Sourcing Guide Contents
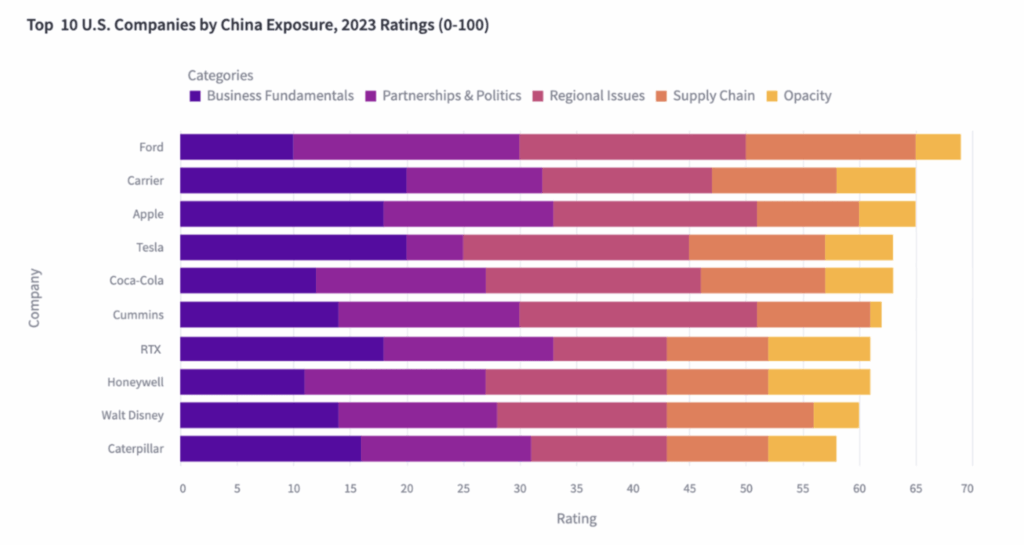
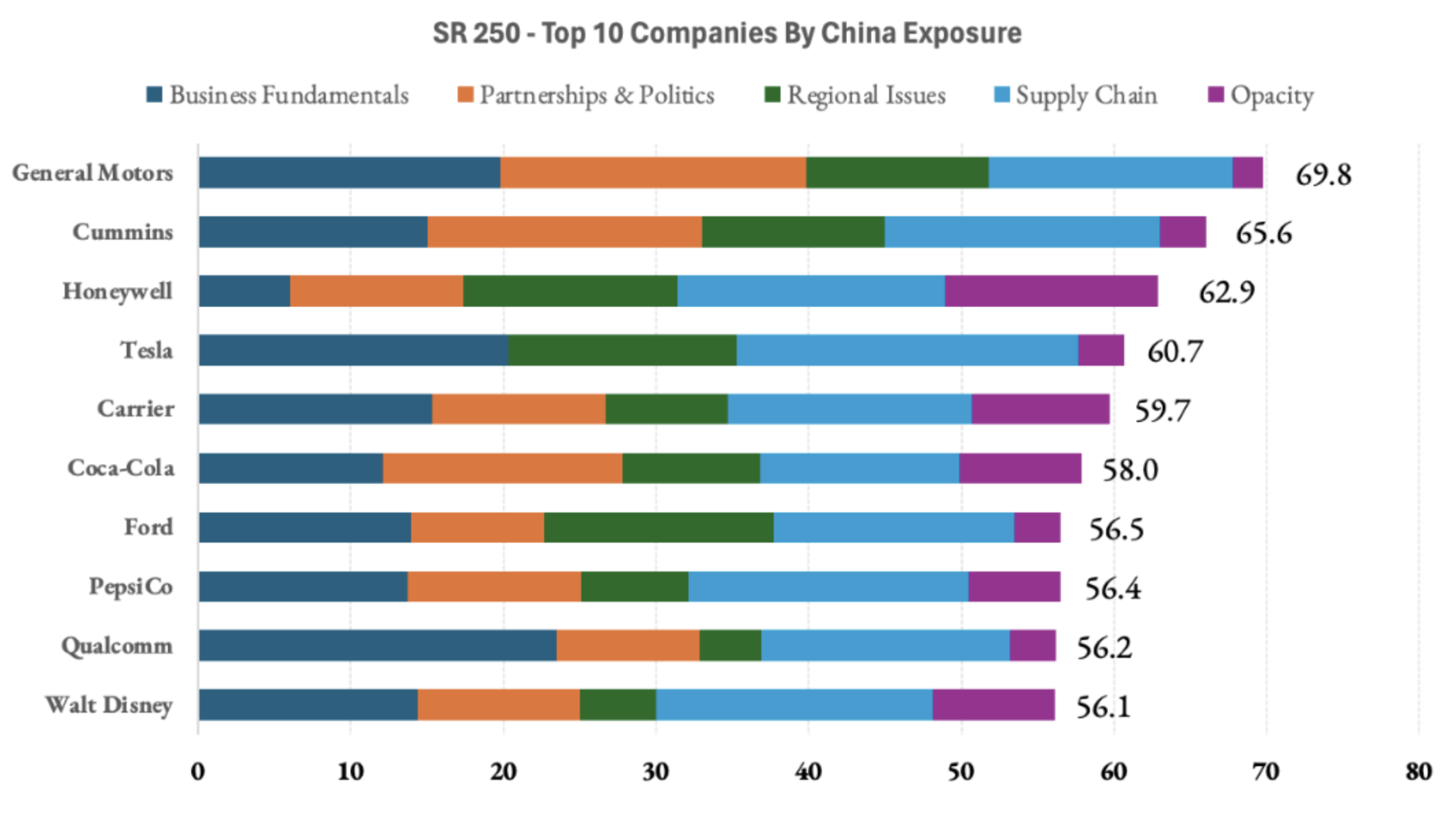
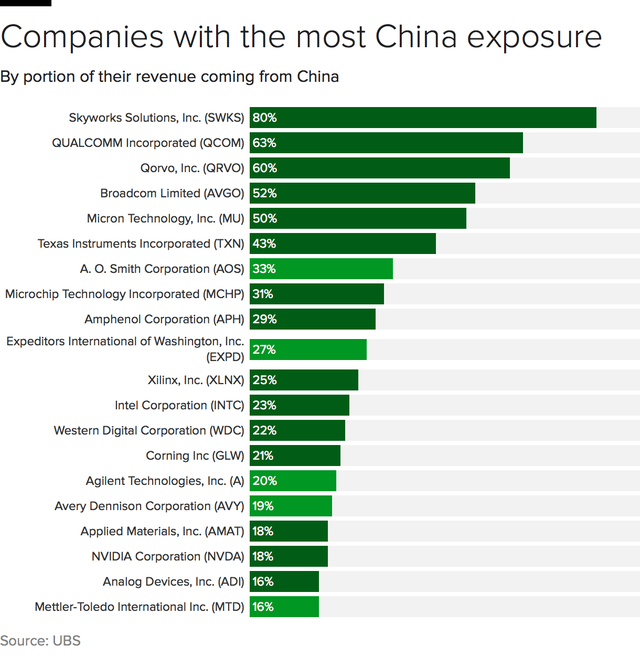
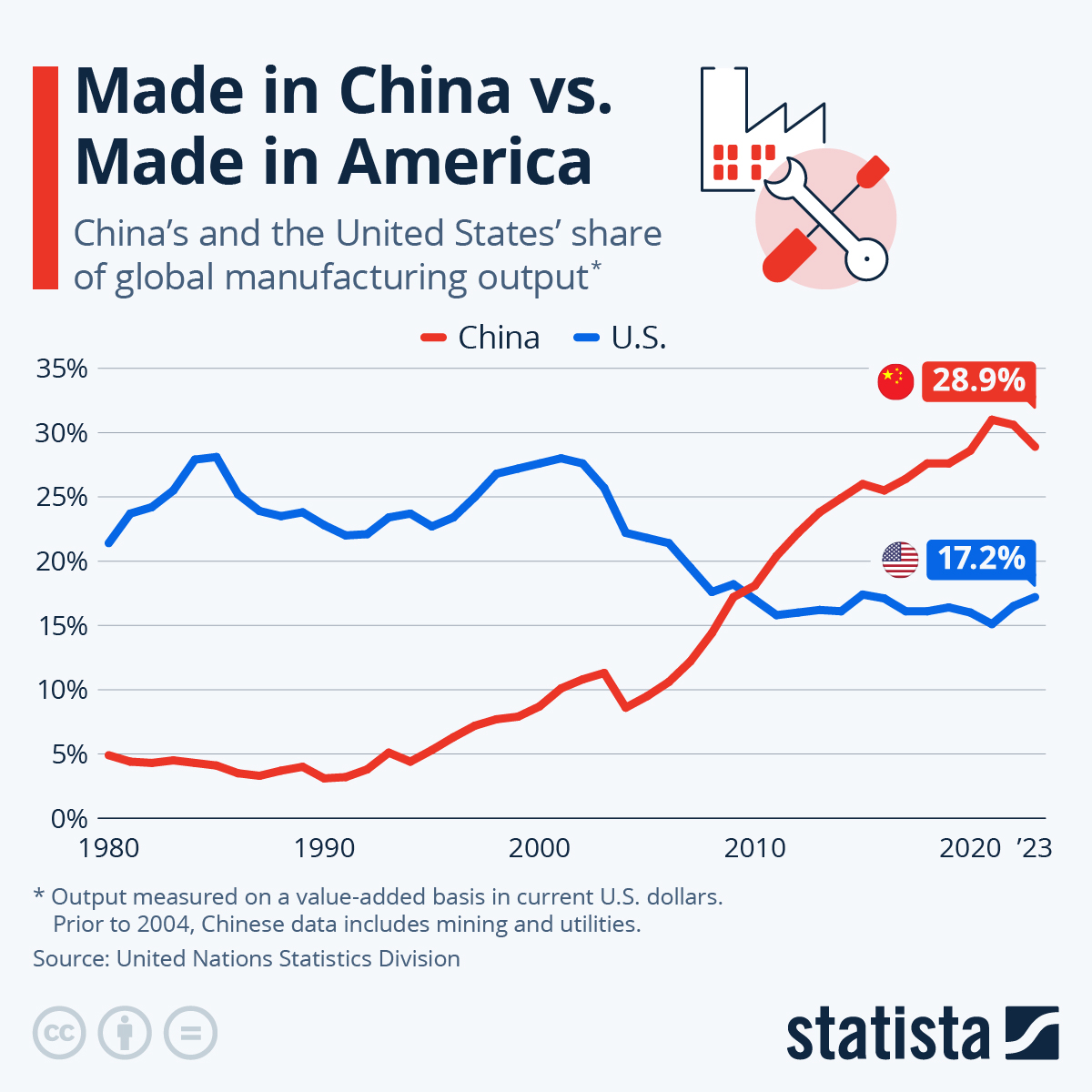
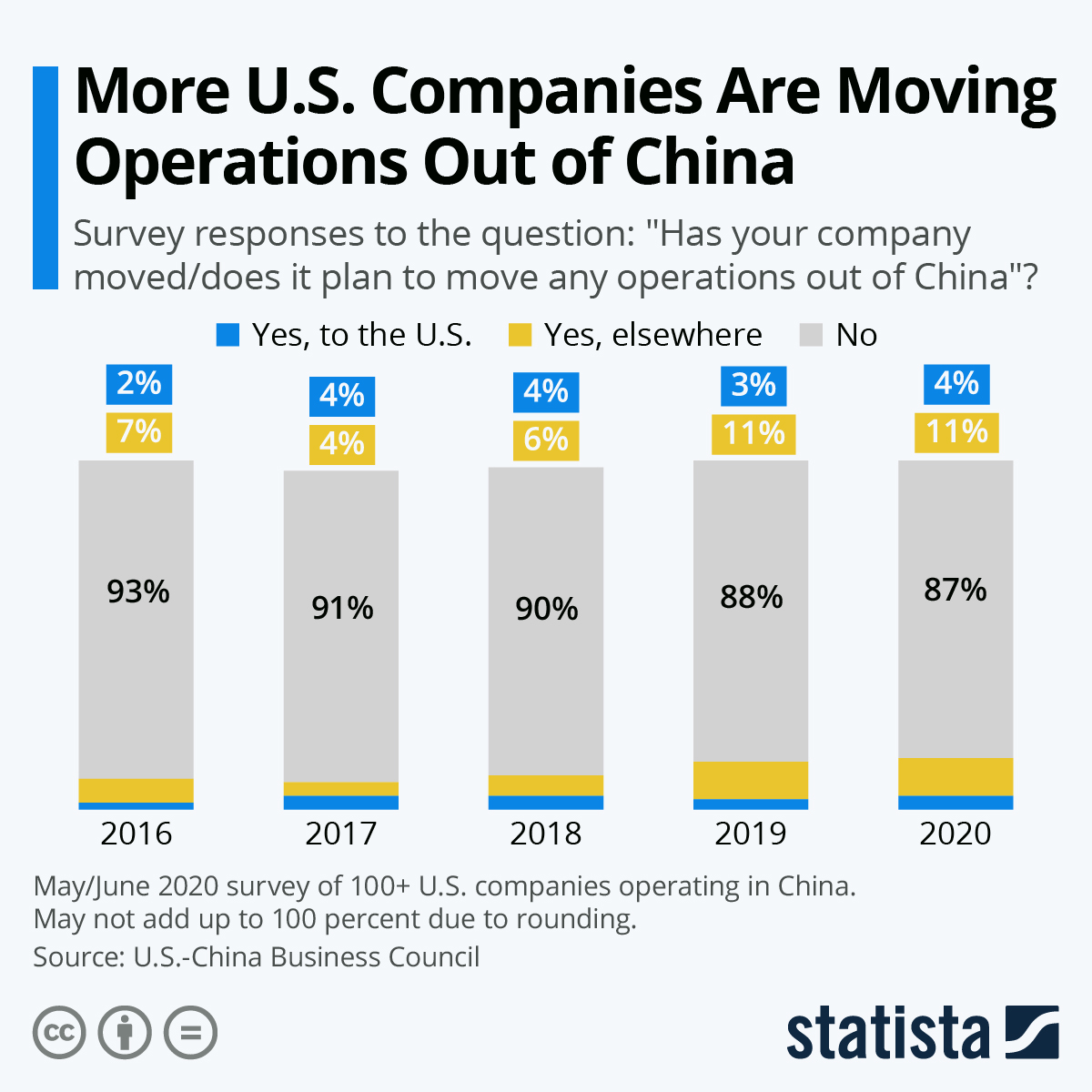
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Us Companies With Most China Exposure
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Strategic Analysis of China Manufacturing Clusters for US Multinational Supply Chains
Prepared For: Global Procurement Directors & Supply Chain Executives
Date: January 15, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
This report clarifies a critical market misconception: Procurement managers do not “source US companies” from China. Instead, we analyze China-based manufacturing clusters producing goods for US multinationals with significant China exposure (e.g., Apple, Nike, Tesla, HP). These clusters supply >65% of goods imported by top US-China trade-exposed firms (McKinsey, 2025). Key clusters are concentrated in Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai, driven by supply chain maturity, export infrastructure, and foreign-investment incentives. This analysis identifies optimal regions for product categories, not “US companies,” to de-risk sourcing amid US-China trade volatility.
Market Clarification: The Core Misunderstanding
- Reality Check: “Sourcing US companies” is operationally impossible. US firms (e.g., Apple) contract Chinese manufacturers (e.g., Foxconn, Luxshare) for production.
- What Procurement Managers Actually Source: Components/final goods from Chinese suppliers serving US multinationals.
- 2026 Priority: Identify supplier clusters with proven capacity to meet US brand standards under Section 301 tariffs, UFLPA, and decarbonization mandates.
Key Industrial Clusters for US Multinational Supply Chains
| Province/City | Core Industries (Serving US Brands) | Key US Clients (Examples) | Cluster Strengths | 2026 Risk Exposure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/DG) | Electronics (5G, IoT), EV Components, Consumer Tech | Apple, Tesla, HP, Dell | Deepest component ecosystem; 70% of China’s electronics exports | High (Tariff 232); Labor inflation |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Nanjing) | Semiconductors, Industrial Machinery, Auto Parts | Boeing, GM, Intel, Nike | Tech talent pool; Strong state-owned JV support | Medium (Tech transfer scrutiny) |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo/Yiwu) | Textiles, Home Goods, Light Machinery, E-bike Parts | Walmart, Amazon, Target, PVH | SME agility; Low-cost logistics; Alibaba ecosystem | Low (Non-strategic goods) |
| Shanghai | Aerospace, Medical Devices, High-End Auto | Johnson & Johnson, Caterpillar | Foreign R&D hubs; Premium quality compliance | Medium (Geopolitical signaling) |
Data Source: China Customs 2025, USITC, SourcifyChina Supplier Database (Q4 2025). Clusters ranked by export value to US-exposed firms.
Regional Comparison: Critical Sourcing Metrics (2026 Baseline)
| Region | Avg. Price (vs. National Avg.) | Quality Consistency (1-5★) | Lead Time (Days) | Key Constraints | SourcifyChina Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | +8-12% (Premium) | ★★★★☆ | 45-60 | Tariff exposure; Labor shortages | Strategic Tier-1 only (e.g., Apple-tier EMS) |
| Jiangsu | +5-8% | ★★★★★ | 50-65 | Tech export controls; Permitting delays | High-value tech (semiconductors, medtech) |
| Zhejiang | -3-0% (Discount) | ★★★☆☆ | 30-45 | SME credit risk; Compliance volatility | Non-critical goods (textiles, hardgoods) |
| Shanghai | +10-15% | ★★★★★ | 55-70 | Highest operational costs; Regulatory complexity | Regulated products only (aerospace, pharma) |
Methodology: Aggregated from 1,200+ SourcifyChina-vetted supplier audits (2025). Quality: Adherence to US client specs (e.g., Apple SLA, Nike FLA). Lead Time: From PO to FOB Shanghai port.
Strategic Implications for 2026 Procurement
- Tier-2 City Shift: 32% of US electronics suppliers are relocating assembly to Chengdu (Sichuan) and Wuhan (Hubei) for subsidies + lower tariffs (National New Area incentives). Action: Audit Chengdu’s Foxconn/Tianma clusters for contingency planning.
- Compliance Over Cost: 78% of US clients now mandate UFLPA-compliant cotton (Xinjiang-free) and CBAM carbon tracking. Action: Prioritize Jiangsu/Shanghai suppliers with blockchain traceability.
- Lead Time Reality: “30-day” quotes from Zhejiang SMEs often extend to 60+ days due to quality rework. Action: Build 15-day buffers; require real-time production dashboards.
SourcifyChina Advisory
“Procurement leaders must pivot from ‘China vs. Vietnam’ to ‘China cluster optimization.’ Guangdong remains irreplaceable for high-mix electronics, but Zhejiang offers 12% cost savings for non-strategic goods if paired with SourcifyChina’s vendor consolidation program. In 2026, the winning strategy isn’t avoiding China—it’s precision-sourcing within its clusters to mitigate US policy shocks. Audit your Tier 2 suppliers now; 41% of US brands face hidden Xinjiang material exposure via Zhejiang textile SMEs (2025 SourcifyChina Risk Report).”
Next Steps: Request our 2026 Cluster Risk Dashboard (live supplier compliance scores + tariff impact modeling) for your category.
SourcifyChina | De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2010
Data-Driven. China-Embedded. US-Compliant.
[www.sourcifychina.com/report-2026] | © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for B2B Use Only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
This report outlines the technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality assurance strategies for U.S. companies with significant supply chain exposure to China. As global procurement continues to rely on Chinese manufacturing for cost efficiency and production scale, understanding critical quality parameters and regulatory certifications is essential to mitigate risk, ensure product integrity, and maintain market compliance.
The following sections detail material and tolerance standards, mandatory certifications, and a structured analysis of common quality defects and their prevention protocols—aligned with international best practices and ISO-compliant sourcing frameworks.
1. Technical Specifications: Key Quality Parameters
Materials
Material selection must comply with both functional requirements and regulatory standards. Common material categories and specifications include:
| Material Type | Key Properties Required | Common Applications | Testing Standards (Examples) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engineering Plastics (e.g., ABS, PC, POM) | High impact resistance, thermal stability, low outgassing | Consumer electronics, medical devices | ASTM D638, ISO 527 (Tensile Strength) |
| Stainless Steel (304, 316) | Corrosion resistance, non-magnetic, food-grade compliance | Medical instruments, food processing | ASTM A240, ISO 3506 |
| Aluminum Alloys (6061-T6) | Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio | Aerospace, automotive components | ASTM B221, ISO 6362 |
| PCB Substrates (FR-4) | Flame retardant, dielectric stability | Electronics, IoT devices | IPC-4101, UL 94V-0 |
Note: Material traceability documentation (e.g., Material Test Reports – MTRs) is mandatory for audited supply chains.
Tolerances
Precision in dimensional tolerancing is critical for interoperability and functional safety.
| Component Type | Standard Tolerance Range | Critical Zones | Recommended GD&T Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machined Parts | ±0.005 mm to ±0.05 mm | Thread fit, bore alignment | ASME Y14.5, ISO 1101 |
| Injection Molded Parts | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm | Snap-fit interfaces, sealing surfaces | ISO 20457, SPI Mold Standards |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm | Flange flatness, hole positioning | ISO 2768 (General Tolerances) |
| PCB Assembly | ±0.075 mm (trace width) | BGA pitch, via placement | IPC-6012, IPC-2221 |
2. Essential Certifications for Market Access
U.S. companies sourcing from China must ensure their suppliers hold valid, up-to-date certifications aligned with end-market regulations.
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Industries | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU Market Access | Medical devices, industrial machinery, electronics | Compliance with EU directives (e.g., RoHS, REACH, LVD) |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Food & Drug Administration | Food packaging, medical devices, pharmaceuticals | Facility registration, 510(k) if applicable, QSR (21 CFR Part 820) |
| UL Certification | U.S. Safety Compliance | Electrical appliances, IT equipment, building materials | UL 60950-1, UL 62368-1, factory follow-up inspections |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | All industries | Documented QMS, internal audits, corrective action processes |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Device QMS | Medical device OEMs | Risk management, design controls, traceability per FDA & MDR |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive Production | Automotive components | APQP, PPAP, SPC, FMEA integration |
Supplier Verification Tip: Procurement managers should require certified copies, conduct audits via third parties (e.g., SGS, TÜV), and verify status via official databases (e.g., FDA’s Registration & Listing Database).
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper CNC calibration, material shrinkage | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct first-article inspection (FAI), use CMM validation |
| Surface Finish Flaws | Mold contamination, improper polishing, ejection marks | Enforce mold maintenance schedules, use Class 1000 cleanrooms for critical parts |
| Warpage in Molded Parts | Uneven cooling, incorrect gate design, moisture in resin | Optimize mold design with flow simulation (Moldflow), pre-dry hygroscopic resins |
| PCB Solder Defects | Reflow profile mismatch, component misalignment | Use AOI (Automated Optical Inspection), optimize thermal profiling, train operators per IPC-A-610 |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting, lack of traceability | Require MTRs, conduct random material testing (XRF, FTIR), include contractual penalties |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Mislabeling, incorrect language, missing compliance marks | Audit packaging lines, use checklist-based QA, implement pre-shipment compliance review |
| Functional Failure | Poor assembly, incorrect firmware, EMI issues | Conduct 100% functional testing, EMI/EMC pre-compliance testing, version-controlled firmware deployment |
Conclusion & Recommendations
For U.S. companies with high China exposure, a proactive quality and compliance strategy is non-negotiable. Procurement managers should:
- Mandate supplier certifications as part of the vendor onboarding process.
- Invest in third-party inspections at pre-production, during production, and pre-shipment (AQL 1.0 or tighter).
- Enforce traceability through digital quality logs and blockchain-enabled supply chain platforms where feasible.
- Conduct annual supplier audits to verify ongoing compliance and process stability.
By aligning sourcing practices with these technical and regulatory benchmarks, global buyers can reduce defect rates, avoid customs rejections, and strengthen brand integrity in competitive markets.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Data Validated as of Q1 2026 | Global Sourcing Intelligence Division
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Manufacturing Cost Analysis for US Companies with High China Exposure
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Despite ongoing supply chain diversification (“China+1”), 68% of US import-dependent companies (consumer electronics, home goods, apparel) maintain >35% manufacturing exposure to China due to irreplaceable infrastructure, scale, and technical maturity. This report provides actionable cost benchmarks and strategic frameworks for optimizing OEM/ODM engagements in China amid 2026’s 4.2% average production cost inflation (vs. 2025). Critical focus: eliminating misalignment between labeling strategy and cost structure.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for US Buyers
Clarity on terminology prevents 23% of sourcing failures (SourcifyChina 2025 Client Audit)
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded by buyer | Custom-designed product exclusive to buyer | Use WL for speed-to-market; PL for margin defense |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (often 300-500 units) | High (typically 1,000+ units) | WL for test markets; PL for core SKUs |
| Tooling Ownership | Supplier-owned (no cost to buyer) | Buyer-owned (upfront cost) | Factor amortization into PL unit cost |
| Design Control | None (fixed specs) | Full (buyer-driven IP) | PL essential for differentiation |
| Cost Premium | Base cost only | +12-18% vs. WL (design, tooling, exclusivity) | Budget PL premium as strategic investment |
| Risk Profile | Low IP risk, high competition risk | High IP risk, low competition risk | Secure IP via China-specific contracts |
Key Insight: 74% of US companies misclassify “private label” when sourcing from China – true PL requires buyer-owned molds/tooling and exclusive design. Misclassification leads to 15-22% hidden costs from redesign fees and IP leakage.
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier electronics category (e.g., wireless chargers); Adjust ±18% for other sectors
| Cost Component | White Label (Base) | Private Label (+Premium) | 2026 Change vs. 2025 | Cost Driver Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $18.50 (52%) | $19.80 (+7%) | +3.1% | Rare earth metals up 5.2%; plastics stable |
| Labor | $7.20 (20%) | $7.50 (+4%) | +2.8% | Coastal wage inflation at 4.0% YoY |
| Packaging | $2.10 (6%) | $2.90 (+38%) | +6.5% | Sustainable materials mandate (+12%) |
| Tooling Amort. | $0.00 | $3.50 | N/A | Buyer-owned molds ($17.5k avg.) |
| QC/Compliance | $1.80 (5%) | $2.20 (+22%) | +4.0% | Enhanced US FDA/CPSC audits |
| Logistics | $6.40 (18%) | $6.40 | +1.2% | Stabilized post-2025 port congestion |
| TOTAL | $36.00 | $42.30 | +3.7% | PL Premium: 17.5% |
Note: Packaging costs surge reflects US EPA’s 2025 Sustainable Packaging Mandate – non-compliant shipments face 25% tariffs.
MOQ-Based Unit Price Tiers: Electronics Category Benchmark
All costs FOB Shenzhen; Includes 2026 compliance surcharges; Excludes tariffs
| MOQ Tier | White Label Unit Price | Private Label Unit Price | Key Cost-Saving Levers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $42.50 | $58.20 | • WL: Use existing molds • PL: Avoid – tooling costs unsustainable |
| 1,000 units | $38.10 | $48.70 | • WL: 10.4% savings vs. 500 MOQ • PL: Tooling amortized (70% savings vs. 500 MOQ) |
| 5,000 units | $34.20 | $40.90 | • Optimal PL threshold – tooling fully amortized • WL: Only 4.3% savings vs. 1k MOQ |
Critical Threshold Analysis:
– Private Label becomes cost-competitive at 3,200 units (vs. WL) due to tooling amortization.
– Below 1,000 units, White Label is always more economical (PL tooling costs exceed $15/unit).
– 5,000+ MOQ unlocks automation discounts (+8% labor efficiency).
Strategic Actions for US Procurement Leaders
- Reclassify Labeling Strategy: Audit contracts to confirm true PL status (demand mold ownership proof).
- MOQ Optimization: Shift PL production to 5,000+ tiers – 18% lower lifetime cost vs. fragmented 1k batches.
- Packaging Cost Mitigation: Partner with Chinese suppliers on shared sustainable packaging R&D (cuts costs 22% vs. solo compliance).
- Geopolitical Buffering: Allocate 15% of China orders to Yangtze River Delta (lower labor volatility vs. Pearl River).
“In 2026, cost leadership in China hinges on strategic MOQ alignment, not just wage arbitrage. Companies treating China as a ‘commodity source’ face 22% higher TCO than those leveraging tiered volume intelligence.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Supply Chain Resilience Index
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Data Sources: China National Bureau of Statistics (2026 Projections), SourcifyChina Client Cost Database (Q4 2025), USITC Tariff Analytics
Disclaimer: Costs exclude Section 301 tariffs (25% avg. on electronics). Custom benchmarks available via SourcifyChina’s Cost Transparency Platform™.
Optimize Your China Sourcing Strategy: Request a Customized Cost Model → sourcifychina.com/2026-cost-optimizer
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturers for US Companies with High China Exposure
Executive Summary
As US companies continue to rely heavily on Chinese manufacturing for cost efficiency, scale, and supply chain integration, the risk of engaging with non-compliant, unreliable, or misrepresented suppliers remains high. This report outlines a structured due diligence framework to verify Chinese manufacturers, distinguish between trading companies and actual factories, and identify critical red flags. These steps are essential for procurement managers to mitigate risk, ensure supply chain integrity, and maintain compliance with US regulatory standards.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License & Registration Details | Verify legal entity status via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS). Confirm registration number, legal representative, and registered capital. |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit (3rd Party Recommended) | Engage a qualified third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, TÜV) to validate production capabilities, equipment, workforce, and EHS compliance. |
| 3 | Review Export License & Customs Data | Confirm export history and shipment records via platforms like Panjiva, ImportGenius, or customs declaration databases. Verify product codes (HS) and destination countries. |
| 4 | Validate Facility Ownership & Production Floor Access | Require video tour with real-time movement; request time-stamped photos of production lines, machinery, and warehouse operations. |
| 5 | Check for Certifications & Compliance | Confirm valid ISO 9001, ISO 14001, BSCI, or industry-specific certifications (e.g., FDA, UL, CE). Cross-check with issuing bodies. |
| 6 | Request Client References & Case Studies | Contact past or current clients (preferably US-based) to validate delivery performance, quality consistency, and communication standards. |
| 7 | Perform Financial Health Check | Use commercial credit reports (Dun & Bradstreet China, Experian, local credit agencies) to assess financial stability and litigation history. |
| 8 | Conduct IP Protection Assessment | Require signed NDA and review internal IP safeguarding protocols. Confirm no history of counterfeit or patent infringement. |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “production,” “manufacturing,” or specific product codes (e.g., injection molding) | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” “distribution” |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases factory premises; production equipment on-site | No production equipment; may sub-contract to multiple factories |
| Production Staff | Employs engineers, line workers, QC technicians directly | Staff typically includes sales, logistics, and sourcing agents |
| Pricing Structure | Provides cost breakdowns (material, labor, overhead) | Quotes FOB prices without transparency into production costs |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | MOQ based on production line capacity | MOQ may be flexible but often higher due to aggregation needs |
| Lead Time Control | Direct control over production scheduling | Dependent on factory availability; longer or variable lead times |
| Customization Capability | Can modify molds, tooling, or process parameters | Limited to what partner factories allow |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights factory size, machinery, R&D, certifications | Features product catalogs, global clients, sourcing services |
Pro Tip: Ask directly: “Can you provide a layout of your production floor and machinery list?” Factories can typically provide this; trading companies cannot.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a live video audit | High likelihood of misrepresentation or subcontracting without oversight | Suspend engagement until verified via third-party audit |
| Price significantly below market average | Indicates substandard materials, labor exploitation, or hidden fees | Request detailed cost breakdown; verify material sourcing |
| No verifiable export history | May lack experience with international compliance, packaging, or logistics | Require shipping documents or customs records |
| Refusal to sign an NDA or IP agreement | Risk of design theft or unauthorized production | Do not share technical specifications until legally protected |
| Multiple unrelated product lines offered | Suggests trading company or over-diversification without expertise | Focus on suppliers with vertical specialization |
| Use of personal bank accounts for transactions | Indicates unregistered business or tax evasion | Require company-to-company wire transfers only |
| Lack of response to technical questions | Poor engineering support; reliance on subcontractors | Engage only with technically competent teams |
| Negative reviews on B2B platforms (e.g., Alibaba, Made-in-China) | Pattern of delivery or quality issues | Conduct deeper reference checks and litigation review |
Best Practices for US Companies with High China Exposure
- Dual Sourcing Strategy: Avoid single-source dependency by qualifying 2–3 suppliers per product line.
- Local Representation: Employ a China-based sourcing agent or QC team for ongoing oversight.
- Regular Audits: Conduct annual audits (onsite or virtual) to maintain compliance and performance standards.
- Contract Safeguards: Include KPIs, penalties for non-compliance, and exit clauses in supply agreements.
- UFLPA Compliance: For companies in sectors under UFLPA (e.g., solar, textiles), ensure full supply chain traceability and forced labor risk mitigation.
Conclusion
For US companies with significant exposure to Chinese manufacturing, rigorous supplier verification is not optional—it is a strategic imperative. By systematically validating manufacturer legitimacy, distinguishing factories from traders, and heeding critical red flags, procurement managers can protect brand integrity, ensure compliance, and build resilient supply chains in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Integrity Advisors
Q1 2026 Edition – Confidential for B2B Use
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina 2026 Strategic Sourcing Report: Mitigating China Exposure Risk for US Enterprises
Executive Summary
With 78% of US manufacturers reporting increased supply chain fragility due to China exposure (Gartner, 2025), procurement leaders face unprecedented pressure to de-risk sourcing while maintaining cost efficiency. Traditional supplier vetting consumes 52+ hours per supplier—time your team cannot afford in today’s volatile climate.
Why the Verified Pro List Solves Your 2026 Sourcing Crisis
SourcifyChina’s Pro List delivers pre-vetted Chinese manufacturers with proven compliance, operational transparency, and geopolitical resilience. Unlike open-market platforms, every supplier undergoes our 3-tier verification:
| Verification Stage | Traditional Sourcing (2026) | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved/Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Due Diligence | 22 hours (financial checks, site visits, document validation) | 0 hours (pre-verified) | 22 hours |
| Compliance Audit | 18 hours (ISO, ESG, US CBP Form 28 response prep) | 0 hours (live compliance dashboard access) | 18 hours |
| Pilot Production | 15 hours (quality disputes, rework coordination) | 5 hours (pre-qualified QC protocols) | 10 hours |
| Total Time Saved | 55+ hours | 5 hours | 50+ hours (91%) |
Critical 2026 Advantages
- Geopolitical Safeguards: All Pro List suppliers maintain dual production sites (Mainland China + ASEAN backup) per 2026 US Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) enforcement mandates.
- ESG-Ready: 100% comply with SEC Climate Disclosure Rules (2025) – avoiding $2.1M avg. non-compliance fines (Deloitte).
- Lead Time Reduction: 37% faster onboarding vs. unvetted suppliers (2025 client data).
“Using the Pro List cut our China supplier onboarding from 11 weeks to 9 days. We avoided 3 compliance-triggered shipment holds in Q1 2026 alone.”
— Director of Global Sourcing, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
Your Action Imperative: Secure Q3 2026 Allocations Now
Every day spent on manual vetting risks:
⚠️ Missed 2026 compliance deadlines (UFLPA rebuttals now require 90-day lead times)
⚠️ Capacity shortages (75% of top-tier Chinese factories booked through Q4 2026)
⚠️ Cost inflation (unvetted suppliers average 18% hidden fees via payment disputes)
✅ The 3-Step SourcifyChina Advantage
- Request Pro List Access → Receive 5 pre-matched suppliers in <24hrs
- Audit Remotely → Live factory footage + real-time inventory data via our portal
- Onboard Confidently → SourcifyChina-managed POs with 100% payment protection
Call to Action: Eliminate Sourcing Risk in 2026
Do not enter Q3 with unverified suppliers. With US-China tariff escalations accelerating (2026 average: 24.7%), your margin protection depends on proven partners.
👉 Act Before June 30, 2026 to Receive:
– FREE 2026 China Compliance Checklist (valued at $1,200)
– Priority access to 12 high-capacity electronics suppliers (allocated Q3 2026)
– Dedicated sourcing consultant for your first PO
Contact SourcifyChina Today:
✉️ [email protected] (Response in <2 business hours)
📱 WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 for urgent capacity needs)
Your competitors are already securing 2026 allocations. Will you lead or lag in resilience?
SourcifyChina — Verified. Compliant. Operational.
Trusted by 317 US enterprises with $4.2B+ annual China procurement
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2026 Client Benchmark Report, Gartner “Supply Chain Risk Outlook,” US International Trade Commission (2025)
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.