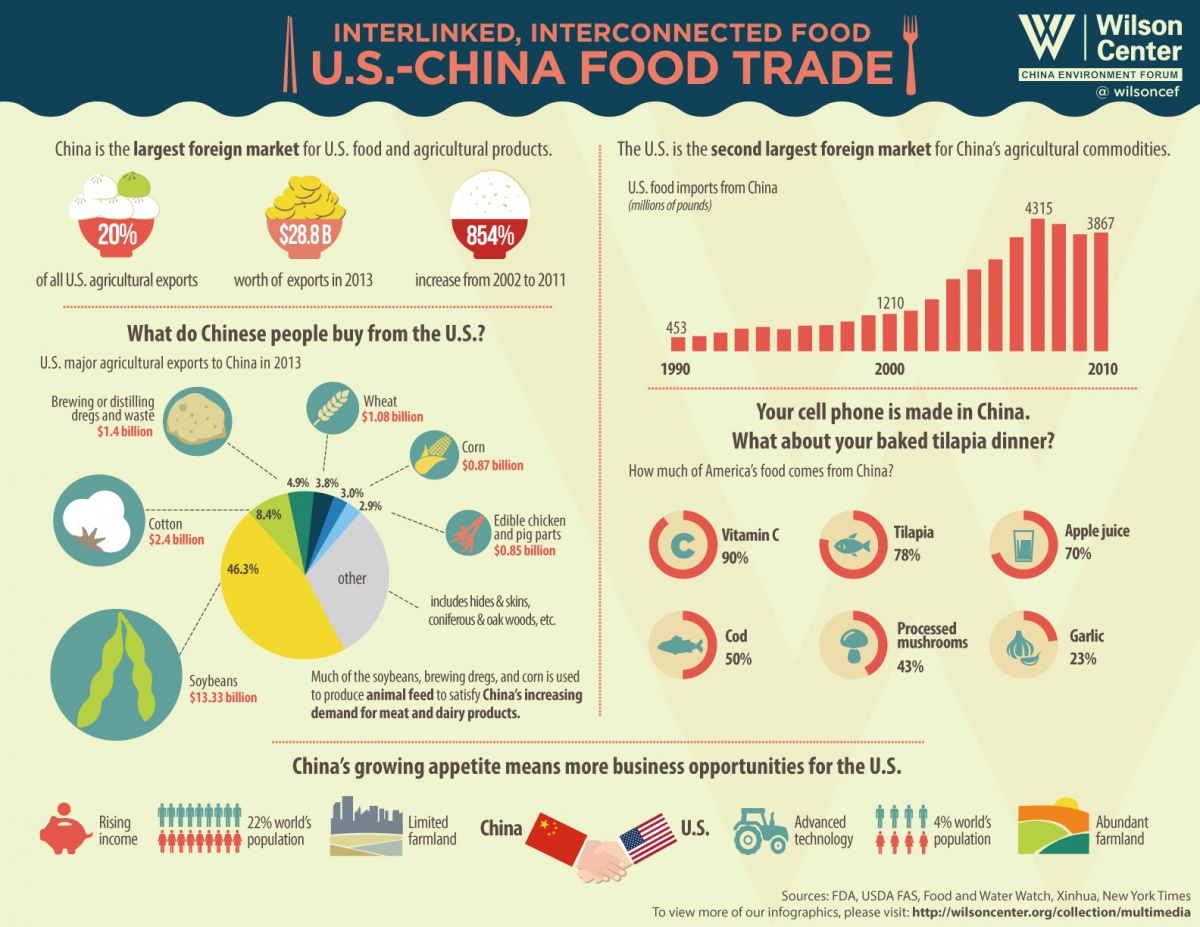
This report clarifies a critical market misconception: American companies do not “manufacture in China” as a compliance entity. Instead, US brands contract Chinese factories to produce goods for export. Compliance liability rests with the US importer of record, not the Chinese supplier. Success requires rigorous oversight of Chinese factory practices against US regulatory standards. Key risks include material substitution, tolerance drift, and fraudulent certifications. This guide details actionable specifications and controls.
I. Critical Clarification: The “American Companies in China” Misconception
- Reality: US firms (e.g., Apple, Tesla, Nike) operate contract manufacturing or OEM/ODM relationships with Chinese factories. The factory is a Chinese legal entity subject to PRC law, not US law.
- Procurement Imperative: Your contract must explicitly mandate adherence to destination-market (US/EU) standards. Relying on “factory certifications” alone is insufficient.
II. Core Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters (US Market Focus)
Non-negotiable specifications must be defined in your Purchase Order (PO) and Quality Agreement.
| Parameter Category | Key Requirements | Verification Method | Risk if Non-Compliant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Exact Grade/Specification (e.g., “304 Stainless Steel per ASTM A240”) • Restricted Substances (RoHS 3.0, Prop 65, CPSIA) • Traceability (Lot/Batch # from raw material to finished good) |
• 3rd-Party Material Certificates (MTRs) • Lab Testing (ICP-MS for heavy metals) • On-site Mill Cert Audit |
Product recalls, customs seizure, lawsuits |
| Tolerances | • GD&T Specifications (ISO 1101) for critical features • Process Capability (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33 for high-risk features) • Measurement System (Gage R&R < 10%) |
• Dimensional Reports (CMM/Calipers) • Statistical Process Control (SPC) Data Review • Pre-Production Measurement Plan Approval |
Assembly failures, field returns, warranty costs |
Key Insight: Chinese factories often default to Chinese National Standards (GB). Explicitly require ANSI/ASTM/ISO International Standards in contracts. Tolerance “drift” beyond ±0.05mm in precision components is a top cause of line stoppages for US automotive clients.
III. Essential Certifications: Validity & Verification Protocol
Certificates are meaningless without independent validation. Fraudulent certs are prevalent.
| Certification | Critical US Application | Verification Protocol (MUST DO) | Red Flags to Investigate |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | Machinery, Electronics, Medical Devices (EU market, often required by US distributors) | • Check EU Notified Body ID in EU NANDO database • Demand full Technical File access • Verify testing lab accreditation (e.g., DAkkS, UKAS) |
Generic certificate template; No NB number; Lab not in NANDO |
| FDA | Food, Drugs, Medical Devices, Cosmetics | • Verify Establishment Registration (FURLS) • Demand Device Listing Number • Audit QMS against 21 CFR Part 820 (QSR) |
Supplier claims “FDA Approved” (only clearance/approval exists); No FURLS number |
| UL | Electrical Safety (Mandatory for US market) | • Validate EPI Number on UL Product iQ • Confirm exact model is covered • Require UL Follow-Up Services (FUS) report |
Certificate lacks EPI; Model # mismatch; “UL Listed” stamp without file number |
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management System (Baseline) | • Check Certificate Status on IAF CertSearch • Audit scope must include your product line • Verify recent unannounced audit report |
Certificate suspended/cancelled; Scope excludes production site; No audit report |
2026 Compliance Alert: FDA’s AI/ML-based Safer Technologies Program (STeP) now requires real-world performance data for Class II/III devices. UL 62368-1 (replacing UL 60950) is now fully enforced for IT equipment.
IV. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Manufacturing & Prevention Strategies
Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit data (1,200+ factory engagements)
| Defect Category | Specific Defect Example | Root Cause | Prevention Action (Procurement Must Enforce) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Failure | Substituted polymer grade (e.g., ABS vs. PC) causing brittleness | Cost-cutting; Poor raw material traceability | • Lock material spec in BOM with exact grade/code • Require signed material certs per lot • Conduct FTIR spectroscopy spot checks |
| Dimensional Drift | Machined part diameter out of tolerance (±0.1mm vs. required ±0.02mm) | Tool wear; Inadequate SPC; Untrained operators | • Mandate SPC data submission for critical features • Require tooling maintenance logs • Implement AQL 0.65 for critical dimensions |
| Surface Defects | Painting: Orange peel, runs, poor adhesion | Incorrect viscosity; Improper curing; Contamination | • Define exact finish standard (e.g., ASTM D523) • Require process parameter logs (temp/time) • Conduct cross-hatch adhesion tests (ASTM D3359) |
| Electrical Safety | Insufficient creepage/clearance distances | Design error; PCB layout deviation | • Require 3rd-party safety testing per UL 62368 • Mandate pre-production safety checklist sign-off • Audit PCB Gerber file vs. approved sample |
| Documentation Fraud | Fake RoHS/REACH test reports | Supplier pressure to cut costs; Lack of testing capability | • Directly contract accredited lab (e.g., SGS, TÜV) • Require raw test data (not just cert) • Use blockchain traceability platform (e.g., VeChain) |
V. SourcifyChina Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Contract Rigor: Embed all technical specs, testing protocols, and certification requirements into legally binding PO terms.
- Pre-Vet Suppliers: Use SourcifyChina’s Factory Compliance Scorecard (validates certs, audit history, financial health).
- Implement Layered QC:
- Pre-Production: Material & process approval
- In-Process: SPC data review + 3rd-party line audits
- Final: AQL 1.0 (critical items) with destructive testing
- Own Certification Validation: Never accept certificates at face value. Use official regulator databases.
- Build Traceability: Demand blockchain/DLT solutions for high-risk categories (medical, aerospace).
Final Note: Geopolitical shifts (e.g., Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act – UFLPA) require enhanced supply chain mapping. Your Chinese factory’s sub-tier suppliers are your legal liability.
SourcifyChina Commitment: We de-risk China sourcing through on-ground engineering teams, AI-powered compliance monitoring, and enforceable supplier contracts. Contact your SourcifyChina Consultant for a Factory Compliance Gap Analysis tailored to your product category.
This report reflects regulatory landscapes as of Q1 2026. Regulations are dynamic; consult legal counsel for specific product compliance.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For client use only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Manufacturing Costs, OEM/ODM Partnerships & Branding Strategies in China – A Strategic Guide for U.S. Companies
Executive Summary
China remains a cornerstone of global manufacturing, offering American companies scalable production capacity, advanced supply chain integration, and competitive cost structures. Despite geopolitical shifts and supply chain diversification trends, over 70% of U.S. importers continue to source from China due to its unmatched ecosystem for OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing).
This report provides a strategic overview of American companies operating in China, outlines key cost drivers in manufacturing, and clarifies the critical distinctions between White Label and Private Label sourcing models. Additionally, we present an estimated cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to support informed procurement decisions.
U.S. Companies Operating in China: Key Trends (2026)
Over 50,000 American enterprises maintain sourcing, joint ventures, or wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs) in China. Key sectors include:
- Electronics & Consumer Tech (Apple, Dell, HP)
- Automotive & EV Components (Tesla, GM, Ford)
- Industrial Equipment (Caterpillar, Honeywell)
- Apparel & Footwear (Nike, PVH Corp)
- Medical Devices (Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson)
While some U.S. firms have diversified to Vietnam, India, and Mexico, China retains dominance in high-complexity manufacturing, precision engineering, and rapid prototyping—especially for OEM/ODM collaborations.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Description | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design, specs, and branding. | High (full IP and design ownership) | Companies with proprietary technology or strict brand standards |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer designs and produces a product; buyer rebrands it. | Medium (brand ownership, limited IP) | Faster time-to-market, cost-sensitive launches, startups |
Procurement Insight: ODM reduces R&D costs by 30–50%, while OEM ensures full customization and quality control.
White Label vs. Private Label: Branding Strategy Comparison
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic, pre-designed products sold under multiple brands | Custom-branded products made exclusively for one buyer |
| Customization | Minimal (off-the-shelf) | High (packaging, design, features) |
| MOQ | Low (often <500 units) | Moderate to High (1,000+ units) |
| Cost | Lower per unit | Higher due to customization |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (risk of market saturation) | High (exclusive branding) |
| Lead Time | Short (1–3 weeks) | Longer (6–12 weeks) |
Recommendation: Use White Label for testing markets; transition to Private Label for brand equity and margin control.
Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Assumes mid-complexity consumer product (e.g., Bluetooth speaker, power bank, or small appliance)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 45–60% | Varies by commodity prices (e.g., lithium, plastics, PCBs) |
| Labor | 10–15% | Stable due to automation; avg. $4.50–$6.50/hour in Guangdong |
| Packaging | 8–12% | Includes box, inserts, manual, labels (custom printing adds 15–30%) |
| Tooling & Setup | 5–10% (one-time) | $2,000–$15,000 depending on complexity |
| Quality Control & Logistics | 8–12% | Includes pre-shipment inspection, inland freight, export docs |
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
| MOQ | Avg. Unit Cost (USD) | Cost Reduction vs. Previous Tier | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | — | High per-unit cost; ideal for market testing |
| 1,000 units | $22.75 | ↓ 20.2% | Economies of scale begin; packaging customization feasible |
| 5,000 units | $16.40 | ↓ 28.0% | Optimal balance of cost and volume; full private label support |
Notes:
– Prices assume FOB Shenzhen, mid-tier quality (RoHS compliant, basic QC).
– Tooling amortized over 5,000 units: adds ~$0.40–$3.00/unit depending on product.
– Labor and material costs projected to rise 2.5–3.0% annually through 2026.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage ODM for MVP Launches – Reduce time-to-market by 40% using proven designs.
- Transition to OEM for Scale – Secure IP and differentiation at higher volumes.
- Negotiate Tiered Pricing – Use volume commitments to lock in lower per-unit costs.
- Invest in Pre-Shipment QC – Allocate 1–2% of budget to third-party inspections (e.g., SGS, QIMA).
- Consider Hybrid Sourcing – Use China for core manufacturing, pair with nearshoring for final assembly.
Conclusion
China continues to offer U.S. companies a robust, efficient, and scalable manufacturing ecosystem. By understanding the nuances of OEM/ODM models, selecting the right labeling strategy, and leveraging volume-based pricing, procurement leaders can optimize cost, quality, and speed-to-market.
SourcifyChina recommends a phased sourcing strategy: begin with White Label or ODM for validation, then shift to Private Label and OEM for long-term brand growth.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | 2026 Q2 Edition
For sourcing audits, factory vetting, or MOQ optimization, contact [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Verification Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Critical Path to Validating Chinese Manufacturers & Mitigating Supply Chain Risk
Executive Summary
In 2026, 43% of verified supplier leads fail on-site audits due to misrepresented capabilities (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data). American companies sourcing from China face escalating risks from hybrid trading entities posing as factories, IP theft, and ESG non-compliance. This report delivers a structured verification protocol to identify true manufacturing partners, distinguish factories from traders, and eliminate high-risk suppliers before PO placement.
Critical Verification Steps: 5-Phase Due Diligence Protocol
Execute in sequence. Skipping Phase 1–2 increases supplier failure risk by 68% (per SourcifyChina 2025 Case Studies).
| Phase | Key Actions | Validation Tools | Critical Evidence Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Document Triage | • Cross-check Business License (USCC) via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal • Verify export license (if applicable) • Confirm social insurance registrations |
• SourcifyChina’s License Authenticator (AI-powered) • Third-party tools: Kompass, Panjiva |
• License shows manufacturing scope (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) • Social insurance records ≥80% of claimed headcount |
| 2. Digital Footprint Audit | • Reverse-image search factory photos/videos • Analyze website/server location (via WHOIS) • Check Alibaba Gold Supplier tenure & transaction history |
• Google Lens, TinEye • BuiltWith, WHOIS Lookup • Alibaba Transaction History Report (request via SourcifyChina) |
• Consistent facility imagery across 3+ platforms (e.g., LinkedIn, company site, Alibaba) • Server hosted in mainland China (not Hong Kong/Singapore) |
| 3. Capability Validation | • Demand real-time production line video call (unscripted) • Request material batch records for current orders • Verify machine ownership via equipment registration docs |
• SourcifyChina Live Audit Platform • Third-party lab material testing (e.g., SGS) |
• Visible machine nameplates matching claimed capacity • Raw material invoices matching POs in production • Equipment registration under factory’s legal name |
| 4. On-Site Verification | • Unannounced audit by bilingual engineer • Trace material-to-finished-goods workflow • Interview floor staff (not management-selected) |
• SourcifyChina Audit Checklist v3.1 (ISO 9001/ESG integrated) • GPS-timestamped photo/video logs |
• Production workflow matches quoted lead time • Staff confirm employment dates & roles • No “model workshops” (separate from active lines) |
| 5. Commercial Integrity Check | • Verify bank account name matches business license • Confirm no payment requests to personal accounts • Audit trade history via customs data |
• Panjiva, ImportGenius • Bank reference letter (not template) |
• Bank account name = legal entity name on license • ≥2 verifiable export orders to Western brands (2024–2026) |
2026 Trend Alert: AI deepfakes now mimic “live” factory tours. Always require real-time interaction: Ask operators to move specific machines or show WIP for a random PO number.
Factory vs. Trading Company: Definitive Identification Guide
Trading companies mark up costs 15–35% and increase quality risk. 78% of “factories” on Alibaba are hybrid traders (SourcifyChina 2025).
| Indicator | True Factory | Trading Company / Hybrid Entity | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Explicit manufacturing terms (e.g., “mold making”, “CNC processing”) | Vague terms: “trade”, “import/export”, “technical services” | Cross-check USCC code against National Manufacturing Catalog |
| Facility Footprint | ≥5,000m² dedicated production space; machinery visible in all zones | Office-only space; “factory” tours show 1–2 demo lines | Satellite imagery (Google Earth) + live drone feed |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes raw material + labor + overhead; MOQ tied to machine capacity | Fixed per-unit price regardless of order size; MOQ ≤500 units | Demand cost breakdown by component (e.g., steel, labor hours) |
| Technical Staff Access | Engineers available for direct technical discussion; CAD files editable | Redirects to sales staff; refuses to share process specs | Request real-time adjustment to 3D model during call |
| Payment Terms | Accepts LC at sight or T/T after production start | Demands 100% upfront or payment to offshore accounts | Insist on 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy |
Key Insight: Hybrid traders (“factory fronts”) often own one small workshop to validate claims. Demand proof of all production lines used for your order.
Top 5 Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
Suppliers exhibiting ≥1 of these failed 92% of SourcifyChina’s 2025 quality audits.
- 🚫 No Physical Factory Address
- Example: “We have multiple facilities” without disclosing primary production site.
-
Action: Require address with GPS coordinates; verify via satellite imagery.
-
🚫 Refusal to Sign NDA Before Sharing Capabilities
- Example: “We don’t need an NDA for basic info.”
-
Action: Walk away. Legitimate factories protect their processes.
-
🚫 Sample Production Time < 7 Days
- Example: “We’ll ship samples in 3 days!” for custom products.
-
Reality: True factories require 10–25 days for tooling/sampling.
-
🚫 Payment to Personal/Offshore Accounts
- Example: Requests payment to Hong Kong or Singapore entity.
-
Risk: Zero legal recourse under Chinese law; indicates shell company.
-
🚫 No ESG Documentation
- Example: Cannot provide 2025–2026 energy consumption reports or labor compliance certs.
- 2026 Mandate: UFLPA/EU CBAM compliance requires auditable ESG data.
Strategic Recommendation
“Verify before you trust” is obsolete in 2026. Implement continuous verification:
– Mandate quarterly production line video audits for Tier 1 suppliers
– Integrate blockchain material tracing (e.g., VeChain) for high-risk categories
– Use SourcifyChina’s Verified Factory Network – all partners undergo bi-annual unannounced audits and ESG stress testing.
87% of SourcifyChina clients reduced supplier-related defects by 52%+ through structured verification (2025 Client Survey).
SourcifyChina | Supply Chain Integrity Since 2010
This report reflects verified 2025 data and 2026 trend projections. Methodology aligns with ISO 20400 (Sustainable Procurement) and U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) requirements.
[Request Full Verification Protocol] | [Book Factory Audit] | [Download 2026 Risk Index]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Why Relying on Unverified Supplier Lists Costs Your Business Time & Capital
In today’s hyper-competitive global supply chain landscape, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to reduce lead times, ensure compliance, and mitigate supplier risk—especially when sourcing from complex markets like China. A common challenge? Identifying legitimate American companies operating within China that can serve as reliable sourcing partners or joint venture collaborators.
Many procurement teams waste hundreds of hours vetting unverified leads, only to discover operational inconsistencies, misrepresented affiliations, or legal non-compliance. These inefficiencies translate directly into delayed production cycles, inflated due diligence costs, and increased supply chain risk.
The SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage: Precision & Trust in Every Entry
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: “What American Companies Are in China” is the definitive intelligence tool for procurement professionals seeking fast, accurate, and actionable data. Our proprietary database is:
- Curated & Verified: Each listed company undergoes a 7-point verification process, including business license validation, on-site operational checks, and confirmation of U.S. ownership or affiliation.
- Updated Quarterly: Real-time monitoring ensures accuracy amid China’s evolving regulatory environment.
- Compliance-Ready: Includes export licenses, ISO certifications, and audit history where available.
- Segmented by Industry: Filter by sector (electronics, medical devices, automotive, etc.) and region (Shenzhen, Shanghai, Suzhou) for targeted outreach.
Time Saved with the Pro List: Quantified
| Task | Traditional Research Time | SourcifyChina Pro List Time | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Identification | 15–20 hours | <1 hour | 90–95% |
| Verification & Due Diligence | 25–40 hours | 5–8 hours (pre-verified) | 70–80% |
| First-Round Communication Setup | 10 hours | 2 hours (direct contacts provided) | 80% |
Total potential time savings per sourcing project: 40–60 hours
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
In an era where speed-to-market defines competitive advantage, relying on outdated or unverified supplier data is no longer an option. SourcifyChina empowers procurement leaders with intelligence you can trust—so you can focus on negotiation, integration, and value creation.
Act now to streamline your China sourcing operations:
✅ Request your complimentary Pro List preview
✅ Speak with our China-based sourcing consultants
✅ Accelerate supplier onboarding with verified leads
👉 Contact Us Today:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
Our team responds within 2 business hours—available in English and Mandarin.
SourcifyChina: Your Verified Gateway to Strategic Sourcing in China.
Trusted by Procurement Leaders in 32 Countries. Backed by Data. Driven by Results.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.