The global water brake dynamometer market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for precision testing in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global dynamometer market size was valued at USD 1.32 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Water brakes, known for their reliability and ability to absorb high torque loads, are a critical component within this segment—particularly in engine performance and emissions testing. As industries prioritize energy efficiency and regulatory compliance, investments in advanced testing systems have surged, reinforcing the strategic importance of high-performance water brake manufacturers. This growing demand, coupled with technological advancements in cooling efficiency and durability, has intensified competition among key players worldwide. Based on market presence, innovation, and global reach, the following ten companies represent the leaders in water brake manufacturing today.
Top 10 Water Brake Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Froude
Domain Est. 2016
Website: froudedyno.com
Key Highlights: Froude is widely recognized as the world’s leader for engine and turbine test systems in gas turbine, aerospace, marine, industrial and automotive markets….
#2 Dynamometers & Flowbenches
Domain Est. 1995
Website: superflow.com
Key Highlights: SuperFlow manufactures water brake, eddy current and AC engine dynamometers for performance and industrial applications. SuperFlow engine dynos test ……
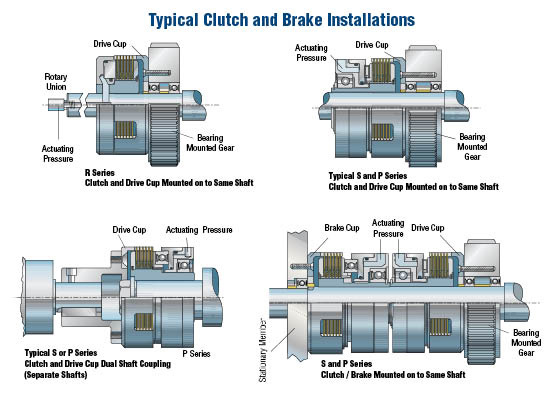
#3 Industrial clutches and brakes
Domain Est. 1995
Website: danfoss.com
Key Highlights: Airflex water-cooled, air-cooled and caliper disc brake solutions are designed for demanding applications that require high torque and horsepower absorption as ……
#4 Svendborg Brakes
Domain Est. 1996
Website: svendborg-brakes.com
Key Highlights: Svendborg Brakes is a global leader in intelligent hydraulic braking solutions and pioneers within hydraulic braking solutions for industries like wind, mining, ……
#5 Water Brakes for Dynamometer Test Stands
Domain Est. 1997
Website: wptpower.com
Key Highlights: WPT Power has been manufacturing water brakes for over 28 years and with three product lines available, the Steel Water Cooled Brake (SWCB), the Copper Water ……
#6 High Speed Water
Domain Est. 2007
Website: mustangae.com
Key Highlights: Mustang Advanced Engineering announces our new high-speed water brake loading units for turbine, pump and motor testing….
#7 Water Brake Engine Dynamometers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: powertestdyno.com
Key Highlights: Our water brake dynamometers (also known as hydraulic dynos) offer the rugged operation and accuracy you need to ensure success….
#8 Magnetic Brake Systems
Domain Est. 2011
Website: magbrakesystems.com
Key Highlights: Magnetic Brake Systems manufactures and sells. magnetic contactless brakes and dynamometers. Our brakes offer high power dissipation, linear torque output ……
#9 Water Brake Absorbers
Domain Est. 2023
Website: precisiondynotech.com
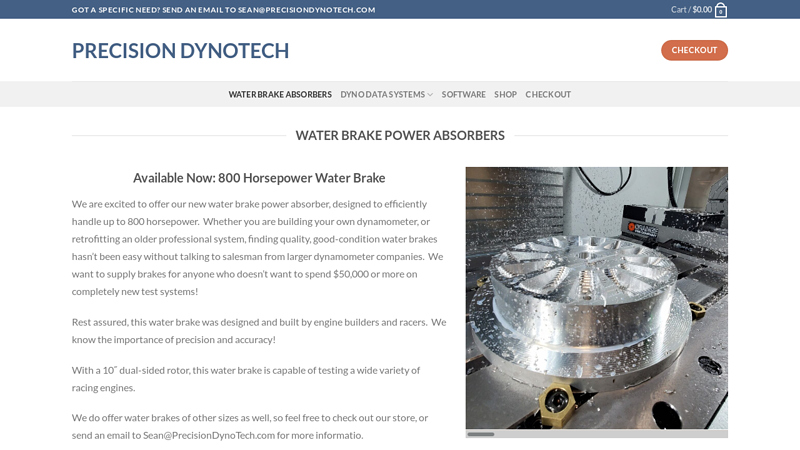
Key Highlights: Available Now: 800 Horsepower Water Brake. We are excited to offer our new water brake power absorber, designed to efficiently handle up to 800 horsepower….
#10 Dynamometers
Website: dyno-one.com
Key Highlights: We provide a wide variety of dynamometers, including AC, DC, EV, Hub, Inertia, and Eddy Current water brake systems….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Water Brake

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Water Brake Systems
The global water brake market is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand for reliable and efficient dynamometer systems in automotive testing, industrial machinery, and renewable energy sectors. As industries prioritize precision in performance evaluation and sustainability in testing processes, water brake dynamometers (WBDs) are gaining renewed attention due to their cost-effectiveness, durability, and ability to handle high torque loads.
One of the key trends shaping the 2026 outlook is the rising adoption of water brake systems in electric vehicle (EV) testing. While traditional dynamometers were primarily designed for internal combustion engines, modern water brake systems are being adapted to accommodate high-speed electric motors. Manufacturers are enhancing cooling efficiency and integrating digital control systems to improve response times and data accuracy, making water brakes a competitive option in hybrid and EV R&D environments.
Another significant trend is the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies. By 2026, smart water brake systems equipped with IoT-enabled sensors and real-time monitoring capabilities are expected to dominate testing laboratories. These advancements allow for remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and seamless data integration with cloud-based platforms, improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to lead market growth, fueled by expanding automotive production in China, India, and South Korea. Government initiatives promoting vehicle efficiency and emissions testing are further accelerating the deployment of dynamometer systems, including water brakes.
Sustainability concerns are also influencing product development. With water consumption being a traditional drawback of water brake systems, manufacturers are introducing closed-loop water recirculation and heat recovery technologies to minimize environmental impact. These eco-friendly designs align with global green manufacturing standards and are likely to be a differentiating factor in the 2026 market.
In summary, the 2026 water brake market will be characterized by technological innovation, expansion into EV testing, and a focus on sustainability. While competition from eddy current and electric dynamometers remains strong, ongoing improvements in performance and integration capabilities position water brake systems as a resilient and evolving solution in power testing applications.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Water Brake (Quality, IP)
Sourcing water brake dynamometers—critical equipment for measuring engine and motor performance—introduces several potential pitfalls, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these risks can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, legal disputes, and financial loss.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Material Specifications
Water brakes operate under high stress, heat, and continuous exposure to water, making material quality essential. A common pitfall is sourcing units made with substandard alloys or coatings that corrode or erode prematurely. Low-grade stainless steel or improper sealing can lead to leaks, contamination, and reduced lifespan. Buyers must verify material certifications (e.g., ASTM, ISO) and request test reports for corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
2. Poor Manufacturing Tolerances
Precision in rotor-stator alignment and internal clearances directly affects performance and heat dissipation. Suppliers from regions with inconsistent manufacturing standards may deliver units with poor tolerances, resulting in vibration, imbalance, and inaccurate torque measurements. Ensure suppliers use calibrated CNC equipment and provide geometric dimensioning and tolerance (GD&T) documentation.
3. Insufficient Testing and Calibration
Some suppliers skip or minimize performance testing to cut costs. Without full-load validation and calibration against traceable standards, the water brake may deliver unreliable data. Always require a factory acceptance test (FAT) protocol that includes torque accuracy verification, thermal performance under load, and dynamic response checks.
4. Lack of Certification and Compliance
Water brakes used in regulated industries (e.g., automotive, aerospace) must comply with standards such as ISO 1585, SAE J1349, or EPA protocols. Sourcing from uncertified manufacturers risks non-compliance, invalidated test results, and potential regulatory penalties. Confirm that the supplier provides documentation of compliance with relevant industry standards.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Risk of IP Infringement
Water brake designs often incorporate patented technologies, especially in rotor dynamics, cooling systems, and control algorithms. Sourcing from unvetted suppliers—particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement—increases the risk of purchasing counterfeit or reverse-engineered units that infringe on existing patents. This can expose the buyer to legal liability, product seizures, or injunctions.
2. Inadequate IP Protection in Contracts
Many procurement agreements fail to include clear IP clauses, such as warranties of non-infringement, indemnification for IP disputes, or ownership of custom modifications. Without these, buyers have little recourse if the supplier uses protected technology or if third parties claim infringement.
3. Exposure of Sensitive Test Data
When integrating water brakes into proprietary test cells, data flows between the dynamometer and control systems. Suppliers with poorly secured software or data interfaces may inadvertently expose performance data or test methodologies. Ensure data encryption, secure firmware, and contractual confidentiality obligations are in place.
4. Dependency on Proprietary Software and Interfaces
Some suppliers lock customers into closed ecosystems by using proprietary communication protocols or software. This can limit integration with existing test systems and create long-term dependency, increasing costs and reducing technical flexibility. Prefer suppliers offering open APIs, standard communication protocols (e.g., CAN, EtherCAT), and modular control interfaces.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits, including facility visits and quality system reviews (e.g., ISO 9001 certification).
– Require detailed technical documentation, material certifications, and performance test reports.
– Include robust IP clauses in procurement contracts, with indemnification and warranty provisions.
– Engage legal counsel to perform IP due diligence, especially when sourcing from high-risk jurisdictions.
– Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record, transparent design practices, and compliance with international standards.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and protection of their innovation when sourcing water brake dynamometers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Water Brake Systems
Overview of Water Brake Systems
Water brake systems are specialized dynamometers used primarily in engine and turbine testing to absorb and measure power output. These systems utilize water as a fluid medium to create resistance, converting mechanical energy into heat, which is then dissipated through a cooling system. Due to their hydraulic nature and integration into industrial testing environments, water brake systems are subject to specific logistical and compliance requirements.
Transportation and Handling Logistics
Packaging and Crating
Water brake systems must be securely packaged to prevent damage during transit. Components such as the rotor, housing, and sensors should be protected with anti-corrosion coatings and moisture barriers. Crating must meet international standards (e.g., ISPM 15 for wooden crates) when shipped across borders.
Shipping Modes
- Freight (Air/Sea/Ground): Large water brake assemblies are typically shipped via freight. Sea freight is cost-effective for international delivery, while air freight may be used for urgent, time-sensitive components.
- Hazardous Material Classification: Water brake systems are generally not classified as hazardous. However, residual oils or hydraulic fluids may require proper labeling under IATA, IMDG, or ADR regulations if present.
Import and Export Documentation
Ensure accurate preparation of commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Export controls may apply if components incorporate sensitive technology (e.g., high-precision sensors), requiring an export license under EAR (Export Administration Regulations) or equivalent.
Regulatory Compliance
Environmental Regulations
- Cooling Water Discharge: Facilities using water brake systems must comply with local environmental laws regarding heated water discharge. Recirculating cooling systems are recommended to minimize thermal pollution.
- Spill Prevention: Secondary containment and drip trays are required to prevent lubricant or coolant leaks. Facilities must adhere to EPA Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) rules if storing large volumes of oil.
Electrical and Operational Safety Standards
- CE Marking (EU): Required for sale within the European Economic Area. Compliance with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU is mandatory.
- UL/CSA Certification (North America): Ensures electrical safety for control systems and sensors. Required by OSHA and local authorities.
- ISO Standards: Adherence to ISO 13849 (safety of machinery) and ISO 9001 (quality management) is recommended for design and manufacturing processes.
Workplace Safety and Installation
- OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent local regulations: Guarding, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and proper signage are required to protect personnel during operation and maintenance.
- Noise and Vibration Control: Water brakes can generate high noise levels; compliance with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.95 or EU Directive 2003/10/EC on noise exposure is essential.
Maintenance and Operational Compliance
Fluid Management
- Use only approved water treatment additives to prevent scaling and biological growth.
- Regular testing of water quality (pH, conductivity, microbial content) to meet facility and environmental standards.
- Proper disposal of spent coolant in accordance with local wastewater regulations (e.g., NPDES permits in the U.S.).
Calibration and Testing Records
- Maintain traceable calibration records for torque and speed sensors per ISO/IEC 17025 standards.
- Periodic audits and compliance checks to ensure continued adherence to performance and safety requirements.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for water brake systems require a coordinated approach across transportation, environmental stewardship, safety, and regulatory domains. Manufacturers, distributors, and end-users must stay informed about evolving standards and ensure documentation, training, and operational procedures support full compliance throughout the system lifecycle.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Water Brake
In conclusion, sourcing a water brake dynamometer requires careful consideration of application requirements, technical specifications, reliability, and supplier credibility. Water brakes offer efficient, cost-effective load absorption for testing engines, motors, and other rotating machinery, particularly in high-power applications where continuous operation and heat dissipation are critical. When selecting a water brake, factors such as torque and speed range, cooling capacity, integration capabilities, and maintenance needs must align with operational demands.
Sourcing from reputable manufacturers or suppliers ensures quality, durability, and access to technical support. Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership—including installation, water treatment, and maintenance—is essential for long-term performance. With proper selection and sourcing, a water brake can provide precise, repeatable, and dependable performance, making it a valuable investment for performance testing and R&D environments.