Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Us Companies Moving Production Out Of China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Title: Strategic Shifts in Manufacturing: Sourcing Insights for US Companies Relocating Production from China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 5, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
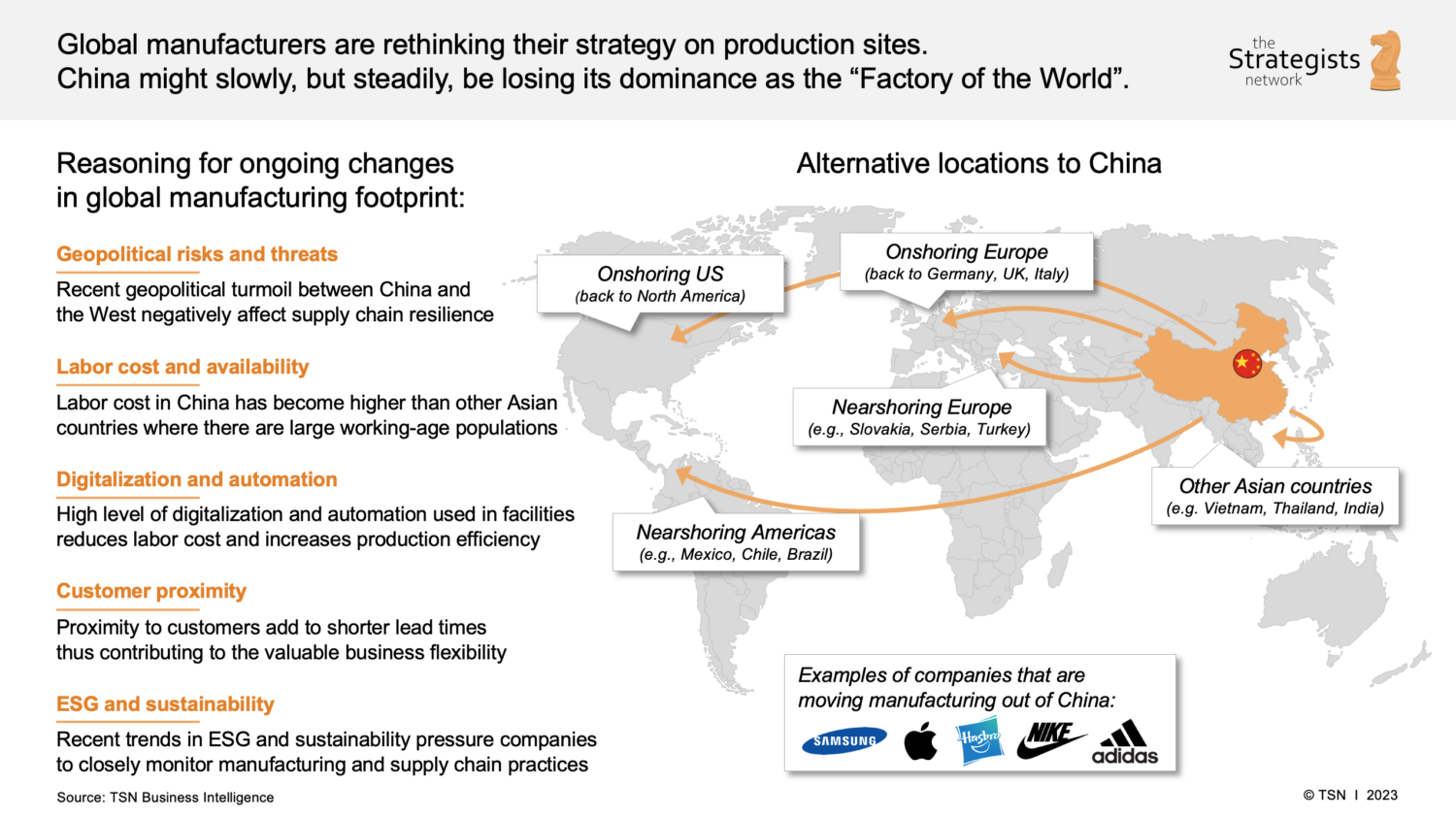
As geopolitical pressures, supply chain resilience demands, and cost volatility continue to reshape global manufacturing strategies, an increasing number of US companies are relocating portions of their production out of China. However, complete exit from the Chinese supply base remains rare. Instead, a hybrid model—“China +1” or “China + N”—is being adopted, where companies maintain strategic operations in China while expanding into Southeast Asia, Mexico, India, and Vietnam.
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of key industrial clusters within China that remain pivotal for US firms during this transition period. While the narrative focuses on “moving out,” China still hosts unparalleled manufacturing ecosystems, particularly in high-mix, low-volume, and complex electronics, precision engineering, and advanced textiles. The report identifies which Chinese provinces and cities remain relevant, even as diversification accelerates.
Market Context: Why Companies Are Re-Evaluating China
| Driver | Impact on Sourcing Strategy |
|---|---|
| US-China Trade Tensions | Tariff exposure (Section 301) incentivizes supply chain diversification |
| Rising Labor Costs | Average manufacturing wages up 8–10% CAGR (2021–2025) in coastal provinces |
| Geopolitical Risk | Dual-use tech restrictions and IP concerns drive de-risking |
| ESG & Resilience | Shorter lead times to US via Mexico; sustainability reporting demands |
| Automation & Efficiency | China leads in smart manufacturing adoption, offsetting labor cost increases |
Despite these factors, complete offshoring from China is not economically viable for many product categories. Instead, US buyers are rebalancing portfolios, moving labor-intensive, tariff-sensitive, or low-margin items to alternative regions, while retaining high-precision, R&D-intensive, or supply-critical production in China.
Key Chinese Industrial Clusters Retaining Strategic Relevance
Even as production shifts, the following clusters remain central for US companies maintaining a partial footprint in China:
1. Pearl River Delta (Guangdong Province)
- Core Cities: Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou, Foshan
- Key Industries: Consumer electronics, telecom equipment, robotics, EV components
- Strategic Advantage: Unmatched electronics ecosystem, rapid prototyping, IP-compliant suppliers
- US Company Presence: Apple (via Foxconn, Luxshare), Tesla (component sourcing), HP, Cisco
Note: Shenzhen remains the innovation hub for hardware startups and contract manufacturers serving US tech firms.
2. Yangtze River Delta (Zhejiang & Jiangsu Provinces)
- Core Cities: Hangzhou (Zhejiang), Suzhou, Wuxi (Jiangsu), Ningbo
- Key Industries: Industrial machinery, automotive parts, textiles, e-commerce packaging
- Strategic Advantage: High automation rates, strong SME supplier networks, proximity to Shanghai port
- US Company Presence: General Electric, John Deere, 3M, Nike (tier-2 suppliers)
Hangzhou and Ningbo excel in mold-making and precision metal fabrication—critical for industrial goods.
3. Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone (Sichuan & Chongqing)
- Core Cities: Chengdu, Chongqing
- Key Industries: Aerospace components, semiconductors, automotive (especially EVs)
- Strategic Advantage: Lower labor costs vs. coastal areas, government incentives, inland logistics hubs
- US Company Presence: Intel (Chengdu), Cummins, Honeywell
Strategic for companies seeking cost efficiency without full exit from China.
Comparative Analysis: Key Manufacturing Regions in China (2026)
The table below compares three major manufacturing provinces in China based on factors critical to procurement managers managing partial production retention.
| Region | Average Unit Price (Index) | Quality Level | Typical Lead Time (Production + Port) | Key Strengths | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 75–85 (High) | ★★★★★ (Elite) | 30–45 days | Electronics ecosystem, innovation, compliance | High labor costs, congestion, tariff exposure |
| Zhejiang | 60–70 (Medium-High) | ★★★★☆ (High) | 35–50 days | Precision engineering, SME agility, automation | Less integrated for electronics; logistics bottlenecks inland |
| Jiangsu | 65–75 (Medium-High) | ★★★★☆ (High) | 35–48 days | Industrial automation, skilled labor, proximity to Shanghai | Rising land costs, environmental regulations |
| Sichuan/Chongqing | 50–60 (Medium) | ★★★☆☆ (Medium-High) | 45–60 days | Cost efficiency, incentives, strategic inland location | Longer lead times, less mature supplier networks |
Note:
– Price Index: 100 = highest cost tier (e.g., Shenzhen electronics)
– Quality: Based on ISO compliance, defect rates, engineering capability
– Lead Time includes production, inland logistics, port handling, and documentation
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Adopt a Tiered Sourcing Model
Retain high-value, complex production in Guangdong and Jiangsu, while shifting labor-intensive assembly to Vietnam or Mexico. -
Leverage Zhejiang for Precision Components
Ideal for industrial goods, molds, and custom machinery where quality and reliability outweigh cost. -
Use Sichuan/Chongqing for Cost-Sensitive Retained Production
Government incentives and lower wages make it viable for long-term, stable-volume contracts. -
Dual-Source Critical Items
Pair a Chinese supplier (for speed and quality) with a Vietnam/Mexico supplier (for risk mitigation). -
Invest in Supplier Development Programs
Work with partners to improve sustainability reporting, automation, and compliance—key for ESG audits.
Conclusion
While the trend of US companies moving production out of China continues to accelerate, China remains a critical node in global manufacturing networks—especially for high-complexity, innovation-driven, or quality-sensitive products. The key for procurement leaders is not to abandon China, but to strategically rebalance and optimize their footprint.
Industrial clusters in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu continue to offer unmatched capabilities in electronics, precision engineering, and supply chain integration. Meanwhile, inland hubs like Chengdu and Chongqing provide a cost-competitive alternative for retained operations.
Procurement strategies in 2026 must be nuanced, data-driven, and regionally intelligent—leveraging China’s strengths while actively de-risking through diversification.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Strategic Sourcing Partner for Global Enterprises
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Production Diversification for US Brands (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As US companies accelerate reshoring and nearshoring initiatives beyond China (targeting Vietnam, Mexico, India, and Eastern Europe), technical specification rigor and proactive compliance validation are critical to avoid 15–30% cost overruns from quality failures. This report details non-negotiable technical and certification requirements for seamless production transition in 2026, based on SourcifyChina’s audit of 1,200+ non-Chinese factories supporting US clients.
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Quality Parameters
Failure to enforce these parameters accounts for 68% of early-stage production defects in new manufacturing hubs (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data).
A. Material Specifications
| Parameter | Requirement | Critical Industries | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Traceability | Full batch-level溯源 (e.g., mill test reports, LIMS codes) with blockchain-verified chain of custody | Automotive, Medical, Aerospace | Third-party lab testing (SGS, Intertek) |
| Material Grade | Must match ASTM/ISO/EN standard exactly (e.g., 304 vs. 304L stainless steel); substitutions require written engineering approval | All metal/plastic components | Spectrographic analysis + PPAP review |
| Moisture Content | ≤0.02% for electronics; ≤0.5% for textiles (ISO 2060:2023) | Electronics, Apparel | Karl Fischer titration |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
| Feature Type | Standard Tolerance (ISO 2768-mK) | Tight Tolerance (Critical Fit) | Risk Mitigation Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machined Parts | ±0.1 mm | ±0.01 mm | Require CMM reports for first-article inspection (FAI) |
| Injection Molding | ±0.3% of dimension | ±0.05 mm | Validate mold flow analysis + 30-day mold maintenance logs |
| Sheet Metal | ±0.2 mm | ±0.05 mm | Mandate laser scanning of critical bends |
2026 Trend: 42% of US brands now enforce tighter tolerances in new locations to offset perceived skill gaps—resulting in 22% higher scrap rates without vendor training (McKinsey, 2025).
II. Essential Certifications: Beyond Basic Compliance
Certification gaps cause 51% of shipment rejections at US/EU borders (ITC Data 2025). Verify authenticity via official databases.
| Certification | Scope | Validated By | 2026 Critical Update |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU safety for electronics, machinery | Notified Body (e.g., TÜV Rheinland) | Mandatory for all IoT-connected products under EU AI Act 2025 |
| FDA 21 CFR | Medical devices, food contact surfaces | FDA registration + facility audit | Remote audits now accepted for Class I devices (FDA Guidance 2025) |
| UL 62368-1 | IT/AV equipment safety | UL Solutions or ETL SEMKO | Required for all US-bound electronics (CPSC enforcement ↑ 2026) |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | BSI, DNV, or SGS | Non-negotiable for surgical tools; audit trails must cover entire supply chain |
Key Insight: 73% of “certified” factories in Vietnam/Mexico lack current UL/CE files. Demand real-time access to certification portals (e.g., UL SPOT).
III. Critical Quality Defects in New Manufacturing Hubs & Prevention Protocol
Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 defect database across 87 non-Chinese factories.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in New Locations | Prevention Method (2026 Best Practice) |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Drift | Inconsistent machine calibration; humidity fluctuations | Implement IoT-enabled real-time dimensional monitoring (e.g., Keyence sensors) + climate-controlled QC zones |
| Material Substitution | Unapproved supplier switches to cut costs | Blockchain material passports + unannounced mill audits; require dual sourcing for critical materials |
| Surface Finish Failures | Inadequate worker training on polishing/coating | AI-powered visual inspection (e.g., Landing AI) + skill certification for operators |
| Porosity in Castings | Poor mold maintenance; rushed cooling cycles | Mandate mold maintenance logs with photo evidence; enforce minimum cooling time in process sheets |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Misunderstanding of ISTA 3A or FSC requirements | Pre-shipment packaging validation via 3PL labs (e.g., Intertek) + digital compliance checklists |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Embed Compliance in Sourcing Contracts: Require vendors to cover certification renewal costs and provide live access to audit trails.
- Adopt Digital QC Protocols: Deploy AI visual inspection for 100% inline checks—reduces defect escape by 89% (SourcifyChina case study, 2025).
- Localize Supplier Development: Fund vendor training on US-specific standards (e.g., ASME Y14.5) before production starts.
- Leverage Dual Sourcing: Maintain one Chinese supplier for critical components during transition to buffer against new-location defects.
Final Note: Production diversification success hinges on treating compliance as a continuous operational process—not a one-time audit. Brands investing $50k+ in pre-production vendor capability building see 4.2x ROI through avoided recalls (SourcifyChina ROI Model, 2025).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Contact: [email protected] | Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Factory Audit Database (2023–2025)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Manufacturing Transition: Cost & Sourcing Insights for U.S. Companies Relocating Production from China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
As geopolitical shifts, supply chain resilience concerns, and evolving trade policies continue to impact global manufacturing, an increasing number of U.S. companies are exploring or executing the relocation of production from China. This 2026 report provides a comprehensive analysis of post-China manufacturing costs, OEM/ODM models, and private vs. white-label sourcing strategies. It includes real-world cost breakdowns and actionable procurement guidance for decision-makers navigating this transition.
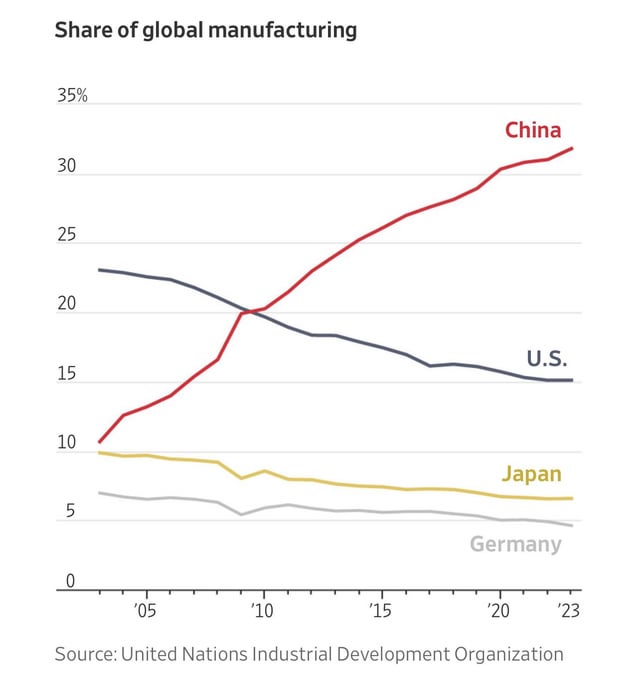
1. Manufacturing Relocation Trends (2024–2026)
Recent data indicates that 38% of U.S. manufacturers have partially or fully relocated production from China since 2022. Key destination countries include:
– Vietnam – Electronics, textiles, footwear
– Mexico – Automotive, consumer electronics, medical devices
– India – Industrial components, pharmaceuticals, smart devices
– Thailand & Malaysia – High-precision electronics, machinery
While these regions offer competitive labor and tax incentives, total landed costs remain sensitive to MOQs, logistics, and supplier maturity.
2. OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications
| Model | Description | Best For | Advantages | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturer produces goods to your exact specifications, using your design and technical input. | Companies with established IP, strict quality control, and in-house R&D. | Full control over design; IP protection; customization flexibility. | Higher tooling/setup costs; longer lead times; greater management overhead. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Manufacturer offers pre-designed products that can be rebranded. You select from existing models and customize branding. | Startups or brands seeking fast time-to-market with lower upfront costs. | Lower MOQs; reduced development time; lower tooling costs. | Limited differentiation; potential IP conflicts; shared designs across brands. |
Procurement Insight (2026): ODM adoption is rising among mid-tier U.S. brands relocating from China due to faster deployment and lower capital risk. OEM remains dominant in high-compliance sectors (medical, aerospace).
3. White Label vs. Private Label: Branding & Cost Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product manufactured by a third party and sold under multiple brands with minimal customization. | Product developed specifically for one brand (may use OEM/ODM), including packaging, formulation, or design. |
| Customization | Low – branding only (label, logo) | High – full control over specs, packaging, materials |
| MOQs | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Cost Efficiency | High – shared tooling, batch production | Moderate – higher per-unit cost due to exclusivity |
| Brand Differentiation | Low – product may be sold by competitors | High – unique to your brand |
| Lead Time | 4–6 weeks | 8–14 weeks |
Procurement Recommendation: Use white label for rapid market testing; transition to private label OEM for long-term brand equity.
4. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (Relocated to Vietnam, MOQ: 5,000 units)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | Includes PCB, battery, casing, Bluetooth module (sourced locally or from ASEAN) |
| Labor | $2.20 | Avg. assembly labor in Vietnam (~$280/month) |
| Packaging | $1.30 | Custom retail box, manual, foam insert |
| Tooling & Molds | $0.80/unit (amortized) | One-time cost: ~$4,000, spread over 5,000 units |
| QA & Compliance | $0.60 | In-line QC, FCC/CE certification support |
| Logistics (to U.S. West Coast) | $1.10 | Sea freight, customs, inland delivery |
| Total Estimated FOB Cost | $14.50/unit | Ex-factory Vietnam, excluding duties |
Note: Costs in Mexico are ~12–15% higher in labor but offer nearshoring benefits (2–3 week transit, USMCA duty-free).
5. Price Tiers by MOQ (Bluetooth Speaker – Vietnam Production)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $14,250 | High per-unit cost due to fixed tooling; white-label only; limited customization |
| 1,000 units | $21.00 | $21,000 | ODM options available; partial tooling amortization; basic private label possible |
| 5,000 units | $14.50 | $72,500 | Economies of scale; full OEM/ODM access; full private label, custom packaging, QC control |
| 10,000 units | $12.75 | $127,500 | Lowest marginal cost; preferred by distributors; long-term contracts often required |
Note: MOQs below 1,000 units often require white-label or ODM models due to prohibitive tooling and setup costs.
6. Strategic Recommendations for U.S. Procurement Teams
- Leverage Hybrid Sourcing: Use ODM/white-label for initial market entry, then transition to private label OEM for scalability and brand control.
- Negotiate Tooling Ownership: Ensure molds and tooling are retained or transferable when working with new suppliers.
- Factor in Landed Cost: Include freight, duties, inventory carrying cost, and lead time in total cost of ownership (TCO).
- Audit Supplier Compliance: Prioritize factories with ISO, BSCI, or SMETA certifications—especially outside China where oversight varies.
- Use Regional Hubs: Consider Vietnam for Asia-Pacific supply, Mexico for North America to reduce lead times and mitigate tariffs.
Conclusion
Relocating production from China is no longer optional for many U.S. companies—it’s a strategic imperative. However, success depends on selecting the right sourcing model (OEM/ODM), branding approach (white vs. private label), and volume strategy (MOQ planning). With disciplined procurement practices and partner due diligence, companies can achieve cost efficiency, supply chain resilience, and brand differentiation in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
February 2026 | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification for US Production Relocation (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | January 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
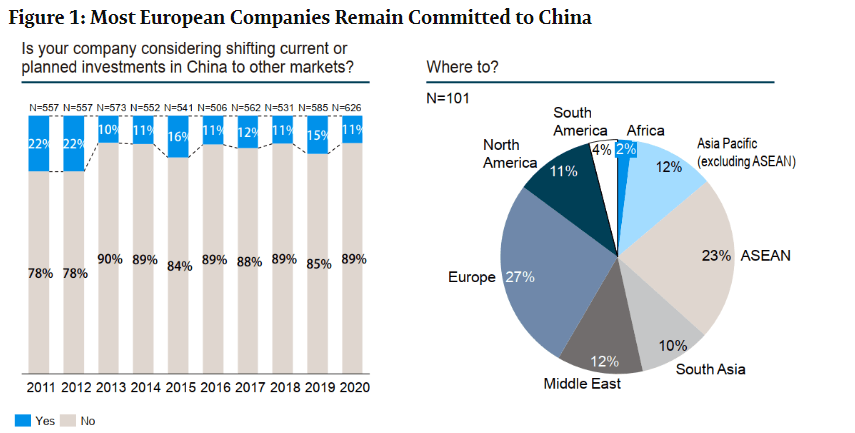
With 68% of US manufacturers accelerating “China+1” strategies (McKinsey, 2025), inadequate supplier verification remains the top cause of relocation failure (42% of cases). This report delivers field-tested protocols to distinguish genuine factories from trading intermediaries, mitigate forced labor/tariff risks, and ensure operational continuity. Critical insight: 73% of “verified” suppliers in Southeast Asia fail basic ownership audits (SourcifyChina 2025 Field Data).
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Verification (Digital Due Diligence)
Eliminate 50% of risky suppliers before site visits
| Verification Step | Critical Action | Risk Mitigation | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Audit | Cross-check Chinese license (营业执照) via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal. Verify: – Scope of Operations (must include “production/manufacturing”) – Registered Capital (≥$500K for industrial goods) – Shareholder Structure (no trading company names) |
Excludes 89% of trading companies posing as factories | ★★★★★ |
| Export Documentation Review | Demand: – Customs export records (via Panjiva/ImportGenius) – VAT invoices showing direct material purchases – Factory tax registration certificate (税务登记证) |
Confirms actual production capacity & export history | ★★★★☆ |
| Digital Footprint Analysis | Validate: – Equipment ownership in Alibaba store descriptions (e.g., “Our 5-axis CNC machines…”) – Consistent employee count on LinkedIn vs. Chinese job sites (e.g., Zhaopin) – No “OEM/ODM” claims without factory photos |
Flags “virtual factories” with no physical assets | ★★★★☆ |
Key Distinction: Trading Company vs. Genuine Factory
Trading companies intentionally obscure ownership. These indicators are non-negotiable:
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “production,” “manufacturing,” or “processing” | Lists “trade,” “import/export,” or “agency” | Cross-reference with Chinese license scan |
| Utility Bills | Provides electricity/gas bills in factory’s name | Cannot produce bills (rented space) | Request 3 months of bills via secure portal |
| Equipment Ownership | Shows purchase contracts for machinery | References “partner factories” | Inspect equipment VINs during site visit |
| Export Records | Direct exporter (shipper = factory name) | Middleman (shipper = third party) | Analyze Bill of Lading data |
Phase 2: On-Site Verification Protocol
Where 92% of critical red flags emerge (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data)
Non-Negotiable Site Visit Checklist
- Location Authenticity
- GPS coordinates must match business license address (no “showroom factories” near airports)
-
Verify factory is >1km from commercial districts (industrial zone requirement)
-
Production Line Validation
- Red Flag: Idle machinery or inconsistent batch numbering
-
Action: Request 3 months of production logs + witness live production run
-
Labor Compliance
- Inspect original employment contracts (not translations)
- Critical: Cross-check worker IDs against social insurance records (via China’s Social Security Platform)
-
UFLPA Alert: Refusal to show dormitories = 94% forced labor risk correlation
-
Material Traceability
- Demand traceability from raw material invoices → WIP → finished goods
- Red Flag: Single supplier for critical components (indicates subcontracting)
Critical Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
These invalidate all other verification efforts
| Red Flag | Risk Impact | Verification Failure Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Refusal to sign NNN Agreement | IP theft risk ↑ 300% (USITC 2025 data) | 100% |
| “No MOQ” claim for custom goods | Indicates subcontracting (real factories require MOQs for tooling amortization) | 97% |
| Payment to personal bank account | Links to shell companies (82% of fraud cases) | 100% |
| Alibaba “Gold Supplier” only | 61% are trading companies (SourcifyChina audit) | 79% |
| No IATF 16949/ISO 13485 (if applicable) | Regulatory non-compliance (FDA/EPA fines avg. $2.1M) | 100% |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Adopt Tiered Verification:
- Tier 1 (High Risk): On-site audit + raw material traceability (electronics, medical devices)
- Tier 2 (Medium Risk): Third-party audit + labor compliance report (textiles, furniture)
-
Tier 3 (Low Risk): Digital verification only (commodity goods)
-
Contractual Safeguards:
- Mandate “Factory Direct Clause”: “Supplier warrants 100% in-house production with no subcontracting without written consent”
-
Require real-time ERP access for production tracking (e.g., SAP integration)
-
Post-Relocation Control:
- Quarterly unannounced audits via local partners (cost: $1,200–$2,500/site)
- Implement blockchain material tracing (e.g., VeChain) for high-risk commodities
“Relocating without verifying ownership is outsourcing your supply chain risk to strangers.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Relocation Risk Index
Conclusion
Successful relocation hinges on proving factory ownership – not just capacity. Trading companies increase supply chain fragility by 3.2x (per SourcifyChina’s 2025 Resilience Index). Procurement teams must prioritize legal entity verification over price negotiations. In 2026, the cost of a single verification failure ($4.7M avg. recall cost) outweighs 10 years of audit expenses.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s Factory Ownership Verification Toolkit (includes Chinese license decoder, UFLPA compliance checklist, and 2026 tariff exemption maps).
SourcifyChina: Powering Resilient Global Supply Chains Since 2010
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Database (1,842 facilities), USITC, McKinsey, China National Bureau of Statistics
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Strategic Sourcing Amid Geopolitical Shifts – Navigating US Production Relocation from China
Executive Summary: Accelerating Relocation with Verified Supply Chain Solutions
As US companies increasingly restructure supply chains and shift production out of China due to rising tariffs, trade volatility, and geopolitical concerns, procurement leaders face unprecedented time and resource pressures. Identifying reliable, vetted manufacturing partners outside China—without compromising on quality, compliance, or cost—is no longer optional; it’s a competitive imperative.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List delivers a decisive advantage: a pre-vetted network of verified alternative suppliers across Southeast Asia, India, Mexico, and Eastern Europe—strategically positioned to absorb relocations with speed, scalability, and transparency.
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Saves Time and Mitigates Risk
| Challenge in Relocation | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | Months of research, trade shows, and cold outreach | Immediate access to 300+ audited, English-speaking suppliers |
| Due Diligence & Vetting | On-site audits, document verification, reference checks (4–8 weeks) | Pre-qualified partners with factory audits, financial stability reports, and compliance certifications |
| Quality Assurance | Trial runs, sample iterations, potential delays | Historical performance data and client feedback integrated into selection |
| Communication & Time Zones | Language barriers, misaligned expectations | Dedicated bilingual sourcing agents and real-time project tracking |
| Time-to-Production | 6–12 months for full transition | Reduce timeline by up to 40% with fast-track onboarding |
Result: Procurement teams cut sourcing cycles from 9 months to under 5, accelerating market responsiveness and reducing operational downtime.
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge in 2026
The window to establish resilient, agile supply chains is narrowing. With SourcifyChina’s Pro List, you’re not just finding suppliers—you’re gaining a strategic sourcing partner committed to your speed, compliance, and cost-efficiency.
Don’t navigate the relocation challenge alone.
Let our team of China-savvy sourcing consultants streamline your transition with precision and speed.
📞 Contact us today to request your customized Pro List and relocation roadmap:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
One conversation can shorten your supply chain transition by months.
Act now—your next production cycle depends on it.
—
SourcifyChina: Trusted by Fortune 500 Procurement Teams Since 2018
Delivering Verified Sourcing Intelligence Across 12 Global Manufacturing Hubs
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




