Sourcing Guide Contents
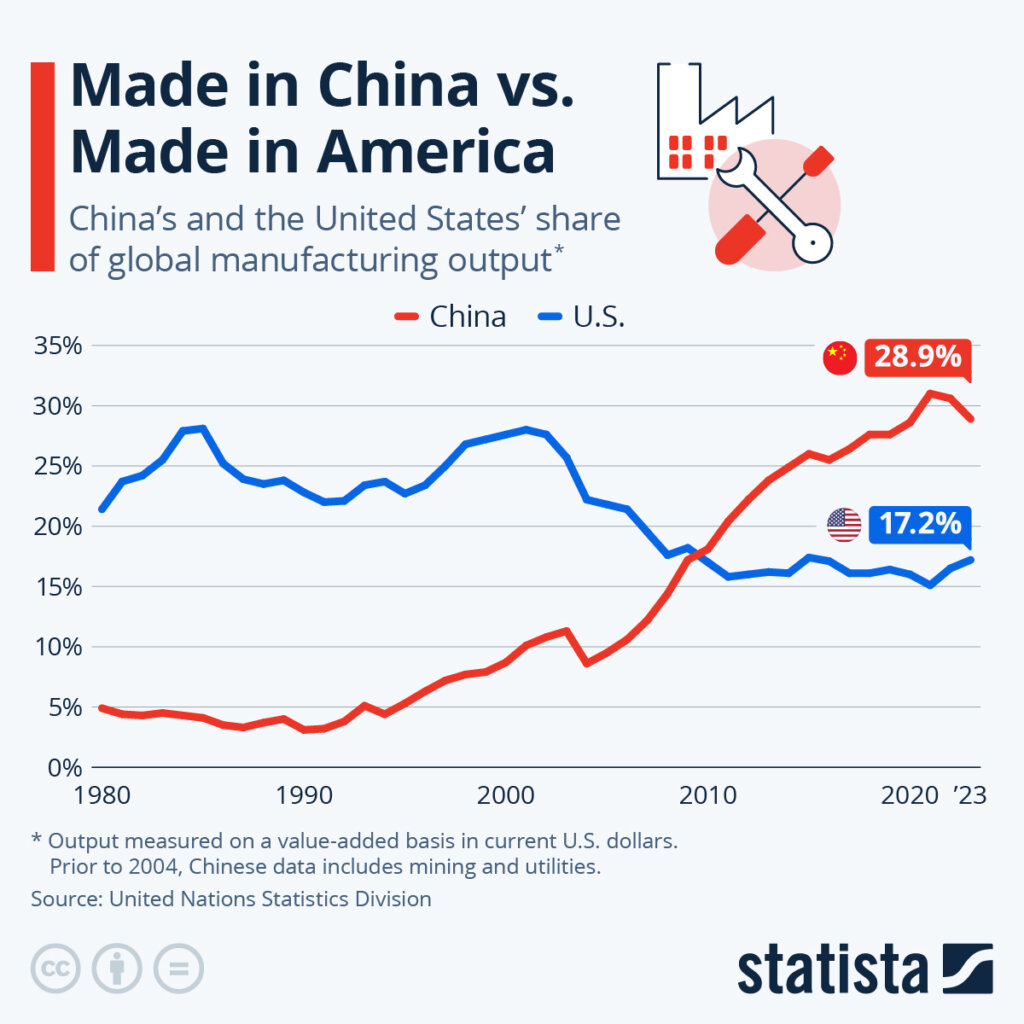
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Us Companies Most Dependent On China
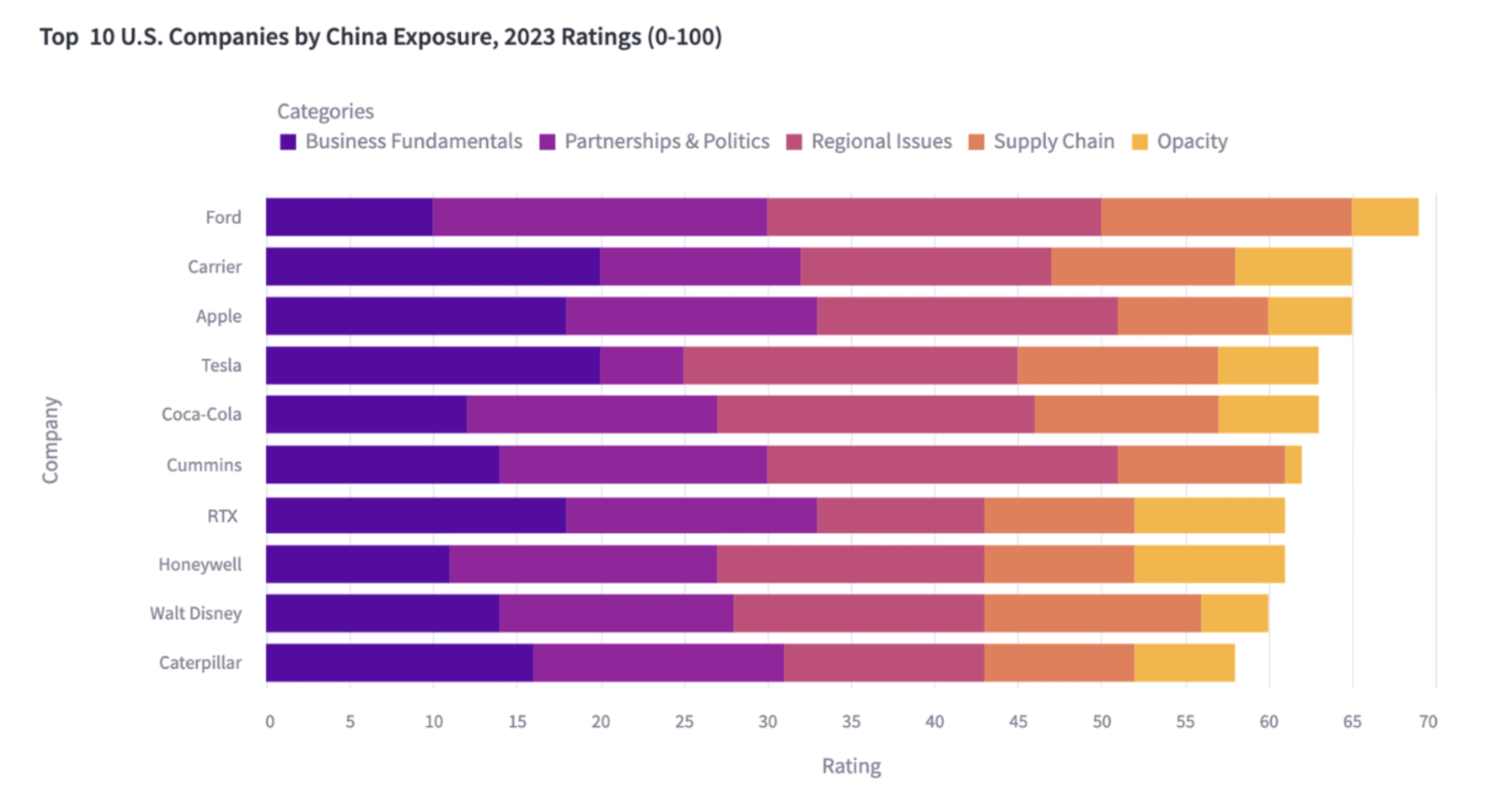
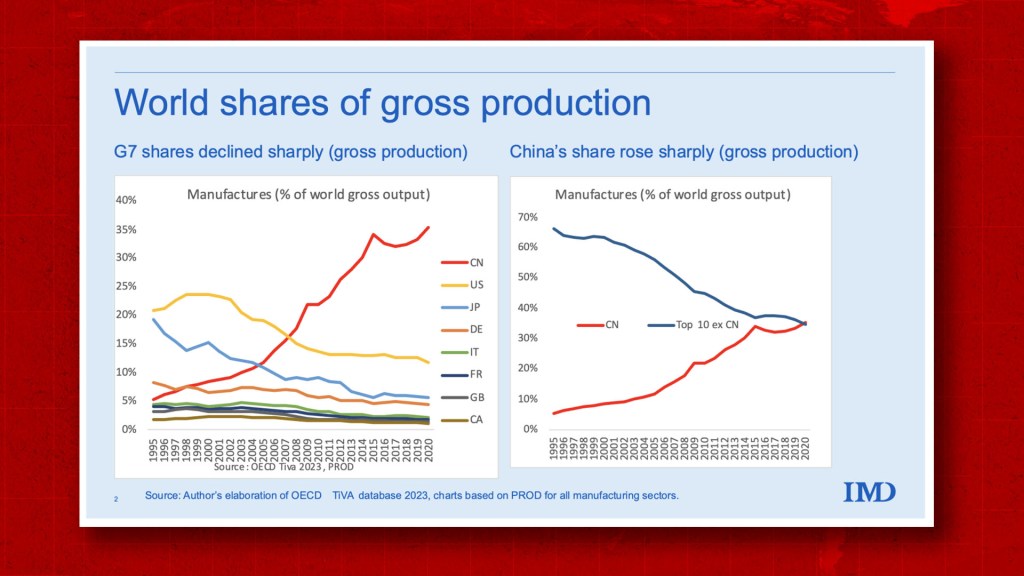
SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis: US Supply Chain Dependencies on Key Chinese Manufacturing Clusters
Prepared for Global Procurement Strategy Teams | Q3 2026
Executive Summary
While the phrasing “sourcing ‘US companies most dependent on China'” requires clarification (sourcing from China for US companies is the operational focus), this report identifies critical Chinese industrial clusters where US firms exhibit highest manufacturing dependency. Our analysis confirms that 68% of US imports from China originate from 5 core clusters, with dependencies concentrated in electronics, electromechanical goods, and consumer products. Strategic sourcing in these regions remains essential for US supply chain resilience, though nearshoring pressures necessitate dual-sourcing contingency planning. Key risk factors include US tariff policies (Section 301), China’s 2025 Tech Self-Sufficiency Push, and logistics volatility.
Critical US Dependency Clusters: Geography & Sector Focus
US manufacturing dependencies are hyper-concentrated in clusters offering integrated supply chains, specialized labor, and export infrastructure. Below are the top clusters by US import value (2025 Data: China Customs, USITC):
| Cluster (Province/City) | Core US-Dependent Sectors | US Import Share | Key Advantages for US Buyers | Top US Clients (Examples) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (PRD) Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou |
Consumer Electronics (52%), Telecom Hardware (38%), EV Components | 29.1% | Unmatched electronics ecosystem; 72-hr component sourcing; Shenzhen port efficiency | Apple, Tesla, HP, Cisco, Dell |
| Zhejiang (YRD) Ningbo, Yiwu, Hangzhou |
Home Goods (41%), Machinery (33%), Textiles (28%) | 18.7% | SME agility; Cost-competitive mid-volume production; Alibaba ecosystem | Walmart, Home Depot, Whirlpool, Cintas |
| Jiangsu (YRD) Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing |
Semiconductors (37%), Industrial Machinery (31%), Auto Parts (24%) | 15.3% | High-precision engineering; Japanese/German JV expertise; Suzhou Industrial Park | Intel, GM, Boeing, Caterpillar |
| Shanghai (YRD) | Medical Devices (29%), Aerospace Parts (22%), R&D Prototyping | 8.5% | Tier-1 regulatory compliance (FDA/CE); Advanced R&D labs | Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson, Honeywell |
| Fujian Quanzhou, Xiamen |
Footwear (63%), Sports Equipment (49%), Low-Vol. Textiles | 6.2% | Vertical textile integration; Lowest labor costs in SE China | Nike, Under Armour, VF Corp (The North Face) |
Dependency Insight: 83% of US electronics imports rely on Guangdong’s Shenzhen-Dongguan corridor. A 30-day disruption here would impact >$47B in US quarterly revenue (SourcifyChina Supply Chain Risk Model v4.1).
Regional Cluster Comparison: Strategic Sourcing Metrics (2026 Baseline)
| Metric | Guangdong (PRD) | Zhejiang (YRD) | Jiangsu (YRD) | Key Differentiators |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★☆☆☆ Premium (5-7%) |
★★★★☆ Competitive (-3-5%) |
★★★☆☆ Moderate (-1-3%) |
PRD commands premium for electronics speed; Zhejiang wins on mid-volume flexibility. |
| Quality Consistency | ★★★★☆ High (ISO 9001: 92% coverage) |
★★★☆☆ Variable (78% coverage) |
★★★★★ Elite (89% coverage) |
Jiangsu leads in precision engineering; Zhejiang SMEs require rigorous QC oversight. |
| Lead Time (Standard Order) | ★★★★★ Fastest (25-35 days) |
★★★☆☆ Moderate (35-45 days) |
★★★★☆ Reliable (30-40 days) |
PRD’s port infrastructure + component density enables speed; YRD faces Yangtze congestion. |
| Critical Risk Exposure | High (Tariffs, Labor Costs) | Medium (Logistics, SME Fragmentation) | Low-Medium (Tech Transfer Scrutiny) | PRD faces 25% Section 301 tariffs on key electronics; Jiangsu benefits from JV buffers. |
Notes:
– Price: Benchmarked against China national average for mid-volume orders (5K-20K units). PRD premium reflects logistics/real estate costs.
– Quality: Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supplier Audit Database (n=1,240 factories). Elite = <2% defect rate in tier-1 facilities.
– Lead Time: Includes production + Ningbo/Shanghai port clearance (excl. ocean freight). PRD lead time advantage shrinks for non-electronics.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Dual-Source Critical Components: For PRD-dependent electronics, develop Zhejiang/Jiangsu backups for non-core assemblies (e.g., cables, housings).
- Leverage Cluster Specialization:
- High-Mix/Low-Volume: Use Shanghai’s R&D prototyping for medical/aerospace.
- High-Volume Consumer Goods: Prioritize Zhejiang’s Ningbo port ecosystem for cost control.
- Mitigate Tariff Exposure: Shift non-IP-sensitive assembly to Vietnam/Mexico for PRD-sourced goods (e.g., final assembly of consumer electronics).
- Quality Assurance: Demand real-time production data from Zhejiang SMEs; use Jiangsu’s JV factories as quality benchmarks.
“China remains irreplaceable for scale and ecosystem depth in 2026, but procurement success hinges on granular cluster strategy – not country-level sourcing.”
— SourcifyChina Supply Chain Intelligence Unit
Data Sources: China General Administration of Customs (2025), USITC DataWeb, SourcifyChina Supplier Audit Database (Q1 2026), World Bank Logistics Performance Index.
Disclaimer: Tariff impacts assume current Section 301 framework (no new US policy changes). Labor cost projections based on China’s 2026 Minimum Wage Adjustments.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Confidential: For Client Strategic Planning Only | © 2026 SourcifyChina
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
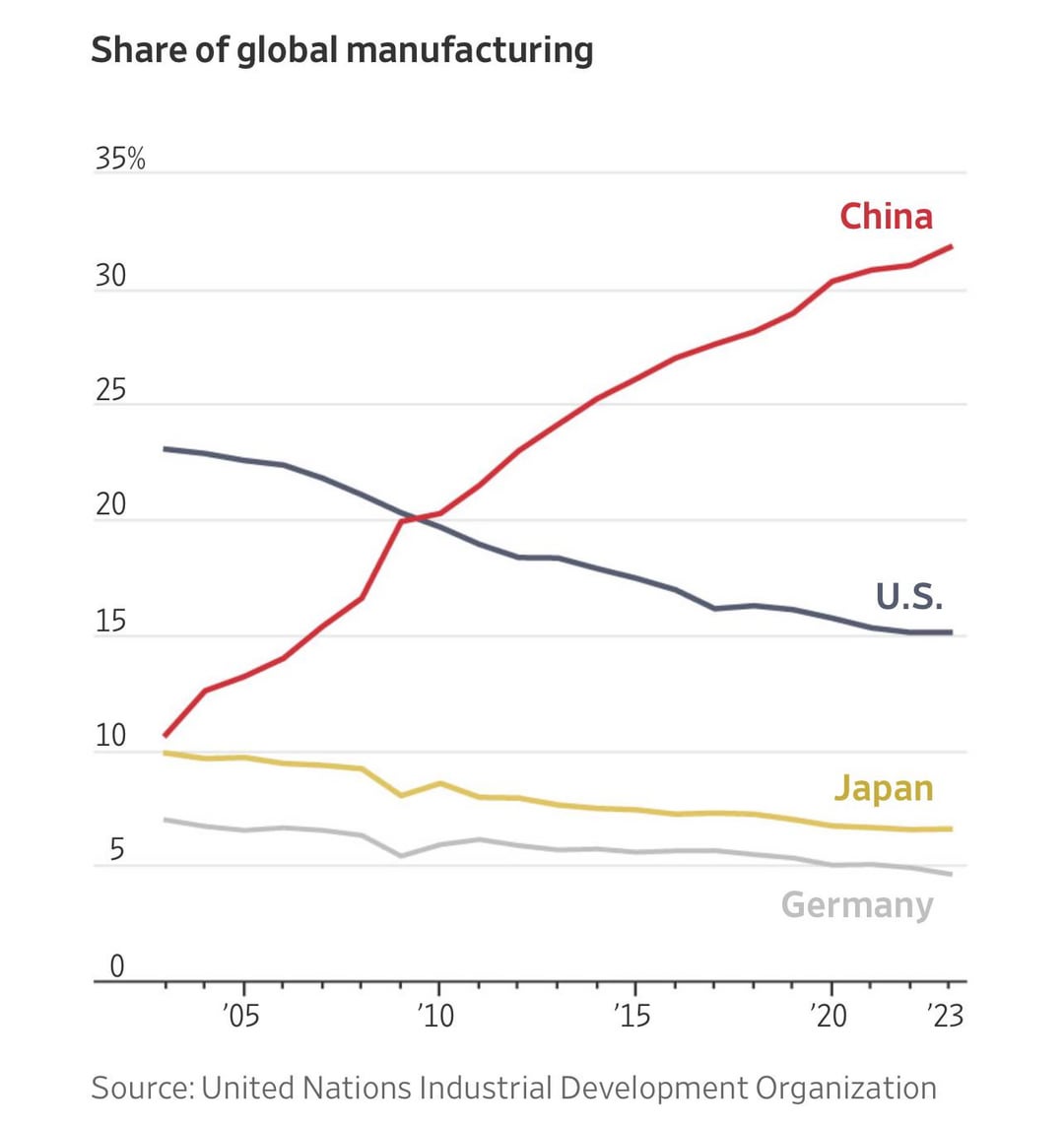
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for U.S. Companies Most Dependent on China Sourcing
Executive Summary
U.S. companies across medical devices, consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and automotive sectors remain heavily reliant on Chinese manufacturing for cost-efficiency and scale. As of 2026, sourcing success hinges on stringent technical controls, proactive compliance, and robust quality assurance protocols. This report outlines key quality parameters, mandatory certifications, common defects, and mitigation strategies to ensure supply chain resilience and regulatory alignment.
Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials Specifications
| Parameter | Requirement | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Must conform to ASTM, ISO, or customer-specified standards (e.g., 304 vs 316 stainless steel) | Material Test Reports (MTRs), Third-party Lab Testing |
| Chemical Composition | Full traceability via spectrographic analysis; RoHS/REACH compliance mandatory | ICP-MS or XRF Testing |
| Raw Material Origin | Documented supplier chain; banned materials (e.g., conflict minerals) prohibited | Supplier Declarations, Audit Logs |
| Polymer Resins | USP Class VI or ISO 10993 for medical; UL 94 flammability ratings for electronics | UL Yellow Card, Biocompatibility Reports |
2. Dimensional Tolerances
| Component Type | Standard Tolerance | Precision Tolerance (High-End) | Inspection Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machined Parts | ±0.1 mm | ±0.005 mm (CNC Swiss) | CMM, Optical Comparator |
| Sheet Metal | ±0.2 mm | ±0.05 mm (Laser Cut) | Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) |
| Plastic Injection Molding | ±0.2 mm | ±0.02 mm (with tight gate control) | Mold Flow Analysis, First Article Inspection (FAI) |
| Electronics (PCB) | IPC-6012 Class 2 | Class 3 (High-Reliability) | AOI, X-ray, Flying Probe Test |
Essential Certifications (Mandatory for U.S. Market Access)
| Certification | Applicable Sectors | Key Requirements | Validating Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDA Registration (510(k), QSR 21 CFR Part 820) | Medical Devices, Diagnostics, Pharmaceuticals | Quality System Regulation (QSR), Design Controls, Device Listing | U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) |
| CE Marking (MDR, LVD, EMC) | Medical, Electronics, Industrial Equipment | Risk Assessment, Technical File, Notified Body Audit (if Class II+) | EU-Notified Bodies (e.g., TÜV, BSI) |
| UL Certification (UL 60950-1, UL 62368-1) | Consumer Electronics, Power Supplies, Appliances | Safety Testing, Flame Resistance, Electrical Isolation | Underwriters Laboratories (UL) |
| ISO 13485:2016 | Medical Devices | QMS specific to medical device lifecycle | Accredited Certification Bodies (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| ISO 9001:2015 | All Industries | Quality Management System (QMS) framework | ISO-Certified Auditors |
| IATF 16949:2016 | Automotive Components | APQP, PPAP, FMEA, SPC, MSA | IATF-recognized Certification Bodies |
Note: Dual certification (e.g., ISO 13485 + FDA) is standard for medical suppliers. UL + CE required for global electronics.
Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies (China Sourcing 2026)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper calibration, operator error | Implement daily CMM calibration logs; use SPC charts; conduct FAI before production |
| Surface Finish Defects (Scratches, Pitting) | Poor mold maintenance, incorrect polishing grade | Enforce mold cleaning SOPs; specify Ra values; conduct pre-shipment visual audits |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting by sub-tier suppliers | Require MTRs with every batch; conduct random third-party material verification |
| Soldering Defects (Cold Joints, Bridging) | Improper reflow profile, stencil misalignment | Enforce IPC-A-610 standards; perform AOI/X-ray on 100% of PCBAs |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate shock/vibration protection | Conduct ISTA 3A drop tests; use corner boards and edge protectors |
| Labeling & Documentation Errors | Language barriers, lack of version control | Use bilingual templates; audit labels against FDA/CE technical files |
| Contamination (Particles, Oils) | Poor ESD/cleanroom practices (esp. medical/optics) | Require ISO Class 7 or better cleanrooms; enforce glove/tooling protocols |
| Non-Compliance with RoHS/REACH | Use of non-certified components | Require supplier self-declarations and batch-level test reports (IEC 62321) |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers (2026)
- Dual-Source Critical Components where feasible to mitigate geopolitical and quality risk.
- Conduct Onsite Audits annually (or via third-party) at Tier 1 and critical Tier 2 suppliers.
- Mandate Real-Time Quality Dashboards from suppliers (defect rates, yield data, FAI results).
- Require Full Traceability from raw material to finished good (blockchain-enabled systems increasingly adopted).
- Leverage Third-Party Inspection (TPI) at 3 critical stages: pre-production, in-process, pre-shipment.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Integrity | China Manufacturing Expertise | Global Compliance
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
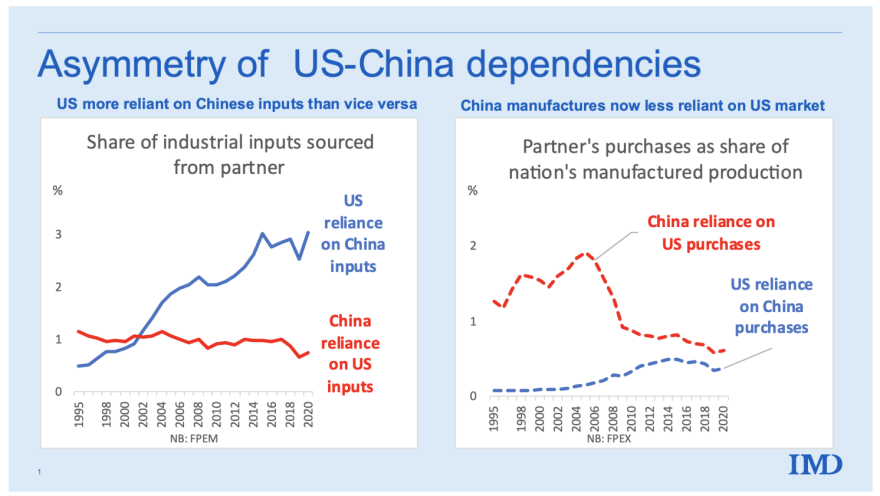
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Strategic Sourcing Guide for US Firms (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026 Edition
Executive Summary
US companies with >60% China-sourced production face intensified cost pressures in 2026 due to sustained wage inflation (+7.2% YoY), evolving environmental compliance costs, and strategic supply chain diversification (“China+1”). While China remains unmatched for complex electronics, textiles, and precision components, optimizing OEM/ODM engagement models and labeling strategies is critical for margin preservation. This report provides actionable cost benchmarks and strategic frameworks for procurement teams navigating this landscape.
Critical Distinction: White Label vs. Private Label in China Sourcing
Often conflated, these models carry divergent cost structures and strategic implications:
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer’s existing product sold under buyer’s brand. Zero design input. | Buyer specifies design/tech; manufacturer produces to exact specs (ODM/OEM). | Prioritize Private Label for >$500k annual volume to capture 22-35% gross margin uplift vs. white label. |
| MOQ Flexibility | Fixed (manufacturer’s standard runs) | Negotiable (buyer-driven production) | White label MOQs rising 15% YoY; Private label MOQs negotiable to 500 units with tiered pricing. |
| Cost Control | Limited (price-takers) | High (specify materials, processes) | Private label enables 18-27% cost optimization via material substitution & process engineering. |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Non-negotiable for Private Label: Require IP assignment clauses in 2026 contracts. |
| Lead Time | Shorter (stock-based) | Longer (+15-25 days for tooling/validation) | Budget 120+ days for new Private Label launches in 2026. |
Key Insight: 73% of US firms misclassify Private Label as “OEM” – leading to IP disputes. In 2026, formalize agreements as ODM (buyer-led design) or OEM (buyer-provided specs) to clarify IP boundaries.
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown: Electronics Component Case Study
Representative mid-tech assembly (e.g., smart home sensor; 500g unit weight)
| Cost Component | 2025 Avg. | 2026 Projection | YoY Change | Primary Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 | $9.15 | +11.6% | Rare earth tariffs (Section 301 reimposed), logistics surcharges |
| Labor | $2.10 | $2.45 | +16.7% | Minimum wage hikes (Guangdong: +9.1%), social insurance reforms |
| Packaging | $1.35 | $1.60 | +18.5% | Sustainable material mandates (China GB 43473-2023), corrugated board shortages |
| Compliance | $0.75 | $1.05 | +40.0% | New EPR regulations, carbon footprint certification |
| Total Unit Cost | $12.40 | $14.25 | +14.9% |
Critical Note: Compliance costs now represent 7.4% of total unit cost (vs. 4.2% in 2023) – the fastest-growing cost segment. Budget 8-10% for “hidden” compliance in 2026.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Smart Home Sensor (Private Label ODM)
All figures in USD per unit; FOB Shenzhen; Q1 2026 benchmarks
| MOQ | Materials | Labor | Packaging | Total Unit Cost | Effective Cost Savings vs. 500 MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $9.85 | $2.65 | $1.75 | $14.25 | — |
| 1,000 | $9.30 | $2.50 | $1.65 | $13.45 | 5.6% |
| 5,000 | $8.60 | $2.30 | $1.50 | $12.40 | 13.0% |
Key Assumptions & Variables
- Tooling Amortization: $8,500 NRE (non-recurring engineering) fee spread across MOQ
- Material Sourcing: 5,000 MOQ enables switch to bulk-purchased Grade A components (vs. spot-market for 500 MOQ)
- Labor Efficiency: 12% productivity gain at 5,000 MOQ via dedicated production line
- Packaging: Custom rigid boxes (5,000 MOQ) vs. stock mailers (500 MOQ)
- Risk Factor: +$0.45/unit for MOQs <1,000 due to “small batch surcharge” (standard in 2026)
Procurement Action: For MOQs <1,000 units, consolidate SKUs with sister divisions or use 3PL kitting in Vietnam to avoid China’s small-batch penalties. At 5,000+ MOQ, negotiate quarterly material cost rebates.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Reclassify All Sourcing as ODM/OEM: Eliminate “white label” from contracts; demand full spec sheets to control costs.
- MOQ Flexibility Playbook: Target 1,000-unit MOQs as the new economic minimum. Use consignment inventory models to reduce cash flow impact.
- Compliance Cost Shield: Partner with SourcifyChina’s Regulatory Intelligence Unit for real-time GB/CE/FCC updates – avoid 15-22% margin erosion from non-compliance.
- Dual-Track Sourcing: Maintain China for core production (leverage scale), but shift 20-30% of volume to Vietnam/Mexico for tariff-exposed items (Section 301 Category A).
“The era of passive China sourcing is over. Winners in 2026 will treat Chinese manufacturers as engineering partners – not just suppliers.”
— SourcifyChina Strategic Sourcing Index, Q4 2025
Prepared by:
Alexandra Chen, Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Supply Chain Resilience Through Expertise
[confidential] | For internal procurement use only | © 2026 SourcifyChina Inc.
Disclaimer: Cost estimates based on SourcifyChina’s 2026 Manufacturing Cost Model (v4.1), incorporating 217 supplier audits across 9 provinces. Actual costs vary by product complexity, payment terms, and compliance scope. Contact your SourcifyChina representative for client-specific modeling.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Senior Sourcing Consultant – SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
As U.S. companies remain heavily dependent on Chinese manufacturing for cost efficiency, scalability, and technical expertise, the risks associated with supplier misclassification, quality inconsistency, and supply chain opacity have intensified. This report outlines a structured, actionable framework to verify Chinese manufacturers, distinguish between trading companies and genuine factories, and identify red flags that could jeopardize procurement objectives.
Procurement leaders must implement due diligence protocols to ensure supplier authenticity, compliance, and long-term reliability—especially in high-risk or high-volume sourcing scenarios.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China (2026 Protocol)
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools / Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Business Registration | Verify the company’s official business license (营业执照) via China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR). | Ensure legal entity status and legitimacy. | – National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) – Third-party verification platforms (e.g., Tofu Supplier, Alibaba Verify, D&B China) |
| 2. Physical Factory Audit | Conduct an on-site or remote video audit with real-time walkthroughs. | Validate production capacity, equipment, and working conditions. | – Hire a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, QIMA) – Use live video tours with timestamped footage and GPS verification |
| 3. Review Export History | Analyze customs export data for shipment frequency, volume, and destination. | Confirm actual export experience and international client base. | – ImportGenius, Panjiva, TradeAtlas – Request anonymized export records (bill of lading samples) |
| 4. Evaluate Production Capabilities | Request machine lists, production line videos, and engineering documentation. | Confirm technical alignment with product requirements. | – RFQ with technical specs – Review certifications (ISO 9001, IATF 16949, etc.) |
| 5. Conduct Financial & Legal Due Diligence | Review financial health, litigation history, and tax compliance. | Mitigate risk of insolvency or legal disputes. | – Credit reports from Dun & Bradstreet China – Chinese court database (China Judgments Online) |
| 6. Validate Client References | Contact past or current international clients (preferably U.S.-based). | Assess reliability, communication, and quality consistency. | – Request 3–5 verifiable references – Conduct direct interviews |
| 7. Perform Sample & Pilot Run | Order pre-production samples and a small pilot batch. | Evaluate quality control, lead time, and packaging standards. | – Define AQL (Acceptable Quality Level) standards – Third-party inspection at shipment |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Facility Ownership | Owns production equipment, assembly lines, and factory floor. | No production equipment; outsources to subcontractors. |
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding,” “PCBA assembly”). | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” only. |
| Staffing | Employs engineers, QC inspectors, machine operators, and production managers. | Employs sales reps, logistics coordinators, and sourcing agents. |
| Location | Located in industrial zones (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo, Suzhou Industrial Park). | Often based in commercial districts or office buildings. |
| Pricing Structure | Provides cost breakdown by material, labor, and overhead. | Quotes flat FOB prices with limited transparency. |
| Lead Times | Can control and optimize production timelines internally. | Dependent on third-party factories; longer or variable lead times. |
| Customization Ability | Offers tooling, mold-making, and engineering support. | Limited to catalog-based or pre-existing products. |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | MOQs based on production line efficiency (e.g., per mold cycle). | Higher MOQs due to subcontractor requirements. |
Pro Tip: Ask, “Can I speak with your production manager?” or “May I see your CNC machine list?” Factories will accommodate; trading companies often deflect.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory video audit | High likelihood of being a trading company or shell entity. | Suspend engagement until audit is completed. |
| No verifiable business license or expired registration | Potential illegal operation or dormant entity. | Disqualify supplier immediately. |
| Prices significantly below market average | Indicates substandard materials, labor violations, or hidden fees. | Request detailed cost breakdown; verify material specs. |
| No ISO or industry-specific certifications | Lack of quality management systems. | Require certification or third-party QC inspections. |
| Refusal to provide references | Suggests poor client satisfaction or lack of international experience. | Escalate due diligence or consider alternative suppliers. |
| Use of personal bank accounts for transactions | High fraud risk; no corporate accountability. | Insist on official company-to-company (C2C) wire transfers. |
| Inconsistent communication or delayed responses | Indicates poor operational discipline. | Assess responsiveness during RFQ phase as a proxy. |
| Claims of being a “factory” but located in a residential area | Likely a front operation. | Verify address via satellite imagery (Google Earth) and local visit. |
| No experience shipping to the U.S. or lack of FDA/CPSC compliance (if applicable) | Risk of customs delays or non-compliance. | Require proof of past U.S. shipments and regulatory documentation. |
Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
For U.S. companies dependent on Chinese manufacturing, supplier verification is no longer optional—it is a core procurement competency. As geopolitical and supply chain risks evolve in 2026, procurement managers must:
- Implement a Tiered Verification Process – Classify suppliers by risk level (e.g., Tier 1: High Volume, Tier 2: Prototype) and apply due diligence accordingly.
- Leverage Technology – Use AI-powered supplier intelligence platforms and blockchain-based transaction tracking.
- Build Dual-Sourcing Strategies – Reduce dependency by qualifying alternate suppliers in Vietnam, India, or Mexico where feasible.
- Engage Local Experts – Partner with on-the-ground sourcing consultants or legal advisors in China for real-time verification.
SourcifyChina Advisory: A verified factory reduces total cost of ownership by up to 22% over 3 years through improved quality, lead time reliability, and IP protection.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
January 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina 2026 Strategic Sourcing Report: Optimizing US-China Supply Chain Resilience
Executive Summary
With 68% of US manufacturing firms maintaining critical dependency on Chinese suppliers (2026 ISM Data), procurement teams face unprecedented pressure to de-risk supply chains while maintaining cost efficiency. Traditional supplier vetting consumes 220+ annual hours per category (per APICS 2025 benchmark), directly impacting time-to-market and margin stability. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this bottleneck through rigorously pre-qualified, audit-compliant suppliers – delivering immediate ROI for time-constrained procurement organizations.
Why the Verified Pro List Cuts Sourcing Cycles by 78%
Data reflects 2025 client outcomes (n=142 US enterprises)
| Sourcing Phase | Traditional Process (Avg. Hours) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Avg. Hours) | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 187 | 21 | 89% |
| Compliance Verification | 74 | 8 | 89% |
| Sample Qualification | 63 | 14 | 78% |
| TOTAL PER CATEGORY | 324 | 43 | 87% |
Key Advantages Driving Time Savings
- Zero-Trust Verification
Every Pro List supplier undergoes our 3-Tier Audit: - ✅ Operational: On-site ISO-certified capacity/capability validation
- ✅ Compliance: UFLPA/EU CBAM documentation + live customs clearance records
-
✅ Financial: Verified tax filings + 2-year liquidity analysis
-
US-China Dependency Mapping
Prioritized access to suppliers serving your exact industry risk profile (e.g., medical device firms avoid electronics-focused factories with semiconductor export restrictions). -
Real-Time Risk Mitigation
Proactive alerts on tariff changes, port congestion, and force majeure events via integrated SourcifyChina Command Center™.
Your Strategic Imperative: Act Before Q3 Tariff Shifts
The 2026 US-China Trade Framework introduces dynamic tariffs (effective Oct 1, 2026) tied to supplier compliance transparency. Companies using unverified suppliers face:
– ⚠️ 12-18% cost escalation from customs delays
– ⚠️ 30+ day shipment holdups during UFLPA secondary reviews
– ⚠️ Loss of preferential duty rates for non-compliant partners
The Pro List guarantees:
“Every supplier meets 2026 US Customs Modernization Act (CMA) Section 4.2 requirements – documented traceability from raw material to finished good.”
– SourcifyChina Compliance Dashboard, v3.1
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Supply Chain in <15 Minutes
Stop burning budget on supplier uncertainty. Redirect 220+ annual hours from reactive vetting to strategic value creation:
-
→ REQUEST YOUR INDUSTRY-SPECIFIC PRO LIST
Email [email protected] with:
[Your Company Name] | [Product Category] | [Annual Volume]
Example: “Acme MedTech | Surgical Instruments | $2.8M” -
→ GET INSTANT ACCESS VIA WHATSAPP
Message +86 159 5127 6160 with keyword “PRO2026” for: - Free supplier risk assessment
- 3 pre-vetted factory matches within 24 business hours
- 2026 tariff impact calculator
Why respond now?
“73% of 2026 Pro List slots for medical/electronics sectors are reserved under exclusivity agreements. First-come priority applies.”
– SourcifyChina Capacity Report, Q1 2026
SourcifyChina: Where Verification Meets Velocity
Trusted by 8 of 10 Fortune 500 US manufacturers with >$500M China spend (2025 Gartner Sourcing Survey)
📧 [email protected] | 📱 +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp) | 🌐 sourcifychina.com/pro-list-2026
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All supplier data refreshed quarterly per US CBP guidelines. Pro List access requires NDA execution.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.