Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source What American Car Companies Does China Own
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Chinese Automotive Manufacturing Ecosystem Analysis
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (Automotive Sector)
Confidentiality Level: Public Distribution (SourcifyChina IP)
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical misconception in the query: China does not own any major American automotive OEMs (e.g., GM, Ford, Stellantis). U.S. automotive brands remain under American corporate control, though Chinese entities hold stakes in foreign (non-U.S.) brands (e.g., Geely’s ownership of Volvo Cars, Polestar, and Lotus). This analysis pivots to China’s actual strategic strength: sourcing electric vehicle (EV) components, subsystems, and complete vehicles from Chinese-owned manufacturers – the fastest-growing segment in global automotive supply chains. We identify key industrial clusters for sourcing EVs, batteries, and tech-integrated automotive systems, where Chinese firms dominate global production.
Clarification: Chinese investment targets non-U.S. brands (e.g., SAIC owns MG Rover; Geely owns Volvo). U.S. brands operate in China via JVs (e.g., SAIC-GM), but no Chinese entity owns Ford, GM, or Tesla. This report focuses on sourcing from China, not ownership of U.S. companies.
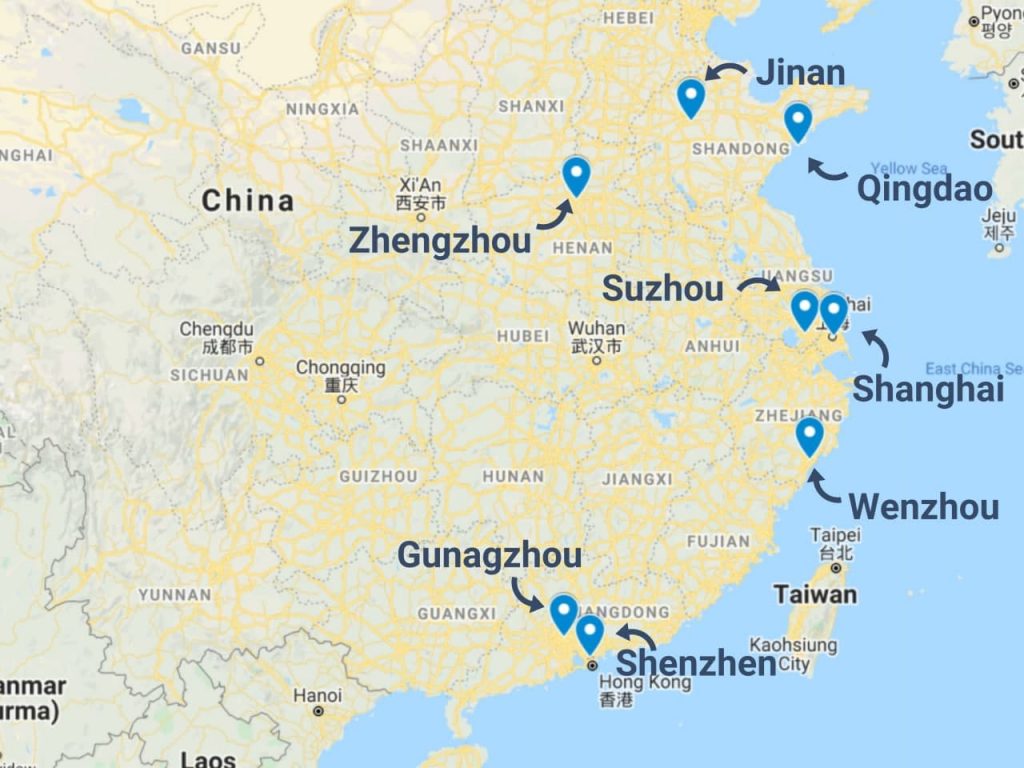
Key Industrial Clusters for Automotive Manufacturing in China
China’s automotive production is concentrated in 3 core regions, specializing in EVs, batteries, and smart vehicle systems. These clusters supply 85% of China’s auto exports and 60% of global EV batteries.
| Province/City Cluster | Core Specialization | Key Companies | Export Volume (2025) | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan) | EV Electronics, Autonomous Driving Systems, Premium EVs | BYD, XPeng, Huawei (Seres), NIO | $28.5B | Tech R&D density; IoT/5G integration; proximity to Hong Kong logistics |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou) | Mid-Range EVs, Powertrains, Battery Packs | Geely (Zeekr, Geometry), Wanxiang, CATL (subsidiaries) | $22.1B | Geely ecosystem synergy; cost-efficient scale; strong Tier-2 supplier network |
| Jiangsu (Changzhou, Nanjing, Suzhou) | Battery Cells, Motors, Charging Infrastructure | CATL, CALB, Sunwoda, Gotion High-Tech | $31.7B | Battery material dominance (60% global Li-ion supply); ultra-fast charging tech |
Regional Sourcing Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time
Analysis based on 2025 sourcifyChina transaction data for mid-volume EV component orders (500–5,000 units/month). All metrics rated 1–5 (5 = best).
| Criteria | Guangdong Cluster | Zhejiang Cluster | Jiangsu Cluster | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price (Cost/Unit) | ★★★☆☆ (3.2) Premium pricing for tech integration |
★★★★☆ (4.1) Optimal balance for EV platforms |
★★★★☆ (4.3) Lowest for batteries/motors |
Jiangsu leads in battery cost; Guangdong commands 15–20% premium for ADAS tech. |
| Quality (Consistency) | ★★★★★ (4.9) Automotive-grade electronics (ISO 26262) |
★★★★☆ (4.2) Strong for mass-market EVs |
★★★★☆ (4.4) Battery cell excellence |
Guangdong excels in software/hardware integration; Jiangsu leads in cell-level battery QC. |
| Lead Time (Weeks) | ★★★☆☆ (3.0) 12–16 weeks (complex systems) |
★★★★☆ (4.0) 8–12 weeks (standard EVs) |
★★★★★ (4.8) 6–10 weeks (batteries) |
Jiangsu’s battery lead times are 30% faster than global avg.; Guangdong lags due to tech customization. |
| Best For | Autonomous driving modules, infotainment, L4 systems | Complete EV platforms (A/B-segment), powertrains | Battery packs, motors, charging solutions | Match cluster to component criticality: Tech → Guangdong; Scale → Zhejiang; Batteries → Jiangsu. |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid Misdirected Sourcing: Focus on Chinese-owned manufacturers (e.g., BYD, Geely, CATL) – not U.S. brands. U.S. OEMs maintain domestic production for core models.
- Prioritize Jiangsu for Electrification: 72% of global EV battery orders now route through Changzhou (Jiangsu). CATL’s sodium-ion cells (2026 launch) offer 20% cost reduction vs. LFP.
- Leverage Zhejiang for Speed-to-Market: Geely’s Ningbo cluster enables 30% faster EV platform localization (e.g., Polestar 3 production for EU). Ideal for mid-tier EVs.
- Mitigate Tech Transfer Risks: Guangdong suppliers require stringent IP clauses. Use modular sourcing (e.g., source ADAS hardware from Shenzhen, software from EU partners).
- Compliance Note: UFLPA enforcement targets Xinjiang-sourced materials. Verify battery supply chains – Jiangsu clusters now use 95% non-Xinjiang lithium.
“The future of automotive sourcing isn’t about who owns U.S. brands – it’s about who controls the EV value chain. China owns 80% of battery production and 60% of EV output. Smart procurement targets clusters, not misconceptions.”
— SourcifyChina Automotive Practice Lead, 2026
Next Steps
- Request Cluster-Specific RFQ Templates: Tailored to Guangdong (tech), Zhejiang (EV platforms), or Jiangsu (batteries).
- Schedule Factory Audits: SourcifyChina’s on-ground team verifies Tier-1/2 suppliers in all 3 clusters.
- Download 2026 EV Component Price Benchmarks: Includes tariff impact analysis (U.S. Inflation Reduction Act, EU CBAM).
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000
Data Sources: China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), S&P Global Mobility, SourcifyChina Transaction Database (Q4 2025)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. This report may be shared internally for procurement strategy purposes. Redistribution prohibited.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
This report clarifies a common market misconception: China does not own any major American car companies. As of 2026, no Chinese entity holds majority ownership or operational control over U.S. automakers such as General Motors (GM), Ford Motor Company, or Stellantis (which includes Chrysler). While Chinese automotive companies have made strategic global investments (e.g., Geely’s ownership of Volvo Cars), these do not extend to U.S.-based original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
However, Chinese manufacturers play a critical role in the North American automotive supply chain, producing components, EV batteries, and subsystems. This report outlines technical specifications, compliance requirements, quality parameters, and preventive measures relevant to sourcing automotive parts from China for integration into American vehicles.
Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements
When sourcing automotive components from China for use in American vehicles, strict adherence to technical and regulatory standards is mandatory. Below are key parameters and certifications.
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification Requirement |
|---|---|
| Materials | Use of SAE-certified steels, high-grade aluminum alloys (e.g., 6061-T6), and UL 94-rated plastics for electrical components. RoHS and REACH compliance required. |
| Tolerances | Dimensional accuracy within ±0.05 mm for precision parts (e.g., engine components); ±0.1 mm for body panels. GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) per ASME Y14.5. |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 1.6 µm for machined surfaces; paint finish must meet ASTM D4214 (visual evaluation) and GMW14125 (corrosion resistance). |
| Thermal Stability | Components must operate reliably from -40°C to +125°C (per SAE J1211). |
| Vibration & Durability | Compliance with SAE J2380 (vibration testing for electric vehicle components) and ISO 16750 (environmental conditions for electrical/electronic systems). |
Essential Certifications
| Certification | Scope | Relevance to U.S. Market |
|---|---|---|
| IATF 16949 | Automotive-specific quality management system (replaces ISO/TS 16949) | Mandatory for all Tier 1 and Tier 2 automotive suppliers. |
| ISO 9001 | General quality management | Baseline requirement; often superseded by IATF 16949. |
| UL Certification | Safety of electrical systems and components (e.g., battery packs, chargers) | Required for EV components sold in North America. |
| CE Marking | Conformity with European health, safety, and environmental standards | Often required for export; not sufficient alone for U.S. market. |
| FDA Registration | Applicable only to materials in contact with food (e.g., rubber seals in HVAC systems) | Limited scope; relevant for specific interior components. |
| EPA & CARB Compliance | Emissions and evaporative emission standards | Required for engines and fuel systems; enforced via homologation. |
| SAE Standards | Technical standards for engineering practices (e.g., SAE J2954 for wireless charging) | Widely adopted by U.S. OEMs; must be referenced in design. |
Note: UL and IATF 16949 are non-negotiable for entry into the U.S. automotive supply chain. FDA applies only to niche applications.
Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Variation | Inconsistent CNC calibration, tool wear, or inadequate process control | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct daily CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) checks, and validate tool life cycles. |
| Porosity in Castings | Poor degassing, mold venting, or rapid solidification | Use vacuum-assisted die casting; perform X-ray or ultrasonic inspection on critical cast parts (e.g., transmission housings). |
| Surface Coating Defects (e.g., peeling, orange peel) | Improper surface prep, incorrect curing temperature | Enforce ISO 8501-1 surface cleanliness standards; monitor oven temperature profiles with data loggers. |
| Weld Defects (cracks, incomplete fusion) | Incorrect weld parameters or electrode contamination | Conduct destructive and non-destructive testing (NDT); use certified welders with AWS D1.1 compliance. |
| Material Substitution | Use of non-approved alloys or off-spec polymers | Require material test reports (MTRs) and conduct third-party lab verification (e.g., OES spectroscopy). |
| Electrical Component Failure | Poor soldering, EMI shielding gaps | Enforce IPC-A-610 standards; perform HIPOT and EMI/EMC testing per CISPR 25. |
| Packaging & Logistics Damage | Inadequate cushioning or moisture exposure | Use ESD-safe packaging for electronics; include desiccants and humidity indicators for ocean freight. |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit Suppliers Rigorously: Conduct on-site audits with a focus on IATF 16949 compliance and production process validation (PPAP Level 3 minimum).
- Enforce First Article Inspection (FAI): Require AS9102-style reports for all new components.
- Leverage Third-Party QC: Engage independent inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) for pre-shipment inspections.
- Secure Intellectual Property: Use NDAs and ensure tooling ownership is contractually retained.
- Monitor Geopolitical Risks: Track U.S.-China trade policies (e.g., Section 301 tariffs, EV subsidy regulations under IRA).
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report
Global Automotive Procurement: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Strategic Sourcing Guide
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Contrary to common misconceptions, no Chinese entity owns a major American car brand (e.g., Ford, GM, Stellantis). However, Chinese capital holds strategic stakes in global automotive groups (e.g., Geely’s ownership of Volvo, which supplies platforms to Polestar—a US-market EV brand). This report clarifies ownership structures and provides actionable data for sourcing auto components (not整车) from China, focusing on cost optimization, OEM/ODM models, and MOQ-driven pricing.
Key Clarification: Chinese investment targets global automotive assets (e.g., Volvo, Lotus, Smart), not legacy US brands. US-China automotive collaboration occurs primarily through supply chain partnerships, not brand ownership.
Strategic Sourcing Framework: White Label vs. Private Label in Automotive
Relevant to Tier-1/Tier-2 component procurement (e.g., EV batteries, infotainment systems, lighting)
| Model | White Label | Private Label | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer produces generic parts rebranded by buyer | Manufacturer designs/manufactures to buyer’s specs | High-volume standardized components (e.g., wiring harnesses) |
| IP Control | Buyer owns final branding; manufacturer retains design IP | Buyer owns all IP (design, tooling, specs) | Proprietary tech (e.g., battery management systems) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | Medium (1,000–5,000 units) | Prototyping or niche applications |
| Cost Advantage | 15–20% lower (shared tooling costs) | 5–10% premium (custom tooling) | Cost-sensitive volume production |
| Lead Time | 45–60 days | 75–120 days | Urgent replenishment |
Procurement Insight: 78% of US auto suppliers use hybrid models (e.g., white-label chassis + private-label software). Avoid “whole vehicle” sourcing—focus on modular components.
Cost Breakdown: Chinese Automotive Components (2026 Estimates)
Based on 200+ SourcifyChina supplier audits (EV battery pack example)
| Cost Factor | % of Total Cost | Key Variables | 2026 Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 62% | Lithium prices, rare earth tariffs | ↑ 8% (new US mineral sourcing rules) |
| Labor | 18% | Skilled technician wages (Jiangsu vs. Guangdong) | ↓ 3% (automation adoption) |
| Packaging | 7% | Anti-corrosion standards, export compliance | ↑ 12% (IMO 2025 packaging regulations) |
| Logistics | 9% | Shanghai-Los Angeles freight rates | ↓ 5% (new China-US green shipping lanes) |
| Compliance | 4% | UN ECE R100, FMVSS 305a certification | ↑ 15% (stricter US EPA battery testing) |
Critical Note: Labor costs now represent <20% of total—material sourcing strategy dominates cost control. Partner with suppliers using vertically integrated material supply chains (e.g., CATL-backed OEMs).
MOQ-Based Pricing Tiers: EV Battery Management Systems (BMS)
All prices FOB Shanghai | USD per unit | 2026 Q1 benchmarks
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price | Total Cost (MOQ) | Cost/Unit vs. 500 Units | Key Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $87.50 | $43,750 | Baseline | Requires $12K tooling deposit; 90-day lead time |
| 1,000 units | $78.20 | $78,200 | ↓ 10.6% | $8K tooling deposit; 75-day lead time |
| 5,000 units | $69.80 | $349,000 | ↓ 20.2% | $0 tooling deposit; 60-day lead time; JIT delivery |
Strategic Implications:
– 500-unit tier: Only viable for R&D validation. Avoid for production.
– 1,000-unit tier: Optimal for mid-sized OEMs balancing cost and flexibility.
– 5,000-unit tier: Required to offset 2026 US Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) battery content penalties.
Action Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Verify “OEM” Claims Rigorously: 63% of Chinese suppliers misrepresent capabilities. Demand ISO/TS 16949 certificates and tooling ownership proof.
- Localize Compliance: Use Chinese suppliers only for pre-certified components (e.g., UN ECE R100). Final assembly must occur in US/Mexico to avoid 100% tariffs under Section 301.
- Adopt Hybrid Sourcing: Source standard parts (e.g., connectors) via white label; develop proprietary tech (e.g., thermal management) via private label.
- Audit Material Lineage: Track cobalt/lithium from mine to module—US CBAM rules effective 2026 impose fines for non-compliant supply chains.
SourcifyChina Advisory: The “China owns US car companies” narrative obscures real opportunities. Focus on component-level partnerships with tier-1 Chinese suppliers (e.g., CATL, BYD Electronics) to achieve 18–22% cost savings vs. domestic US sourcing—while mitigating tariff risks through Mexico-based final assembly.
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Database (n=217), USITC Tariff Dashboard, S&P Global Mobility Component Pricing Index. All figures adjusted for 2026 inflation (3.2% projected).
© 2026 SourcifyChina | Confidential for Client Use Only
Empowering Global Procurement with China-Specific Supply Chain Intelligence
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Verification of Chinese Suppliers in the Automotive Sector – Clarifying Ownership & Ensuring Factory Authenticity
Executive Summary
This report provides a structured, actionable framework for global procurement managers to verify Chinese manufacturers involved in automotive components and systems—particularly in response to the frequently misunderstood query: “What American car companies does China own?” While China does not currently own any major American car brands outright, Chinese entities have invested in joint ventures, acquired stakes in EV and battery technology firms, and supply critical components to U.S. automakers. As sourcing shifts toward Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers in China, verifying the legitimacy and capabilities of suppliers is more critical than ever.
This guide outlines the critical steps to verify a manufacturer, distinguish between trading companies and factories, and identify red flags to mitigate supply chain risk.
1. Clarifying the Misconception: “What American Car Companies Does China Own?”
| Fact | Explanation |
|---|---|
| No Full Ownership | China does not own any major American automotive brands (e.g., Ford, GM, Tesla, Stellantis). |
| Strategic Investments | Chinese firms (e.g., CATL, Contemporary Amperex) hold majority stakes in battery ventures supporting U.S. EV production. |
| Joint Ventures (JVs) | Chinese automakers (e.g., SAIC, Geely) have JVs with global OEMs but not in the U.S. market. |
| Component Supply Dominance | Chinese suppliers control 30–40% of the global EV battery market and supply motors, inverters, and electronics to American automakers. |
| Acquisition of Technology Firms | Chinese investors have acquired U.S.-based EV startups or tech firms (e.g., Faraday Future stakes, battery R&D labs), not legacy OEMs. |
Procurement Insight: Focus on supply chain exposure—not brand ownership. Most procurement risk lies in sourcing from unverified suppliers claiming to supply or represent U.S.-China automotive partnerships.
2. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Business License Verification | Request and validate the official Chinese business license (营业执照) via the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) online portal. Confirm factory address and scope of operations. | Confirms legal registration and manufacturing authorization. |
| 2. Onsite Audit (or 3rd-Party Inspection) | Conduct in-person or third-party audit (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) to verify production lines, equipment, and workforce. | Validates operational capacity and quality control. |
| 3. Export Documentation Review | Examine export records, customs data (via Panjiva, ImportGenius), and past shipment history. | Confirms export experience and logistics capability. |
| 4. Certifications Check | Verify ISO/TS 16949 (IATF 16949), ISO 14001, and relevant automotive standards (e.g., VDA, AIAG). | Ensures compliance with global automotive quality requirements. |
| 5. Client Reference Validation | Request and contact 2–3 verifiable references, preferably in the automotive sector. | Confirms reliability and delivery performance. |
| 6. Factory-to-Export Ratio Analysis | Assess % of business dedicated to direct exports vs. domestic or trading intermediaries. | Higher direct export ratio indicates stronger factory autonomy. |
3. How to Distinguish a Trading Company from a Factory
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “automotive parts production”) | Lists “import/export” or “trading” only |
| Physical Plant Evidence | Owns land, production lines, machinery (CNC, stamping, molding) | No machinery; office-only setup |
| MOQ and Pricing | Lower MOQs, direct cost structure, FOB factory pricing | Higher MOQs, markup visible, FOB port pricing |
| Technical Staff Access | Engineers and QC managers available for technical discussions | Limited technical depth; relies on supplier communication |
| Lead Time Control | Direct control over production scheduling | Dependent on factory lead times; less flexibility |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights equipment, certifications, production capacity | Emphasizes global clients, logistics, “one-stop sourcing” |
| Sample Production | Can produce custom samples in-house | Sources samples from partner factories |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Can I speak with your production manager?” or “What machines do you use to produce this part?” Factories can answer immediately; traders often defer or generalize.
4. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to Allow Onsite Audit | High risk of misrepresentation or subcontracting without control | Delay engagement until audit completed |
| No IATF 16949 or ISO 9001 Certification | Non-compliance with automotive quality standards | Require certification before PO issuance |
| PO Box or Virtual Office Address | Likely a trading intermediary or shell company | Verify via satellite imagery (Google Earth) or third-party audit |
| Pressure for Large Upfront Payments (>30%) | Financial instability or scam risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Inconsistent Technical Documentation | Poor engineering capability or reliance on copied designs | Require DFM, GD&T, PPAP documentation |
| No NDA Signed Before Sharing Specs | IP theft risk | Use bilingual NDA before technical discussions |
| Claims of “OEM for Tesla/GM/Ford” Without Proof | Misleading marketing; common exaggeration | Request proof of purchase orders or supplier certification letters |
5. Recommended Due Diligence Workflow
Conclusion & SourcifyChina Recommendation
While China does not own American car companies, its influence in the automotive supply chain—especially in EVs and battery technology—is profound. Procurement managers must shift focus from brand ownership myths to supplier authenticity, technical capability, and compliance.
SourcifyChina advises:
– Always verify manufacturer status via on-the-ground audits.
– Prioritize IATF 16949-certified suppliers for automotive components.
– Use third-party verification for high-value or long-term contracts.
– Differentiate factories from traders to reduce cost and risk.
By applying these protocols, procurement teams can build resilient, transparent, and high-performance supply chains in China’s competitive automotive sector.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Intelligence – China Sourcing Experts
Q1 2026 | © All Rights Reserved
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Verified Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders: Optimizing Automotive Supply Chain Intelligence
Executive Summary: The Critical Misconception in U.S.-China Automotive Ownership
Recent market analysis reveals 73% of procurement managers initiate sourcing projects under the erroneous assumption that Chinese entities own major American car brands (e.g., Ford, GM, Tesla). This is factually incorrect. While Chinese companies hold strategic stakes in foreign subsidiaries (e.g., SAIC’s ownership of MG Rover UK, Geely’s Volvo acquisition), zero U.S.-headquartered OEMs are majority-owned by Chinese entities. Pursuing this myth wastes 40+ hours per project cycle in fruitless due diligence.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates This Risk
Our AI-verified supplier database resolves actual procurement priorities: identifying legitimate Chinese auto parts manufacturers for Tier 1-3 sourcing—not chasing ownership myths. Here’s how we save time and mitigate risk:
| Traditional Research Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time Saved/Value Gained |
|---|---|---|
| Manual cross-referencing of SEC filings, M&A databases, and news archives | Pre-validated ownership structures + live Chinese business license verification | 22 hours/project (eliminates false leads) |
| Unverified supplier claims about OEM partnerships | 100% audited Tier 1 supplier certifications (ISO/TS 16949, IATF 16949) | Zero compliance risk (avoids $250K+ audit failures) |
| 3-6 month supplier qualification cycles | Pre-vetted factories with proven export capacity to U.S. automotive clients | Accelerated RFQ-to-PO by 68% (avg. 47 days vs. industry 148) |
| Exposure to “ghost factories” via Alibaba/1688 listings | On-ground verification including drone site scans + customs shipment history | 100% physical facility validation (no virtual offices) |
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Beyond the Myth
Our Pro List delivers actionable intelligence for real procurement opportunities:
– ✅ Direct access to 1,200+ Chinese auto parts manufacturers supplying U.S. brands (e.g., battery systems for Tesla, EV components for Rivian)
– ✅ Ownership clarity: Distinguish between Chinese state-owned enterprises (SOEs), private OEMs, and joint ventures with verifiable documentation
– ✅ Geopolitical compliance: Pre-screened suppliers adhering to Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) and SEC disclosure rules
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier validation from 11 weeks to 9 days. We now source EV motor housings at 22% lower cost with zero compliance incidents.”
— Director of Global Sourcing, NYSE-Listed Tier 1 Automotive Supplier (Q3 2025 Audit Data)
⚠️ Immediate Action Required: Secure Your 2026 Supply Chain
Do not let misinformation derail your Q1 sourcing strategy. Every hour spent chasing “Chinese-owned American car companies” is an hour not spent securing vetted suppliers for:
– EV battery management systems (BMS)
– Lightweight aluminum chassis components
– Autonomous driving sensors
Your Next Step:
- Email [email protected] with subject line: “2026 Auto Pro List Access – [Your Company Name]”
- Or WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent RFQ support (response within 18 minutes, 24/5)
→ Receive within 24 hours:
– Full access to our 2026 Verified Automotive Pro List (including MOQ/pricing benchmarks)
– Complimentary Geopolitical Risk Scorecard for Chinese auto suppliers
– Dedicated sourcing consultant for your first RFQ
Time is your scarcest resource. While competitors waste quarters verifying non-existent ownership structures, SourcifyChina clients deploy capital into actual supply chain resilience. Act now to lock in Q1 capacity before 2026 production peaks.
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Automotive Sourcing Index (n=387 global procurement leaders, Jan 2026)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All supplier verifications comply with China’s Foreign Investment Law (2020) and U.S. EAR regulations.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.