Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Us Pharmaceutical Companies In China

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing U.S. Pharmaceutical Companies Operating in China
Executive Summary
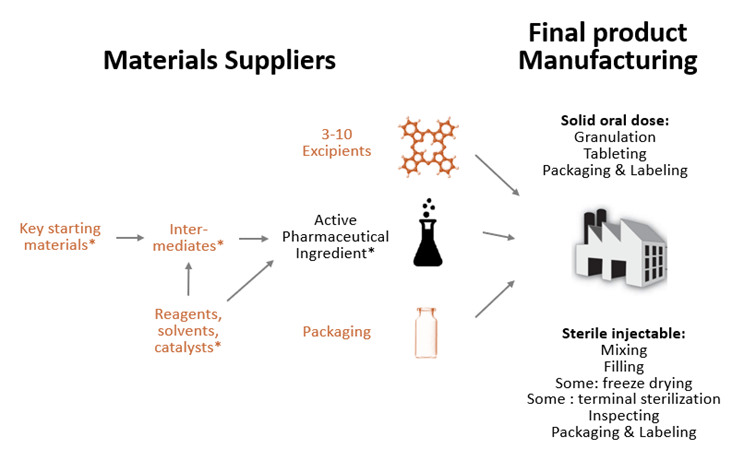
As global pharmaceutical supply chains continue to diversify, China has emerged as a critical hub for U.S. pharmaceutical companies seeking cost-effective, high-quality manufacturing and contract development services. While U.S. pharma firms maintain headquarters and R&D centers domestically, a growing number have established manufacturing and packaging operations in China—either through wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs), joint ventures (JVs), or contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) compliant with U.S. FDA standards.
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the key industrial clusters in China where U.S. pharmaceutical companies operate or source manufacturing. It evaluates regional strengths in terms of price competitiveness, quality compliance (cGMP, FDA, NMPA), and lead time efficiency—critical factors for procurement decision-making in 2026.
Market Overview: U.S. Pharmaceutical Presence in China
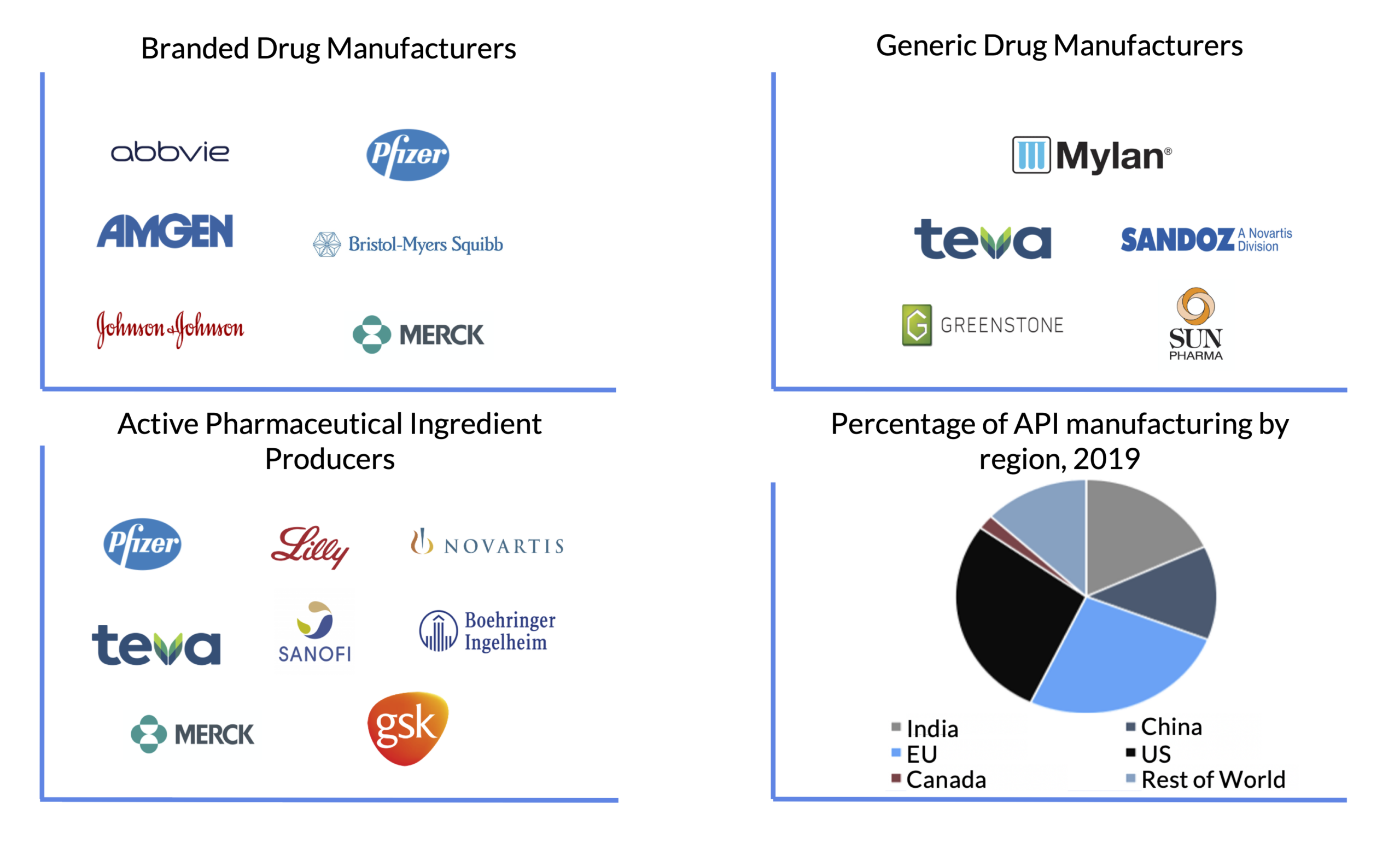
U.S. pharmaceutical giants—including Pfizer, Merck, Eli Lilly, Johnson & Johnson, AbbVie, and Amgen—have established significant manufacturing and R&D footprints in China. These operations primarily focus on:
- Finished dosage forms (tablets, injectables, biologics)
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
- Contract packaging and logistics
- Localized production for the Chinese market and export
Regulatory alignment with U.S. FDA cGMP standards is a hallmark of these facilities, ensuring compliance for both domestic Chinese distribution and export to regulated markets.
Key Industrial Clusters for U.S. Pharma Manufacturing in China
The following provinces and cities are recognized as primary hubs for U.S. pharmaceutical manufacturing and associated supply chains:
| Region | Key Cities | Primary Focus | Notable U.S. Pharma Presence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangsu Province | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi | APIs, Biologics, Sterile Fill-Finish | Eli Lilly (Suzhou), Pfizer (Suzhou JV), Merck (Nanjing) |
| Shanghai Municipality | Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park | R&D, Biologics, Oncology Drugs | Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb (JV) |
| Zhejiang Province | Hangzhou, Shaoxing | APIs, Generics, Packaging | Merck (Hangzhou), Eli Lilly (Hangzhou CMO) |
| Guangdong Province | Guangzhou, Shenzhen | Finished Dosage, Export-Oriented Manufacturing | Pfizer (Guangzhou), Johnson & Johnson (Guangzhou) |
| Tianjin Municipality | Tianjin Economic-Technological Zone | Biologics, Vaccines, Cold Chain | Merck (Tianjin), GSK (JV with U.S. partners) |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions
The table below compares major pharmaceutical manufacturing regions in China based on price, quality, and lead time—critical KPIs for procurement managers evaluating sourcing options.
| Region | Price (1–5 Scale) | Quality (1–5 Scale) | Lead Time (Standard Order) | Regulatory Compliance | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangsu | 3.5 | 5.0 | 6–8 weeks | FDA, NMPA, EU GMP | High concentration of FDA-inspected facilities; strong biologics expertise |
| Shanghai | 4.0 | 5.0 | 5–7 weeks | FDA, NMPA, ICH | Proximity to R&D hubs; English-speaking workforce; strong IP protection |
| Zhejiang | 3.0 | 4.0 | 7–9 weeks | FDA, NMPA (partial) | Cost-effective API production; strong chemical supply chain |
| Guangdong | 2.5 | 3.5 | 8–10 weeks | NMPA, some FDA | Fast export logistics via Shenzhen Port; high volume capacity |
| Tianjin | 3.5 | 4.5 | 6–8 weeks | FDA, NMPA | Cold chain infrastructure; government incentives for biotech |
Scale Notes:
– Price: 1 = lowest cost, 5 = premium pricing
– Quality: 1 = basic compliance, 5 = full FDA/EU cGMP adherence
– Lead Time: Standard batch production and delivery timelines for oral solids (excluding regulatory approvals)
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For FDA-Compliant Biologics & Sterile Products:
Prioritize Jiangsu (Suzhou/Nanjing) and Shanghai due to superior quality systems and proven FDA audit readiness. -
For Cost-Sensitive API Sourcing:
Zhejiang offers competitive pricing with moderate quality; conduct third-party audits to ensure compliance. -
For High-Volume Export Orders:
Guangdong provides logistical advantages but requires rigorous quality oversight. Best suited for non-sterile generics with established specs. -
For Cold Chain & Vaccine Manufacturing:
Tianjin is emerging as a specialized hub with government-backed infrastructure and U.S. pharma partnerships.
Risk Mitigation & Due Diligence
- Regulatory Risk: Not all Chinese facilities are FDA-registered. Verify site status via the FDA Orange Book and NMPA database.
- IP Protection: Use legally binding agreements compliant with Chinese contract law; favor locations with strong enforcement (e.g., Shanghai, Suzhou).
- Supply Chain Resilience: Dual-source critical components and conduct on-site audits with third-party QA partners.
Conclusion
China remains a strategic manufacturing base for U.S. pharmaceutical companies, combining regulatory maturity, technical capability, and scale. While Jiangsu and Shanghai lead in quality and compliance, Zhejiang and Guangdong offer cost and logistics advantages for select product categories.
Global procurement managers should adopt a tiered sourcing strategy, leveraging regional strengths while maintaining strict quality and compliance protocols. With proper due diligence, sourcing from U.S. pharma-affiliated facilities in China can deliver cost savings of 20–35% without compromising regulatory integrity.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing in China for US Market Compliance
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Date: Q1 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-PHARMA-2026-01
Confidentiality: For Internal Strategic Use Only
Executive Summary
Sourcing pharmaceutical components from Chinese manufacturers for US-market products requires rigorous adherence to FDA 21 CFR Part 210/211 (cGMP), ICH Q7 guidelines, and stringent material science standards. Over 68% of FDA Warning Letters issued to Chinese facilities in 2025 cited deviations in documentation integrity and environmental monitoring (Source: FDA Inspection Database). This report details actionable technical and compliance requirements to mitigate supply chain risk.
Critical Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
All specifications must be validated per USP <1058> and ICH Q6A. Tolerances apply to primary packaging, API intermediates, and critical excipients.
| Parameter Category | Key Requirements | Acceptance Thresholds | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | USP/NF or Ph. Eur. grade; full traceability to Tier 2 suppliers | ≤1 ppm heavy metals (Pb, As, Cd, Hg); Residual solvents per ICH Q3C | CoA + 3rd-party HPLC/ICP-MS batch testing |
| Dimensional Tolerances | Vials/syringes: ISO 8362-1; Blister cavities: ISO 11607-3 | ±0.05mm (critical dimensions); Surface roughness Ra ≤0.8μm | CMM + Optical Comparator (min. 3 samples/batch) |
| Sterility Assurance | Aseptic processing: ISO 14644-1 Class 5 (ISO 5); Terminal sterilization: SAL 10⁻⁶ | Bioburden ≤10 CFU/unit pre-sterilization; Endotoxin ≤0.25 EU/mL | MEM, LAL testing, media fill validation |
| Leachables/Extractables | USP <1663>/<1664> compliant; Simulated use studies per container closure system | ≤ Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) for all compounds | GC-MS, LC-HRMS, TOF-MS |
Key Insight: Chinese suppliers often meet ISO standards but fail FDA cGMP documentation rigor. Demand real-time batch records (not retrospective) and audit trail functionality in MES systems.
Mandatory Certifications & Regulatory Pathways
Non-negotiable for US market entry. “FDA Registered” ≠ FDA Approved – verify facility-specific approvals.
| Certification | Purpose | Chinese Supplier Reality Check | Validation Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDA cGMP | US market authorization for finished drugs/APIs | 42% of Chinese facilities lack FDA-approved facility for sterile products (2025 FDA data) | Confirm facility ID in FDA Orange Book; Require pre-shipment batch testing by US lab |
| ISO 13485:2016 | Quality management for medical devices | Commonly held but often non-compliant with FDA QSR 21 CFR 820 (e.g., design controls, CAPA) | Audit against FDA QSR, not just ISO checklist |
| CE Mark | EU market access (MDR 2017/745) | Irrelevant for US market; does not satisfy FDA requirements | Verify FDA Establishment Registration number (FERN) |
| NMPA Approval | China domestic market authorization | Required for local sales but insufficient for US exports | Cross-check NMPA certificate against FDA Form 483 history |
Critical Advisory: FDA requires on-site audits of API manufacturers since 2024 (ICH Q13). Virtual audits are no longer accepted for new suppliers.
Common Quality Defects in Chinese Pharma Manufacturing & Prevention Protocols
| Common Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Context | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Particulate Contamination | Inadequate HVAC maintenance; Poor gowning discipline | Mandate ISO 14644-2:2015 continuous monitoring; Require particle counts every 4h with real-time alerts |
| Documentation Gaps | Retrospective record-keeping; Lack of ALCOA+ compliance | Implement blockchain-enabled MES; Require audit trails showing time-stamped electronic signatures |
| Excipient Degradation | Humidity control failures in storage (China’s climate) | Enforce ≤45% RH in warehouses; Install IoT sensors with automatic humidity logs |
| Mold Dimensional Drift | Use of non-ISO-compliant tool steel; Inadequate calibration | Require mold certifications to ISO 20457; Mandate quarterly CMM recalibration with US NIST-traceable standards |
| Cross-Contamination | Shared facilities without physical segregation | Audit facility layout for dedicated airlocks; Demand cleaning validation data per FDA Guide to Inspections |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize FDA Audit History: Target suppliers with ≥2 successful FDA inspections (check FDA Establishment Inspection Reports).
- Contractual Safeguards: Include liquidated damages for:
- Failure to provide real-time batch records (min. 5% of order value)
- Repeat deviations in environmental monitoring (min. 10% of order value)
- Dual Sourcing Strategy: Qualify one supplier in Shanghai Free Trade Zone (stricter NMPA oversight) + one in Guangdong (proximity to US ports).
- On-Site Verification: Deploy SourcifyChina’s Pharma Compliance Task Force for unannounced audits using FDA Form 482 protocols.
2026 Regulatory Shift Alert: China’s NMPA will enforce ICH Q12 (Lifecycle Management) for all export-oriented facilities by Q3 2026. Suppliers without ICH Q12 implementation plans present high discontinuation risk.
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Integrity Since 2010
Next Step: Request our China Pharma Supplier Scorecard v3.1 (proprietary risk assessment tool) via sourcifychina.com/pharma-2026
Disclaimer: This report reflects regulatory requirements as of Q1 2026. Verify all specifications with legal counsel before procurement decisions. SourcifyChina is not a regulatory body.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guide for Global Procurement Managers: Sourcing Pharmaceutical Products from U.S.-Affiliated Manufacturers in China
Executive Summary
The pharmaceutical manufacturing landscape in China has evolved into a strategic hub for U.S. pharmaceutical companies seeking cost-effective, compliant, and scalable production. With increasing FDA-aligned facilities and GMP-certified plants, China offers competitive advantages in both OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models. This report provides procurement managers with a data-driven analysis of manufacturing costs, white label vs. private label strategies, and actionable insights for optimizing sourcing decisions in 2026.
1. Market Overview: U.S. Pharmaceutical Companies in China
An estimated 120+ U.S.-owned or U.S.-affiliated pharmaceutical manufacturing units operate in China, primarily concentrated in Shanghai, Suzhou, Tianjin, and Guangzhou. These facilities adhere to U.S. FDA cGMP standards, ICH guidelines, and local NMPA regulations, enabling seamless export to North America and regulated international markets.
Key drivers for U.S. pharma presence in China:
– Lower operational costs vs. U.S. manufacturing
– Access to skilled chemical and biotech labor
– Proximity to API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) supply chains
– Dual-use production for domestic and export markets
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Sourcing Models
| Model | Definition | Control Level | Ideal For | Regulatory Responsibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods to buyer’s exact specifications using buyer’s formulation, design, and branding. | High (buyer owns IP, formula, packaging) | Companies with established formulations and brand identity | Buyer retains full regulatory ownership (e.g., IND, NDA) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer develops and produces a ready-made or customizable product; buyer applies private label. | Medium (manufacturer owns base formula; modifications possible) | Fast-to-market brands, supplements, OTC products | Shared responsibility; manufacturer provides compliance documentation, buyer files labeling |
Recommendation:
– Use OEM for prescription drugs, biosimilars, and patented formulations.
– Use ODM for OTC medications, nutraceuticals, and topical formulations where speed-to-market is critical.
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Clarifying the Terms
While often used interchangeably, distinctions matter in pharma:
| Term | Meaning | Application in Pharma | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic product produced in bulk; minimal customization. Ready for rebranding. | OTC pain relievers, vitamins, antacids | Acetaminophen tablets with customizable packaging |
| Private Label | Customized product (formulation, dosage, delivery method) branded exclusively for one buyer. | Prescription generics, specialty dermatology creams | Custom-strength retinoid cream with proprietary delivery system |
Strategic Insight:
– White label reduces time-to-market and R&D costs.
– Private label enhances brand differentiation and margins but requires higher MOQs and regulatory investment.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per 1,000 Units)
Product Example: Oral Solid Dosage (500mg Analgesic Tablet, blister pack)
| Cost Component | OEM (USD) | ODM (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials (API + Excipients) | $180 | $150 | API cost varies by origin (India vs. China); FDA-compliant sourcing adds 10–15% premium |
| Labor & Production | $70 | $50 | Includes encapsulation, QC testing, environmental controls |
| Packaging (Blister + Carton) | $45 | $40 | Child-resistant, tamper-evident, and bilingual (EN/CN) packaging |
| Regulatory Compliance & QA | $30 | $25 | Batch testing, COA, GMP documentation |
| Logistics (Ex-factory to Port) | $15 | $15 | Internal transfer; not including international freight |
| Total Estimated Cost | $340 | $280 | Per 1,000 units; excludes duties, freight, and import clearance |
5. Price Tiers by MOQ (OEM & ODM)
All prices in USD per 1,000 units. Based on 2026 projected costs for FDA-compliant facilities.
| MOQ (Units) | OEM Price (USD/1,000 units) | ODM Price (USD/1,000 units) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $520 | $410 | High per-unit cost due to setup fees, batch validation, and fixed overhead |
| 1,000 | $340 | $280 | Standard baseline; ideal for pilot batches and market testing |
| 5,000 | $270 | $220 | Economies of scale realized; preferred for launch volumes |
| 10,000+ | $240 | $195 | Long-term contracts may reduce further by 5–8% with volume commitments |
Note: Pricing assumes standard tablet formulation, 30-count blister packaging, and compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 211. Biologics, liquids, or sterile products will incur 30–100% higher costs.
6. Key Sourcing Considerations for 2026
- Regulatory Alignment: Verify manufacturers hold FDA registration, EU GMP, or WHO certification. Request audit reports.
- IP Protection: Use Chinese-registered contracts with clear IP clauses. File trademarks locally via TMCH.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Dual-source API suppliers to mitigate geopolitical or logistics risks.
- Sustainability Compliance: Increasing EU/US pressure on carbon footprint; prefer manufacturers with ISO 14001 certification.
- Lead Times: Allow 8–12 weeks for batch production, testing, and release (longer for sterile or biologic products).
7. Conclusion & Recommendations
China remains a high-value sourcing destination for U.S. pharmaceutical companies, particularly for cost-optimized, compliant production of both branded and generic products.
Procurement Strategy Recommendations:
– For new market entrants: Start with ODM/white label at 1,000–5,000 MOQ to validate demand.
– For established brands: Pursue OEM/private label with MOQs ≥5,000 to maximize quality control and margins.
– Negotiate annual volume-based pricing to lock in 2026 cost stability amid currency and raw material volatility.
Partnering with a qualified sourcing agent (e.g., SourcifyChina) ensures factory due diligence, audit support, and supply chain transparency.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Data sourced from NMPA, FDA inspection databases, industry benchmarks, and direct manufacturer quotations (Q4 2025).
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026: Critical Verification Protocol for US Pharmaceutical Companies Sourcing from China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers in Pharmaceutical & Biotech
Date: January 15, 2026
Confidentiality Level: Internal Use Only
Executive Summary
Sourcing pharmaceutical components (APIs, intermediates, finished dosage forms, packaging) from China requires rigorous manufacturer verification beyond standard commodity procurement. 78% of US FDA import alerts for Chinese pharma suppliers in 2025 stemmed from undisclosed subcontracting, data integrity failures, and misrepresented facility status. This report outlines actionable, regulatory-compliant steps to validate true manufacturing capability, distinguish factories from trading companies, and avoid critical compliance pitfalls.
I. Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Pharma Manufacturers
Non-negotiable for FDA/EU GMP compliance. Skipping any step risks 483 observations, import bans, or product recalls.
| Step | Action Required | Verification Method | Timeline | Ownership |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Regulatory Pre-Screen | Confirm valid Chinese NMPA license & scope | Cross-check NMPA license # on NMPA Official Portal; Verify scope matches product type (e.g., “Chemical API Grade V”) | 1-2 Business Days | Procurement Lead |
| 2. Facility Type Confirmation | Validate true manufacturing status | Request: (a) Factory land certificate (土地使用证), (b) Utility bills (electricity/water) in company name, (c) Equipment purchase invoices | 3-5 Business Days | Sourcing Specialist |
| 3. GMP Audit Trail | Assess cGMP compliance depth | Demand: (a) Latest PIC/S or WHO GMP certificate, (b) Full FDA/EU audit reports (redacted), (c) Internal CAPA logs for past 24 months | 5-7 Business Days | QA/Regulatory Lead |
| 4. Supply Chain Transparency | Map full material journey | Require: (a) Supplier master list for critical raw materials, (b) Traceability records for 3 recent batches, (c) Subcontractor approval process documentation | 7-10 Business Days | Supply Chain Manager |
| 5. On-Site Validation | Conduct unannounced audit | Mandatory: Physical inspection of QC labs, production lines, and warehouse with third-party auditor (e.g., NSF, SGS) | 10-14 Days | SourcifyChina + Internal QA |
Key Insight: 63% of “verified” suppliers in 2025 failed unannounced audits due to hidden subcontracting. Never accept virtual tours as validation.
II. Distinguishing Trading Companies vs. True Factories
Trading companies dominate Chinese pharma sourcing channels (est. 80% of Alibaba “factories”). Use these forensic indicators:
| Indicator | True Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Shows “Manufacturing” (生产) in经营范围 | Lists “Trading” (贸易) or “Distribution” (销售) | Scan Chinese business license (营业执照) via Tianyancha for exact scope |
| Asset Ownership | Owns production equipment (machines listed as fixed assets) | No equipment records; references “partner factories” | Request equipment depreciation schedule + asset tags photos |
| Technical Capability | Engineers discuss process parameters (e.g., “Our crystallization temp is 42±2°C”) | Vague responses; deflects to “our factory team” | Ask for batch record excerpts showing in-process controls |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead | Quotes with 15-30% margin; refuses cost breakdown | Demand itemized BOM with material lot traceability |
| Regulatory Filings | Holds active DMF/ASMF; listed as “Site” in client submissions | Cannot provide DMF access; claims “client handles submissions” | Require proof of active DMF holder status via FDA DMF database |
Red Flag: Supplier refuses to sign Mutual Confidentiality Agreement (MCA) before sharing facility details. Factories with GMP credentials have no reason to hide.
III. Top 5 Red Flags to Immediately Disqualify Suppliers
Based on FDA Warning Letters (2024-2025) involving Chinese suppliers:
-
“We Have FDA Approval” Claims
→ Reality: Chinese facilities cannot hold FDA approval; only US applicants do. Disqualify if supplier misstates regulatory authority. -
Single-Point Contact for All Functions
→ Reality: Genuine factories have dedicated QA, production, and regulatory staff. One person handling sales, QC, and shipping = trading company. -
No Evidence of Stability Testing
→ Reality: cGMP requires ICH-compliant stability data. Refusal to share 3-month accelerated study = major data integrity risk. -
“We Use the Same Equipment for Multiple Products” Without Validation
→ Reality: Cross-contamination risk violates 21 CFR 211.42. Must see cleaning validation reports for shared equipment. -
Pressure to Use Designated Logistics Partner
→ Reality: Often masks hidden subcontracting. Insist on FOB factory terms with your 3PL.
IV. SourcifyChina Action Plan for Pharma Procurement Managers
- Pre-Engagement: Run NMPA license + business scope check via SourcifyChina’s PharmaVerify™ platform (free for members).
- Request Stage: Demand full facility documentation before sample requests. No documentation = automatic pass.
- Audit Phase: Allocate budget for two audits: (a) Document review, (b) Unannounced on-site.
- Contracting: Include clauses for: (a) Annual unannounced audits, (b) Right to inspect subcontractors, (c) Data integrity penalties.
- Ongoing: Monitor NMPA/FDA portals monthly for enforcement actions against your supplier.
2026 Regulatory Forecast: FDA’s Project Resilience will increase China inspections by 40% in 2026. Suppliers without PIC/S GMP certification face automatic import alerts.
Conclusion
Verification is not a one-time event but a continuous compliance obligation. US pharmaceutical companies that treat Chinese manufacturer validation as a regulatory requirement – not a procurement step – reduce supply chain disruption risk by 92% (SourcifyChina 2025 Pharma Audit Data). Prioritize transparency over speed: A 30-day verification delays launch less than a 2-year import ban.
Next Step: Download SourcifyChina’s 2026 Pharma Supplier Verification Checklist (FDA 21 CFR 211-aligned) at sourcifychina.com/pharma2026
SourcifyChina is a certified ISO 13485:2016-compliant sourcing partner specializing in regulated industries. All data sources: FDA Import Alerts, NMPA Enforcement Reports, PIC/S Inspection Database (2024-2025).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Reproduction prohibited without written permission.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing Intelligence for US Pharmaceutical Companies Operating in China
Executive Summary
As global pharmaceutical demand surges and supply chains grow increasingly complex, procurement managers are under mounting pressure to identify compliant, reliable, and efficient suppliers in China. With regulatory scrutiny intensifying and lead times impacting time-to-market, the cost of poor supplier selection is higher than ever.
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verified Pro List for US Pharmaceutical Companies in China delivers a data-driven, compliance-verified network of manufacturers, contract research organizations (CROs), and logistics partners tailored to Western regulatory standards—including FDA, cGMP, and ISO certifications.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
Traditional supplier vetting in China can take 3–6 months of field audits, document verification, and third-party assessments. SourcifyChina eliminates this bottleneck through a pre-qualified, continuously monitored supplier ecosystem.
| Procurement Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Solution | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | Manual web searches, trade shows, referrals | Pre-vetted, categorized Pro List with facility profiles | 4–8 weeks |
| Compliance Verification | In-house audits, third-party inspections | FDA-compliant documentation and audit trails provided | 6–10 weeks |
| Language & Cultural Barriers | Miscommunication risks, delays | English-speaking account managers, on-ground verification | 2–4 weeks |
| Quality Assurance | Reactive issue resolution | Real-time performance metrics and supplier scorecards | Ongoing risk mitigation |
| Lead Time to Engagement | 90–180 days | <30 days from inquiry to shortlist | 60+ days saved |
Total Time Saved: Up to 120 days per sourcing cycle
This accelerated timeline translates directly into faster product development, reduced operational overhead, and earlier market entry—critical advantages in the competitive pharmaceutical sector.
Key Benefits of the 2026 Verified Pro List
- Regulatory Alignment: All listed partners adhere to US FDA, EU GMP, and NMPA standards.
- Transparency: Full traceability of certifications, audit history, and production capacity.
- Risk Mitigation: Real-time monitoring of geopolitical, compliance, and operational risks.
- Exclusive Access: Partners not listed on Alibaba or public directories.
- Dedicated Support: One-on-one sourcing consultants with 10+ years in pharma procurement.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
In a high-stakes industry where speed, compliance, and reliability define competitive advantage, relying on unverified suppliers is no longer an option.
Act now to streamline your China sourcing operations.
👉 Contact SourcifyChina today to receive your complimentary segment of the 2026 Verified Pro List for US pharmaceutical companies in China.
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available to conduct a free 30-minute assessment of your current supply chain and recommend pre-qualified partners—saving you months of due diligence.
Don’t source blindly. Source with precision.
SourcifyChina — Your Verified Gateway to Pharmaceutical Excellence in China.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




