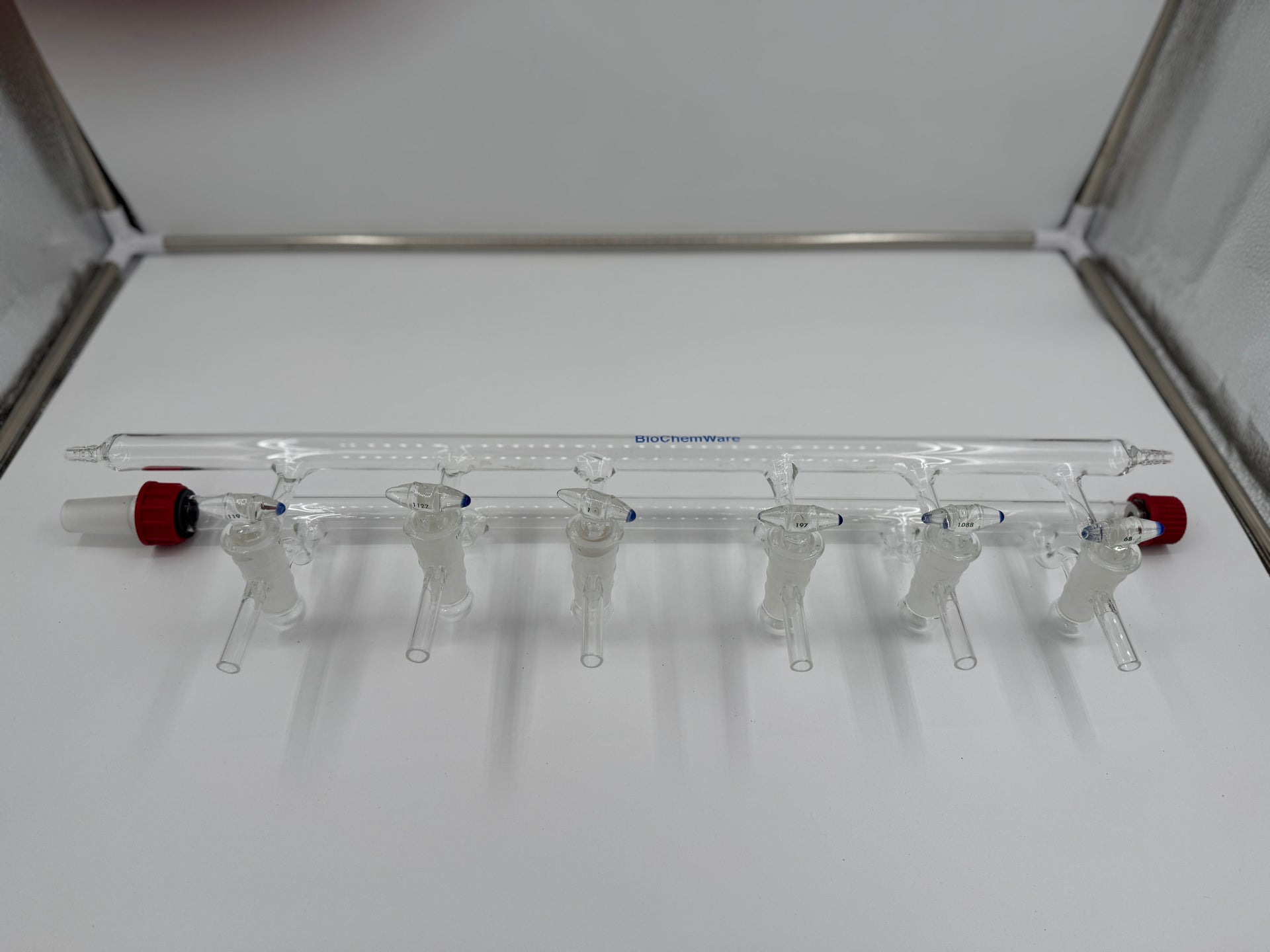
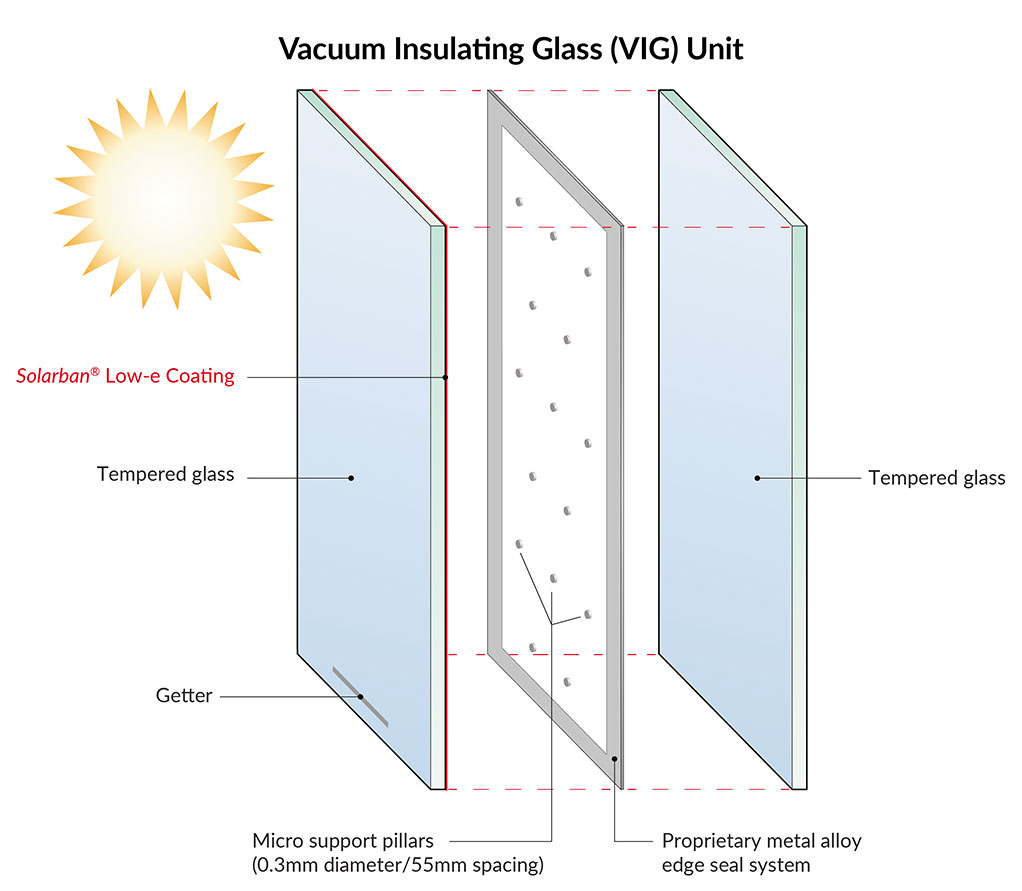
The global vacuum glassware market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across pharmaceutical, chemical, and research laboratory sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the vacuum glassware market was valued at approximately USD 580 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by the increasing need for high-precision laboratory equipment, particularly in emerging economies investing in R&D infrastructure. Additionally, advancements in materials science and a growing emphasis on process efficiency in analytical and industrial applications are reinforcing market momentum. As demand for reliable, high-performance vacuum systems rises, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, quality, and global reach—shaping the future of scientific instrumentation. The following list highlights the top 10 vacuum glassware manufacturers leading this evolution.
Top 10 Vacuum Glassware Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Kurt J. Lesker Company
Domain Est. 1995
Website: lesker.com
Key Highlights: As a leading manufacturer and distributor of high-quality vacuum products, we pride ourselves on delivering exceptional solutions tailored to your needs….
#2 Leading Vacuum Glass Manufacturers Worldwide
Domain Est. 2021
Website: vacuum-glass.com
Key Highlights: This article will analysis the main vacuum glass manufacturers around the world,their production technology and features….
#3 New Vacuum Pumps from Ace Glass
Domain Est. 1996
Website: aceglass.com
Key Highlights: Founded 1936 in Vineland, NJ, Ace Glass Incorporated is a leader and innovator of scientific glassware, lab equipment and glass apparatus….
#4 BRANDTECH Scientific
Domain Est. 1996
Website: brandtech.com
Key Highlights: BRAND manufactures quality liquid handling products, consumables and precision glassware that makes it easy for you to achieve precise and reliable results….
#5 Vacuum Glassware & Manifolds
Domain Est. 1996
Website: dwk.com
Key Highlights: Our vacuum glassware is specially designed to give you the highest possible recovery of extracted analytes from a range of water samples….
#6 Vacuum
Domain Est. 1998
Website: chemglass.com
Key Highlights: VacuuBrand · Vacuum Gauges · Vacuum Manifold Schlenk Line Systems · Vacuum Manifolds · Vacuum Pumps · Vacuum Regulators · Vacuum Traps · Vacuum Tubing….
#7 Leybold
Domain Est. 2001
Website: leybold.com
Key Highlights: Look no further than Leybold. We have been delivering vacuum pumps, systems, accessories, services and tailor-made vacuum solutions for almost 170 years….
#8 vacuum glass
Domain Est. 2013
Website: landvac.net
Key Highlights: LandVac is a new generation Tempered Vacuum Insulated Glass developed and patented by LandGlass. LandVac defines quality life with new standard….
#9 Vacuum Insulated Glass
Domain Est. 2021
Website: thermglass.com
Key Highlights: VIG is the first Insulated glass which eliminates heat transfer and has thermal conductivity (U-Value) of almost zero….
#10 Vacuum Glazing
Website: fineoglass.eu
Key Highlights: FINEO is the new generation of insulating glass. This vacuum glazing, with its unrivalled thinness, provides optimal thermal and acoustic comfort….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Vacuum Glassware

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Vacuum Glassware
The global vacuum glassware market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, rising demand across multiple industries, and growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainable materials. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Increased Adoption in Renewable Energy and Building Efficiency
Vacuum glassware, particularly vacuum insulated glass (VIG), is gaining momentum in the construction and architecture sectors due to its superior thermal insulation properties. With stricter global energy regulations and the push for net-zero buildings, demand for high-performance glazing solutions is rising. In 2026, VIG is expected to be increasingly integrated into residential, commercial, and public infrastructure projects, especially in cold and temperate climates. -
Innovation in Manufacturing Technologies
Advancements in production techniques—such as low-temperature sealing, precision edge-pumping, and automated quality control—are reducing manufacturing costs and improving yield rates. These innovations are expected to enhance scalability and affordability, making vacuum glassware more accessible beyond niche markets. By 2026, manufacturers investing in R&D for ultra-thin, lightweight, and smart-integrated vacuum glass are likely to dominate the competitive landscape. -
Growth in Consumer Appliances and Laboratory Applications
Vacuum glass is seeing expanded use in high-end consumer products such as smart ovens, refrigerators, and specialty cookware, where thermal insulation improves energy efficiency and safety. Simultaneously, demand is rising in scientific and pharmaceutical laboratories for vacuum-sealed glass containers and equipment due to their reliability in preserving sample integrity. This dual growth across household and industrial applications will contribute to market expansion. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers to adopt recyclable materials and reduce carbon footprints. Vacuum glassware, with its long lifespan and energy-saving benefits, aligns with green building certifications (e.g., LEED, BREEAM). By 2026, companies emphasizing sustainable sourcing, low-emission production, and end-of-life recyclability will gain a competitive edge. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, led by China and Japan, remains a manufacturing and innovation hub for vacuum glassware. However, Europe and North America are expected to witness faster adoption due to stringent energy codes and retrofitting initiatives. Emerging markets in India and Southeast Asia may see gradual uptake as urbanization and infrastructure investments accelerate. -
Integration with Smart Building Systems
The convergence of vacuum glass with smart technologies—such as electrochromic coatings, embedded sensors, and IoT connectivity—is creating opportunities for dynamic glazing solutions. In 2026, smart vacuum glass systems capable of adjusting transparency, temperature, and energy absorption in real time are expected to gain traction in high-tech commercial buildings and luxury residences.
In conclusion, the 2026 vacuum glassware market will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and cross-sector integration. Companies that align with energy efficiency goals, invest in advanced manufacturing, and respond to regional regulatory landscapes will be best positioned for growth.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Vacuum Glassware: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing vacuum glassware—such as dewars, vacuum insulated panels (VIPs), double-walled flasks, and laboratory glassware—requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failures, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls in these two critical areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Vacuum Integrity and Long-Term Performance
One of the most critical quality issues is the failure to maintain a stable vacuum over time. Poorly manufactured vacuum seals or substandard getter materials can lead to vacuum decay, drastically reducing thermal insulation performance. Buyers often assume all vacuum glassware performs equally, but variations in manufacturing processes (e.g., edge sealing techniques, outgassing procedures) significantly impact longevity.
2. Use of Substandard or Inconsistent Materials
Sourcing from suppliers who use low-grade borosilicate glass, improper sealants, or inferior metal components can compromise durability, thermal shock resistance, and safety. Inconsistent raw material sourcing leads to batch-to-batch variability, making it difficult to ensure reliable performance in sensitive applications.
3. Lack of Standardized Testing and Certification
Many suppliers, especially in emerging markets, do not adhere to international standards (e.g., ISO 9001, ASTM standards for vacuum insulation). Without third-party testing for vacuum retention, thermal conductivity, or mechanical strength, buyers risk receiving non-compliant or unsafe products.
4. Poor Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control
Inconsistent annealing, improper evacuation techniques, or manual assembly errors can introduce weak points. Suppliers with outdated equipment or insufficient quality control (QC) protocols may pass defective units, increasing field failure rates.
5. Inadequate Packaging and Handling Guidance
Vacuum glassware is highly sensitive to mechanical stress and temperature fluctuations. Poor packaging or lack of handling instructions during shipping can result in microfractures or seal damage, which may not be immediately visible but compromise performance over time.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Unintentional Infringement of Patented Designs or Technologies
Many advanced vacuum glassware designs—especially those used in high-efficiency insulation or scientific instruments—are protected by patents. Sourcing generic or “compatible” versions without due diligence may lead to infringement, resulting in legal action, import bans, or costly redesigns.
2. Supplier Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
Some suppliers may use reverse-engineered manufacturing techniques or copy proprietary designs without authorization. Even if the end product appears identical, this exposes the buyer to IP litigation, particularly in markets with strong IP enforcement (e.g., EU, U.S., Japan).
3. Lack of IP Clauses in Supply Agreements
Contracts that fail to specify IP ownership, liability for infringement, or confidentiality of design specifications leave buyers vulnerable. Without clear terms, disputes over design rights or unauthorized use of proprietary technology can arise.
4. Exposure of Proprietary Designs to Unauthorized Third Parties
When sourcing custom vacuum glassware, sharing detailed technical drawings with multiple suppliers increases the risk of design leakage. Suppliers in regions with weak IP enforcement may reproduce and sell the design to competitors.
5. Misrepresentation of IP Status by Suppliers
Some suppliers may falsely claim their products are “patent-free” or “open design” to attract buyers. Failing to verify these claims through patent searches or legal counsel can result in costly IP violations downstream.
Mitigation Strategies
- Implement rigorous supplier qualification processes, including on-site audits and material traceability checks.
- Require test reports and certifications for vacuum retention, thermal performance, and mechanical durability.
- Conduct IP due diligence before sourcing, including freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses and patent landscaping.
- Include robust IP clauses in contracts, specifying ownership, indemnification, and confidentiality.
- Work with trusted partners in regions with strong quality control and IP protection frameworks.
- Limit distribution of sensitive designs and use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) with all suppliers.
By proactively addressing both quality and IP risks, organizations can ensure reliable, safe, and legally compliant vacuum glassware sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Vacuum Glassware
Vacuum glassware, such as Dewar flasks, vacuum-insulated containers, and specialized laboratory glassware, requires careful handling, packaging, labeling, and documentation due to its fragility, potential for implosion, and specific regulatory considerations. This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance practices to ensure safe and compliant transportation.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent breakage, implosion, and exposure during transit.
- Internal Cushioning: Use inert, non-abrasive materials (e.g., foam inserts, bubble wrap, or molded pulp) to immobilize the glassware and absorb shocks. Ensure no direct contact between glass components.
- Rigid Outer Containers: Employ double-walled corrugated fiberboard or wooden crates capable of withstanding stacking and handling forces. Reinforce corners and edges.
- Vacuum Integrity Protection: Maintain protective caps or plugs on glass joints and valves. Avoid subjecting packages to rapid pressure changes or extreme temperatures that could compromise the vacuum seal.
- Orientation Marking: Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” indicators to guide proper handling.
- Moisture and Temperature Control: Use desiccants if moisture-sensitive and consider insulated packaging for temperature-sensitive applications.
Regulatory Classification & Documentation
Vacuum glassware may be subject to various regulatory frameworks depending on its contents and construction.
- UN/DOT Classification: Vacuum glassware itself is generally not hazardous unless it contains regulated substances (e.g., cryogenic liquids, chemicals, or radioactive materials). If empty and clean, it is typically classified as non-hazardous freight.
- Hazardous Materials (HAZMAT): If the glassware contains residual hazardous substances or is used to transport controlled materials, compliance with 49 CFR (U.S.) or ADR/IATA/IMDG (international) is required. This includes proper UN packaging, labeling (e.g., Class 3, 6.1, 8, etc.), and shipping papers.
- Export Controls: High-vacuum or precision glassware may be subject to export regulations (e.g., EAR – Export Administration Regulations) if used in sensitive technologies. Verify ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) if applicable.
- Customs Documentation: Provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Clearly describe the item as “Vacuum Glassware – Laboratory/Industrial Use” to avoid customs delays.
Transportation & Carrier Coordination
Select and manage carriers with expertise in handling delicate scientific equipment.
- Mode Selection: Air freight is preferred for speed but requires adherence to IATA regulations if hazardous contents are present. Ground transport (e.g., LTL or parcel) is suitable for non-hazardous shipments within regions.
- Temperature & Pressure Considerations: Avoid unpressurized cargo holds or extreme environments that may cause implosion. Coordinate with carriers to maintain stable conditions when possible.
- Chain of Custody: Use tracking systems and require signature upon delivery. Consider using carriers with experience in laboratory or scientific equipment logistics.
- Insurance: Declare full value and ensure coverage includes breakage and implosion risks.
Import/Export & Trade Compliance
Ensure international shipments meet destination country requirements.
- Product Standards: Verify compliance with local safety and material standards (e.g., CE marking in Europe, CCC in China).
- Restricted Materials: Confirm that glass composition (e.g., borosilicate) or coatings do not contain substances restricted under REACH, RoHS, or other chemical regulations.
- Customs Valuation: Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) code (e.g., 7017.20 for laboratory glassware) to prevent misclassification and duty miscalculations.
Safety & Emergency Protocols
Prepare for potential incidents involving breakage or implosion.
- Spill Kits: Include in shipments containing hazardous residuals, per regulatory requirements.
- Emergency Response Information: Provide 24/7 contact details and SDS (Safety Data Sheets) if hazardous materials are involved.
- Training: Ensure warehouse and logistics staff are trained in handling fragile glass items and responding to breakage incidents (e.g., proper cleanup and ventilation for cryogenic residues).
Recordkeeping & Audits
Maintain documentation to support compliance and traceability.
- Retention Period: Keep shipping records, SDS, export licenses, and customs filings for at least 3–5 years, depending on jurisdiction.
- Internal Audits: Regularly review packaging, labeling, and documentation procedures to ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulations.
Adhering to this guide ensures the safe, legal, and efficient transport of vacuum glassware across global supply chains. Always consult with regulatory experts and carriers to verify requirements specific to your shipment.
Conclusion for Sourcing Vacuum Glassware
Sourcing vacuum glassware requires careful consideration of several key factors, including material quality, design specifications, manufacturing standards, and supplier reliability. High-performance applications in laboratories, pharmaceuticals, and research settings demand glassware that ensures thermal insulation, structural integrity, and vacuum stability. Selecting suppliers with proven expertise, compliance with international standards (such as ISO or ASTM), and robust quality control processes is essential to ensure product safety and longevity.
Additionally, evaluating cost-effectiveness, lead times, and after-sales support contributes to a successful sourcing strategy. Building strong relationships with reputable manufacturers—whether local or international—can enhance supply chain resilience and enable customization when needed. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing approach ensures that vacuum glassware meets technical requirements, supports operational efficiency, and aligns with both safety and budgetary objectives.