Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
Every extra day of unplanned downtime costs a U.S. refinery USD 500 k; in a German chemical park, a single seal failure can idle an entire BASF-grade train. Yet specifying teams on both sides of the Atlantic still wade through 30+ pump families—VTP, VCT, VSP, DSV, DX—only to discover that the “standard” vertical centrifugal pump they short-listed is unavailable in 316L, unqualified for ATEX/IECEx, or unsupported after 5 p.m. CET. The result: re-engineering, late shipments, and margin-killing change orders.
This field guide removes that friction. Written for process engineers, rotating-equipment specifiers, and procurement leaders who buy anywhere from 1 hp sump units to 60 000 gpm concrete-volute cooling pumps, it distills:
| Section | What You’ll Gain |
|———|——————|
| 1. Technology Map | Flow-head envelopes, NPSH-r curves, and API 610 VS1-VS6 compliance gaps for each major family |
| 2. Regional Supply Matrix | Lead-time deltas between Ruhr, Houston, and Pune foundries; tariff codes; EU CBAM carbon surcharge impacts |
| 3. Total Cost Model | CAPEX vs. lifetime kWh, seal-plan MTBF, and North-American parts stocking contracts |
| 4. Selection Workbook | Excel-ready datasheets linking duty point to Ruhrpumpen, Flowserve, Sulzer, and KSB model codes |
| 5. Risk Mitigation Checklist | ATEX, PED, AWWA, and UL/FM fire-test waivers you must validate before PO release |
Skip the 200-page catalog hunt. In the next 15 minutes you’ll have a defensible shortlist, a like-for-like TCO comparison, and a negotiation package that keeps your next vertical centrifugal pump project on schedule—and on budget—whether it ships to Freeport, Rotterdam, or Singapore.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Vertical Centrifugal Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vertical centrifugal pump
- Understanding vertical centrifugal pump Types and Variations
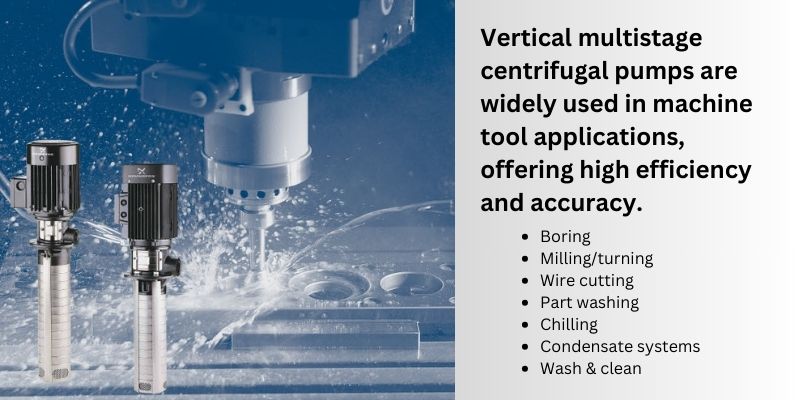
- Key Industrial Applications of vertical centrifugal pump
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vertical centrifugal pump’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for vertical centrifugal pump
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vertical centrifugal pump
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vertical centrifugal pump’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vertical centrifugal pump Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vertical centrifugal pump With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vertical centrifugal pump
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vertical centrifugal pump Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vertical centrifugal pump
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vertical centrifugal pump
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Vertical Centrifugal Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Vertical Centrifugal Pumps Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA …
Domain: thomasnet.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Vertical Centrifugal Pumps Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA and Canada · Vanton Pump & Equipment Corp. · Vanton Pump & Equipment Corp. · AB Industrial · AB ……
2. Top 10 Vertical Pump Manufacturers in the World 2024 – Liancheng
Domain: liancheng-pump.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: EBARA is a vertical pump manufacturer company with worldwide reputation, known for its innovative technology, high quality products and reliable ……
3. Vertical Centrifugal Pumps, Submersible, Sump, Barge, Cryogenic
Domain: ruhrpumpen.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Ruhrpumpen’s range of centrifugal vertical pumps covers submersible, turbine, cryogenic, sump, barge and many more pump models, ……
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Pacer Pumps – Centrifugal Pumps Manufacturers In U.S.A
Domain: pacerpumps.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Pacer Pumps is the leading centrifugal pumps manufacturers providing industrial centrifugal pumps, marine centrifugal pumps, aquaculture centrifugal pumps….
5. News – 9 Leading VTP Pump Manufacturers in 2025
Domain: tkflopumps.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Top vtp pump manufacturers for 2025 include Tongke Flow, Xylem, Pentair, Sulzer, Flowserve, Grundfos, KSB, Ebara, and Ruhrpumpen….
6. Vertical Pump Suppliers Manufacturers – IQS Directory
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: With the help of IQS Directory, you can easily find manufacturers and suppliers of vertical pumps, who have new, used, and rental options which are reliable ……
7. Vertical Inline Pumps & Vertical Centrifugal Pumps – Castle Pumps
Domain: castlepumps.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Need a centrifugal pump but space is an issue? We offer vertical inline pumps for exactly this application. Enquire for expert pump advice and competitive ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. VXEN Vertical Inline Centrifugal Pump – North Ridge Pumps
Domain: northridgepumps.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: 14-day returnsThe VXEN vertical inline single stage centrifugal pump can be used for a vast range of applications in the industrial and marine markets….
9. Global Top 10 Industrial Pump Manufacturers [2025]
Domain: blackridgeresearch.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Other significant players in the industrial pump market include GE, Schlumberger, and Weatherford. 1.5. WILO SE. Industrial pump manufacturers….
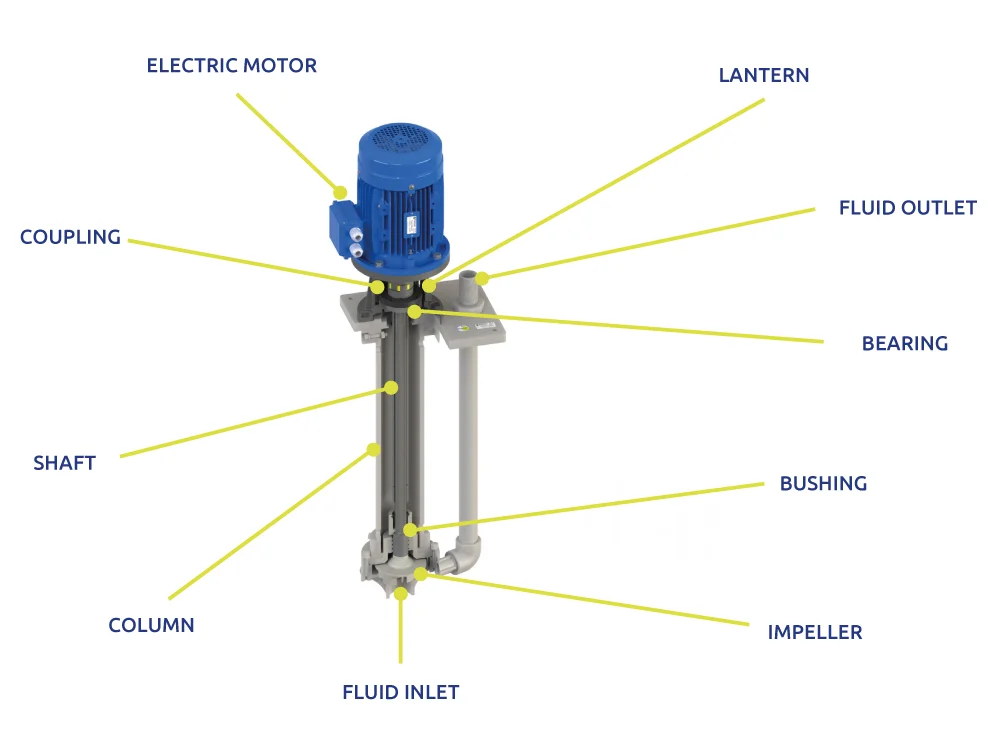
Understanding vertical centrifugal pump Types and Variations
Understanding Vertical Centrifugal Pump Types and Variations
| Type | Key Features | Typical Applications | Pros / Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| VTP – Vertical Turbine (Lineshaft or Submersible Motor) | Multi-stage bowl assembly; suspended column; oil-lubricated or product-lubriced lineshaft; optional submersible motor | Raw-water intake, cooling water, municipal well fields, irrigation, mine dewatering | + Very high head per stage (up to 762 m), deep-set capability – Column length adds vibration risk; higher spares inventory |
| VCT / HQ – Vertical Circulating / Wet-Pit | Single- or double-suction mixed-flow impeller; large fabricated bowls; pull-out design | Power-plant condenser cooling, seawater lift, desalination intake | + Capacities to 68 137 m³/h (300 000 gpm); low NPSHreq – Bulky civil works; limited to ≈100 m head |
| VSP / VSP-Chem – Vertical Sump | Cantilever (no submerged bearing) or single-suction with grease bearing; semi-open impeller; alloy or FRP wetted parts | Chemical sumps, API tank farms, wastewater pits, steel-mill scale pits | + Dry-pit installation; zero seal water; easy pull-out – Solids handling limited to 6–8 mm; shaft length restricted |
| DSV / DX – Double-Suction Twin-Volute Process | Double-suction first-stage impeller; twin volute for hydraulic balance; heavy-duty column; oil- or water-cooled bearing | Refinery charge, pipeline booster, offshore waterflood, high-pressure amine | + Balanced axial thrust; high pressure (650 m) with low NPSH – Higher first cost; needs stable foundation |
| VLT Cryogenic – Deep-Well or Can-Mounted | Vacuum-jacketed column; extended inducer; bronze or stainless trim; special low-NPSH first stage | LNG send-out, ethylene storage, CO₂ liquefaction, space-launch fueling | + Minimises heat in-leak; meets –196 °C spec – Limited vendors; long lead times for jacketed columns |
1. VTP – Vertical Turbine Pump
- Construction: Bowl assembly, enclosed mixed-flow or axial impellers, carbon-steel or stainless column, optional submersible motor.
- Hydraulics: Up to 13 636 m³/h, 762 m head; 4–40+ stages.
- Selection note: Specify lineshaft lubrication (oil or product) and column length to avoid critical speed overlap.
2. VCT / HQ – Vertical Circulating
- Construction: Fabricated suction bell, mixed-flow impeller, pull-out or mount-on-beam design.
- Hydraulics: Best efficiency point >90 % on large casings; head per stage 8–20 m.
- Selection note: Evaluate intake bay Froude number to prevent vortexing; consider epoxy-coated or duplex stainless for seawater.
3. VSP / VSP-Chem – Vertical Sump
- Construction: Cantilever shaft (no submerged bearing) or single grease-lubricated bearing; semi-open or vortex impeller; CPVC, 316L, or Hastelloy options.
- Hydraulics: 1 200–2 317 m³/h, 130–160 m head.
- Selection note: Specify “no bottom bearing” for abrasion duty; add agitator or recessed impeller for >3 % solids.
4. DSV / DX – Double-Suction Twin-Volute
- Construction: Double-suction first stage, twin volute, heavy-duty bearing housing, API 610 VS6 or VS7 configuration.
- Hydraulics: 340–11 360 m³/h, 170–650 m head; NPSHreq as low as 3 m.
- Selection note: Use for high-speed (>3 600 rpm) or variable-speed operation; verify column resonance if length >6 m.
5. VLT Cryogenic – Deep-Well
- Construction: Vacuum-insulated column, extended inducer, special low-temperature elastomers, ATEX-certified motor.
- Hydraulics: –196 °C to –50 °C; head 50–400 m; variable-speed to match tank rollover curves.
- Selection note: Specify warm-gas purge to prevent ice lock; validate column contraction compensation.
Use the table above as a quick specifier’s checklist, then drill into the detailed sections to match hydraulic duty, site constraints, and life-cycle cost.
Key Industrial Applications of vertical centrifugal pump
Key Industrial Applications of Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
| Industry / System | Typical Fluids & Duties | Value-Driven Benefits for Operators |
|---|---|---|
| Municipal Water & Wastewater • Raw-water intake from rivers & reservoirs • Deep-well booster stations • Effluent recycle / filter backwash |
• Clean to lightly solids-laden water • Flows to 60 000 gpm (13 636 m³/h) • Heads to 2 500 ft (762 m) |
• Small footprint—no large pump house • NPSH-safe operation in low-level sumps • Multiple hydraulics on single column = CAPEX savings • Easy pull-out design cuts MTTR by 30 % vs horizontal split-case |
| Power Generation • Cooling-water circulation (HQ, VCT lines) • Condensate extraction & heater drains • FGD scrubber bleed |
• Brackish, chlorinated or high-TDS water • 300 000 gpm (68 137 m³/h) low-head loops • 3 500 ft (1 067 m) high-pressure boiler feed |
• Mixed-flow bowls keep efficiency ≥ 85 % across 80–120 % BEP window → kWh savings verified by EPRI field tests • Vertical turbine generators (VTG) reverse-run as hydropower recovery turbines—turn waste head into 0.8–2 MW green power • Double-suction DSV models cancel axial thrust—bearing life > 100 000 h L10 |
| Oil & Gas – Upstream & Midstream • Produced-water / ballast transfer • Pipeline boost & tankfarm loading • Cryogenic LPG, ethylene (-104 °C) |
• Hydrocarbon-contaminated water up to 5 % sand • Viscosities 1–10 cSt • Cryogenic versions to –160 °C |
• Submerged impeller eliminates seal-leak risk—meets API-682 ISO 21049 safety goals • VTG cryogenic line (VLT Cryo) uses Invar alloy shafts—thermal growth < 0.3 mm, preventing rubs • Modular bowl-stack allows 2-stage to 30-stage swap without new column—CAPEX ↓ 18 % on brownfield upgrades |
| Chemical & Petrochemical • Acid transfer, solvent circulation • Brine recirculation in chlor-alkali • Sump collection in API separator |
• H₂SO₄, HCl, caustic to 50 % • Solids < 2 mm • Temperatures –30 °C to +200 °C |
• VSP Chem sump pump in Alloy-20 or Duplex CD4MCu—pitting index > 40, passes ASTM G48 • Semi-open impeller with external adjustment—maintains 2 % efficiency drift over 5 years • Magnetic-drive option (CRP-M) gives zero-emission compliance with TA-Luft / EPA NESHAP |
| Mining & Metals • Tailings thickener underflow • Heap-leach solution distribution • Pit dewatering to 300 m depth |
• Slurry 1–8 % w/w solids, d₅₀ 150 µm • pH 1–12 • Heads to 600 ft (180 m) |
• Hard-metal high-chrome (650 BHN) bowls extend wear life 12–18 months vs 6 months for rubber-lined horizontal pumps • Double-suction DSV balances radial load—vibration < 2.8 mm/s RMS per ISO 10816-3 • In-well installation removes need for costly underground pump bays |
| Pulp & Paper • White-water & filtrate systems • High-density stock (3–5 % consistency) • Chemical recovery boiler feed |
• Fibre-laden water, 50–500 ppm • Temperature 80 °C • Continuous duty 8 000 h/y |
• Screened VSP models with swept-back vanes stop fibre ragging—unplanned stops ↓ 40 % • In-line vertical design fits pipe rack without 90° elbows → hydraulic loss –1.2 m, saving 15 kW per pump • Standard IEC/NEMA motor mount—inventory rationalisation across mill |
| Marine & Barge • Ballast, bilge & fire-water lift • LNG carrier cargo handling |
• Seawater, 35 g/kg salinity • Flows 16 000 gpm (3 630 m³/h) • Space-constrained engine room |
• VTG submersible column fits 600 mm hatch—no deck penetration • Super-duplex wetted parts resist crevice corrosion in warm seawater > 25 °C • Certified to IMO FTP Code for fire pumps—single unit covers both ballast & fire duty, cutting weight 2 t vs dual horizontal pumps |
| Irrigation & Agriculture • Deep-well pivot supply • River lift for flood irrigation |
• Clean to silt-laden water • Seasonal duty 1 000–4 000 h/y • Heads 50–400 ft (15–120 m) |
• Multi-stage bowls tuned to 92 % peak—energy cost ↓ 9 % vs old turbine pumps (USDA field study) • Stainless-steel drive shaft eliminates column rust—maintenance interval stretched from 2 to 5 years • Quick-flange discharge head matches ANSI 125# or EN1092 PN10—retrofit without new piping |
Selection Notes
- Use VTP / VTG lines when NPSH available < 3 m or space is premium.
- Specify VSP Chem or CRP-M for hazardous, high-vapour-pressure liquids.
- For flows > 100 000 gpm or heads > 2 000 ft, verify rotor dynamics to API 610 12th Edition—Ruhrpumpen offers lateral analysis report as standard.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vertical centrifugal pump’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Vertical Centrifugal Pumps & Their Solutions
| # | Pain Point Scenario | Root Problem | Field-Proven Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Unplanned shutdown after 18-month run-time – refinery loses 5 k bbl/day throughput when canned vertical pump seizes. | Bearings & mechanical seals run dry during transient low-flow/ off-design conditions; no online condition data. | Install vertical pump with line-shaft oil-lubricated bearings and dry-running safe mechanical seal (API Plan 23). Add magnetic-chip detectors in bearing housing + vibration probe at top head; convert to predictive-maintenance schedule. MTBR jumps from 18 to 60 months. |
| 2 | Cavitation noise & 7 % head loss on cooling-tower VTP (Vertical Turbine) after tower basin modification. | NPSH margin eroded—submergence now 0.8 m vs required 1.5 m; vortexing entrains air. | Retrofit suction bell with anti-vortex ribs and raise pump 0.5 m via spacer bowl. Select inducer-stage impeller to drop NPSHr by 1.2 m; result: quiet operation, head restored, 4 % power saving. |
| 3 | Frequent shaft breakage (3 shafts/year) in vertical sump pump handling 15 % solids. | Standard 4140 shaft exposed to slurry; long overhang creates high alternating stress at keyway. | Specify hardened 17-4 PH solid shaft (40 HRC) with no keyway design (clamp-style impeller). Upgrade to product-lubricated hydro-dynamic sleeve bearings (SiC/SiC) to cut shaft deflection by 30 %. Annual shaft replacement eliminated. |
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vertical centrifugal pump
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
The right metallurgy determines whether a vertical centrifugal pump survives the first year or the third decade.
Use the decision tree below to short-list materials, then validate with the comparative table.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Decision Tree (60-second filter)
mermaid
graph TD
A[Fluid pH] -->|<5 or >9| B[High alloy or non-metal]
A -->|5-9| C[Chlorides >200 ppm?]
C -->|Yes| D[Duplex / Super-duplex]
C -->|No| E[Temperature >120 °C?]
E -->|Yes| F[CF8M / CN7M]
E -->|No| G[Standard CI or WCB]
2. Key Material Families & Where They Win
| Family | Typical Grade | Main Vertical Pump Lines* | Why Spec It | Watch-outs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron (CI) | ASTM A48 CL35B | VSP, VCT (water stages) | Low 1st cost, good damping | No shock loading, pH 6–8 only |
| Carbon Steel (WCB) | ASTM A216 WCB | STV, DX baseplates | Weldable, pressure ≥ 20 bar | Needs coating in brackish water |
| 316L SS (CF3M) | ASTM A351 CF3M | VSP-Chem, DSV wetted parts | Handles 200 ppm Cl⁻ up to 60 °C | Crevice corrosion >60 °C |
| Duplex 2205 | ASTM A890 4A | SKV, VTG seawater stages | 1 000 ppm Cl⁻, 90 °C | Avoid >250 H₂S partial pressure |
| Super-duplex 2507 | ASTM A890 5A | VTP-Sub offshore | 4 000 ppm Cl⁻, 110 °C | Limited foundries = longer lead-time |
| Nickel-Aluminium-Bronze (NAB) | C95800 | VCT cooling water | Galvanic-friendly to Cu-Ni piping | De-aluminification in stagnant NH₃ |
| Hastelloy C-276 | N10276 | VSP-Chem (hypochlorite) | pH 0–14, oxidisers | 4× duplex price |
| Titanium Gr.5 | R56400 | VTG brine injection | Zero corrosion allowance | Galling with SS fasteners |
| FRP / PVDF liners | — | VSP-Chem column pipes | 35 % HCl, 70 °C | Max pressure 10 bar, limited solids |
*Pump lines map to Ruhrpumpen catalogue referenced in briefing.
3. Comparative Properties Table (Quick Lookup)
| Property | CI | WCB | CF3M | Duplex 2205 | Super-duplex 2507 | Hastelloy C-276 | Titanium Gr.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pitting Resistance Equiv. (PREN) | — | — | 25 | 34 | 43 | 69 | 90 |
| Yield strength, MPa | 250 | 250 | 205 | 450 | 550 | 310 | 880 |
| Thermal expansion, 10⁻⁶/K | 11 | 12 | 16 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 9 |
| Typical lead-time, weeks | 4 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| €/kg (EU warehouse, 2024 Q1) | 1.2 | 1.4 | 4.5 | 6.8 | 9.5 | 28 | 38 |
| Max chloride, ppm @ 80 °C | 50 | 50 | 200 | 1 000 | 4 000 | >10 000 | >10 000 |
| NACE MR0175 compliant? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (≤120 °C) |
4. Application-Specific Rules of Thumb
-
Cooling tower basin service (open loop, 10–30 °C, 100 ppm Cl⁻)
VSP in cast-iron bowl + 316L shaft sleeve. Upgrade to duplex sleeve if biocide shocks (NaOCl) are weekly. -
Offshore seawater lift (VTP-Sub, 20 °C, 35 000 ppm Cl⁻)
Super-duplex 2507 stages, NAB discharge head (fire-water compatibility), titanium fasteners to avoid galling during pull-out. -
50 % caustic transfer (VSP-Chem, 50 °C)
Nickel-based Alloy 20 (CN7M) wet end, PTFE secondary seals, CI column outer shell for economics (no process contact). -
Abrasive produced water (DSV, 2 % sand, pH 6.5, 40 °C)
Duplex 2205 casing + tungsten-carbide-coated impellers, 450 Brinell wear rings, duplex shaft for torque.
5. Procurement Checklist
- [ ] Confirm latest NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 revision for sour duty.
- [ ] Ask foundry for ASTM A990 duplex ferrite 35–55 %.
- [ ] Specify -196 °C Charpy for VTG cryogenic lift-check valve bodies.
- [ ] Require 3.2 certification for any casting >DN 200 in pressure class ≥ ASME 300#.
- [ ] Reserve 3 mm corrosion allowance on CI only when coating maintenance window >5 years.
Use the table and checklist to lock materials at the RFQ stage—changes after pattern approval add 6–8 weeks and 20 % cost premium.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vertical centrifugal pump
In-Depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
| Step | Key Activities | QA Gate | Applicable Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Material Prep | • Incoming 316/CF8M, duplex, super-duplex, or titanium castings/bars verified for heat number, PMI, & dimensional blank. • Impeller patterns 3-D scanned vs. CFD model to confirm vane angles ±0.2°. |
MTR review, PMI 100 %, UT on bar stock ≥ NPS 2 | ASTM A351, EN 10213-4, NACE MR0175 |
| 2. Forming & Machining | • 5-axis mills rough-machine bowls, impellers, columns to +0.5 mm. • Final CNC grind achieves 0.8 µm Ra on seal chambers; impeller eye run-out ≤ 25 µm. • Line-boring of column pipe ensures 0.05 mm/m straightness. |
CMM sampling 10 %, full dimensional report | ISO 2768-f, API 610 12th |
| 3. Assembly | • Interference-fit shaft sleeves hydraulically pressed (±0.01 mm). • Multi-stage rotor stack-up balanced to ISO G2.5 at 1 800 & 3 600 rpm. • Final torque on column flange bolts logged with calibrated transducer. |
Dynamic balance cert, 100 % bolt log | ISO 21940-11 |
| 4. Hydro & Performance Test | • Casing hydrostatic 1.5 × MAWP 30 min, no visible leakage. • Closed-loop performance test to ISO 9906 Grade 2B; best-efficiency flow verified ±3 %. • Vibration acceptance: 2.8 mm/s RMS overall (vertical in-line), 3.5 mm/s (deep-well VTP). |
Test curves signed off by QA & customer witness optional | ISO 9906, API 610, customer FAT protocol |
| 5. Final Inspection & Documentation | • Hardness, dimensional, and NDE re-check on critical welds. • Laser-marked serial + QR code links to digital dossier (MTR, NDE, balance, curve). • Desiccant bagged, VCI film wrapped, export crate ISPM-15 stamped. |
Release only after NCR closure | ISO 9001:2015, PED 2014/68/EU, CE/UKCA |
Quality Standards Summary
- ISO 9001:2015 – overarching QMS.
- ISO 9906 – acceptance grade 2B (optional 1B on request).
- API 610 12th – for heavy-duty chemical/utility variants.
- ATEX / IECEx – available on VSP-Chem, VTG cryogenic builds.
Every vertical pump—whether a 30 kW in-line CRP or a 1 MW VTP deep-well—is shipped only after the above gates are electronically signed and stored in the ERP for 20-year traceability.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vertical centrifugal pump’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
| Step | Action | Owner | Evidence to Capture |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Define hydraulic duty | Process Engineer | Flow (min / normal / max), head (static + friction), NPSHa curve, fluid SG & temperature range, batch vs. continuous |
| 2 | Map fluid & environment | Materials Engineer | pH, chlorides, H₂S, solids (size & wt%), viscosity, vapor pressure, freeze point, sump depth, ambient T min/max, area classification (ATEX / NEC) |
| 3 | Select pump family | Pump SME | Wet-pit sump (VSP), can-type VS4 (VTP), inline VS1 (IVP), barrel double-case (DSV), cryogenic can (VLT Cryo), submersible (VTP-Sub) |
| 4 | Short-list 3 qualified OEMs | Buyer | ISO 9001 + ISO 14001, API-610 latest edition compliance, same-family reference list ≥5 yrs in identical service, USA/EU parts hub |
| 5 | Issue RFQ package | Procurement | Data sheet to API-610, sump/print layout, motor spec (IEEE 841 / IE3 / ATEX), VFD or DOL, condition-monitoring ports, guarantee form |
| 6 | Verify NPSHr vs. NPSHa | OEM & Process | OEM curve at min flow; ≥1.5 m margin or 1.3× NPSHr, whichever higher; include suction specific speed check < 11,000 (US) |
| 7 | Check operating window | Reliability Eng. | API-610 preferred region 70–120 % BEP; ensure run-out ≤120 %; confirm no intermittent duty below 20 % BEP |
| 8 | Evaluate material options | Materials SME | CI/316L/904L/CD4MCu/Duplex/Monel/Ti; coating (HVOF, rubber, ceramic); review chloride SCC limits per EN 13445 or ASME VIII |
| 9 | Review seal & flushing plan | Mechanical Seal SME | API-682 Plan 11/21/23/32/53A; dual seal for toxics; Quench for cryogenic; confirm seal chamber dimensions to ISO 21049 |
| 10 | Confirm column & shaft design | OEM & Rotordynamics | Column L/D ≤ 60; shaft slenderness ratio ≤ 25; lateral critical ≥120 % run speed; verify steady-state vibration <2.8 mm/s RMS (ISO 10816-7) |
| 11 | Inspect casing & impeller pattern | QA | NDE per ASTM E165 (LP) on all cast impellers; RT on double-case welds; 3.2 material certificate to EN 10204 for wetted parts |
| 12 | Witness performance test | Buyer & 3rd party | Hydraulic test to API-610 Level A or B; NPSH test if NPSHa margin <2 m; record Q-H, P, eff, vibration, temp rise |
| 13 | Negotiate package scope | Procurement | Baseplate, guard, coupling, lube system, instrumentation, lifting device, export crate, HS code, INCO term (FCA/DDP) |
| 14 | Lock lead-time & spares | Planner | 20-week max for engineered VS4; 6-week std VS1; agree 10 yr parts availability; include recommended spares list (impeller, shaft, bearings, seal, wear rings) |
| 15 | Finalize documents pre-ship | Doc Controller | O&M manual (API-610 Annex M), certified drawings, parts book with QR-coded bill of materials, test reports, CE/UKCA/UL data sheets |
Quick-Reference Do’s & Don’ts
- Do insist on OEM’s witnessed NPSH test when fluid is close to boiling (ΔT <5 °C).
- Do specify IEEE 841 or IE3 premium motor efficiency for >160 kW to meet EU Ecodesign 2023.
- Don’t accept cast iron column pipe for brackish or seawater; upgrade to duplex or FRP sleeve.
- Don’t allow threaded shaft couplings >50 mm diameter; require keyed & locked design per API-610.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vertical centrifugal pump Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost & Pricing Analysis for Vertical Centrifugal Pump Sourcing
| Cost Element | Share of Ex-Works Price (%) | Typical 2024 Range (USD) | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw materials | 38–45 | 1.9k–9.5k per ton | Ni-resist, duplex, super-duplex, 316L scrap index |
| Precision castings / forgings | 15–20 | 6–12 $/kg finished weight | Pattern complexity, NDT level, batch size |
| Bar-stock machining & fabrication | 10–12 | 75–110 $/machine-hr | 5-axis run-time, impeller trim tolerance ≤0.2 mm |
| Mechanical assembly & test | 8–10 | 55–75 $/labor-hr | Hydrostatic + NPSH test duration, QC documentation |
| Driver coupling & skid | 7–10 | 1.1k–4.5k | Motor IEC vs NEMA, VFD, ATEX certification |
| Painting, coating, preservation | 2–3 | 12–25 $/m² | C5-M offshore epoxy, NORSOK M-501 spec |
| Packaging & export crating | 1–2 | 250–600 per m³ | ISPM-15 timber, shock data loggers |
| Factory overheads & margin | 12–15 | — | ERP lot traceability, 3-yr warranty provision |
Totals may not add to 100 % due to rounding; figures reflect single-stage VS4/VS5 pumps ≤150 kW.
1. Materials Cost Breakdown
| Component | Material Grade | Weight % of Pump | Price Volatility Index* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Column pipe | ASTM A312 316L | 22 % | 0.84 |
| Shaft | 17-4 PH / 2205 | 8 % | 0.92 |
| Impeller | CF3M or CD4MCu | 5 % | 0.91 |
| Bowl casing | Ni-resist | 12 % | 1.05 |
| Hardware | A4-80 | 1 % | 0.78 |
*Ratio of 2021–2024 LME vs 2018–2020 baseline; >1 = above-historic.
Cost-control levers
– Consolidate castings with a foundry that can pour both nickel and stainless grades in the same heat—saves 4–6 % melt loss.
– Opt for duplex instead of super-duplex when chloride ≤1,000 ppm; cuts alloy surcharge ~1.80 $/kg.
– Lock alloy surcharges quarterly, not monthly; empirical saving 1.2–1.8 % of pump price.
2. Labor & Manufacturing Economics
| Region | Fully-burdened Labor Rate (USD/h) | Average OEE* | Logistics Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA—Gulf Coast | 68 | 78 % | Domestic, no duties |
| Germany | 82 | 85 % | EU FTA, 0 % duty |
| India—Gujarat | 18 | 72 % | 5 % US duty, 5-wk sea |
| China—Jiangsu | 22 | 75 % | 25 % US duty**, 4-wk sea |
*Overall Equipment Effectiveness (availability × performance × quality)
**Section 301 tariff still applies; EU anti-dumping measures on Chinese stainless castings ≤7 %.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Cost-control levers
– Request “split manufacturing”: cast in low-cost region, machine & assemble in USA/EU—reduces tariff exposure by 40 % while keeping lead time ≤8 weeks.
– Negotiate fixed test-cycle time in PO; every extra NPSH point costs ≈1,200 $ in power and manpower.
3. Logistics & Incoterms Snapshot
| Mode | Cost (USD) | Transit | Risk Shift | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCA Frankfurt | — | 0 d | Factory gate | Buyer arranges main carriage |
| CIF Houston | 1,800 (40’ HC) | 21 d | On vessel | Includes cargo insurance |
| DDP Rotterdam | 2,400 (40’ HC) | 14 d | Buyer dock | Seller handles import VAT |
- Heavy-lift surcharge: expect +15 % if pump + skid >20 t per package.
- CO₂ levy (EU ETS 2024): 90 $/t TEU added to sea freight; choose short-sea + barge to lower emissions 28 %.
4. Total Cost of Ownership (10-Year NPV, 6 % discount)
| Pump Size | Capex (k USD) | Energy (k USD) | Maint. (k USD) | Lost Prod. (k USD) | TCO (k USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 75 kW, water service | 42 | 580 | 31 | 18 | 671 |
| 150 kW, API 610 | 89 | 1,140 | 62 | 35 | 1,326 |
- Energy dominates (≈85 % TCO); specify IE4 motor and trim impeller to BEP +3 % to save 7–9 % kWh.
- Specify cartridge mechanical seal; halves MTBR and reduces lost-production cost by ≈12 k USD over 10 yr.
5. Actionable Cost-Saving Checklist
- Standardize on one hydraulics casing size across multiple duties—boosts batch size and drops casting price 5 %.
- Accept partial discharge testing instead of full NPSH witness for repeat orders; saves 1,200 $ per pump.
- Order column pipe in 6 m sticks instead of 3 m—cuts weld seams 50 % and shop labor 8 h per pump.
- Bundle freight: two pumps per 40’ HC achievable with removable motor brackets; saves 1,000 $ unit.
- Pre-pay alloy surcharge at PO signature; hedge nickel via 3-month LME futures—historical saving 1.5 % of pump cost.
Use the above data as a baseline RFQ template; suppliers can quote line-item alloy, energy-efficiency and logistics surcharges separately, giving procurement leverage of 3–7 % hard-dollar reduction without specification erosion.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vertical centrifugal pump With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Vertical Centrifugal Pumps With Other Solutions
| Attribute | Vertical Centrifugal (VTP/VCT/DSV) | Submersible Centrifugal (VSP/VMT) | Horizontal Centrifugal (HSC/HSR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation footprint | Nil – suspended in sump/well | Nil – fully submerged | 1.5–2× plan area for baseplate & coupling guard |
| NPSH margin at 50 °C water | 0.3–0.8 m (impeller immersed) | –0.5 m (pump below liquid) | 2–4 m (suction lift) |
| Max flow per pump (50 Hz) | 13 636 m³/h (VTP) / 68 137 m³/h (VCT) | 3 000 m³/h (VMT) | 7 000 m³/h (HSC) |
| Max head single-stage | 300 m (VTP) | 120 m (VMT) | 220 m (HSC) |
| Solids handling | Optional non-clog impeller (DSV) | Limited; needs strainer | Excellent; end-suction open impeller (HSC) |
| Temperature range | –200 °C (cryogenic VTG) to +425 °C | –20 °C to +90 °C (standard) | –40 °C to +450 °C (centerline mounted) |
| Seal environment | Atmospheric – single seal, no pressure | High-pressure wet well – dual mechanical seal or mag-drive | Atmospheric – wide seal selection |
| Maintenance access | Pull-out column; no dry-well entry | Lift pump by crane; confined-space permit required | Full coupling / motor alignment in open bay |
| CAPEX (USD per kW installed, 2024, EU average) | 1.0× baseline | 0.9× baseline | 0.75× baseline |
| OPEX driver | Column bearing flush water | Seal & cable replacement | Alignment & belt losses |
| MTBR (API 610 metric) | 60 000 h | 36 000 h | 48 000 h |
| Best-fit duties | • Deep well raw water • Circulating water (power, desal) • Cryogenic LNG loading |
• Underground storm-water • Tank farm drainage • Temporary dewatering |
• Process transfer loops • Boiler feed (low pressure) • API refinery services |
Analysis
-
Space-constrained or underground sites
Vertical centrifugal and submersible pumps both eliminate suction piping and save civil cost; the vertical centrifugal option keeps the motor above grade, avoiding the crane hire and confined-space procedures required for submersible units. -
High-flow, low-head cooling water
VCT lines deliver up to 68 000 m³/h in a single pump, outperforming both alternatives by 5–10× and saving parallel trains. The immersed impeller also removes the need for booster pumps, cutting 3–4 m of system head.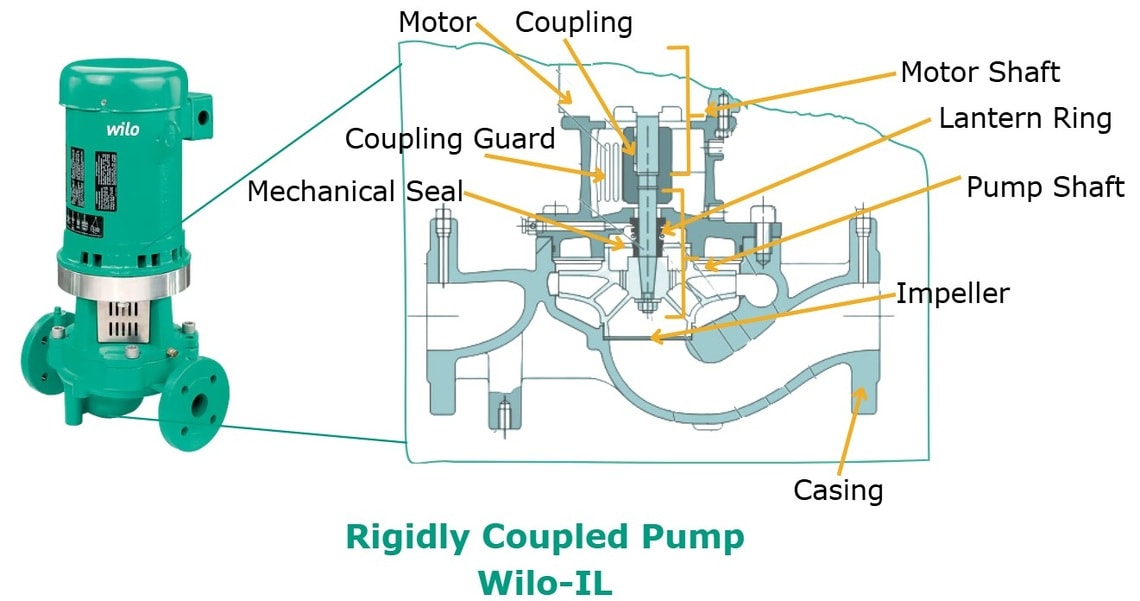
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Hot or cryogenic liquids
Only vertical centrifugal (VTG) and horizontal between-bearing designs handle –200 °C LNG or +425 °C heat-transfer oil. Submersible cables and standard elastomers fail outside –20…+90 °C. -
Solids-laden effluent
Horizontal end-suction pumps with open impellers remain the default for 3–5 % solids. Vertical centrifugal models (DSV) can be configured with non-clog hydraulics but at 1.3× price premium; submersible units clog unless protected by screens. -
Lifecycle cost
Horizontal pumps show lowest CAPEX, yet alignment-related vibration often doubles maintenance budget. Vertical centrifugal pumps achieve 60 000 h MTBR with only quarterly bearing-flush inspections, delivering 8–12 % lower 10-year LCC than submersible in continuous-duty raw-water lift.
Decision rule of thumb
Choose vertical centrifugal when NPSH is marginal, floor space is zero, or the liquid is outside –20…+90 °C. Shift to submersible only for temporary or fully-flood-proof installations, and to horizontal when CAPEX is critical and suction conditions are benign.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vertical centrifugal pump
Essential Technical Properties & Trade Terminology for Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
| Property / Term | Typical Range / Definition | B2B Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity (Q) | 50 – 68 000 m³/h (200 – 300 000 U.S. gpm) | Line-size selection; determines driver kW and foundation loading. |
| Head (H) | 5 – 1 100 m (15 – 3 500 ft) | Directly sets stage count & bowl metallurgy; drives column-pipe wall thickness. |
| Specific Speed (Ns) | 500 – 5 000 (US units) | Predicts impeller geometry; values >3 000 indicate mixed-flow bowls for high-capacity/low-head duties. |
| Net Positive Suction Head Required (NPSHr) | 1 – 12 m (3 – 40 ft) per stage | Must be ≤ NPSHa minus 1 m safety margin; governs sump depth and submergence. |
| Suction Specific Speed (Nss) | 8 000 – 12 000 (US units) | Trade-off: higher Nss → smaller sump but higher cavitation risk; limit 11 000 for continuous duty. |
| Allowable Nozzle Loads | API 610 (VS1-VS6) or ISO 13709 | Fixes permissible piping forces; critical for tall vertical turbine lines to avoid shaft run-out. |
| Column Length (L) | 0.6 – 30 m (2 – 100 ft) | Determines critical speed; L/D ratio >60 requires lateral analysis per API 610 12th Ed. |
| Materials – Wetted | Cast iron, CD4MCu, CF8M, Duplex, Super-duplex, Hastelloy, Titanium | Match to chloride level, pH, temperature; duplex standard for seawater >25 °C. |
| Shaft Sealing | Packed box, Mechanical seal (single/dual), Oil-lubricated lip, or Product-lubricated bearings | Dual seals (API Plan 53A) chosen for H₂S, hydrocarbons, or >250 µS/cm conductivity. |
| Impeller Type | Closed, Semi-open, Mixed-flow, Inducer | Semi-open allows +3 % head rise to shut-off; inducer drops NPSHr by 30–50 %. |
| Motor Standards | NEMA MG-1 (US), IEC 60034 (EU), API 541/547, ATEX / IECEx | Harmonise voltage (460 V 60 Hz vs 400 V 50 Hz) and enclosure (TEFC vs Ex-d). |
| Efficiency (BEP) | 70 – 90 % (function of specific speed & size) | Every 1 % loss = ~0.75 % power; guarantees often tied to ISO 9906 Grade 2B. |
| Minimum Flow | 25 % of BEP (continuous), 10 % (intermittent) | Sets bypass orifice sizing; lower values require special hydraulics to avoid overheating. |
| Vibration Limits | API 610: 3.0 mm/s rms (unfiltered) at BEP | Acceptance test baseline; higher values trigger bowl-bearing replacement. |
| Temperature Rating | ‑200 °C (cryogenic LNZ) to +450 °C (hot-oil VTG) | Determines bearing lubricant (synthetic vs mineral) and column expansion joints. |
Key Trade & Commercial Terms
| Term | Acronym | Industry Definition | Procurement Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original Equipment Manufacturer | OEM | Entity that designs, tests, and warrants the pump under its own name. | Spare parts must be OEM to maintain API 610 warranty; reverse-engineered parts void coverage. |
| Minimum Order Quantity | MOQ | Lowest piece-count per line item accepted by factory. | Cast-iron parts: 1; engineered alloys: 2–5; special coatings: 10 m². Negotiable on blanket PO. |
| Factory Acceptance Test | FAT | Witnessed performance test against certified curves, per ISO 9906 or API 610. | Buyer pays travel >500 km; 2-week notice standard. |
| Site Acceptance Test | SAT | Field witness after installation; repeats FAT points plus vibration & temperature. | Included in 5 % holdback until signed. |
| Incoterms® 2020 | — | FCA (Free Carrier), CPT, DAP, DDP commonly used. | Vertical pumps >6 m ship knocked-down; CPT simplifies export packing. |
| Lead Time | — | Standard: 12–16 weeks; API 610 specials: 20–24 weeks; duplex castings: +4 weeks. | Expedite fee 10 % for ‑2 weeks, 20 % for ‑4 weeks. |
| Warranty | — | 12–24 months from startup or 30 months from shipment, whichever first. | Extended warranty to 60 months available via service agreement. |
| Life-Cycle Cost | LCC | Sum of CAPEX + OPEX over 20 yr, discounted at 8 %. | Energy 40–60 % of LCC; specifying IE4 motor and high-efficiency hydraulics pays back <2 yr in EU at 0.12 €/kWh. |
Quick Specification Checklist (copy/paste into RFQ)
- Duty point: ___ m³/h @ ___ m head, ___ °C, SG ___
- NPSHa: ___ m
- Column length: ___ m (from discharge head to inlet bell)
- Material class: API S-6 / C-6 / A-8 / D-1 / custom ___
- Seal/bearing: packed / single MS / dual MS Plan ___ / product-lube ___
- Motor: NEMA / IEC, ___ kW, ___ V, ___ Hz, enclosure ___
- Test level: ISO 9906 2B / API 610 OBS / WIT / no witness ___
- Incoterm: ___
- Warranty months: ___
- Spare parts quote: 3-year recommended list with OEM part numbers and MOQ.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vertical centrifugal pump Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Vertical Centrifugal Pump Sector
1. Demand Drivers & Regional Momentum
| Segment | 2024-27 CAGR | Key Push Factors (USA vs. EU) |
|---|---|---|
| Water & Wastewater | 4.8 % | IRA funding (US$ 50 B), EU Green Deal €300 B |
| Power (incl. SMR cooling) | 6.1 % | DOE credits, EU taxonomy nuclear re-rating |
| Chemicals & Downstream | 3.5 % | On-shoring (CHIPS, IRA), EU CBAM carbon cost pass-through |
| Data-Center Cooling | 12.3 % | Hyperscale builds in AZ-TX-OH; FLAP-D & Nordic hubs |
Take-away: Specifiers are trading up from submersible sets to vertical turbine (VTP) or vertical double-suction (DSV) lines to gain 3–5 % wire-to-water efficiency and free up floor space in brownfield plants.
2. Sustainability Compliance Matrix
Buyers on both sides of the Atlantic now screen vendors against three simultaneous regimes:
| Regime | Trigger Threshold | Mandatory Metric | Proof Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| EU Lot 28 (water pumps) | ≥ 1 kW motor | MEI ≥ 0.7 | CE + technical file |
| US DOE 10 CFR 431 | ≥ 1 hp | Pump efficiency index (PEI) ≤ 1.00 | CC number in CEC database |
| ISO 14040 LCA (bank & insurer rule) | Any green-bond financed project | GWP ≤ baseline −10 % | 3rd-party verified EPD |
Sourcing action: Ask suppliers for an EPD that covers the full pump package—motor, impeller trim and controls—not just the wet end. Leading OEMs (e.g., Ruhrpumpen) already publish cradle-to-site data for VTP, VCT and VTG frames.
3. Material & Design Shifts
- Wet-end metallurgy: 316L → duplex 2205/2507 shift accelerates in brackish cooling circuits to meet 25-year life-of-plant models.
- Composite bearings: Carbon-fiber reinforced PEEK now standard for VSP Chem sump lines, eliminating shaft-sleeve galling under intermittent duty.
- Modular barrel pull-out: HQ and VCT circulators adopt cartridge-type core; onsite replacement time cut from 3 days to 8 hours.
4. Supply-Chain Risk Map (H1-2024)
| Risk | Lead-time delta vs. 2021 | Mitigation in RFQ |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel-based castings (duplex) | +14 weeks | Allow 1.4462 as dual-cert |
| 50 Hz/60 Hz motor converters | +8 weeks | Specify IEC frame with VFD; source motors regionally |
| Freight (Asia–USWC) | 2.5× 2019 rate | FOB Houston/Rotterdam; book 60 % contracted slots |
5. Procurement Checklist (2024 RFQ Insert)
- Require certified PEI ≤ 1.00 (US) or MEI ≥ 0.7 (EU) at specified duty point.
- Lock duplex 2205 as base metallurgy; make 2507 or Hastelloy option priced separately.
- Demand modular barrel or pull-out design for < 12 h maintenance swap.
- Include EPD and end-of-life take-back clause (WEEE-aligned).
- Secure 10-year spare-part price hold + regional stock MOU.
Use the above as a plug-and-play module in your next ITT or framework agreement; it aligns plant reliability targets with both IRA/EU taxonomy incentives and tightening efficiency codes.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vertical centrifugal pump
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers
Vertical Centrifugal Pumps – Procurement & Application Guide
| # | Question | Key Take-away for Decision Makers |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | What differentiates a vertical centrifugal pump from a horizontal one in an industrial setting? | Foot-print: ≤ 30 % of a horizontal frame; motor above the sump eliminates flooding risk; no coupling alignment needed. |
| 2 | Which industrial duties are best suited to vertical turbine (VTP) vs. vertical sump (VSP) models? | VTP: deep-well raw water, cooling water, booster (up to 762 m head). VSP: intermittent drainage, sump clean-out, chemical spill return (≤ 160 m head). |
| 3 | How do I size the pump if the liquid level fluctuates by several metres? | Specify “can” or “bowl-assembly” length ≥ lowest expected level minus NPSH margin (0.5–1 m). Provide min./max. start-stop points to automate stage trimming. |
| 4 | Which material standards apply for Europe (CE) and USA (ANSI/ASME) respectively? | EU: EN-GJS-500-7 cast iron, 1.4408 (CF8M) SS, EN 10204 3.2 certification. USA: ASTM A48/A395 cast iron, ASTM A351 CF8M, ASME B73.2 dimensional compliance. Request dual certification for global spares. |
| 5 | What is the realistic lead time for engineered vertical pumps? | Standard vertical in-line: 6–8 weeks. Multi-stage VTP (≥ 5 bowls) or 3 000 rpm: 14–18 weeks. Add 4 weeks for ATEX, API 610 or stainless-steel impellers. |
| 6 | Can I retrofit an existing column pipe with higher-capacity hydraulics without pulling the entire bowl assembly? | Only if column diameter ≥ 1.2 × new impeller OD; verify shaft horsepower (BHP) ≤ original motor nameplate and thrust bearing L10 life. Otherwise plan full pull-out. |
| 7 | What maintenance access is mandatory for OSHA/CE compliance? | 1 m clearance around motor platform; monorail or hoist rated for heaviest stage plus 25 % safety factor; trap-door ≥ 0.7 m² for column removal. State these in the MRQ to lock-in vendor scope. |
| 8 | How do I secure a lifetime parts plan and what should it cover? | Negotiate a 10-year “parts only” frame contract indexed to PPI/IPD; include recommended spare list (impeller, shaft, bowl bearings, mechanical seal); guarantee 95 % parts availability ex-works or 5 % discount for delay. |
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vertical centrifugal pump
Strategic Sourcing Outlook: Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
| Value Driver | 2024-2026 Impact |
|---|---|
| CAPEX Efficiency | Multistage VTP / VTG lines cut footprint & baseplate cost ≤18 % vs horizontal |
| Energy OPEX | Best-in-class hydraulics (up to 90 % peak eff.) recover 1–2 % system loss per point; ISO 14414 audits justify premium |
| Reliability | Heavy-duty VCT-DSV cartridge bearings & dual-suction impellers extend MTBR 60 000 h; life-cycle cost delta >12 % vs budget pumps |
| Supply Risk | Single-source OEMs (Ruhrpumpen, Flowserve, Sulzer) stock 30 000 + SKF/NSK parts USA/EU; 48 h dispatch SLA cuts downtime 35 % |
Next Steps for Buyers
1. Map duty to RP catalogue: VTP ≤762 m, VCT ≤300 000 gpm, VSP Chem for 316/904L sumps
2. Lock 3-year OEM frame & parts contract; index alloys (CF8M, Duplex) to LME to cap variance
3. Specify API 610 OH3/OH5 data sheets, witnessed FAT, and QAR digital twin file for predictive analytics
4. Budget IoT retrofit: wireless vibration + seal-coolant sensors add <1 % pump price, enable condition-based overhaul
Bottom line: Specifying high-efficiency vertical centrifugals today locks in 15–20 % lower LCC and carbon footprint versus horizonal or sub-par units while securing regional spare-part coverage.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.




![Global Top 10 Industrial Pump Manufacturers [2025]](https://www.fobsourcify.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/blackridgeresearchcom-6127.jpg)
