The residential renewable energy landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by rising energy costs, growing environmental awareness, and advancements in compact turbine technology. Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) are emerging as a viable solution for urban and suburban homes, offering omnidirectional wind capture, lower noise profiles, and aesthetic integration compared to traditional horizontal axis models. According to Grand View Research, the global small wind turbine market, which includes turbines typically under 100 kW capacity, was valued at USD 950.3 million in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.8% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing residential demand for off-grid power solutions and supportive government incentives. As homeowners seek sustainable and decentralized energy sources, manufacturers are innovating to deliver efficient, low-maintenance VAWTs tailored for domestic use. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers leading this shift, evaluated on product performance, reliability, customer feedback, and technological advancements in the home VAWT sector.
Top 10 Vertical Axis Wind Turbine For Home Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Small Wind Turbine Manufacturers, Suneco Wind Turbines Group.
Domain Est. 2009
Website: wind-turbine-generator.com
Key Highlights: Suneco Wind Turbine is one of the leading small wind turbine generator suppliers and companies of wind turbines from 300w to 200kw….
#2 Wind Turbines
Domain Est. 1997
Website: us.vestas.com
Key Highlights: Discover the global leader in sustainable wind energy. We offer a range of onshore wind turbines and offshore wind turbines for your new wind project….
#3 Vertical Axis Wind Turbine for
Domain Est. 1997
#4 Oy Windside Production Ltd
Domain Est. 1998
Website: windside.com
Key Highlights: Windside wind turbines are designed for performance, reliability, & safety in extreme wind conditions up to 60 m/s (216 km/h), and all weather conditions….
#5 Vertical Axis Wind Turbines – buy VAWTs
Domain Est. 2000
Website: freen.com
Key Highlights: Discover high-efficiency Freen vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) for homes and businesses. Buy the best vertical wind turbines at competitive prices….
#6 Atlas Vertical Wind Turbine Generator (10 KW)
Domain Est. 2007
Website: tesup.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 7-day returnsExplore the World’s best-selling vertical wind turbine for homes: TESUP Atlas 10KW. Generates 10000W, harnessing wind potential with customizable blades….
#7 Windspire Verticle Axis Wind Turbines, 750W, 2kW, 3kW, 5kW …
Domain Est. 2009
Website: windspireenergy.com
Key Highlights: Windspire Vertical Axis Wind Turbines are available in 750w, 2 kW, 3kW and 5kW wind turbine systems. All of our wind turbines are available with options….
#8 Hi-VAWT
Domain Est. 2009
Website: hi-vawt.com.tw
Key Highlights: Vertical Axis Small Wind Turbines. About VASWT · Why VASWT · Features and Benefits · VASWT Applications. Featured Products. DS-300 VAWT · DS-700 VAWT · DS-1500 ……
#9 Flower Turbines
Domain Est. 2013
Website: flowerturbines.com
Key Highlights: Our vertical axis wind turbines are the perfect solution to your energy needs. Combining beauty with function, our sustainable energy solutions deliver ……
#10 Small Wind Guidebook
Domain Est. 1999
Website: energy.gov
Key Highlights: Vertical-axis wind turbines consist of two types: Savonius and Darrieus. A Savonius turbine can be recognized by its “S” shaped design when viewed from above….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Vertical Axis Wind Turbine For Home

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Vertical Axis Wind Turbines for Home Use
The market for Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs) designed for residential applications is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, policy support, and shifting consumer preferences toward decentralized renewable energy. Here’s an in-depth analysis of the key trends expected to shape the home VAWT market in 2026:
1. Increased Urban Adoption Due to Design Advantages
Unlike traditional Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs), VAWTs are compact, omnidirectional, and operate efficiently in turbulent wind conditions—making them ideal for urban and suburban rooftops. By 2026, rising urbanization and space constraints will accelerate demand for VAWTs in densely populated areas where conventional turbines are impractical.
2. Technological Improvements Enhancing Efficiency
Ongoing R&D efforts are addressing historical drawbacks such as lower efficiency and reliability. Innovations in blade design (e.g., helical configurations), advanced composite materials, and integration with magnetic or gearless generators are expected to improve energy output and noise reduction. By 2026, next-generation VAWTs could achieve energy conversion efficiencies nearing 35%, making them more competitive with solar PV systems.
3. Integration with Smart Home Energy Systems
VAWTs are increasingly being designed to integrate seamlessly with home energy management systems (HEMS), battery storage (e.g., lithium-ion and solid-state), and solar arrays. By 2026, hybrid solar-wind residential systems will become more common, enabling 24/7 renewable power generation and greater energy self-sufficiency.
4. Government Incentives and Net-Zero Policies
National and municipal governments aiming to meet net-zero emissions targets by 2050 are introducing subsidies, tax rebates, and feed-in tariffs for small-scale wind installations. Countries like Germany, Japan, and the United States are expected to expand residential renewable incentives by 2026, directly benefiting the VAWT sector.
5. Growing Consumer Awareness and DIY Market Expansion
Public awareness of climate change and energy independence is rising. By 2026, a growing segment of homeowners will seek off-grid or partially independent energy solutions. This will fuel the DIY and plug-and-play VAWT market, with manufacturers offering modular, easy-to-install systems targeting tech-savvy consumers.
6. Competitive Pricing and Cost Parity Progress
While VAWTs currently have higher upfront costs than solar panels, economies of scale and manufacturing improvements are expected to lower prices by 2026. Combined with longer lifespans and lower maintenance needs, the levelized cost of energy (LCOE) for residential VAWTs is projected to decrease by 20–30% over the next few years.
7. Emergence of Aesthetic and Architectural Integration
VAWTs are being reimagined not just as energy devices but as architectural features. Design-focused models with sleek, modern aesthetics will gain traction among homeowners and developers seeking sustainable yet visually appealing solutions. By 2026, collaborations between turbine manufacturers and architects could lead to VAWTs embedded into building facades and balcony railings.
8. Regional Market Variations
Europe and East Asia are expected to lead adoption due to supportive regulations and high energy costs. In contrast, North America may see slower but steady growth, driven by rural and suburban homeowners. Emerging markets in Latin America and Southeast Asia could become new frontiers post-2026 as financing models and infrastructure improve.
Conclusion
By 2026, the residential VAWT market will transition from a niche alternative to a viable component of the distributed energy landscape. Success will depend on continued innovation, supportive policies, and consumer education. As energy decentralization gains momentum, VAWTs are well-positioned to play a growing role in the sustainable homes of the future.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Vertical Axis Wind Turbines for Home Use (Quality & IP)
Sourcing a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) for residential use can be challenging, especially when balancing performance expectations, long-term durability, and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
Many low-cost VAWTs on the market use substandard materials such as brittle plastics, corrosion-prone metals, or undersized bearings. These lead to premature wear, imbalance, and structural failure—especially under real-world wind conditions. Consumers may overlook certifications or independent testing data, assuming all turbines are equally durable. Always verify material specifications, corrosion protection (e.g., anodized aluminum or stainless steel), and load ratings.
Overstated Power Output and Efficiency Claims
Manufacturers often advertise peak power outputs under ideal laboratory conditions, which rarely reflect actual residential performance. VAWTs generally have lower efficiency than horizontal axis turbines, particularly in turbulent urban environments. Be cautious of exaggerated claims like “5000W output” with a 1.5m tall unit—real-world output is typically 10–30% of such figures. Request real-world performance data or third-party validation.
Lack of Certification and Safety Standards Compliance
Many VAWTs lack compliance with international safety and performance standards such as IEC 61400 (small wind turbines) or UL 6142. This increases risks related to electrical safety, structural failure, or noise emissions. Sourcing uncertified units may also void home insurance or violate local zoning regulations. Always confirm compliance with relevant regional standards.
Inadequate Intellectual Property (IP) Protection and Design Copying
The VAWT market has numerous products that closely resemble patented designs (e.g., variations of the Savonius or Darrieus rotors). Some manufacturers may infringe on existing IP, either intentionally or through ignorance. Purchasing such a product could indirectly support IP violations and may lead to legal complications, especially in commercial resale or large-scale deployment. Research the manufacturer’s patents, design registrations, and original engineering to verify legitimacy.
Poor Aerodynamic Design and Noise Issues
Inefficient blade profiles or unbalanced rotor designs can lead to excessive vibration and noise—often a concern in residential neighborhoods. Some VAWTs produce a low-frequency “whooshing” sound that disturbs occupants. Evaluate noise ratings (in dB) and inquire about blade design optimization. Proprietary aerodynamic enhancements are often protected by IP, so lack of innovation may signal a copycat product.
Insufficient Warranty and After-Sales Support
Many VAWT suppliers offer limited or no warranty, particularly for offshore or online-only brands. Without accessible technical support or spare parts, maintenance becomes impractical. Check warranty duration, coverage scope (e.g., bearings, blades, generator), and availability of local service centers.
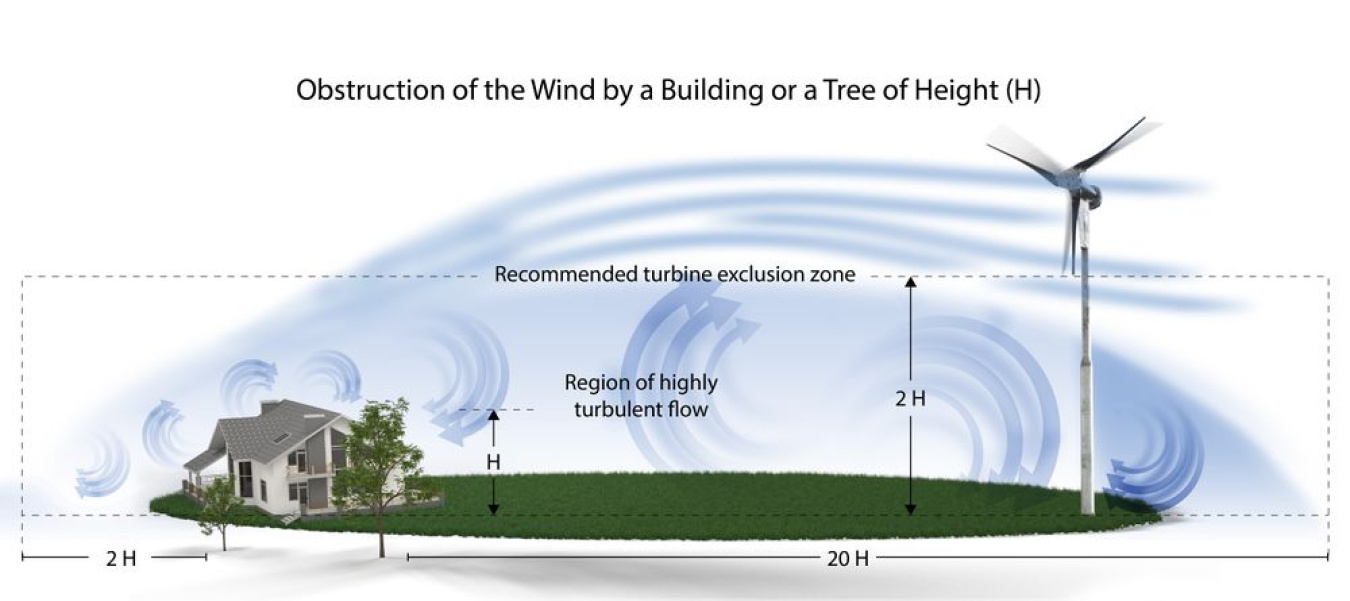
Misalignment with Local Wind Conditions
VAWTs perform differently depending on wind speed, turbulence, and site topography. Sourcing without assessing site-specific wind data can lead to disappointing results. Some designs are unsuitable for low-wind or gusty urban areas. Ensure the turbine’s cut-in speed and operational range match your local conditions.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: research manufacturer reputation, verify certifications, demand realistic performance data, and confirm original design and IP ownership. Choosing a quality, legally compliant VAWT ensures safer, more reliable, and sustainable home energy generation.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT) for Home Use
Understanding VAWT Technology and Home Applications
Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs) are wind energy systems with a vertically oriented rotor shaft, allowing them to capture wind from any direction without needing to yaw. They are often chosen for residential use due to their compact size, quieter operation, and ability to function in turbulent urban or suburban wind environments. However, proper logistics planning and compliance with regulations are essential for safe and legal operation.
Sourcing and Procurement
When purchasing a home VAWT, obtain equipment from reputable manufacturers or certified distributors. Confirm that the turbine meets international standards such as IEC 61400-2 (small wind turbines) and includes a full technical datasheet. Consider factors such as rated power output, cut-in and survival wind speeds, noise levels, and structural requirements. Importing turbines may require compliance with local electrical and safety certifications (e.g., CE, UL, or CSA).
Transportation and Handling
VAWTs are typically shipped in modular kits to simplify transport. Use appropriate handling equipment (e.g., forklifts, cranes) during unloading to avoid component damage. Store parts in a dry, secure location prior to installation. Ensure all personnel involved in delivery and handling are trained in basic safety protocols, especially when dealing with blades, towers, and electrical components.
Site Assessment and Zoning Compliance
Before installation, conduct a site assessment to evaluate wind resources, turbulence, and proximity to structures or trees. Confirm local zoning regulations allow small wind turbines—many municipalities have height restrictions (e.g., 35–60 feet above ground), setback requirements, and noise limits (typically under 50 dB at property lines). Some areas require permits for turbine installation, especially if the tower exceeds a certain height.
Building and Electrical Permits
Secure necessary permits from your local building or planning department. Submit engineering drawings, turbine specifications, and a site plan. An electrical permit is also required if the VAWT will be grid-connected. The system must comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the U.S. (or equivalent local standards), including proper grounding, overcurrent protection, and disconnect switches.
Installation Requirements
Installation should be performed by a qualified technician or certified installer. The foundation must support the turbine’s weight and dynamic loads—common options include concrete footings or ground anchors. Mounting on rooftops requires structural evaluation to ensure the building can handle additional wind loading. Follow manufacturer guidelines for tower assembly, turbine alignment, and wiring.
Grid Interconnection and Net Metering
If connecting to the utility grid, coordinate with your local utility company. Most require an interconnection agreement and compliance with IEEE 1547 (standard for distributed energy resources). Install a grid-compliant inverter and ensure the system includes anti-islanding protection. Explore net metering programs to receive credit for surplus electricity fed back into the grid.
Safety and Maintenance Logistics
Install warning labels and restrict access to the turbine during operation. Schedule routine inspections for bolts, bearings, and electrical connections. Keep a maintenance log and replace worn parts promptly. Ensure the system includes a manual brake or shutdown mechanism for emergencies.
Environmental and Noise Compliance
Verify that the VAWT operates within local noise ordinances, particularly in residential neighborhoods. Avoid locations near protected wildlife areas or migratory bird paths. Some jurisdictions require an environmental impact assessment for turbines, although this is less common for small residential units.
Decommissioning and End-of-Life Planning
Include decommissioning plans in your compliance strategy. This involves safe removal of the turbine, tower, and foundation, with proper disposal or recycling of components (e.g., composites, metals, electronics). Check local regulations on scrap disposal and land restoration requirements.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintain all compliance documents, including permits, inspection reports, warranties, and maintenance records. These are critical for insurance purposes, resale of property, and demonstrating regulatory adherence during audits.
By carefully managing logistics and ensuring full compliance with local, state, and national regulations, homeowners can safely and legally harness wind energy using vertical axis turbines.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine for Home Use
Sourcing a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) for residential use can be a viable and sustainable investment for homeowners seeking renewable energy solutions. VAWTs offer several advantages over traditional horizontal axis turbines, including omnidirectional wind capture, quieter operation, lower maintenance needs, and a more compact, aesthetically pleasing design suitable for urban and suburban environments. These features make them particularly well-suited for integration into residential properties with space or zoning constraints.
However, careful consideration must be given to local wind conditions, turbine efficiency, installation requirements, and regulatory guidelines to ensure optimal performance and return on investment. Prospective buyers should evaluate product quality, reliability, warranty, and manufacturer reputation when sourcing a VAWT, and consider hybrid solar-wind systems to enhance energy consistency.
While VAWTs may not generate as much power as their horizontal counterparts in low-wind areas, they serve as a complementary energy source that supports energy independence and reduces carbon footprint. With ongoing advancements in VAWT technology, increased availability, and growing support for decentralized energy systems, sourcing a vertical axis wind turbine can be a practical and forward-thinking step toward a more sustainable home energy strategy.