The global tungsten market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across high-performance industrial and technological applications. According to Grand View Research, the global tungsten market size was valued at USD 6.1 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is largely fueled by the metal’s exceptional properties—such as the highest melting point of all metals, superior density, and excellent wear resistance—making it indispensable in sectors ranging from aerospace to electronics. As demand surges, leading tungsten metal manufacturers are scaling production and innovating to meet the needs of advanced manufacturing, defense systems, and renewable energy technologies. Behind this expansion are nine critical applications that define the strategic importance of tungsten in today’s industrial landscape.
Top 9 Uses Of Tungsten Metal Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tungsten Metal
Domain Est. 2007
Website: us.misumi-ec.com
Key Highlights: Major Applications of Tungsten in Manufacturing ; Manufacturing Tooling, Cutting tools, drills, dies, and molds, Exceptional hardness and wear …Missing: “-ebay” “-pinterest”…
#2 Tungsten Uses Then and Now
Domain Est. 1996
Website: metalcutting.com
Key Highlights: But in 2007 and now, tungsten coated rolls are used in the manufacture … Facebook Reddit Pinterest LinkedIn Email · Share · NEXT CONTENT. custom ……
#3 Industries Using Tungsten Alloys
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mttm.com
Key Highlights: Tungsten alloys are used in large container inspection devices. They are also used in airport security in package, luggage, and personal X-ray devices. Oil and …Missing: “-ebay”…
#4 Properties and Applications of Tungsten
Domain Est. 1999
Website: azom.com
Key Highlights: This video demonstrate the chemical properties of tungsten and the everyday applications of tungsten in particularly the electrical applications of tungsten.Missing: “-ebay” “-pin…
#5 How Tungsten is used in Everyday Items
Domain Est. 2011
Website: tungstenringsco.com
Key Highlights: The tungsten metal is known for its strength and versatility. In … FacebookTwitterLinkedinRedditWhatsappGoogle+TumblrPinterestVkEmail ……
#6 What Are the Applications of Tungsten?
Domain Est. 2013
Website: samaterials.com
Key Highlights: They are mainly used to manufacture various tools, such as drills, milling cutters, female molds, and male molds. Tungsten Carbide Based …Missing: “-ebay” “-pinterest”…
#7 What Is Tungsten Used For?
Domain Est. 2014
Website: alloysintl.com
Key Highlights: Use in high-temperature components like jet engines, lighting fixture filaments, and furnace parts · Use in electricity-conducting materials like electrodes, …Missing: “-ebay” “…
#8 What Are the Uses of Tungsten?
Domain Est. 2017
Website: heavytungsten.com
Key Highlights: Its functionality can be present in many valuable applications that can include electrical uses, manufacturing uses, construction, chemical, and of course a ……
#9 Top 20 Applications of Tungsten Metal: An In
Domain Est. 2018
Website: aemmetal.com
Key Highlights: Tungsten is crucial in producing heavy alloys for aerospace and defense. Its high density and strength make it perfect for components like counterweights, …Missing: “-ebay” “-pi…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Uses Of Tungsten Metal
Uses of Tungsten Metal: 2026 Market Trends
Aerospace and Defense Applications
By 2026, the aerospace and defense sectors are expected to be leading drivers of tungsten metal demand. Its high density, exceptional strength at elevated temperatures, and excellent radiation shielding properties make it ideal for aerospace components such as counterweights, gyroscopes, and missile guidance systems. The global push toward advanced military technologies, including hypersonic weapons and drone systems, will increase the need for high-performance materials. Tungsten’s ability to withstand extreme conditions ensures its continued integration into critical defense systems, with North America and Asia-Pacific regions showing the highest growth potential.
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
Tungsten is a vital material in semiconductor manufacturing, particularly for interconnects and gate electrodes in advanced integrated circuits. As the semiconductor industry moves toward smaller node technologies (e.g., 3nm and below), tungsten’s low resistivity and thermal stability are becoming increasingly valuable. By 2026, rising demand for AI chips, electric vehicles, and 5G infrastructure will accelerate tungsten consumption in the electronics sector. Investments in semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) in the U.S., Europe, and East Asia are expected to further stimulate tungsten demand, especially for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) tungsten films.
Renewable Energy and Green Technologies
The global shift toward renewable energy will influence tungsten usage in energy storage and generation systems. Tungsten alloys are used in high-temperature components of concentrated solar power (CSP) plants and in wear-resistant parts for wind turbine gearboxes. Additionally, tungsten-based catalysts are being explored for hydrogen production through water splitting. By 2026, increased R&D in green hydrogen and next-generation nuclear reactors (e.g., fusion technology) may open new avenues for tungsten, particularly in plasma-facing components due to its high melting point and low sputtering rate.
Medical and Radiation Shielding Devices
In the healthcare sector, tungsten’s high density and X-ray attenuation make it a preferred material for radiation shielding in medical imaging and cancer therapy equipment. By 2026, expanding access to diagnostic imaging and radiotherapy in emerging markets will boost demand for tungsten-based collimators, shielding containers, and syringe shields. Furthermore, the development of compact, high-precision radiotherapy machines will favor tungsten over traditional lead due to its superior shielding efficiency and environmental safety.
Industrial Tools and Wear-Resistant Coatings
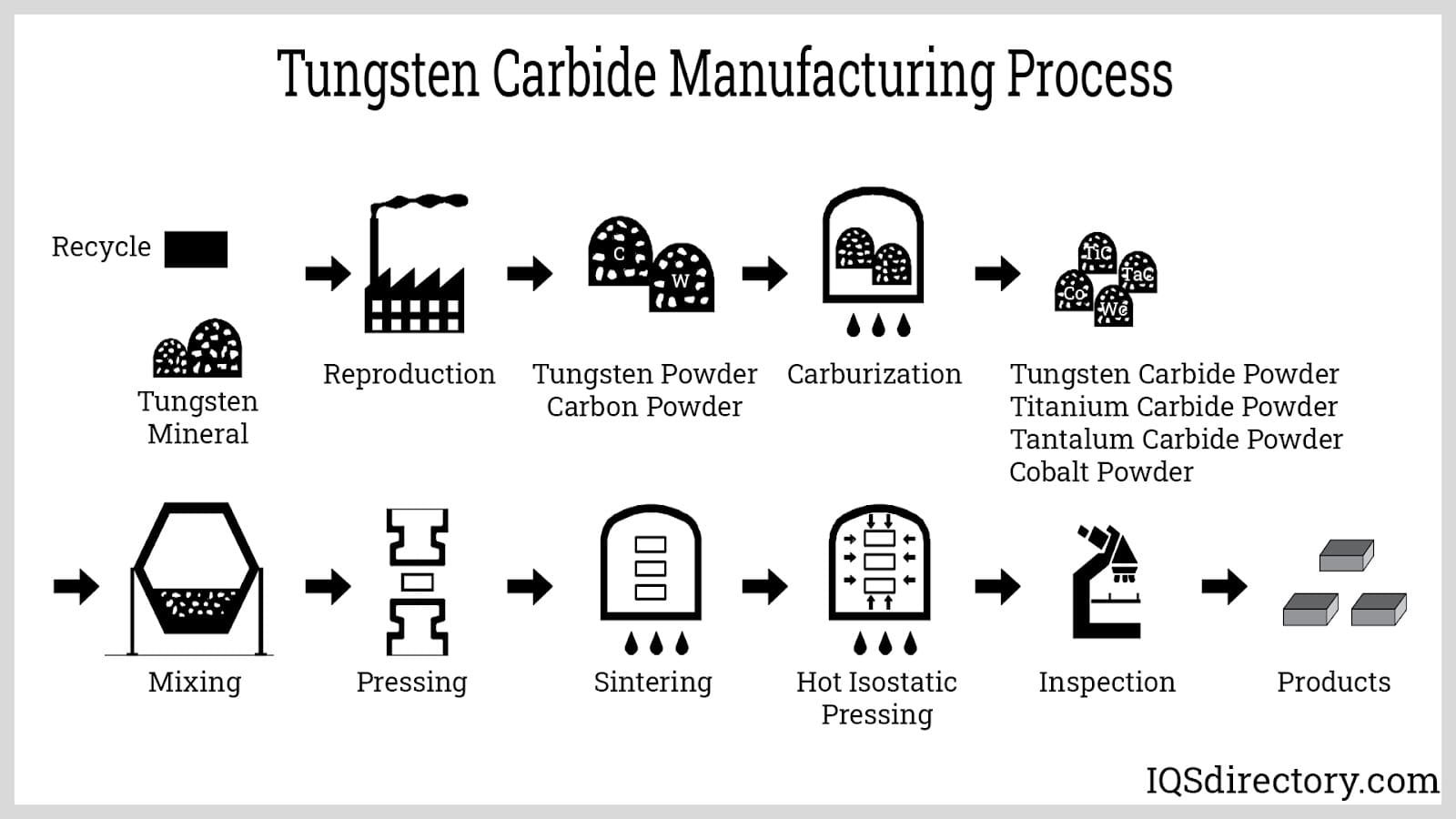
Tungsten carbide, derived from tungsten metal, remains indispensable in cutting, drilling, and machining tools. The manufacturing and oil & gas industries rely heavily on tungsten-based tools for their durability and heat resistance. By 2026, automation and smart manufacturing will require longer-lasting, high-precision tools, further increasing tungsten carbide consumption. Additionally, advancements in thermal spray coatings using tungsten alloys will enhance equipment lifespan in harsh environments, especially in mining and construction.
Emerging Applications and Technological Innovations
Innovations in nanotechnology and additive manufacturing (3D printing) are creating new uses for tungsten. Tungsten nanoparticles are being studied for catalytic and electronic applications, while 3D-printed tungsten components are emerging in aerospace and medical devices. By 2026, these niche but high-growth areas could significantly diversify tungsten’s application base. Moreover, research into tungsten-based superalloys for next-generation jet engines and space exploration vehicles may unlock further demand.
Supply Chain and Sustainability Considerations
As demand rises, supply chain resilience and sustainable sourcing will become critical. China dominates global tungsten production, raising concerns about supply concentration. By 2026, efforts to diversify supply through recycling and secondary production—especially from end-of-life tools and electronics—will gain momentum. Sustainable mining practices and regulatory frameworks will shape the long-term viability of tungsten markets, influencing pricing and availability across industries.
In summary, the 2026 outlook for tungsten metal is characterized by strong growth across high-tech and industrial sectors, driven by performance advantages and evolving technological needs. Strategic investments in recycling, material innovation, and supply diversification will be key to meeting future demand sustainably.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Tungsten Metal: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing tungsten metal, a critical material for high-performance applications like aerospace, defense, electronics, and medical devices, involves navigating significant challenges beyond basic procurement. Two major areas of risk—material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection—can lead to costly failures, project delays, and legal complications if not proactively managed. Understanding these common pitfalls is essential for successful and secure sourcing.
H3: Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Purity and Composition:
- Pitfall: Tungsten’s performance is highly sensitive to impurities (e.g., oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, metallic contaminants like iron, nickel, cobalt). Suppliers may provide material that meets a broad specification (e.g., “99.95% W”) but contains impurities detrimental to the specific application (e.g., high oxygen causing embrittlement in high-temperature applications, or iron contamination affecting magnetic properties).
- Consequence: Component failure under stress, reduced lifespan, unexpected processing behavior (e.g., cracking during sintering), or compromised performance in the final product.
- Mitigation: Define application-specific purity requirements with strict limits on critical impurities. Require detailed Certificates of Analysis (CoA) from the supplier, specifying the test methods used (e.g., GDMS, ICP-MS, LECO). Consider independent third-party verification for critical batches.
-
Undisclosed or Inconsistent Processing History:
- Pitfall: The physical properties (density, grain size, microstructure, mechanical strength, ductility) of tungsten are heavily dependent on its processing history (powder production method, pressing technique, sintering atmosphere/temperature/time, potential subsequent working like swaging or rolling). Suppliers might source from multiple sub-contractors or use varying internal processes without disclosing this.
- Consequence: Batch-to-batch variability in material performance, difficulty in achieving consistent results in manufacturing (e.g., inconsistent machining behavior, forming cracks), failure to meet design specifications.
- Mitigation: Require detailed process specifications and traceability documentation from the supplier. Audit supplier facilities if feasible. Establish long-term partnerships with suppliers who guarantee process consistency. Clearly define required microstructure and mechanical properties, not just chemical composition.
-
Substandard or Non-Compliant Material:
- Pitfall: Sourcing from suppliers using recycled tungsten (e.g., from carbide scrap) without adequate purification, or sourcing from regions with lax quality control, can lead to material that doesn’t meet specifications. This includes potential for counterfeit material.
- Consequence: Catastrophic failure in critical applications, safety hazards, damage to brand reputation, rejection by end customers.
- Mitigation: Prioritize suppliers with strong reputations and robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001:2015 certified). Implement rigorous incoming inspection protocols (chemical analysis, metallography, density measurement, mechanical testing). Understand the supplier’s raw material sourcing and traceability chain.
H3: Intellectual Property (IP) Related Pitfalls
-
Unintentional Disclosure of Proprietary Processes:
- Pitfall: To ensure the tungsten meets specific requirements, a buyer might need to disclose details about their application, required performance parameters, or even aspects of their manufacturing process to the supplier. Without proper agreements, this information can be misused.
- Consequence: Loss of competitive advantage, potential for the supplier (or their competitors) to replicate the buyer’s technology or product, weakening of patent positions.
- Mitigation: Always establish a strong Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) before any technical discussions begin. Clearly define the scope of confidential information and the obligations of the supplier. Limit disclosures to only what is absolutely necessary.
-
Lack of Clarity on IP Ownership in Customized Solutions:
- Pitfall: If a supplier develops a specialized tungsten alloy, form, or processing method specifically for a buyer’s unique application, ambiguity arises: who owns the IP rights to this new development? Standard supplier terms often grant them ownership.
- Consequence: The buyer may be locked into a single supplier for the customized material, face unexpected royalty demands, or find competitors using the same innovation.
- Mitigation: Negotiate IP ownership clauses upfront in the supply contract. For developments driven by the buyer’s needs and specifications, strive to secure ownership or an exclusive, royalty-free license. Clearly define background IP (pre-existing) vs. foreground IP (newly developed).
-
Supplier’s Use of Infringing Technology:
- Pitfall: The supplier might use patented processes (e.g., specific powder synthesis, sintering techniques) or source material produced using infringing methods to manufacture the tungsten supplied. The buyer, by using the resulting component, could be implicated in patent infringement.
- Consequence: Risk of being sued for patent infringement by the true patent holder, leading to injunctions, damages, and reputational damage.
- Mitigation: Include robust warranties and indemnification clauses in the supply agreement. Require the supplier to warrant that the materials and processes used do not infringe third-party IP and to defend and indemnify the buyer against any infringement claims arising from the supplied material. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s technology sources where possible.
Conclusion:
Sourcing tungsten metal effectively requires moving beyond price and lead time. Proactively addressing quality pitfalls ensures material reliability and performance, while robust IP management safeguards innovation and competitive advantage. Success hinges on clear specifications, stringent quality controls, thorough due diligence, and legally sound contracts with well-defined IP and confidentiality terms. Treating sourcing as a strategic partnership, with open communication governed by strong agreements, is key to mitigating these critical risks.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Uses of Tungsten Metal
Tungsten (chemical symbol W), a high-density, high-melting-point refractory metal, is widely used across industrial, military, aerospace, electronics, and medical applications due to its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to heat and corrosion. However, its strategic importance and potential dual-use nature (civilian and military applications) necessitate strict logistics and regulatory compliance measures globally. This H2 section outlines key considerations in the logistics and compliance framework for handling, transporting, trading, and using tungsten metal.
1. Regulatory Classification & Export Controls
Tungsten metal and its alloys are subject to export control regulations due to their use in defense technologies, such as armor-piercing munitions, missile components, and radiation shielding.
- United States (EAR & ITAR):
- Tungsten metal and certain alloys are listed under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) administered by the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS).
- Specific tungsten products (e.g., powder, heavy alloys, or forms used in munitions) may fall under ECCN 1C009 (materials for military use) or 1C107 (tungsten alloys with specific density or composition).
- Exports to embargoed countries (e.g., Iran, North Korea, Russia) or entities on the Entity List require a license.
-
If integrated into defense articles, tungsten components may fall under ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations).
-
European Union:
- Regulated under the EU Dual-Use Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2021/821).
- Tungsten powders and alloys may be listed in Category 1 (Materials, Chemicals, “Microorganisms”, and Toxins) or Category 9 (Aerospace and Propulsion).
-
Export licenses are required for controlled tungsten products destined for high-risk regions.
-
Wassenaar Arrangement:
- As a member, many countries align controls with Wassenaar guidelines, which include tungsten-based materials used in kinetic energy penetrators or high-temperature aerospace components.
2. International Trade & Documentation
- Customs Classification (HS Codes):
- Common HS codes for tungsten metal include:
- 8101.20 – Unwrought tungsten
- 8101.30 – Tungsten powder
- 8101.92 – Waste and scrap of tungsten
- 7202.60 – Ferrotungsten
-
Accurate classification is crucial to avoid customs delays, penalties, or misdeclaration risks.
-
Required Documentation:
- Commercial invoice detailing material specifications (purity, form, alloy composition)
- Certificate of Origin
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS/SDS)
- Export license (if applicable)
- End-User Statement (for dual-use items)
3. Transportation & Storage Logistics
- Mode of Transport:
- Tungsten metal (in ingot, rod, or powder form) is generally non-hazardous but heavy and dense.
- Powdered tungsten is classified under UN 3089, ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, SOLID, N.O.S. if deemed harmful to aquatic life.
-
Shipping via air, sea, or land must comply with IMDG (sea), IATA (air), or ADR (road) regulations where applicable.
-
Packaging:
- Use moisture-resistant, sealed containers for powders to prevent oxidation or contamination.
-
Secure heavy forms (ingots, rods) to prevent shifting during transit.
-
Storage:
- Store in dry, well-ventilated areas to prevent oxidation.
- Isolate tungsten powder from oxidizers and flammable materials.
- Comply with OSHA (U.S.) or local occupational safety standards for handling metal dust.
4. Environmental, Health & Safety (EHS) Compliance
- OSHA & GHS (U.S.):
- Tungsten metal is not classified as highly toxic, but tungsten carbide-cobalt mixtures may pose respiratory and carcinogenic risks.
-
Employers must provide hazard communication training and use engineering controls (ventilation) when handling powders.
-
REACH (EU):
- Tungsten metal is registered under REACH; downstream users must comply with safety data sheet (SDS) requirements.
-
Tungstate ions may be subject to environmental restrictions under Annex XIV (Authorization List) if released in significant quantities.
-
RoHS & Conflict Minerals:
- While tungsten is not restricted under RoHS, it is one of the 3TG minerals (Tungsten, Tin, Tantalum, Gold) subject to SEC Rule 13p-1 (Dodd-Frank Act).
- Companies using tungsten in electronic products must conduct due diligence and report whether their tungsten is “conflict-free” (not financing armed groups in the DRC or adjoining countries).
5. Supply Chain Due Diligence
- Implement a responsible sourcing program aligned with OECD Due Diligence Guidance.
- Conduct audits of suppliers, especially those sourcing from China (dominant producer), Rwanda, or the DRC.
- Use platforms like Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) and Conflict-Free Sourcing Initiative (CFSI) to validate smelter and refiner status.
6. Industry-Specific Compliance
- Aerospace & Defense: Requires strict traceability, material certification (e.g., AMS, ASTM B76), and adherence to ITAR or EAR where applicable.
- Medical Devices: Tungsten used in radiation shielding or surgical tools must comply with FDA (U.S.) or MDR (EU) regulations, including biocompatibility testing.
- Electronics: Tungsten in semiconductors (e.g., CVD tungsten films) must meet purity and contamination standards.
Conclusion
The logistics and compliance landscape for tungsten metal is shaped by its strategic value, dual-use potential, and environmental considerations. Companies must maintain vigilant documentation, classification, and due diligence practices throughout the supply chain. Proactive adherence to export controls, environmental regulations, and ethical sourcing standards ensures legal compliance and supports sustainable, responsible use of tungsten across global industries.
In conclusion, tungsten metal is a critical and versatile material with a wide range of sourcing applications due to its exceptional properties, including high melting point, density, strength, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Its use spans key industries such as aerospace, defense, electronics, energy, and manufacturing—particularly in the production of cutting tools, electrical components, lighting, and radiation shielding. Responsible sourcing of tungsten is essential to ensure environmental sustainability, ethical mining practices, and supply chain transparency, especially given its classification as a conflict mineral in certain regions. As global demand for high-performance materials rises—driven by advancements in technology and green energy—securing reliable, traceable, and sustainable sources of tungsten will remain a strategic priority for industries worldwide. Continued innovation in recycling and alternative materials may also play a crucial role in mitigating supply risks and reducing environmental impact in the future.