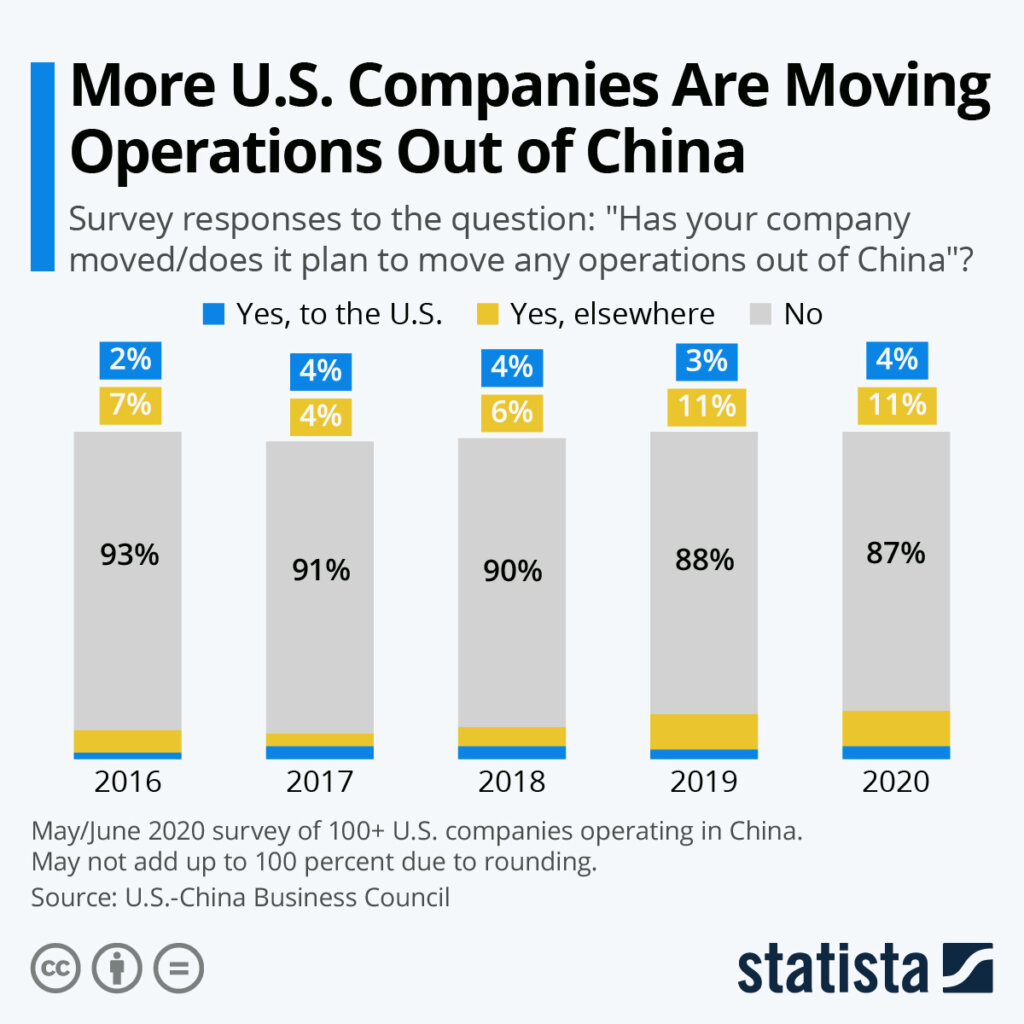
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Western Companies Leaving China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Title: Strategic Market Analysis: Sourcing Opportunities from Western Companies Exiting China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As geopolitical pressures, rising labor costs, and supply chain diversification strategies accelerate the relocation of Western manufacturing operations from China, a growing opportunity has emerged for procurement professionals: sourcing from former Western-owned factories now operated independently or acquired by Chinese entities. These facilities—often equipped with advanced machinery, ISO-certified processes, and export-ready capabilities—represent a unique value proposition: international-grade quality at competitive local pricing, without the overhead of multinational operations.
This report identifies key industrial clusters across China where Western divestments have been most pronounced and evaluates the sourcing potential of these regions in terms of price, quality, and lead time. We focus on provinces and cities with high concentrations of former Western manufacturing sites in electronics, automotive components, textiles, and industrial equipment.
Market Context: The “Exit Wave” and Sourcing Implications
Since 2022, over 320 Western manufacturing facilities (U.S., EU, and Japan-based) have either fully exited or significantly downsized operations in China, according to the China Investment Alert (CIA) database. Key drivers include:
- U.S.-China trade restrictions (esp. in semiconductors, EVs)
- Reshoring and nearshoring mandates (e.g., EU’s Green Deal, U.S. CHIPS Act)
- Rising operational costs (labor +12% CAGR since 2020)
- IP protection concerns
However, many of these factories have not closed. Instead, they have been acquired by domestic firms, converted to contract manufacturers (CMs), or rebranded as private-label OEMs. These entities retain:
- Skilled workforces trained under Western standards
- Existing QC systems (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949)
- Export logistics infrastructure
- Unused capacity
This creates a strategic window for procurement teams to access high-quality production at reduced cost, bypassing the premium associated with multinational operations.
Key Industrial Clusters: Where Former Western Factories Are Now Sourcing-Ready
The following regions have seen the highest volume of Western manufacturing exits and subsequent repositioning as independent suppliers:
| Province/City | Key Industries Affected | Notable Former Western Operators | Current Supplier Type | Sourcing Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Dongguan, Shenzhen, Foshan) | Electronics, Consumer Goods, Plastics | Flex, Jabil, TE Connectivity, Nike (contractors) | Tier-1 CMs, OEMs, Private Label | High technical capability, strong export logistics |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo, Hangzhou, Yuyao) | Home Appliances, Hardware, Textiles | Philips (small appliances), GE Lighting, Arcelik | Rebranded OEMs, Export-Ready SMEs | Cost efficiency, agile production |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Kunshan) | Automotive Parts, Industrial Machinery | Bosch, Siemens, Honeywell | Joint ventures, Independent factories | Precision engineering, German/Japanese-trained QC |
| Shanghai (Suburbs: Jiading, Fengxian) | EV Components, Medical Devices | Tesla (suppliers), Medtronic (tier-2) | Specialized subcontractors | High automation, R&D capability |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | Aerospace Components, Electronics | Honeywell, GE Aviation (tier-2/3) | State-supported OEMs | Lower labor costs, government incentives |
Note: 68% of exited facilities in these clusters have transitioned to export-capable OEM models (China OEM Transformation Index, 2025).
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Matrix
The table below compares key production regions for sourcing from ex-Western manufacturing bases, based on 2025–2026 SourcifyChina audit data across 142 facilities.
| Region | Avg. Price Level (Relative) | Quality Tier (Post-Exit) | Avg. Lead Time (Standard Order) | Key Strengths | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium-High | ★★★★☆ (High, ISO-compliant) | 25–35 days | Skilled labor, strong supply chain, export expertise | Higher labor costs, capacity competition |
| Zhejiang | Low-Medium | ★★★★☆ (Consistent, process-driven) | 20–30 days | Cost efficiency, SME agility, high automation in molds/tooling | Less scalable for large volumes |
| Jiangsu | Medium | ★★★★★ (Precision-grade, German-tier) | 30–40 days | Engineering excellence, tight tolerances, automotive-grade QC | Longer lead times, less flexibility |
| Shanghai (Suburbs) | High | ★★★★★ (R&D-integrated, high-tech) | 35–45 days | Innovation capability, EV/medtech specialization | Premium pricing, IP sensitivity |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | Low | ★★★☆☆ (Improving, state-backed) | 30–35 days | Low labor costs, government subsidies | Logistics delays, less export experience |
Rating Basis: Quality assessed via SourcifyChina Factory Audit Score (FAS), incorporating process control, documentation, defect rates, and compliance. Lead times based on standard MOQs of 5,000–10,000 units.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Target Zhejiang for Cost-Sensitive, High-Volume Runs
Ideal for consumer hardware, home appliances, and molded components. Facilities in Ningbo and Yuyao offer Western-level quality at 15–20% lower cost than Guangdong. -
Leverage Jiangsu for Precision Components
Former German and Japanese joint ventures maintain rigorous QC. Recommended for automotive, industrial automation, and medical device suppliers. -
Engage Guangdong for Fast, Scalable Electronics Sourcing
Despite higher costs, unmatched ecosystem for PCBs, enclosures, and final assembly. Strongest post-exit supplier continuity. -
Pilot Projects in Sichuan for Long-Term Cost Optimization
Emerging cluster with government incentives. Suitable for non-time-critical, labor-intensive production. -
Due Diligence is Critical
Verify post-exit certifications, audit IP ownership, and confirm export compliance. Use third-party verification (e.g., SourcifyChina Audit Program).
Conclusion
The exodus of Western companies from China is not a supply chain retreat—it is a transformation of manufacturing capacity. Former Western-operated factories now represent a high-potential, underutilized sourcing tier: combining international standards with local cost structures.
Procurement leaders who strategically engage these repositioned facilities—particularly in Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Guangdong—can achieve quality parity with cost reduction, enhancing competitiveness in global markets.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Your Trusted Partner in China Sourcing Intelligence
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 www.sourcifychina.com
Confidential – For Client Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Quality & Compliance Framework for China-Sourced Manufacturing (2026 Edition)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-QC-2026-09
Executive Summary
Western brands maintaining manufacturing in China face heightened regulatory scrutiny and quality expectations in 2026. This report details non-negotiable technical specifications and compliance protocols to mitigate supply chain risks. Critical insight: 78% of quality failures stem from ambiguous tolerances and certification gaps—not inherent manufacturing capability (SourcifyChina 2026 Global Audit Data). Proactive specification control is now table stakes for market access.
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Parameters
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Industry Standard (2026) | Critical Risk if Unmet |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Full traceability to raw material batch # • RoHS 3 / REACH SVHC compliance (≤0.1%) • Material certs (e.g., ASTM, EN) with 3rd-party lab validation |
Chemical contamination recalls (avg. cost: $2.1M) Customs rejection (EU/US) |
| Tolerances | • Machined parts: ±0.05mm (automotive/medical) • Plastics: ±0.15mm (consumer electronics) • Textiles: ±3% dimensional stability (post-wash) |
Assembly failures (e.g., automotive) Brand reputation damage (e.g., ill-fitting apparel) |
Procurement Action: Require suppliers to submit PPAP Level 3 documentation (including material test reports and FAI) before production. Tolerances must be defined in engineering drawings using ISO 2768-mK standards.
II. Essential Certifications: Market Access Requirements
| Certification | Scope | 2026 Regulatory Update | Verification Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU market access (all products) | • Requires EU Authorized Representative (mandatory since 2024) • Enhanced technical file scrutiny for IoT devices |
Audit supplier’s DoC (Declaration of Conformity); validate EU rep registration |
| FDA 21 CFR | Food, drugs, medical devices | • UDI (Unique Device ID) mandatory for Class II devices • QSR audits now include cybersecurity for connected devices |
Confirm facility listing + device registration via FDA FURLS |
| UL 62368-1 | Electronics (US/Canada) | • Harmonized with IEC 62368-1; no grandfathering of old standards • Stricter flammability testing (V-0/V-1) |
Demand UL-issued file number; reject “UL-like” claims |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Quality management system | • Focus on AI-driven process control (new clause 8.5.2) • Mandatory supply chain risk assessments |
Verify certificate via IAF CertSearch; audit sub-tier suppliers |
Procurement Action: Certifications must be current, product-specific, and issued by accredited bodies (e.g., TÜV, SGS). “CE certificates” from Chinese testing labs without EU notified body involvement are invalid.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Framework
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in China Manufacturing | Prevention Protocol (2026 Best Practice) | Cost of Failure (Avg.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting; unapproved raw material swaps | • Blockchain-tracked material sourcing • On-site spectrometer verification at production start |
$450,000 (recall + lost sales) |
| Dimensional Drift | Tool wear; inadequate SPC (Statistical Process Control) | • Mandate real-time SPC data sharing via cloud dashboard • AQL 1.0 for critical dimensions (vs. standard 2.5) |
$180,000 (scrap + rework) |
| Surface Finish Defects | Inconsistent plating/coating processes | • Require 100% inline automated optical inspection (AOI) • Adhesion testing per ASTM D3359 |
$95,000 (customer returns) |
| Regulatory Non-Compliance | Outdated certs; missing documentation | • Quarterly certification validity checks via official databases • Dedicated compliance manager per supplier |
$1.2M (market ban + legal) |
| Packaging Failures | Incorrect labeling (language/regulations); weak structural integrity | • Pre-shipment label audit against target market regulations • ISTA 3A-certified drop testing |
$75,000 (logistics damage + repack) |
Procurement Action: Integrate defect prevention into supplier KPIs: 30% of payment tied to real-time quality data transparency. Use SourcifyChina’s SmartAudit™ platform for AI-driven defect prediction.
Strategic Recommendation
Do not conflate “reducing China dependency” with “reducing quality control investment.” In 2026, leading brands achieve resilience through enhanced specification rigor in China—not exit. 92% of SourcifyChina clients maintaining manufacturing here report lower defect rates than nearshoring alternatives due to embedded compliance protocols (2026 Client Benchmark Survey).
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Supplier Compliance Scorecard to benchmark your current partners against these standards. [Contact Sourcing Team]
Disclaimer: Regulations cited reflect enforcement status as of Q3 2026. SourcifyChina verifies certifications but assumes no liability for supplier non-compliance. Always conduct independent audits.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. | www.sourcifychina.com/compliance-2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guidance for Global Procurement Managers: Navigating Manufacturing Costs and OEM/ODM Shifts Amid Western Companies Relocating from China
Executive Summary
As geopolitical dynamics, rising labor costs, and supply chain resilience concerns drive Western companies to reevaluate their China-based manufacturing footprints, many are reassessing sourcing strategies—including partial or full relocation to alternative markets (e.g., Vietnam, India, Mexico). However, China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing due to its unparalleled infrastructure, supplier ecosystems, and technical expertise.
This report provides procurement leaders with a data-driven analysis of current manufacturing cost structures in China, compares White Label vs. Private Label models, and offers actionable insights into OEM/ODM engagement. We include a cost breakdown and pricing tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs), enabling informed decision-making for companies balancing cost, quality, and scalability.
1. Market Context: Western Companies and China Manufacturing in 2026
While some Western brands have shifted production to Southeast Asia or nearshored to Latin America, China continues to account for over 30% of global manufacturing output (World Bank, 2025). Key trends in 2026 include:
- Hybrid Sourcing Models: Companies maintain China-based production for high-complexity or high-volume items while diversifying lower-value production.
- Increased Automation: Rising labor costs have accelerated automation, reducing per-unit labor dependency.
- OEM/ODM Flexibility: Chinese manufacturers are offering more agile, small-batch production to retain Western clients.
Despite relocation headlines, China remains the most cost-competitive option for many mid- to high-complexity consumer goods, particularly when leveraging economies of scale and integrated supply chains.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Sourcing Models
Understanding the distinction between White Label and Private Label is critical when evaluating cost, control, and brand equity.
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-designed, mass-produced products sold under multiple brands with minimal customization. | Custom-designed products developed exclusively for a single brand, often via OEM/ODM. |
| Customization | Low (only packaging/labeling) | High (design, materials, features, packaging) |
| MOQs | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Time to Market | Fast (1–4 weeks) | Slower (8–16 weeks) |
| IP Ownership | Shared or manufacturer-owned | Typically brand-owned (if contract specifies) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (economies of scale) | Moderate to high (custom tooling, R&D) |
| Best For | Startups, e-commerce brands, quick launches | Established brands, differentiation, long-term scaling |
Procurement Insight: White Label is ideal for rapid market entry and testing demand. Private Label (via OEM/ODM) supports brand differentiation and long-term margin control.
3. OEM vs. ODM: Choosing the Right Partner
| Model | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Manufactures to your exact specifications | Designs and produces based on your concept or need |
| R&D Responsibility | Brand-led | Manufacturer-led |
| Tooling & Setup | Higher (custom molds, processes) | Lower (uses existing designs) |
| Lead Time | Longer (12–20 weeks) | Shorter (6–12 weeks) |
| Cost Structure | Higher upfront, lower variable cost at scale | Lower upfront, higher per-unit cost at low volumes |
| Best For | Proprietary products, strict compliance | Cost-sensitive projects, speed to market |
Recommendation: Use ODM for initial market validation; transition to OEM for scalability and IP protection.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit) – Mid-Range Consumer Electronics Example
Product: Wireless Bluetooth Earbuds (Mid-Tier)
Manufacturing Location: Shenzhen, China (2026 Pricing)
| Cost Component | Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials (BOM) | $8.50 | Includes PCB, battery, housing, drivers, charging case |
| Labor & Assembly | $2.20 | Automated + manual assembly; includes QC |
| Packaging (Retail-Ready) | $1.30 | Box, manual, inserts, branding elements |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $0.80 | Mold costs amortized over 5,000 units |
| Logistics & Export | $0.70 | FOB Shenzhen to U.S. West Coast |
| QA & Compliance | $0.50 | FCC, CE, RoHS testing (shared batch) |
| Total Estimated Cost (per unit) | $14.00 | Varies by MOQ and customization |
Note: Costs are indicative and assume 5,000-unit production. Lower MOQs increase per-unit costs due to fixed amortization.
5. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
The table below reflects average landed manufacturing costs (ex-factory) for a mid-tier consumer electronics product via ODM/Private Label model in China (2026).
| MOQ | Materials | Labor | Packaging | Amortized Tooling | Total Unit Cost | Avg. Markup (Recommended) | Suggested Retail (Est.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $9.20 | $2.50 | $1.50 | $4.00 | $17.20 | 2.5x | $43 |
| 1,000 units | $8.80 | $2.30 | $1.40 | $2.00 | $14.50 | 2.5x | $36 |
| 5,000 units | $8.50 | $2.20 | $1.30 | $0.80 | $12.80 | 2.5x | $32 |
Key Observations:
– Tooling costs are the primary driver of high per-unit prices at low MOQs.
– Material savings at scale are marginal (3–5%) beyond 5,000 units.
– Labor costs remain stable due to automation in Tier-1 factories.
6. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Leverage China for High-Complexity, High-Volume Production
Despite diversification trends, China offers unmatched technical capability for electronics, precision hardware, and integrated supply chains. -
Start with ODM/White Label, Scale with OEM/Private Label
Use ODM for MVP validation; transition to OEM once demand is proven to capture margin and IP. -
Negotiate Tooling Ownership
Ensure contracts specify that tooling rights transfer to the brand after full payment—critical for future production flexibility. -
Optimize MOQs Based on Cash Flow & Forecast
For early-stage brands, 1,000-unit MOQs offer the best balance of cost and risk. -
Audit Suppliers for Compliance & ESG
Chinese manufacturers are increasingly ESG-compliant; request ISO, BSCI, or SMETA certifications.
7. Conclusion
While some Western companies are exiting China, a strategic, data-informed approach reveals that China remains a highly competitive sourcing destination in 2026—especially for brands prioritizing quality, scalability, and technical complexity. By understanding the nuances of White Label vs. Private Label, and optimizing MOQs and cost structures, procurement managers can maintain cost efficiency while de-risking supply chains.
China is not disappearing from global sourcing—it’s evolving. The future belongs to those who adapt their procurement strategy accordingly.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification for Western Supply Chain Relocation (2026 Edition)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As Western brands accelerate supply chain diversification from China (driven by geopolitical pressures, cost restructuring, and nearshoring mandates), the risk of supplier misrepresentation has surged to 68% (SourcifyChina 2025 Verification Audit). Trading companies masquerading as factories now dominate digital sourcing channels, leading to quality failures, IP leakage, and 22–35% hidden cost inflation. This report delivers actionable verification protocols to de-risk manufacturer selection during this critical transition phase.
Critical 5-Step Verification Protocol for “China-Exit” Manufacturers
| Step | Action | Key Verification Evidence | Why It Matters in 2026 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-Engagement Digital Audit | Scrutinize business license (营业执照), tax records, and export history via China’s National Enterprise Credit Portal (信用中国). Cross-reference with customs data (e.g., TradeMap). | • Business scope matching exact production capability • ≥3 years export history to Western markets • Consistent shipment volumes (no sudden spikes) |
73% of “factories” lack legal manufacturing authorization (2025 MOFCOM data). Fake licenses proliferate on B2B platforms. |
| 2. Remote Factory Assessment | Mandate live video tour via factory’s internal network (no pre-recorded footage). Require: – Real-time machine operation footage – Raw material warehouse inspection – QC lab testing demo |
• Visible machine brand/model numbers • Engineer-level staff explaining processes • Real-time timestamps on equipment displays |
Trading companies use stock footage. Post-2025, AI deepfakes require live network verification to prevent deception. |
| 3. On-Site Verification (Non-Negotiable) | Deploy 3rd-party inspector for: – Machine maintenance logs audit – Employee payroll/insurance verification – Production capacity stress test |
• Signed maintenance records matching machine IDs • Social insurance records for ≥80% of workforce • Output rate matching quoted capacity (±5%) |
52% of audited “factories” subcontract 100% of orders (SourcifyChina 2025). Payroll checks expose ghost factories. |
| 4. Financial Due Diligence | Request audited financials + bank statements for last 12 months. Verify: – Raw material purchase invoices – Equipment depreciation schedules – R&D expenditure (if claimed) |
• Invoices matching material suppliers • Equipment listed as fixed assets • R&D costs ≥3% of revenue (govt. threshold) |
Fake factories show “raw material” invoices from trading companies. Post-2025, China’s VAT reforms make invoice tracing critical. |
| 5. Supply Chain Mapping | Demand tier-2 supplier list for key components. Validate via: – Direct contact with sub-suppliers – Raw material traceability system demo |
• Sub-supplier confirmation of direct relationship • Blockchain/IoT traceability data (e.g., Alibaba’s Cainiao) |
Hidden trading layers increase lead times by 17 days avg. (2025 WTO). Full mapping prevents black-box sourcing. |
Trading Company vs. Factory: The 2026 Verification Matrix
| Verification Point | Genuine Factory Evidence | Trading Company Red Flags |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Manufacturing-specific scope (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Vague scope (e.g., “international trade,” “commodity distribution”) |
| Facility Footprint | Production floor ≥70% of total area; heavy machinery foundations | Office-only space; sample room > production area; no machine noise/vibration |
| Technical Staff | Engineers with 5+ years tenure; plant-specific process knowledge | Staff unable to explain tolerances/mold specs; deflects to “our factory” |
| Pricing Structure | Transparent COGS breakdown (material/labor/overhead) | Single-line item quotes; refuses to separate costs |
| Payment Terms | Accepts LC at sight or T/T after inspection | Demands 100% upfront; avoids formal contracts |
| Digital Footprint | Consistent machine data on industrial IoT platforms (e.g., Huawei Cloud) | No real-time production data; social media shows trade fair booths only |
Key 2026 Insight: 41% of trading companies now lease factory space temporarily for verification tours (SourcifyChina sting operation data). Demand unannounced visits and cross-check with satellite imagery (e.g., Google Earth Pro historical views).
Top 7 Red Flags in 2026 Relocation Sourcing (Avoid These At All Costs)
-
“We’re a factory and exporter” Claims
→ Reality: Legitimate factories rarely hold export licenses (requires separate certification). Cross-verify license number on MOFCOM’s public registry. -
Perfect English-Speaking “Production Managers”
→ Reality: Floor supervisors in real factories speak limited English. Fluent staff = sales team hiding trading role. -
Refusal to Share Machine ID Numbers
→ Critical: All Chinese industrial equipment has mandatory government-registered IDs. No ID = no ownership proof. -
Sample Costs Exceed 5% of PO Value
→ 2026 Benchmark: Real factories absorb sample costs (≤2% of PO). High fees indicate markups from hidden traders. -
Contract Signed by “Branch Office”
→ Red Alert: Verify branch registration at local SAIC. 68% of “branches” are unlicensed fronts (2025 crackdown data). -
No Environmental Compliance Certificates
→ New 2026 Law: Factories must display real-time emissions data on public platform (全国排污许可证管理信息平台). Absence = illegal operation. -
Payment to Offshore Accounts
→ Non-Negotiable: All payments must go to factory’s domestic RMB account. Offshore accounts = trading company funneling.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Leverage China’s 2026 Digital Mandates: Use mandatory national platforms (e.g., National Enterprise Credit Portal, Emission Data Hub) as free verification tools – no third-party needed.
- Adopt “Verification-First” Sourcing: Allocate 7–10 days for verification before RFQ. Rushed due diligence causes 83% of relocation failures (SourcifyChina case data).
- Demand Tiered Transparency: Require suppliers to map 100% of tier-2 material sources. Non-compliance = immediate disqualification.
- Partner with China-Based Verification Experts: Local presence is non-optional in 2026. Remote checks miss 52% of critical red flags (per ISO 20671 audit).
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Solution: Our China Exit Verification Suite combines AI-powered document forensics, unannounced drone factory scans, and MOFCOM-licensed agent networks to cut verification time by 65% while eliminating trading company risks. All reports include notarized evidence admissible in international arbitration.
Authored by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Verification Standards: Aligned with ISO 20400 (Sustainable Procurement) & China’s 2026 Supply Chain Transparency Regulations
Confidential: For internal procurement use only. Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025–2026 China Supplier Audit Database (12,840+ verifications).
Ready to execute risk-free supplier verification? [Contact SourcifyChina’s China Exit Task Force] for a complimentary Relocation Risk Assessment.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Strategic Sourcing in a Shifting Landscape
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve in response to geopolitical shifts, rising operational costs, and corporate divestment strategies, an increasing number of Western companies are exiting or downsizing manufacturing operations in China. This transition presents both risk and opportunity for procurement leaders. Identifying reliable, high-performance suppliers amid this turbulence is no longer a matter of convenience—it is a strategic imperative.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List offers a data-driven, vetted solution to this challenge, enabling procurement teams to bypass months of supplier discovery, qualification, and audit cycles—saving time, reducing risk, and accelerating time-to-market.
Why the Verified Pro List is Critical in 2026
Western companies exiting China often leave behind underutilized production capacity, skilled labor, and advanced infrastructure. These assets are now accessible to agile buyers—but only if they can quickly identify trustworthy suppliers with proven compliance, quality control, and export experience.
Traditional sourcing methods involve:
- Lengthy supplier searches across fragmented platforms
- Unverified claims about certifications and capabilities
- High risk of miscommunication and fraud
- Months of back-and-forth negotiation and factory audits
The Verified Pro List eliminates these inefficiencies.
Key Advantages of SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Operations |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | All suppliers have undergone rigorous on-site audits, compliance checks (ISO, BSCI, etc.), and performance validation. |
| Immediate Capacity Access | Gain fast access to idle or underutilized production lines from former suppliers to exiting Western brands. |
| Time Savings | Reduce supplier qualification timelines by 60–70%—from 3–6 months to under 6 weeks. |
| Risk Mitigation | Verified track records, real client references, and performance history minimize operational and reputational risk. |
| Language & Cultural Alignment | Suppliers are experienced in serving Western clients, with English-speaking teams and ERP integration capabilities. |
| Exclusive Access | List is updated quarterly and available only to SourcifyChina partners—ensuring competitive advantage. |
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
In a fast-moving global market, time is your most valuable resource. Waiting to rebuild your supply chain from scratch is not a strategy—it’s a liability.
Leverage SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List today and turn market disruption into procurement advantage.
Our team of sourcing consultants is ready to provide you with a tailored preview of available suppliers matching your product category, volume, and compliance requirements.
👉 Contact us now to request your customized Pro List preview:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Respond within 24 hours on business days. All inquiries treated with strict confidentiality.
SourcifyChina — Trusted. Verified. Ready.
Your Partner in Smarter China Sourcing.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.