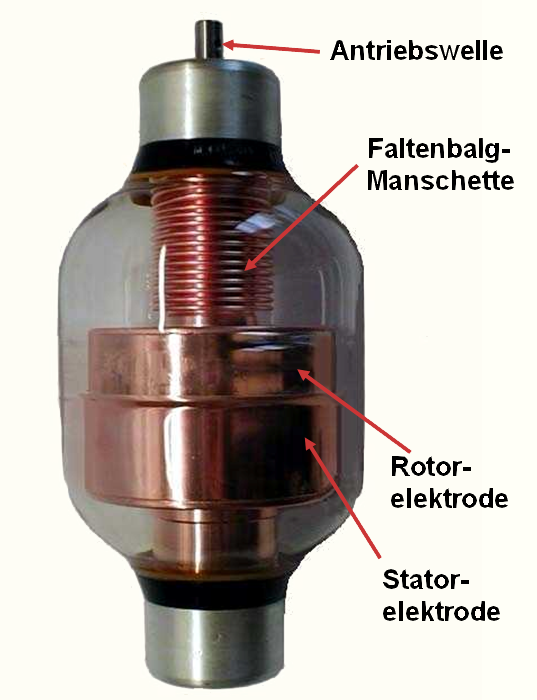
The global vacuum capacitor market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for high-power RF components in industries such as telecommunications, aerospace, defense, and medical equipment. According to Grand View Research, the global RF and microwave components market was valued at USD 23.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030—growth underpinned by advancements in 5G infrastructure, radar systems, and industrial heating technologies, all of which rely heavily on high-performance vacuum capacitors. As critical elements in resonant circuits and impedance matching networks, vacuum capacitors offer superior thermal stability, low loss, and long operational life under demanding conditions. With rising investments in next-generation communication systems and high-energy physics research, the need for reliable, precision-engineered vacuum capacitors has never been greater. This backdrop sets the stage for the top eight manufacturers leading innovation, quality, and market share in this specialized segment.
Top 8 Vacuum Capacitor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Capacitor
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: Murata offers ceramic, polymer aluminum, single-layer microchip, variable, silicon, film, and various other types of capacitors. See selection guide….
#2 Your Source for Vacuum Capacitors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lbagroup.com
Key Highlights: LBA’s Vacuum Capacitor Store is your factory dealer specializing in GREENSTONE, COMET, & JENNINGS fixed and variable vacuum capacitors….
#3 China Vacuum Capacitor Manufacturers and Suppliers
Domain Est. 2022
Website: njhighhope.com
Key Highlights: High Hope is a professional high quality Vacuum Capacitor Manufacturers and Suppliers in China. Our best selling Vacuum Capacitor have been sold around the ……
#4 Fixed & Variable Vacuum Capacitors For Sale
Domain Est. 1997
Website: pentalabs.com
Key Highlights: Explore our full line of vacuum capacitors, available in both fixed and variable configurations. These high-performance components are designed for precision ……
#5 Lineup of Vacuum Capacitors
Domain Est. 2010
Website: meidensha.com
Key Highlights: We develop and manufacture highly reliable vacuum capacitors. There are two methods to produce the vacuum products: the constant air exhausion method by vacuum ……
#6 Vacuum Capacitors And Hardware
Domain Est. 2015
Website: relltubes.com
Key Highlights: Richardson Electronics offers a wide variety of vacuum capacitors ranging from 12pF to 5,000pF and covering test voltages of 5kV to 60 kV….
#7 Vacuum Capacitors
Domain Est. 2015
Website: dc-components.com
Key Highlights: Vacuum Capacitors use a high vacuum as the dielectric instead of air or other insulating material. They have commonly used in high-voltage (5000 volts (5 kV)) ……
#8 Vacuum Capacitors
Domain Est. 2020
Website: pct.comet.tech
Key Highlights: Comet Vacuum Capacitors are recommended to improve the performance of equipment used in the Semiconductor, Flat Panel Display, Battery and Broadcast industry….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Vacuum Capacitor

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Vacuum Capacitors
As the global demand for high-performance electronic components grows across critical industries, vacuum capacitors are poised for significant advancements and market expansion by 2026. Driven by innovations in materials, rising energy efficiency standards, and the proliferation of high-power industrial and communication systems, the vacuum capacitor market is expected to experience robust growth and strategic transformation.
1. Rising Demand in Renewable Energy and Power Transmission
By 2026, the renewable energy sector—particularly wind and solar power—is anticipated to be a major growth driver for vacuum capacitors. These components are essential in high-voltage power conditioning systems, inverters, and grid-tied energy storage solutions due to their high reliability, low losses, and exceptional thermal stability. With increasing investments in smart grids and high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission systems, vacuum capacitors will play a crucial role in ensuring efficient and stable power delivery.
2. Expansion in RF and Telecommunications Infrastructure
The rollout of 5G and the development of 6G research platforms will continue to accelerate the need for high-power RF (radio frequency) systems. Vacuum capacitors are integral to RF amplifiers, antenna tuning units, and broadcast transmitters due to their ability to handle high voltages and frequencies with minimal dielectric loss. In 2026, this sector is expected to see increased adoption of compact, high-efficiency vacuum capacitors designed for dense urban communication networks and next-generation satellite communications.
3. Growth in Industrial and Scientific Applications
Industrial heating, plasma generation, and medical equipment such as MRI machines and cancer therapy accelerators rely heavily on vacuum capacitors for stable and precise power control. Advancements in semiconductor manufacturing and fusion energy research are also expected to contribute to market growth. By 2026, demand from research institutions and high-tech industrial facilities will further solidify vacuum capacitors as mission-critical components in advanced technology ecosystems.
4. Technological Innovation and Miniaturization
Manufacturers are focusing on developing smaller, more durable vacuum capacitors with enhanced voltage ratings and longer operational lifespans. Innovations in vacuum sealing techniques, electrode materials (e.g., advanced alloys and coatings), and automated manufacturing processes are expected to reduce costs and improve performance. In 2026, expect to see greater integration of vacuum capacitors into modular power systems and hybrid electronic architectures.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, is projected to lead market growth due to strong investments in electronics manufacturing, renewable energy, and telecommunications. North America and Europe will maintain steady demand, supported by defense modernization programs, aerospace developments, and stringent energy efficiency regulations. Strategic partnerships between capacitor manufacturers and system integrators are likely to increase, especially in defense and aerospace applications.
6. Sustainability and Regulatory Influences
Environmental regulations targeting hazardous materials (e.g., SF₆ in gas-insulated systems) are pushing industries toward greener alternatives. Vacuum capacitors, being inherently eco-friendly and maintenance-free, are increasingly favored over oil- or gas-filled capacitors. By 2026, compliance with international environmental standards will further boost their adoption across industrial and utility sectors.
Conclusion
The 2026 vacuum capacitor market will be shaped by technological innovation, growing energy demands, and expanding applications in high-tech industries. With a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6–8% from 2021 to 2026, the market is set to exceed USD 250 million in value. Companies that invest in R&D, sustainability, and strategic industry partnerships will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this high-reliability niche of the electronic components sector.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Vacuum Capacitors (Quality & IP)
Sourcing vacuum capacitors—critical components in high-power RF applications such as broadcast transmitters, industrial heating, and medical equipment—requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to system failures, safety hazards, and legal risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Overlooking Quality Certification and Standards Compliance
One of the most common mistakes is assuming all vacuum capacitors meet industry standards. Low-cost suppliers may not adhere to essential certifications such as:
- IEC 61270 or MIL-PRF-125 standards for high-voltage performance.
- RoHS and REACH compliance for hazardous substances.
- Lack of proper Type Testing Reports or Factory Acceptance Testing (FAT) documentation.
Pitfall: Accepting components without verified test reports or third-party certifications can result in premature failures, inconsistent performance, or unsafe operation under high-voltage stress.
Best Practice: Require full compliance documentation and conduct independent batch testing when possible, especially for mission-critical applications.
2. Inadequate Vacuum Integrity and Hermetic Sealing
The core value of a vacuum capacitor lies in its hermetically sealed vacuum environment, which prevents arcing and ensures longevity. Poor manufacturing practices can compromise:
- Seal integrity due to substandard welding or brazing.
- Outgassing from internal materials, leading to pressure rise over time.
- Use of inferior getter materials that fail to maintain vacuum.
Pitfall: Capacitors with compromised vacuum degrade over time, increasing risk of internal arcing, short circuits, or catastrophic failure.
Best Practice: Source from manufacturers with proven vacuum sealing processes and request Residual Gas Analysis (RGA) or Helium Leak Test results.
3. Misrepresentation of Electrical Parameters
Suppliers, especially non-reputable ones, may exaggerate or falsify performance specs such as:
- Voltage rating (DC or peak RF)
- Current handling capacity
- Q factor (quality factor)
- Temperature coefficient
Pitfall: Overrated components can fail under actual operating conditions, leading to system downtime or damage to associated equipment.
Best Practice: Cross-check specifications with independent test data or request sample validation under real-world conditions.
4. Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
Some suppliers sell capacitors that mimic well-known brands (e.g., Jennings, CPI, or Voltronics) but are reverse-engineered clones or outright counterfeits. These copies often use inferior materials and lack proper IP licensing.
Pitfall: Using counterfeit parts risks poor reliability and exposes the buyer to intellectual property (IP) infringement claims, especially in export markets or regulated industries.
Best Practice: Purchase only from authorized distributors or directly from OEMs. Verify part markings, packaging, and traceability with the original manufacturer.
5. Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) and Licensing Issues
Many high-performance vacuum capacitor designs are protected by patents, especially in construction techniques, contact materials, or getter systems. Sourcing from unauthorized manufacturers may involve:
- Use of patented technologies without licensing.
- Infringement on proprietary vacuum processing methods.
Pitfall: End users or integrators can be held liable for using equipment containing IP-infringing components, leading to legal action, product recalls, or customs seizures.
Best Practice: Conduct due diligence on supplier IP compliance. Request documentation showing legitimate licensing or design freedom-to-operate (FTO).
6. Lack of Long-Term Supply Chain Stability
Vacuum capacitors often have long operational lifespans (10–20 years). However, some suppliers may go out of business or discontinue models without notice.
Pitfall: Inability to source replacement parts leads to costly redesigns or system obsolescence.
Best Practice: Choose suppliers with a proven track record and long-term product support. Consider obsolescence management and availability of last-time buy (LTB) options.
7. Poor Thermal and Mechanical Design for Application
Not all vacuum capacitors are suited for every environment. Issues arise when:
- Thermal expansion mismatches cause seal failure.
- Mounting configurations don’t match the application (e.g., incorrect bushing sizes or flange types).
- Vibration resistance is inadequate for mobile or industrial settings.
Pitfall: Mechanical stress leads to micro-cracks, vacuum leaks, and early failure.
Best Practice: Collaborate with the supplier during the design phase to ensure form, fit, and function compatibility.
Conclusion:
Sourcing vacuum capacitors involves more than comparing price and specs. Ensuring quality requires scrutiny of manufacturing standards, testing, and materials, while IP risks demand attention to authenticity and legal compliance. Partnering with reputable, transparent suppliers and conducting thorough due diligence mitigates these common pitfalls and ensures reliable, safe, and legally compliant system integration.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Vacuum Capacitors
Overview
Vacuum capacitors are specialized electronic components used in high-voltage, high-frequency applications such as RF transmitters, medical equipment, and industrial heating systems. Due to their construction and potential electrical hazards, their logistics and compliance requirements must be carefully managed to ensure safety, regulatory adherence, and efficient handling.
Packaging and Handling
Vacuum capacitors are sensitive to mechanical shock, moisture, and electrostatic discharge (ESD). Proper packaging is essential to maintain performance and safety:
– Use anti-static packaging materials to prevent ESD damage.
– Secure capacitors in rigid inner containers with cushioning (e.g., foam inserts) to prevent movement during transit.
– Seal packaging in moisture-resistant bags if stored or shipped in humid environments.
– Label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “ESD Sensitive” indicators.
– Avoid stacking heavy items on top of capacitor packages.
Transportation Regulations
Vacuum capacitors are generally not classified as hazardous materials under international transport regulations (e.g., IATA, IMDG, ADR), provided they contain no hazardous dielectrics or radioactive components. However:
– Confirm the absence of restricted substances per RoHS and REACH regulations.
– If capacitors incorporate beryllium oxide (BeO) in insulators—rare but possible—special handling and labeling per OSHA and DOT regulations apply due to toxicity risks.
– Shipments containing high-voltage components may be subject to inspection; include technical data sheets and declarations of conformity.
Import/Export Compliance
International movement of vacuum capacitors may trigger export control requirements:
– Check if the capacitor falls under dual-use regulations (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation, U.S. EAR). High-power RF capacitors may be controlled under ECCN 3A001 due to use in radar or telecommunications.
– Obtain necessary export licenses if shipping to embargoed or restricted countries (e.g., sanctioned regions per OFAC or EU lists).
– Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes—typically under 8532.22 or 8532.29 for fixed capacitors.
– Maintain records of end-user statements and compliance certifications for audit purposes.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
- Ensure compliance with the EU’s Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive and REACH regulations.
- Confirm that manufacturing processes adhere to WEEE guidelines for future end-of-life management.
- Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) if requested, especially if materials of concern (e.g., BeO, lead solder) are present.
- Follow OSHA and local workplace safety standards when handling or installing capacitors, particularly due to high-voltage retention risks.
Storage Conditions
- Store in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 5°C to 40°C).
- Avoid exposure to corrosive gases, direct sunlight, or condensation.
- Keep in original packaging until ready for use to minimize contamination and damage.
- Rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) principles to prevent aging-related performance degradation.
Documentation Requirements
Maintain and provide the following for logistics and compliance audits:
– Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
– RoHS and REACH compliance declarations
– Export control classification documentation (ECCN or equivalent)
– Packing list and commercial invoice with accurate technical specifications
– SDS, if applicable
– End-user undertakings for controlled exports
Disposal and End-of-Life
- Vacuum capacitors are not typically hazardous waste unless containing regulated materials.
- Disassemble and recycle metals (e.g., copper, aluminum) through certified e-waste handlers.
- Follow local regulations for electronic component disposal; do not landfill intact units.
- Discharge capacitors safely before disposal to eliminate electrical hazards.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for vacuum capacitors ensures safe handling, legal shipment, and environmental responsibility. Always verify technical specifications, regulatory classifications, and destination-specific requirements prior to distribution.
Conclusion for Sourcing Vacuum Capacitors
Sourcing vacuum capacitors requires a careful evaluation of technical specifications, supplier reliability, application requirements, and long-term performance needs. These high-performance components are essential in critical applications such as RF amplifiers, broadcast transmitters, medical equipment, and aerospace systems, where stability, high voltage tolerance, and low loss characteristics are paramount.
After assessing various suppliers and market options, it is evident that selecting a reputable manufacturer with a proven track record in quality and consistency—such as CPI, Amplier, or Tecate Group—is crucial. Key considerations include capacitance range, voltage rating, current handling, thermal performance, mechanical durability, and compliance with international standards (e.g., RoHS, ISO, MIL-SPEC).
Additionally, lead times, availability of custom configurations, and technical support play a significant role in ensuring supply chain resilience. Given the specialized nature of vacuum capacitors, establishing long-term partnerships with trusted suppliers can help mitigate risks associated with obsolescence, delivery delays, and performance variability.
In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach—balancing technical fit, quality assurance, cost-efficiency, and supplier capability—is essential for successfully integrating vacuum capacitors into high-reliability systems. Prioritizing these factors will ensure optimal performance, reduced downtime, and long-term value in demanding electronic applications.