The global variable AC power source market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision power testing in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics. According to Mordor Intelligence, the AC power supply market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% during the forecast period 2024–2029, fueled by rising adoption of automated testing systems and stringent regulatory standards for power quality. Similarly, Grand View Research values the broader power supply market in the billions, with robust growth attributed to advancements in renewable energy integration and electric vehicle development—applications that require highly reliable, programmable AC power sources. As industrial and R&D applications demand tighter control over voltage, frequency, and waveform characteristics, leading manufacturers are focusing on scalability, energy efficiency, and digital integration. This growing technical demand underscores the importance of high-performance variable AC power source solutions, positioning key players at the forefront of innovation and market expansion.
Top 9 Variable Ac Power Source Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 MEAN WELL Switching Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meanwell.com
Key Highlights: MEAN WELL is one of the world’s few standard power supply mainly professional manufacturers, covering 0.5 to 25600W products are widely used in industrial ……
#2 AC Power Source
Domain Est. 1996
Website: chromaate.com
Key Highlights: AC Power sources with wide ranges of voltage, current, and power for simulating AC mains and line fault conditions with measurements….
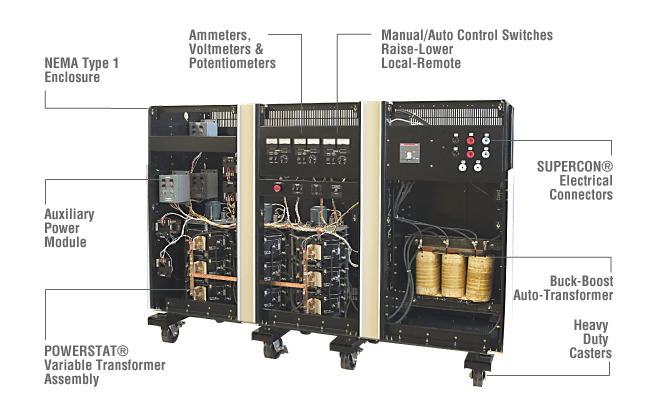
#3 Variable AC Power Source
Domain Est. 2016
Website: specialtyproducttechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Superior Electric designs, manufacturers, and markets variable AC power sources using our wide range of POWERSTAT® and Volt- Pac® Variable Auto-Transformers….
#4 Product Families
Domain Est. 1996
Website: advancedenergy.com
Key Highlights: Advanced Energy’s CoolX modular product family offers a versatile series of configurable AC-DC solutions, ranging from 600 W to 3000 W. This family ……
#5 Variable AC & DC Power Supplies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: circuitspecialists.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $149 · 30-day returnsShop for power supplies including benchtop, programmable, and 12 volt power supplies as well as variacs and step up/down transformers….
#6 Adaptive Power Systems: APS
Domain Est. 2003
Website: adaptivepower.com
Key Highlights: Adaptive Power Systems offers an extensive line of programmable electronic loads for DC and AC load applications in R&D, ATE and Production….
#7 AMETEK Programmable Power
Domain Est. 2007
Website: programmablepower.com
Key Highlights: The AMETEK Programmable Power designs, manufactures, and markets precision, ac & dc programmable power supplies, electronic loads, application-specific ……
#8 AC Power Sources
Domain Est. 2012
Website: keysight.com
Key Highlights: Keysight provides basic and performance AC power sources to help you test AC-powered devices. Portfolio includes single and three-phase AC power supplies….
#9 Variable DC Power Supply
Domain Est. 2023
Website: variabledcpowersupply.com
Key Highlights: Our variable dc power supplies include: programmable power supply, bench power supply, high voltage power supply, and high precision power supply….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Variable Ac Power Source
2026 Market Trends for Variable AC Power Sources
The global market for Variable AC Power Sources is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving energy landscapes, and expanding industrial applications. Key trends shaping the market include:
Growing Demand in Renewable Energy Integration
The increasing deployment of solar and wind power systems necessitates advanced power conversion and grid stabilization solutions. Variable AC power sources are critical for simulating grid conditions, testing inverter performance, and ensuring seamless integration of renewable energy into existing power networks. As countries accelerate their clean energy transitions, demand for high-precision, programmable AC sources for R&D and certification testing will surge.
Rise of Electrification and EV Testing Infrastructure
The automotive sector, particularly electric vehicle (EV) and EV charging station development, is a major growth driver. Variable AC power sources are essential for testing onboard chargers, power electronics, and grid interaction of EVs. By 2026, stringent regulatory standards and the need for interoperability will require comprehensive testing under variable voltage and frequency conditions, boosting adoption across automotive OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers.
Advancements in Semiconductor and Power Electronics Testing
With the proliferation of wide-bandgap semiconductors (e.g., SiC and GaN), there is heightened demand for power sources capable of high-frequency operation, fast transient response, and low harmonic distortion. These components require precise and dynamic power simulation during development and production testing. Manufacturers are expected to adopt more compact, energy-efficient, and digitally controlled variable AC sources to meet these requirements.
Increased Adoption of Smart Grid and Microgrid Technologies
Microgrids and smart grid systems require rigorous testing under diverse operating scenarios. Variable AC power sources enable simulation of islanding, voltage sags, swells, and frequency deviations. As utilities and industrial facilities invest in resilient and decentralized energy systems, the need for advanced power simulation tools will grow, especially in mission-critical sectors like healthcare, data centers, and defense.
Shift Toward Modular and Regenerative Systems
Environmental and cost concerns are driving demand for regenerative AC power sources that return unused energy to the grid rather than dissipating it as heat. By 2026, regenerative models are expected to gain market share due to their energy efficiency and lower operating costs. Additionally, modular designs offering scalability and remote monitoring via IoT integration will become standard, enabling flexible deployment in automated test environments.
Geographic Expansion and Regional Regulatory Influence
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain a dominant market due to strong manufacturing bases in electronics and automotive sectors. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will see growth fueled by strict energy efficiency regulations and investments in smart infrastructure. Compliance with international standards (e.g., IEC, UL, IEEE) will increasingly influence product design and testing protocols.
In summary, by 2026, the variable AC power source market will be characterized by higher performance, greater energy efficiency, and deeper integration with digital test systems, driven by the convergence of renewable energy, electrified transportation, and advanced manufacturing.
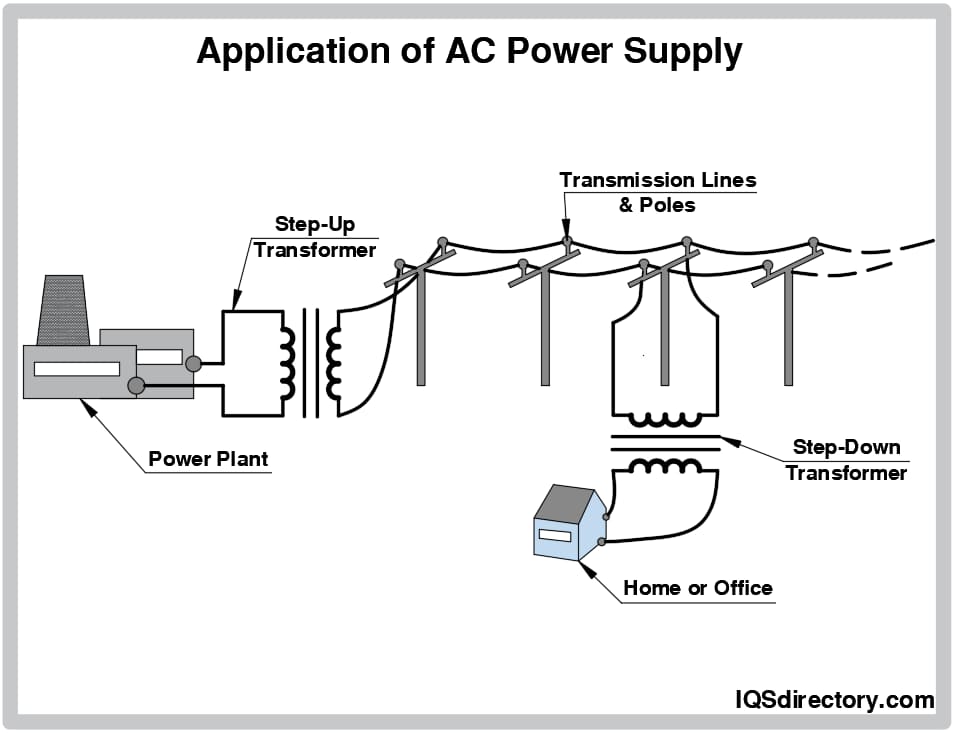
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Variable AC Power Source (Quality, IP Protection)
Sourcing a variable AC power source—especially one suitable for testing, manufacturing, or R&D—requires careful consideration beyond basic specifications. Overlooking key aspects related to quality and Ingress Protection (IP) rating can lead to equipment failure, safety hazards, and costly downtime. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Price Over Build Quality
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting a lower-cost unit without verifying component quality. Cheaply built power sources may use substandard transformers, capacitors, or control circuitry, leading to:
- Inconsistent output voltage and frequency
- Poor regulation under load
- Premature failure due to overheating
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI) affecting sensitive test environments
Best Practice: Inspect build materials, brand reputation, warranty terms, and customer reviews. Invest in units from reputable manufacturers with proven track records in power electronics.
2. Ignoring Input Power Compatibility
Many variable AC sources are designed for specific input voltages (e.g., 208V, 240V, or 480V) and phases (single- or three-phase). Sourcing a unit incompatible with your facility’s power infrastructure leads to:
- Inability to power the unit
- Need for costly transformers or rewiring
- Overloaded circuits and tripped breakers
Best Practice: Verify input voltage, phase, and frequency requirements match your site’s power supply before purchase.
3. Overlooking Output Waveform Quality
Some lower-cost variable AC sources generate modified sine waves or high total harmonic distortion (THD), which can damage sensitive equipment or invalidate test results.
Risks:
– Malfunction of electronic loads (e.g., switch-mode power supplies)
– Inaccurate performance during product testing
– Overheating in motors or transformers
Best Practice: Ensure the unit provides a clean sine wave with low THD (<3%) and stable frequency output, especially for compliance and certification testing.
4. Misunderstanding or Misapplying IP Ratings
The Ingress Protection (IP) code indicates resistance to dust and moisture, but it’s often misunderstood. Common errors include:
- Assuming all “industrial” units are suitable for harsh environments
- Confusing IP ratings with general ruggedness or cooling method
- Installing a low-IP-rated unit (e.g., IP20) in environments with dust or humidity
Example Pitfall: Using an IP20-rated unit (protected only against finger contact, no dust/moisture protection) in a factory with airborne particulates can lead to internal contamination and short circuits.
Best Practice: Match the IP rating to the operating environment:
– IP20: Clean, climate-controlled labs
– IP44 or higher: Industrial floors with dust or occasional splashes
– IP65: Harsh environments requiring dust-tight and water-jet resistance
5. Neglecting Cooling and Ventilation Requirements
High-power variable AC sources generate significant heat. Units with inadequate cooling or poor ventilation design can:
- Throttle output under sustained load
- Trigger thermal shutdown
- Reduce lifespan of internal components
Best Practice: Check cooling method (fan-forced, convection, liquid), required clearances, and ambient temperature limits. Ensure installation location supports proper airflow.
6. Skipping Safety and Compliance Certifications
Units lacking proper safety certifications (e.g., CE, UL, IEC 61010) pose serious risks:
- Electrical shock hazards
- Non-compliance with lab or facility safety standards
- Voided insurance in case of incident
Best Practice: Confirm the unit meets relevant regional and application-specific safety standards before deployment.
7. Underestimating Maintenance and Service Support
Low-cost units may lack accessible service channels or spare parts availability. This leads to:
- Extended downtime when failures occur
- High cost of third-party repairs
- Obsolescence due to discontinued support
Best Practice: Choose suppliers with strong technical support, local service centers, and long-term parts availability.
Conclusion:
Avoiding these common pitfalls requires due diligence in evaluating both technical quality and environmental protection (IP) when sourcing a variable AC power source. Prioritize reliability, waveform integrity, safety certifications, and suitability for the intended operating environment to ensure long-term performance and safety.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Variable AC Power Source
Product Classification & Regulatory Overview
Variable AC Power Sources are electronic test equipment designed to simulate various AC input conditions for testing electrical devices. Due to their electrical nature and international usage, compliance with regional and international standards is essential. These units fall under industrial electronics and are subject to regulations related to electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), energy efficiency, and hazardous substance restrictions.
Common regulatory frameworks include:
– IEC/EN 61010-1: Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use.
– CE Marking (EU): Mandatory conformity for products sold in the European Economic Area, covering EMC (2014/30/EU), Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU), and RoHS (2011/65/EU).
– FCC Part 15 (USA): Governs electromagnetic interference for digital devices.
– UL/CSA 61010-1 (North America): Safety certification for laboratory and industrial equipment.
– PSE (Japan): Required for electrical appliances under the DENAN Law.
– KC Certification (South Korea): Mandatory safety and EMC approval.
– CCC (China): China Compulsory Certification for specified product categories.
Ensure the product carries the appropriate certifications for each destination market prior to shipment.
Packaging & Transportation Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to protect sensitive electronic components during transit:
- Internal Packaging: Use anti-static foam, bubble wrap, or molded inserts to prevent movement and electrostatic discharge (ESD).
- External Packaging: Utilize double-walled corrugated cardboard or wooden crates for heavy or high-value units. Clearly label with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack.”
- Climate Considerations: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture, or condensation. Use desiccant packs in sealed packaging if shipping through humid or variable climates.
- Shipping Modes:
- Air Freight: Suitable for urgent deliveries. Comply with IATA regulations for lithium batteries if applicable (e.g., backup batteries in control systems).
- Sea Freight: Cost-effective for bulk shipments. Use moisture-resistant wrapping and container desiccants.
- Ground Transport: Ideal for regional distribution; ensure shock/vibration protection.
Import/Export Documentation
Accurate documentation ensures smooth customs clearance:
- Commercial Invoice: Must detail product description, HS code, value, country of origin, and buyer/seller information.
- Packing List: Includes weight, dimensions, and quantity per package.
- Certificate of Conformity (CoC): Issued by manufacturer or third-party lab, confirming compliance with target market regulations.
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB): Legal receipt of goods and contract of carriage.
- Export License: May be required if shipping to embargoed countries or if the product contains controlled technology (check EAR or ITAR if applicable).
- Import Permits: Some countries require pre-approval for electrical testing equipment.
HS Code & Tariff Classification
Use the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code for accurate customs classification. For Variable AC Power Sources, likely codes include:
- 8504.31 or 8504.33: Static converters (e.g., AC-AC converters or inverters).
- 9030.33: Apparatus for measuring or checking voltage, current, or power.
- 8543.70: Other electrical machines with individual functions.
Confirm the exact code with local customs authorities, as classifications may vary by function and design. Misclassification can lead to delays or penalties.
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
End-of-life management must comply with environmental regulations:
- RoHS (EU): Restricts the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous substances. Ensure compliance documentation is available.
- WEEE (EU): Requires producers to facilitate recycling of electronic waste. Register with national WEEE authorities if selling directly to EU customers.
- REACH (EU): Addresses chemical substances; provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) if requested.
- Local E-Waste Laws: Follow national recycling programs (e.g., EPA guidelines in the USA, PROs in Canada, or WEEE-like schemes in Asia).
Labeling & User Documentation
Proper labeling and manuals are essential for compliance and user safety:
- Product Labels: Include CE, UL, FCC, or other applicable marks; input/output ratings; serial number; manufacturer details; and warnings per IEC 61010-1.
- User Manual: Must be provided in the official language(s) of the destination country. Include safety instructions, installation procedures, compliance statements, and troubleshooting.
- EC Declaration of Conformity: Required for CE-marked products, listing applicable directives and standards.
Summary & Best Practices
To ensure smooth logistics and compliance:
1. Verify all certifications for target markets before shipping.
2. Use robust, ESD-safe packaging and climate protection.
3. Prepare complete and accurate documentation.
4. Classify under the correct HS code.
5. Provide multilingual user manuals and compliance declarations.
6. Follow environmental compliance for both sales and end-of-life.
Consult local regulatory experts or third-party compliance services when entering new markets to mitigate risks and ensure full adherence.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Variable AC Power Source
In summary, sourcing a variable AC power source requires careful consideration of application requirements, technical specifications, and budget constraints. Whether for testing, research, industrial processes, or power quality analysis, a reliable variable AC power supply—such as an AC power source, variable transformer (e.g., Variac), or programmable AC power supply—should offer precise voltage and frequency control, clean output waveform (low THD), sufficient power capacity, and protective features.
Modern electronic AC power sources provide advantages over traditional autotransformers through features like digital control, programmability, isolation, and simulation of grid conditions (e.g., sags, surges, harmonics). When selecting a source, compatibility with the device under test, safety certifications, and ease of integration are critical factors.
Ultimately, investing in a high-quality, appropriately sized variable AC power source enhances testing accuracy, equipment reliability, and operational efficiency. Sourcing from reputable manufacturers or suppliers with technical support ensures long-term performance and compliance with industry standards.