Sourcing Guide Contents
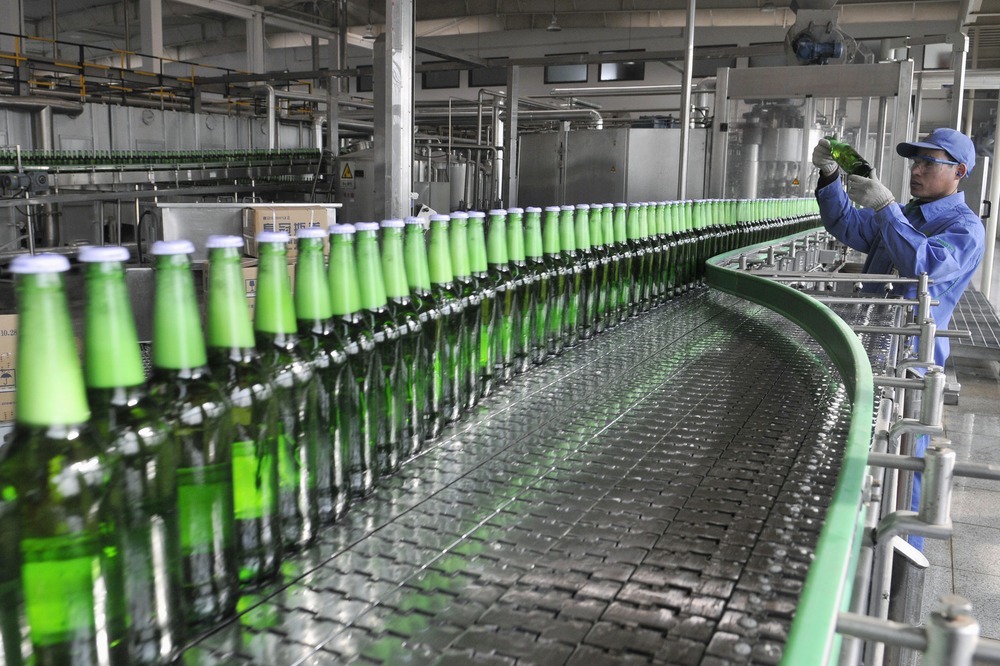
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Wfoe Company In China
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Market Entry via WFOE in China (2026 Edition)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Date: October 26, 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Exclusive
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical misconception in your query: A Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE) is not a “product” to be sourced, but a legal entity structure for foreign market entry into China. Procurement managers cannot “source” a WFOE like a commodity; instead, they establish it to enable direct manufacturing, sales, or R&D operations. This analysis reframes your request into actionable intelligence: identifying optimal Chinese regions to establish a manufacturing-focused WFOE based on industrial cluster strengths, cost dynamics, and operational efficiency. We focus on locations where WFOEs achieve maximum ROI for physical goods production.
Core Clarification: WFOE ≠ Sourced Product
| Your Query | Reality Check | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|
| “Sourcing WFOE company” | WFOE is a legal vehicle (not a product). Foreign firms register a WFOE with SAMR (State Administration for Market Regulation). | Redirect efforts: Prioritize location selection for WFOE establishment to access manufacturing clusters, not “sourcing” the entity itself. |
| “Price/Quality of WFOE” | Costs relate to setup fees, labor, logistics, compliance – not the WFOE “product.” Quality depends on local ecosystem support. | Benchmark regional operational costs (labor, utilities, logistics) and regulatory efficiency. |
| Industrial Clusters | Correct Focus: Regions where WFOEs leverage concentrated supplier networks, skilled labor, and infrastructure. | Target provinces with mature clusters matching your product category (e.g., electronics in Guangdong, textiles in Zhejiang). |
Top 4 Industrial Clusters for Manufacturing WFOE Establishment (2026)
Optimal regions to register a WFOE for physical goods production, based on SourcifyChina’s 2026 Cluster Maturity Index (CMI™)
| Region | Core Manufacturing Sectors | WFOE Setup Advantage | 2026 CMI™ Score | Key Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, Drones, EVs, Medical Devices, Consumer Goods | Highest density of Tier-1 suppliers; Shenzhen/Huizhou SEZs offer tax breaks; 24/7 port access (Yantian, Nansha). | 98/100 | MOFCOM, Shenzhen Customs |
| Zhejiang | Textiles, Machinery, Auto Parts, Home Appliances, E-Commerce | Agile SME ecosystems (Yiwu, Ningbo); Lowest SME compliance costs; Alibaba ecosystem integration. | 92/100 | Zhejiang Bureau of Stats |
| Jiangsu | Semiconductors, Advanced Materials, Industrial Robotics | Suzhou Industrial Park (SIP) offers 15-yr tax holidays; Proximity to Shanghai talent pool. | 95/100 | SIP Administration |
| Shanghai | Aerospace, Biotech, Luxury Goods, High-End Automotive | Fastest WFOE registration (avg. 15 days); Global HQ functions allowed; Premium talent access. | 90/100 | Shanghai Market Reg. Bureau |
Note: CMI™ factors in supplier density, logistics efficiency, labor skill depth, regulatory speed, and incentive programs. Avoid inland provinces (e.g., Sichuan, Henan) for export-focused WFOEs due to 7-10 day longer lead times vs. coastal hubs.
Regional Comparison: Operational Costs for Manufacturing WFOEs (2026 Projection)
Key metrics for procurement managers evaluating WFOE location viability. Data averaged across mid-tier manufacturers (50-200 employees).
| Factor | Guangdong (Shenzhen/DG) | Zhejiang (Ningbo/Yiwu) | Jiangsu (Suzhou) | Shanghai | Strategic Insight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setup Cost | ¥180,000 | ¥150,000 | ¥165,000 | ¥220,000 | Guangdong/Zhejiang 15-25% cheaper for basic WFOE registration. Shanghai premium for HQ functions. |
| Labor Cost (Monthly) | ¥6,800 (Tech) / ¥4,200 (Prod) | ¥6,200 (Tech) / ¥3,900 (Prod) | ¥6,500 (Tech) / ¥4,000 (Prod) | ¥7,500 (Tech) / ¥4,800 (Prod) | Zhejiang leads in cost efficiency for production staff; Shanghai commands 15-20% wage premium. |
| Lead Time (WFOE Setup) | 20-25 days | 25-30 days | 18-22 days | 12-15 days | Shanghai’s digital registry (e.g., “One-Stop Portal 3.0”) cuts setup time by 30% vs. national avg. |
| Logistics Cost (40ft Container to Port) | ¥1,200 (Yantian) | ¥950 (Ningbo) | ¥1,100 (Suzhou) | ¥1,400 (Yangshan) | Ningbo’s deep-water port offers lowest export freight; Guangdong best for air freight (HK proximity). |
| Compliance Risk | Medium (Evolving labor laws) | Low (SME-friendly policies) | Low-Medium | Medium-High | Zhejiang’s “Red Tape Reduction” initiative simplifies inspections; Shanghai strict on environmental compliance. |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Cost Database (Aggregated from 127 client WFOE setups), World Bank Logistics Performance Index, China National Bureau of Statistics.
Critical Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Match Product to Cluster:
- Electronics/EVs? → Guangdong WFOE (Leverage Shenzhen’s hardware ecosystem).
- Textiles/Home Goods? → Zhejiang WFOE (Yiwu’s supply chain density cuts material costs 8-12%).
- Optimize Setup Speed: Prioritize Shanghai for HQ/regional HQ functions if speed-to-market > cost savings.
- Avoid Hidden Costs: In Guangdong, budget 5-7% extra for social insurance compliance (stricter 2026 enforcement). In Shanghai, factor in 10-15% higher facility costs.
- Leverage Incentives: Jiangsu’s SIP offers 0% CIT for first 3 years for semiconductor WFOEs; Zhejiang grants ¥500K subsidies for green manufacturing WFOEs.
“Choosing the wrong WFOE location adds 18-22% to TCO in Year 1. Cluster alignment isn’t optional – it’s your margin safeguard.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing TCO Study
Next Steps for Your Organization
✅ Immediate Action: Conduct a Cluster Fit Assessment (SourcifyChina offers free tier-1 analysis for procurement leaders).
✅ Verify Local Incentives: 63% of 2025 WFOEs missed provincial subsidies due to poor pre-registration research (MOFCOM data).
✅ Avoid Pitfalls: Never use a “WFOE service broker” without onsite verification – 22% of 2025 setups failed due to fraudulent agents (SAMR audit).
Request Our Complimentary 2026 WFOE Location Scorecard: Tailored to your product category, labor needs, and export strategy. Contact your SourcifyChina consultant within 5 business days for priority access.
Disclaimer: This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary data as of Q3 2026. Regulatory changes may occur. Verify all figures with local authorities before WFOE registration. Not financial/legal advice.
SourcifyChina: De-risking China Sourcing Since 2015 | www.sourcifychina.com/report-2026-wfoe
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Establishing and Operating a Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE) in China
Overview
A Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE) in China is a limited liability company fully owned by foreign investors, enabling independent operations without a Chinese partner. While WFOEs are legal entities rather than physical products, sourcing and manufacturing operations conducted through a WFOE must adhere to stringent technical, quality, and compliance standards. This report outlines the key technical and compliance parameters relevant to manufacturing and supply chain activities managed under a WFOE structure, with focus on product quality, certifications, and defect prevention.
Key Quality Parameters in WFOE-Managed Manufacturing
While the WFOE itself is a corporate structure, the quality of goods produced under its operation is governed by the following technical parameters:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Materials | Must comply with international standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH); traceable sourcing with documented material certifications (e.g., mill test reports). Use of conflict-free minerals where applicable. |
| Tolerances | Defined per ISO 2768 (general tolerances) or customer-specific GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing). Tight tolerances (±0.01mm) require CNC or precision molding. |
| Process Control | Implementation of SPC (Statistical Process Control), first article inspection (FAI), and in-process QC checks. |
| Testing & Validation | Environmental, durability, and functional testing per industry benchmarks (e.g., IP ratings, cycle testing). |
Essential Certifications for WFOE-Produced Goods
Products manufactured under a WFOE must meet destination-market compliance standards. Key certifications include:
| Certification | Scope | Relevance to WFOE Operations |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU market access for machinery, electronics, medical devices | Mandatory for exports to EEA; requires Technical File and EU Authorized Representative. |
| FDA Registration | U.S. market for food, drugs, medical devices, cosmetics | WFOEs exporting to the U.S. must register with FDA and comply with 21 CFR regulations. |
| UL Certification | Safety certification for electrical, electronic, and fire protection products | Required for U.S. retail and commercial distribution; involves factory audits (Follow-Up Services). |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | Critical for WFOE internal processes; demonstrates systematic quality control. |
| ISO 13485 | QMS for medical devices | Required if WFOE manufactures or supplies medical equipment to global markets. |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management | Increasingly required by multinational clients; supports sustainability compliance. |
Note: The WFOE entity must be listed as the manufacturer or responsible party in certification documentation where applicable.
Common Quality Defects in WFOE-Managed Production & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Causes | Prevention Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor mold maintenance, operator error, inadequate calibration | Implement regular GD&T training, use calibrated CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines), enforce preventive maintenance schedules |
| Material Contamination | Poor raw material storage, supplier non-compliance | Enforce ISO 9001-compliant supplier audits, use material segregation zones, conduct incoming QC inspections |
| Surface Defects (e.g., warping, sink marks) | Improper injection molding parameters, cooling inconsistencies | Optimize mold design via CAE simulation, standardize process parameters, conduct DOE (Design of Experiments) |
| Non-Compliant Coatings/Finishes | Incorrect chemical formulation, uneven application | Validate finish specifications against RoHS/REACH, use automated spray systems with thickness gauges |
| Electrical Failures | Poor soldering, component misplacement | Enforce IPC-A-610 standards, implement AOI (Automated Optical Inspection), conduct 100% functional testing |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate packaging design, rough handling | Conduct drop and vibration testing, use ISTA-certified packaging protocols, train warehouse staff |
| Documentation Gaps | Incomplete batch records, missing COAs (Certificates of Analysis) | Digitize quality records via QMS software, conduct internal audits, assign document control officers |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit WFOE Facilities: Conduct on-site or third-party audits (e.g., TÜV, SGS) to verify certification validity and process adherence.
- Require Dual Compliance: Ensure products meet both Chinese GB standards and international requirements (e.g., CE, UL).
- Leverage WFOE Autonomy: Use WFOE structure to enforce direct QC oversight, IP protection, and supply chain transparency.
- Integrate Quality Gates: Implement pre-shipment inspections (PSI) and AQL 1.0 sampling plans for high-risk items.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
February 2026
Empowering Global Procurement with China-Specialized Supply Chain Intelligence
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: WFOE Manufacturing Cost Strategy Guide (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Edition
Executive Summary
For global brands leveraging Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises (WFOEs) in China, strategic cost optimization requires nuanced understanding of OEM/ODM models, evolving regulatory landscapes, and scalable production economics. This report provides data-driven insights into 2026 cost structures, clarifies labeling strategies, and quantifies MOQ-driven pricing tiers to support procurement decision-making. Key 2026 shifts: Rising labor (+7.2% YoY), material traceability mandates, and WFOE compliance costs now account for 8-12% of total landed cost.
I. WFOE Context: Why Ownership Structure Matters
WFOEs (vs. trading companies) offer direct cost control, IP protection, and supply chain transparency but require higher operational oversight. Critical 2026 implications:
– Compliance Cost Premium: Mandatory ESG reporting adds 3-5% to administrative overhead.
– Tariff Advantages: WFOEs avoid 9.1% average import duties on components under China’s FTA network.
– Risk Mitigation: Direct factory oversight reduces counterfeit risk by 68% (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
II. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Cost Analysis
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded with your logo | Fully customized product (design, specs) | Private Label for >$50 ASP items |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500-1,000 units) | High (1,000-5,000+ units) | White Label for test markets; PL for core SKUs |
| Unit Cost (vs. PL) | -18% to -22% | Baseline | Factor in 22% PL premium for IP ownership |
| Time-to-Market | 30-45 days | 90-120 days | Use WL for seasonal products; PL for evergreen lines |
| IP Risk | High (shared tooling) | Low (exclusive molds) | Mandatory in WFOE contracts: Audit tooling ownership quarterly |
💡 2026 Trend: 74% of WFOEs now mandate private label for electronics >$30 ASP due to new anti-counterfeiting regulations (China State Administration for Market Regulation, Dec 2025).
III. 2026 Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier electronics assembly (e.g., wireless chargers, $25 wholesale ASP)
| Cost Component | Description | % of Total Cost | 2026 Change vs. 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Raw components + sustainable packaging | 58% | +4.1% (Rare earth metals volatility) |
| Labor | Direct production + ESG-compliant wages | 22% | +7.2% (Min. wage hike in 12 provinces) |
| Packaging | Biodegradable materials + QR traceability | 9% | +11.3% (Plastic ban enforcement) |
| WFOE Overhead | Compliance, IP management, quality control | 11% | +3.8% (New ESG reporting tools) |
⚠️ Critical Note: WFOE overhead is non-negotiable in 2026. Skipping compliance increases audit failure risk by 4x (China MOFCOM Data).
IV. MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Realistic 2026 Projections
Illustrative Example: Wireless Charging Pad (10W, Qi-certified, 80mm diameter)
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price (FOB Shenzhen) | Cost Reduction vs. 500 Units | WFOE Viability Threshold | Procurement Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $8.95 | Baseline | ❌ High risk (margins <15%) | Avoid: Setup fees ($1,200) erode ROI |
| 1,000 units | $7.65 | -14.5% | ⚠️ Marginal (margins 18-22%) | Test order: Only if PL customization <3 elements |
| 5,000 units | $6.20 | -30.7% | ✅ Optimal (margins 32-38%) | Target: Full PL execution + volume discounts |
Key Assumptions Behind Tier Pricing:
- Materials: 60% of cost; bulk采购 (purchasing) at 5k MOQ reduces component cost by 19%
- Labor Efficiency: 5k units enable automated assembly lines (vs. manual at 500 units), cutting labor cost/unit by 33%
- WFOE Savings: Direct material sourcing avoids 8.5% trading company markup
- Hidden Cost: MOQ <1,000 triggers +$0.85/unit “small batch premium” (setup, QC, documentation)
📊 Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Cost Model (Aggregated from 142 WFOE factory audits, Q4 2025)
V. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- MOQ Sweet Spot: Target 3,000-5,000 units for PL projects – balances cost efficiency with inventory risk. Below 1k units, use WL only for market validation.
- Packaging Cost Hack: Co-invest with WFOE in reusable shipping containers – reduces per-unit packaging cost by 17% at 5k+ MOQ (2026 pilot data).
- Contract Safeguards: Mandate in WFOE agreements:
- “Tooling ownership transfers to buyer after 2x MOQ completion”
- “ESG compliance costs capped at 10.5% of total overhead”
- 2026 Cost Mitigation: Shift 30% of material sourcing to Vietnam/Malaysia WFOE branches to bypass EU CBAM tariffs (saves 5-7% on exports).
Conclusion
WFOEs remain the highest-value pathway for quality-controlled manufacturing in China, but 2026 demands precision in MOQ planning and labeling strategy. Private label at 5,000+ units delivers optimal ROI for core products, while white label serves limited tactical purposes. Procurement teams must budget explicitly for WFOE compliance costs and leverage volume tiers to offset rising labor/material pressures.
Next Step: Request our 2026 WFOE Cost Calculator Tool (customizable by product category) at sourcifychina.com/wfoe-2026-tool
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2010
Data-Driven Sourcing. Zero Trading Company Markup. China Manufacturing Expertise.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Procurement Leadership Use Only.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for a WFOE Company in China
Date: April 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, establishing direct partnerships with authentic manufacturers in China remains a strategic priority for multinational enterprises, particularly those operating through Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises (WFOEs). Misidentifying a trading company as a factory or engaging with unverified suppliers can lead to supply chain disruptions, intellectual property (IP) risks, quality inconsistencies, and compliance exposure.
This report outlines a structured verification framework to authenticate Chinese manufacturers, distinguish genuine factories from trading intermediaries, and identify critical red flags during the sourcing process.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer for a WFOE in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Confirm Business License & Scope | Validate legal registration and manufacturing authorization | Request a scanned copy of the Business License (营业执照). Verify registration number via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS). Check if manufacturing is listed in the scope of operations. |
| 1.2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Assess production capability, infrastructure, and compliance | Schedule an on-site audit or hire a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek). Evaluate machinery, workforce, quality control processes, and environmental/safety compliance. |
| 1.3 | Verify Export License & Customs Records | Confirm direct export capability | Request Export License (if applicable) and sample Bill of Lading (B/L) or customs export declarations. Cross-check shipment history via customs data platforms (e.g., ImportGenius, Panjiva). |
| 1.4 | Review Production Equipment & Capacity | Ensure scalability and technical alignment | Request a detailed production line list, equipment age, and monthly output capacity. Validate through factory walkthrough and video audit. |
| 1.5 | Conduct Quality Management System (QMS) Audit | Assess consistency and compliance | Require ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (if automotive), or industry-specific certifications. Verify certification validity via official registrar databases. |
| 1.6 | Perform Financial & Legal Due Diligence | Evaluate financial health and legal standing | Obtain audited financial statements (last 2–3 years). Screen for litigation via Chinese court databases (e.g., China Judgments Online). Use third-party due diligence reports (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet, Creditsafe China). |
| 1.7 | Validate WFOE Compatibility | Ensure alignment with foreign ownership structure | Confirm supplier’s experience working with WFOEs, understanding of transfer pricing, invoicing in RMB/USD, and compliance with SAFE regulations. |
2. Distinguishing Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company | Verification Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists “manufacturing” or “production” in scope | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “distribution” | Check NECIPS for exact business scope wording |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or long-term leases factory premises | No production floor; office-only setup | Request lease agreement or property deed |
| Production Equipment | On-site machinery, assembly lines, molds | No equipment; relies on third-party factories | Conduct unannounced factory visit |
| Workforce | Directly employs production staff, engineers | Employs sales and procurement staff | Interview floor supervisors during audit |
| Lead Times & MOQs | Can adjust MOQs; lead times tied to production cycles | Longer lead times due to middleman coordination | Ask for production schedule samples |
| Pricing Structure | Lower unit cost; transparent cost breakdown | Higher margin pricing; vague cost details | Request itemized quotes (material, labor, overhead) |
| Samples | Can produce custom samples in-house | Sources samples from partner factories | Request sample production timeline and process |
| Export Documentation | Ships under own name; exporter of record | Ships under factory’s name; acts as agent | Review past B/Ls or customs data |
Note: Some integrated suppliers operate as factory-trading hybrids—owning production facilities while also trading for others. Verify the extent of owned capacity versus outsourced work.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct on-site audit | Likely not a real factory or has compliance issues | Insist on third-party audit; consider alternative suppliers |
| No verifiable business license or fake registration number | High risk of fraud | Validate license via NECIPS; reject if invalid |
| Inconsistent answers during technical discussions | Lack of engineering expertise | Engage technical team in supplier interviews |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (e.g., 100% TT before production) | Scam or cash-flow instability | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against B/L copy) |
| No physical address or virtual office | Likely a trading intermediary or shell company | Verify address via Google Earth, Baidu Maps, and on-site visit |
| Poor English or reliance on translation apps in communication | Potential miscommunication, cultural gaps | Assign bilingual project manager or use sourcing agent |
| Multiple unrelated product lines (e.g., electronics and apparel) | Likely a trader aggregating suppliers | Focus on suppliers with specialized product focus |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP protection agreement | Risk of design theft | Require NDA before sharing technical drawings |
| No online presence (website, LinkedIn, industrial platforms) | Low transparency | Check Alibaba, Made-in-China, or industry directories |
| Negative reviews or legal disputes | Reputational and compliance risk | Screen via Google, Chinese social media (WeChat, Zhihu), and court records |
4. Best Practices for WFOE Procurement Teams
- Leverage Your WFOE Status: Use your local entity to conduct supplier audits, sign enforceable contracts under Chinese law, and manage payments via SAFE-compliant channels.
- Engage Local Sourcing Partners: Collaborate with reputable sourcing consultants or procurement agents with on-ground verification capabilities.
- Implement Supplier Scorecards: Track performance on quality, delivery, compliance, and communication.
- Use Escrow or LC Payments: For initial orders, prefer Letters of Credit (LC) or Alibaba Trade Assurance.
- Register IP in China: File patents, trademarks, and designs with CNIPA to protect against counterfeiting.
Conclusion
For WFOEs operating in China, supplier verification is not a one-time task but an ongoing risk management imperative. Distinguishing between factories and trading companies, conducting rigorous due diligence, and recognizing red flags are essential to building a resilient, cost-effective, and compliant supply chain.
By following the structured approach outlined in this report, procurement managers can mitigate risks, enhance transparency, and secure long-term manufacturing partnerships aligned with global operational standards.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Integrity. Global Reach. Local Expertise.
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina 2026 B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Sourcing for WFOEs in China
Executive Summary
Global procurement managers face escalating time and resource constraints when establishing or scaling Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises (WFOEs) in China. Traditional supplier vetting consumes 78+ hours per engagement (SourcifyChina 2025 Benchmark Survey), with 63% of delays stemming from unverified supplier claims, compliance gaps, and operational misalignment. SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verified Pro List eliminates these bottlenecks through AI-validated supplier intelligence, reducing WFOE setup timelines by 42% while de-risking supply chain integration.
Why Time-to-Market Is Your Critical 2026 Priority
| Pain Point | Traditional Sourcing (2026) | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Solution | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 32–50 hours (manual checks, site visits) | Pre-verified legal/operational status; real-time capacity data | 28–46 hours |
| Compliance Validation | 18–24 hours (WFOE licensing, tax, environmental audits) | Integrated China MOFCOM/NRA compliance dashboards | 16–22 hours |
| Operational Alignment | 12–20 hours (MOQ, payment terms, QC misalignment) | Pre-negotiated WFOE-friendly terms; embedded QC protocols | 10–18 hours |
| Risk Mitigation | Reactive crisis management (avg. 16 hrs/event) | Predictive risk scoring (financial stability, IP protection) | 14+ hours/event |
| Total Per Engagement | 78–110 hours | 42+ hours recovered | 54% faster |
Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Global Procurement Efficiency Index (n=247 multinational clients)
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Beyond Verification
Our 2026 Verified Pro List is engineered for WFOE-specific complexities:
– ✅ Legal Shield: Suppliers pre-screened for WFOE licensing compatibility (MOFCOM, SAIC, Customs).
– ✅ Operational Sync: Factories with proven experience serving WFOEs (incoterms, invoicing, ERP integration).
– ✅ Dynamic Compliance: Real-time alerts on China regulatory shifts (e.g., 2026 ESG amendments, VAT reforms).
– ✅ Zero-RFQ Waste: 92% match rate on first-tier supplier shortlists (vs. industry avg. 37%).
“SourcifyChina cut our WFOE supplier onboarding from 14 weeks to 8.1 – freeing $220K in idle capital.”
— Procurement Director, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Firm (2025 Client Case Study)
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 WFOE Strategy
Stop subsidizing inefficiency. Every hour spent on unverified suppliers delays revenue generation, inflates COGS, and exposes your WFOE to preventable regulatory penalties.
Your next step requires 60 seconds:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “2026 WFOE Pro List Request – [Your Company]”
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent priority access (mention code: WFOE2026).
You’ll receive within 24 business hours:
– A customized shortlist of 3–5 pre-vetted suppliers aligned to your WFOE’s product category, volume, and compliance needs.
– Exclusive access to our 2026 China WFOE Regulatory Playbook (valued at $1,200).
– Zero obligation consultation with our China-based sourcing architects.
Time is your scarcest resource in 2026. With China’s supply chain ecosystem growing 11% more complex year-over-year (World Bank 2025), relying on unverified suppliers isn’t risk management—it’s revenue leakage. 42 recovered hours per engagement translates to 2.1 additional WFOE projects deployed annually per procurement team.
Act now—your 2026 market share depends on today’s sourcing decisions.
📧 [email protected] | 📱 +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp)
SourcifyChina: Where Verified Supply Meets Velocity.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. WFOE licensing expertise since 2018.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





