The global vacuum toilet market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for water-efficient sanitation solutions in transportation, commercial buildings, and off-grid applications. According to Grand View Research, the global vacuum toilet market size was valued at USD 1.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2024 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by rising environmental regulations, especially in the rail and marine sectors, where weight reduction and water conservation are critical. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence highlights a growing adoption of vacuum toilet systems in smart city infrastructure and sustainable building projects, with Asia-Pacific emerging as a key growth region due to rapid urbanization and infrastructure development. As demand surges, leading manufacturers are innovating to enhance system efficiency, durability, and integration with digital monitoring platforms. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top players shaping the market becomes essential for stakeholders across industries.
Top 10 Vacuum Toilet Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 agile® Vacuum Toilets
Domain Est. 1996
Website: rtx.com
Key Highlights: The agile® toilet is designed and pre-certified as a direct replacement for the OEM vacuum toilets on the A320, 737, 747, 757, 767 and 777 aircraft. Collins ……
#2 EcoLoo Vacuum Toilet System
Domain Est. 1998
Website: polyjohn.com
Key Highlights: Our vacuum toilet systems use pure vacuum technology, eliminating the need for macerating pumps. This innovative design delivers exceptional performance, safety ……
#3 Qua-vac
Domain Est. 2000
Website: quavac.com
Key Highlights: At Qua-vac we design, produce, and deliver environmentally friendly vacuum sewerage systems for wastewater treatment….
#4 Evac
Domain Est. 1996
Website: evac.com
Key Highlights: Evac’s vacuum toilets and collection solutions save up to 85% of water per use compared to gravity alternatives….
#5 Airvac is the world leader in vacuum sewer system technolo
Domain Est. 1996
Website: airvac.com
Key Highlights: We create solutions that utilize a vacuum sewer system to move liquids and wastewater for municipalities and industries throughout the world….
#6 Vacuum toilets from Wärtsilä
Domain Est. 1996
Website: wartsila.com
Key Highlights: Wärtsilä vacuum toilets have been designed to be mechanically simple, operationally reliable, and stylish in appearance….
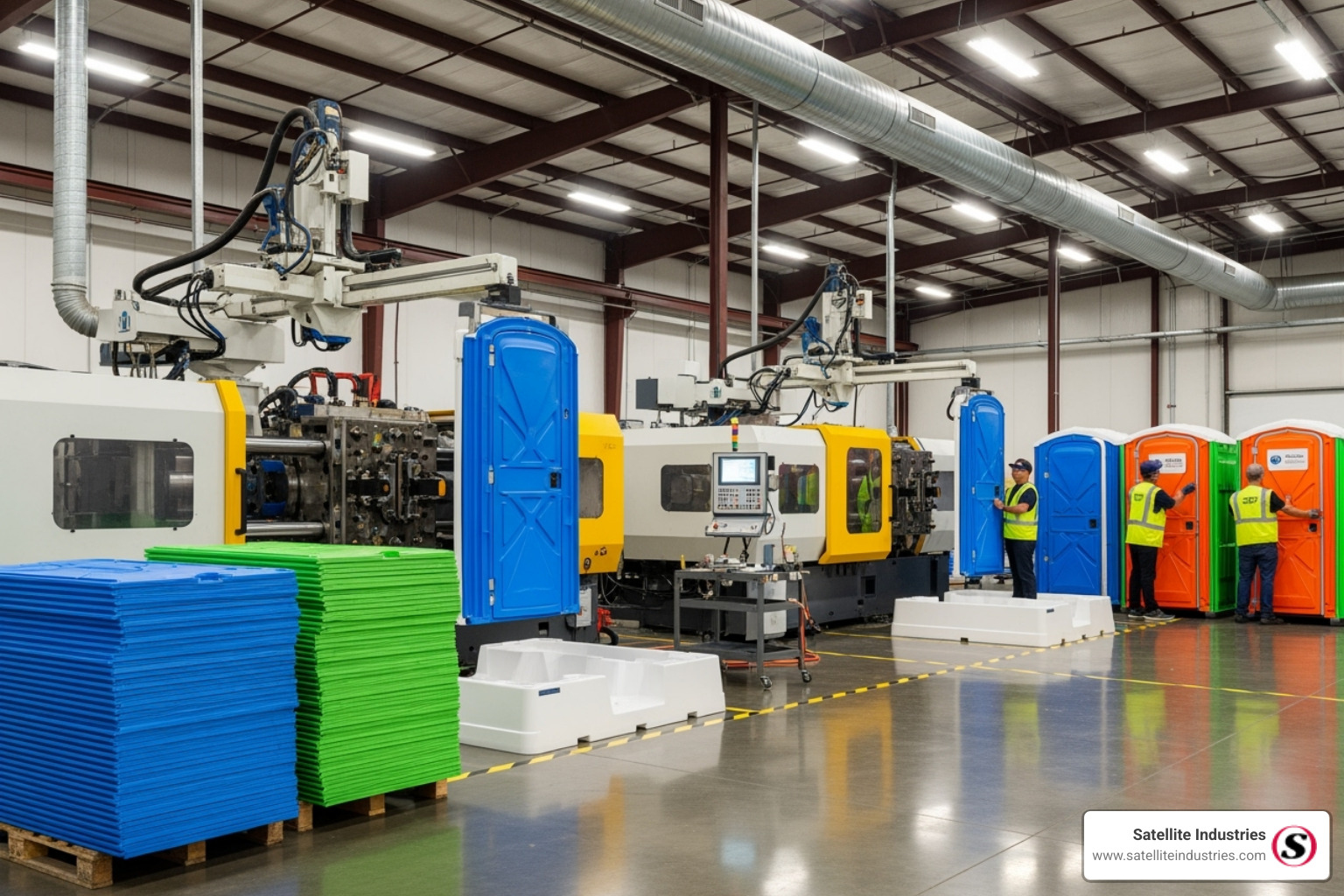
#7 Satellite Industries
Domain Est. 1998
Website: satelliteindustries.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture portable toilets and Portable restrooms, restroom, vacuum services, trucks/tanks, deodorizers, hand wash units and other accessories for ……
#8 Dometic VacuFlush Toilets
Domain Est. 1998
Website: environmentalmarine.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $100The powerful vacuum flush system is clean and odor-free, instantaneously evacuating bowl contents into the holding tank and thoroughly rinsing the bowl….
#9 Vacuum Toilets
Domain Est. 2000
Website: acornvac.com
Key Highlights: Vacuum toilets are designed for use with a vacuum system. They come in on-floor and wall-mounted varieties….
#10 High quality vacuum toilets by Jets
Domain Est. 2003
Website: jetsgroup.com
Key Highlights: Jets offers toilets, urinals and squat pans in high quality china as well as in stainless steel….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Vacuum Toilet

H2: Market Trends for Vacuum Toilets in 2026
The vacuum toilet market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, and shifting end-user demands across key industries such as transportation, commercial buildings, and off-grid applications. Several prominent trends are expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years.
1. Rising Demand in Transportation Sectors
The aviation and rail industries remain major drivers of vacuum toilet adoption. Airlines continue to retrofit older fleets and commission new aircraft with lightweight, water-efficient sanitation systems to reduce fuel consumption and operational costs. Similarly, high-speed rail and metro systems—especially in Asia-Pacific and Europe—are increasingly integrating vacuum toilets to enhance passenger comfort while minimizing water usage. By 2026, the transportation segment is projected to retain the largest market share, supported by global infrastructure development and urban mobility expansion.
2. Emphasis on Water Conservation and Sustainability
With growing concerns over water scarcity and environmental regulations, vacuum toilets are gaining attention for their ability to use up to 90% less water than conventional flush systems. Governments and private institutions in water-stressed regions are incentivizing the adoption of water-saving technologies. This trend is expected to boost demand in commercial buildings, eco-resorts, and public facilities. The push for green building certifications (e.g., LEED, BREEAM) will further accelerate installations in sustainable construction projects.
3. Technological Innovation and Smart Integration
Vacuum toilet systems are becoming smarter and more connected. By 2026, integration with IoT-enabled monitoring systems will allow for predictive maintenance, real-time usage analytics, and remote diagnostics—particularly valuable in large-scale deployments such as airports, cruise ships, and stadiums. Manufacturers are investing in antimicrobial surfaces, touchless operation, and energy-efficient vacuum pumps to enhance hygiene and performance.
4. Growth in Off-Grid and Remote Applications
Vacuum toilets are increasingly being adopted in off-grid homes, recreational vehicles (RVs), and disaster relief settings due to their low water dependency and ease of installation. As decentralized sanitation gains traction in developing regions and rural areas, vacuum systems offer a viable alternative to traditional sewage infrastructure. This trend is supported by NGOs and government programs focused on improving sanitation access.
5. Regional Market Expansion
While North America and Europe remain mature markets with steady growth, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest CAGR by 2026, fueled by rapid urbanization, expanding rail networks (e.g., India’s high-speed rail projects), and rising environmental awareness. China and Japan are leading in technological innovation, while Southeast Asian countries are increasing adoption in tourism and transportation sectors.
6. Competitive Landscape and Product Differentiation
Key players such as Geberit, Evac, and Lueders are focusing on R&D to differentiate their offerings through modular designs, noise reduction, and compatibility with renewable energy systems. Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships are anticipated to intensify as companies seek to expand their global footprint and service capabilities.
In conclusion, the vacuum toilet market in 2026 will be shaped by a convergence of ecological responsibility, technological innovation, and infrastructure modernization. As industries and governments prioritize resource efficiency and operational sustainability, vacuum toilets are set to transition from niche solutions to mainstream sanitation infrastructure.
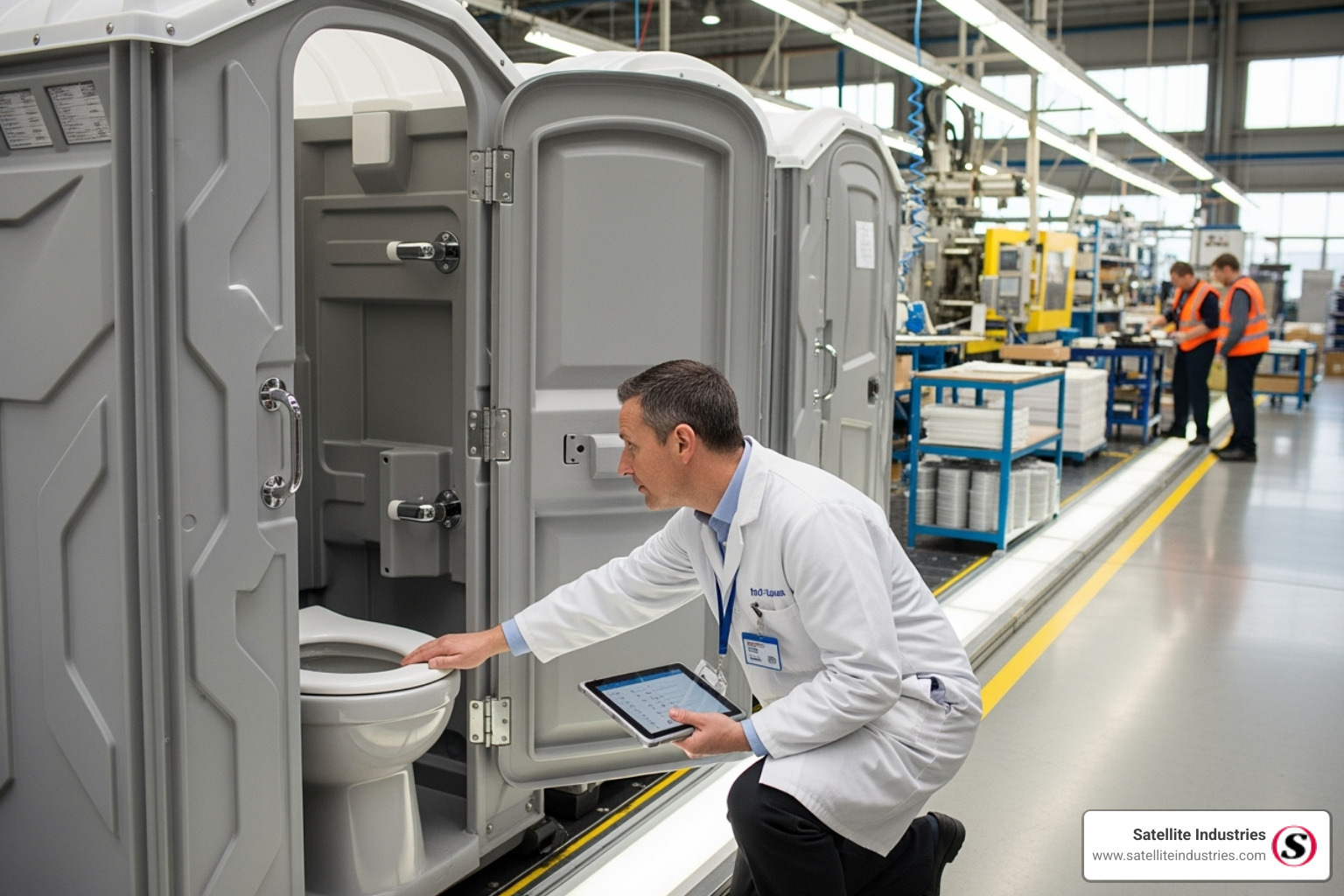

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Vacuum Toilets (Quality & IP Rating)
Sourcing vacuum toilets—especially for demanding environments like marine, rail, or remote facilities—requires careful attention to both quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking these aspects can lead to costly failures, maintenance issues, and safety hazards. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Quality
Many buyers focus on upfront cost, opting for cheaper models without evaluating long-term durability. Low-quality vacuum toilets often use substandard materials (e.g., thin plastic housings, inferior seals), leading to:
- Frequent breakdowns and leaks
- Reduced suction efficiency
- Higher lifecycle costs due to repairs and replacements
Always assess the manufacturer’s reputation, material certifications, and design robustness.
2. Ignoring IP Rating Requirements
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating indicates a fixture’s resistance to dust and water. In wet or high-humidity environments (e.g., ships, offshore platforms), specifying an inadequate IP rating is a critical error.
- Pitfall: Selecting a toilet with IPX4 (splash-resistant) for a washdown area requiring IP66 or higher.
- Consequence: Water ingress into electrical components, leading to system failure or safety hazards.
Ensure the IP rating matches the installation environment—typically IP65 or higher for marine and outdoor applications.
3. Overlooking Certification Standards
Vacuum toilets used in regulated industries must comply with international standards (e.g., ISO 8099 for marine sanitation, EN 1986-1 for construction). Failure to verify certifications can result in:
- Non-compliance penalties
- Installation rejections
- Voided warranties
Always request test reports and certification documentation from suppliers.
4. Poor Supplier Vetting
Sourcing from unknown or unverified suppliers increases the risk of counterfeit or non-conforming products. Red flags include:
- Unwillingness to provide technical data
- Vague product specifications
- No after-sales support or spare parts availability
Choose suppliers with proven experience in vacuum sanitation systems and strong customer references.
5. Underestimating Maintenance and Spare Parts
Even high-quality systems require maintenance. Sourcing a model with limited availability of spare parts or technical support leads to:
- Extended downtime
- Workarounds that compromise hygiene or performance
Verify spare parts accessibility and service network coverage before purchase.
6. Mismatched System Integration
Vacuum toilets must integrate with vacuum collection systems, piping, and control units. A common mistake is selecting a toilet that is incompatible with existing infrastructure.
Always confirm:
- Vacuum pressure requirements
- Pipe diameter and layout compatibility
- Control interface (e.g., sensors, flush logic)
7. Inadequate Environmental Testing
Some suppliers claim high IP ratings or durability without third-party validation. Ensure the product has undergone:
- Salt spray testing (for marine use)
- Cycle testing (e.g., 100,000+ flushes)
- Temperature and humidity chamber testing
Request test results to validate performance claims.
Conclusion
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in supplier selection, technical validation, and environmental matching. Prioritize quality, verify IP ratings and certifications, and ensure long-term supportability to ensure reliable and safe operation of vacuum toilet systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Vacuum Toilets
Overview
Vacuum toilets are specialized sanitation systems commonly used in environments where water conservation, weight reduction, and efficient waste management are critical—such as in aircraft, trains, marine vessels, and eco-friendly buildings. Due to their technical nature and international usage, their logistics and compliance requirements involve multiple regulatory frameworks, transportation standards, and installation protocols.
Regulatory Compliance
International Standards
Vacuum toilet systems must comply with relevant international standards to ensure safety, performance, and environmental protection. Key standards include:
– ISO 8514: Specifies requirements for aircraft toilet systems, including vacuum performance, waste tank integrity, and odor control.
– EN 16146: European standard for non-sewered sanitation systems, including vacuum toilets, covering hygiene, safety, and environmental impact.
– IMO MEPC.227(64): Applies to marine vacuum toilet installations, regulating discharge of effluents and blackwater treatment.
– ASME A112.19.4: U.S. standard for flush valve toilets, including vacuum-assist types, focusing on performance and water efficiency.
Environmental and Health Regulations
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency): In the U.S., vacuum toilets used in recreational vehicles or marine applications must adhere to EPA regulations on waste containment and discharge.
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Ensure that materials used in vacuum toilet components (e.g., plastics, valves) are free from restricted hazardous substances.
- NSF/ANSI 62: Applies when vacuum systems are used in potable water-connected settings; ensures no backflow contamination.
Transportation and Logistics
Packaging Requirements
- Vacuum toilets must be securely packaged to prevent damage during transit.
- Use moisture-resistant, shock-absorbent materials to protect sensitive components such as vacuum pumps, sensors, and control panels.
- Clearly label packages with handling instructions: “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.”
Shipping Classification
- Vacuum toilet systems are generally classified as Class 8544 (Electrical Apparatus) or Class 9023 (Laboratory/Testing Equipment) under the Harmonized System (HS Code), depending on configuration.
- If containing batteries or electronic controls, ensure compliance with UN 3481 (Lithium-ion batteries) regulations when applicable.
- Confirm IATA/ICAO rules for air freight if shipping internationally, particularly for units with electronic modules.
Import/Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Certificate of Conformity (CE, UKCA, or other region-specific mark)
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill
- Customs Declaration Form
- Test Reports (e.g., pressure test, electrical safety)
Ensure all documentation clearly specifies the product as a “Vacuum Toilet System” to avoid misclassification.
Installation and Operational Compliance
Site Preparation
- Confirm compatibility with local plumbing and electrical standards.
- Provide adequate ventilation for odor and gas management, especially in enclosed spaces.
- Install backflow prevention devices per local plumbing codes (e.g., IPC or UPC in the U.S.).
Certification and Inspection
- Engage certified technicians for installation.
- Conduct performance testing post-installation, including vacuum draw time, flush cycle, and leak detection.
- Obtain sign-off from local health or building authorities where required.
Maintenance and Waste Disposal
Scheduled Maintenance
- Follow manufacturer-recommended intervals for cleaning tanks, inspecting seals, and servicing vacuum pumps.
- Maintain logs for compliance audits, especially in commercial transport (e.g., airlines, cruise ships).
Waste Handling
- Blackwater from vacuum toilets must be disposed of at approved waste reception facilities.
- For marine use, adhere to MARPOL Annex IV discharge rules.
- On land, partner with licensed waste treatment providers compliant with local environmental regulations.
Training and Documentation
User and Technician Training
- Provide operational training for end users to prevent misuse (e.g., flushing non-approved materials).
- Train maintenance staff on troubleshooting, part replacement, and safety procedures.
Record Keeping
- Retain installation certificates, maintenance logs, compliance test results, and safety data sheets (SDS) for key components.
- Update documentation for any system modifications.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for vacuum toilets ensures operational safety, regulatory adherence, and environmental protection. By following international standards, preparing accurate shipping documentation, and implementing structured maintenance protocols, organizations can avoid delays, penalties, and system failures. Always consult local authorities and the manufacturer for region-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Vacuum Toilets
In conclusion, sourcing vacuum toilets presents a forward-thinking solution for water conservation, operational efficiency, and sustainable sanitation across various applications such as transportation (trains, aircraft, ships), commercial buildings, and remote or water-scarce areas. Their ability to use significantly less water (up to 90% less than conventional flush toilets) while maintaining effective waste removal makes them an environmentally and economically viable choice.
When sourcing vacuum toilets, it is essential to consider factors such as system compatibility, installation requirements, maintenance support, durability, and compliance with relevant industry standards. Partnering with reputable manufacturers and suppliers ensures reliable performance, access to technical expertise, and long-term after-sales service.
Ultimately, investing in vacuum toilet technology supports sustainability goals, reduces water and sewage treatment costs, and enhances hygiene in high-traffic or resource-limited environments. As global demands for efficient and eco-friendly sanitation grow, sourcing vacuum toilets is a strategic and responsible decision for modern infrastructure development.