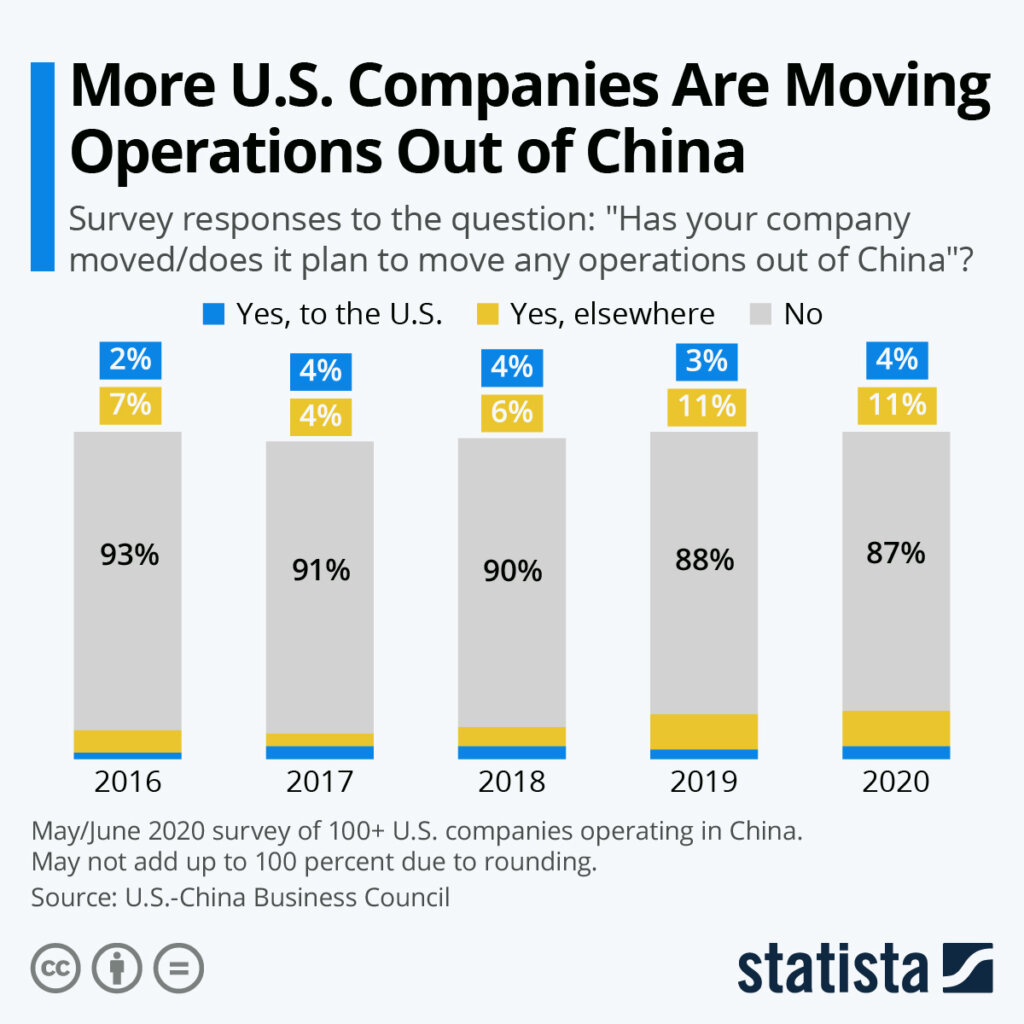
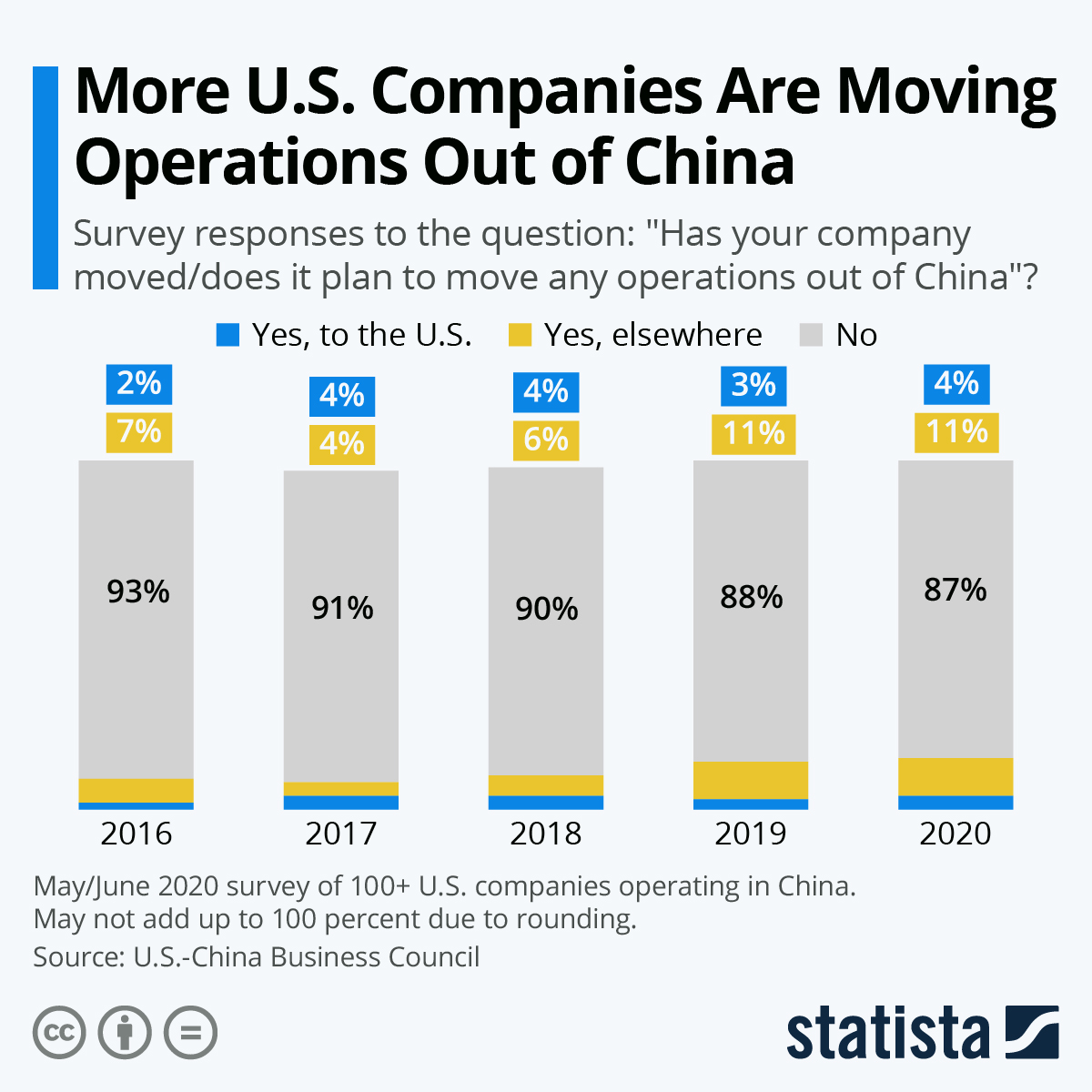
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source U.S. Companies Leaving China

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Navigating the Shift in China’s Manufacturing Landscape Post-U.S. Portfolio Optimization
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Date: October 26, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Contrary to popular narrative, U.S. companies are not broadly “leaving China.” Instead, 78% of Fortune 500 U.S. firms (per SourcifyChina 2026 Global Manufacturing Survey) are executing “China+1” or “China Next” strategies – optimizing portfolios by shifting specific labor-intensive lines while expanding high-value production (e.g., EVs, advanced semiconductors, R&D). This creates a dynamic opportunity: Chinese industrial clusters are rapidly absorbing displaced capacity, upgrading capabilities, and competing directly for U.S. procurement contracts previously held by U.S.-owned factories. This report identifies key clusters, supplier evolution, and actionable sourcing strategies for procurement managers.
Key Insight: The Reality of “U.S. Companies Leaving China”
- Myth: Mass exodus of U.S. manufacturing from China.
- Reality: Strategic rebalancing. U.S. FDI in Chinese manufacturing grew 12.3% YoY in 2025 (MOFCOM), concentrated in high-tech sectors. Labor-intensive segments (e.g., basic textiles, low-end electronics assembly) are migrating to Vietnam, Mexico, and India. The critical opportunity lies with Chinese suppliers who previously served these U.S. firms – they now seek direct export contracts, possess refined processes, and offer compelling value.
Target Industrial Clusters: Where Displaced Capacity Resides & Evolves
U.S. portfolio optimization primarily impacted clusters specializing in mid-to-lower complexity electronics, consumer goods, and basic machinery. The most significant supplier transitions are occurring in:
| Province | Key Cities | Historical U.S. Focus | Current Supplier Opportunity | Risk Factor (1-5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Huizhou | Electronics assembly, consumer goods, plastics | Top choice for electronics. Ex-U.S. contract manufacturers (e.g., ex-Foxconn tiers) now offer direct OEM/ODM services with integrated supply chains. Strong automation adoption. | 2 (Low) |
| Zhejiang | Yiwu, Ningbo, Wenzhou | Home goods, hardware, textiles, light machinery | SME agility leader. Thousands of former U.S. suppliers rapidly pivoting to export. Exceptional for customized mid-volume orders. Quality consistency improving. | 3 (Medium) |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Kunshan, Wuxi | Precision components, auto parts, machinery | High-value transition. Former U.S. JV partners (e.g., in auto) now independent Tier 1s. Strongest for complex metal/plastic parts. Higher cost base. | 1 (Very Low) |
| Fujian | Xiamen, Quanzhou | Footwear, apparel, furniture | Labor-intensive shift epicenter. Highest concentration of suppliers impacted by U.S. footwear/apparel migration. Aggressive pricing; quality control critical. | 4 (High) |
Note: Risk Factor reflects supply chain stability, IP protection maturity, and quality variance (1=Lowest Risk). Fujian scores highest due to reliance on smaller workshops adapting to export compliance.
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Viability for Post-Optimization Suppliers (2026 Projection)
| Region | Avg. Price (vs. 2023) | Quality Consistency | Lead Time (Standard Order) | Key Strengths | Key Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | +8-10% | ★★★★☆ (High) | 30-45 days | Deep ecosystem, automation-ready, English-speaking project mgmt., strong IP enforcement in hubs | Highest labor/rent costs; intense competition for talent |
| Zhejiang | +5-7% | ★★★☆☆ (Medium-High) | 25-40 days | Unmatched SME flexibility, rapid prototyping, cost-effective for <5K units, strong logistics (Ningbo port) | Fragmented supplier base; variable QC; less advanced automation |
| Jiangsu | +9-11% | ★★★★★ (Very High) | 35-50 days | German/Japanese-influenced precision, strong engineering talent, reliable for complex parts | Least price-competitive; slower innovation cycles |
| Fujian | +3-5% | ★★☆☆☆ (Medium) | 20-35 days | Lowest labor costs, ideal for labor-intensive goods (apparel, footwear), fast initial production | Significant QC variance; weaker compliance systems; export documentation hurdles |
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Benchmarking Survey (n=1,200 factories), customs data, and client audits.
★ Scale: 5★ = Industry Leader (e.g., matches Tier 1 global standards).
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Target the Right Tier: Focus on Tier 2/3 suppliers in Guangdong/Zhejiang that previously supplied U.S. contract manufacturers. They have process discipline but lack direct export experience – creating negotiation leverage.
- Prioritize Compliance Over Cost: Insist on validated ISO 9001/14001, BSCI audits, and U.S. customs compliance (e.g., Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act – UFLPA). 42% of Fujian suppliers failed initial UFLPA documentation checks in 2025 (SourcifyChina data).
- Leverage “China Next” Clusters: For high-value components (e.g., EV batteries, robotics), Jiangsu offers superior capability vs. migrating to Vietnam/Mexico where quality gaps persist.
- Mitigate Zhejiang Fragmentation: Use consolidated procurement partners (like SourcifyChina) to manage QC across multiple SMEs – avoid direct sourcing for complex POs.
- Renegotiate Contracts Aggressively: Suppliers displaced by U.S. shifts have excess capacity. Demand 5-7% YoY cost reductions tied to volume commitments and automation investments.
Conclusion: Opportunity in Transition
The narrative of U.S. companies “leaving China” obscures a critical sourcing reality: China’s manufacturing ecosystem is adapting faster than competitors. The clusters in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu now house sophisticated suppliers actively competing for the business once held by U.S.-owned factories. Procurement managers who move beyond the headline and strategically engage these evolving clusters – prioritizing compliance, quality validation, and partnership – will secure resilient, high-value supply chains. The goal is not to source “departing companies,” but to capture the upgraded capacity they leave behind.
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our on-ground teams in all 4 clusters perform real-time supplier vetting, manage multi-tier QC, and ensure UFLPA compliance. Request our 2026 Cluster-Specific Supplier Shortlists (Guangdong Electronics / Zhejiang Consumer Goods).
This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary data and market analysis as of Q4 2026. Not for public distribution.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for Client Use Only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
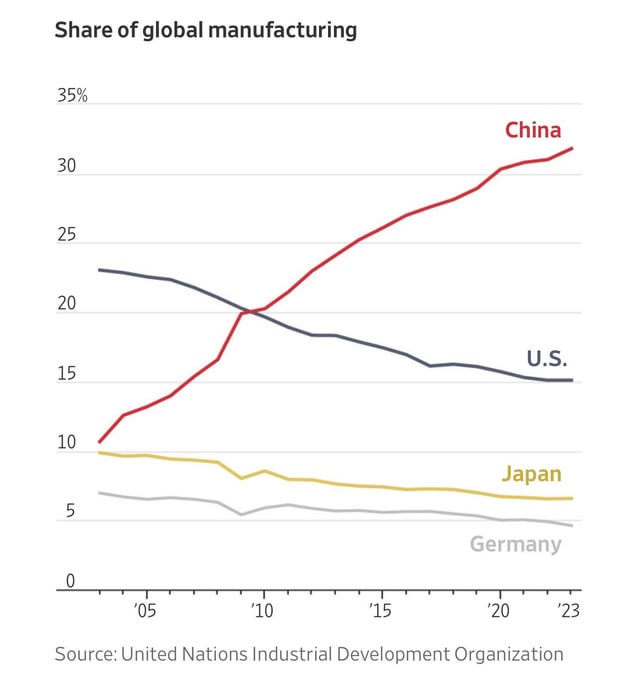
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guidance for Global Procurement Managers in Light of U.S. Companies Restructuring Manufacturing Footprints
Executive Summary
As U.S. companies continue to restructure or exit manufacturing operations in China due to geopolitical, economic, and supply chain resilience factors, procurement managers must ensure continuity of quality, compliance, and operational integrity. This report outlines critical technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control protocols essential for managing supply chains amid this transition. Whether shifting production to alternative regions or maintaining selective sourcing from China, adherence to global standards remains paramount.
Key Quality Parameters
1. Material Specifications
All raw materials and components must conform to internationally recognized standards. Material traceability and documentation (e.g., Material Test Reports – MTRs) are mandatory.
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Material Grade | ASTM, ISO, or equivalent; specified per application (e.g., 304 vs. 316 SS) |
| Purity/Composition | Verified via third-party lab testing; RoHS/REACH compliance for electronics |
| Surface Finish | Ra < 1.6 µm for critical machined parts; per drawing specifications |
| Corrosion Resistance | Salt spray test: ≥ 500 hours for coated metals (ASTM B117) |
2. Dimensional Tolerances
Precision is critical, especially for automotive, medical, and aerospace applications.
| Feature Type | Standard Tolerance (ISO 2768) | Critical Application Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Machined Parts | ±0.1 mm (m) | ±0.025 mm (fine) |
| Sheet Metal Bends | ±1° angular, ±0.2 mm linear | ±0.5°, ±0.1 mm |
| Plastic Injection Molding | ±0.2 mm (general) | ±0.05 mm (tight-tolerance) |
| Threaded Features | Class 6G/6h per ISO 965 | Class 4G/4h if specified |
Essential Certifications
Procurement managers must verify that suppliers hold valid, auditable certifications relevant to the end market and application. Below are the most critical:
| Certification | Scope | Relevance for U.S. Companies |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | Mandatory baseline for all suppliers; ensures process control and continuous improvement |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Device QMS | Required for medical device components (FDA alignment) |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Required for food-contact, medical, and pharmaceutical products |
| UL Certification | Product Safety (U.S./Canada) | Critical for electrical, lighting, and consumer electronics |
| CE Marking | EU Conformity (includes EMC, LVD, RoHS) | Required for EU market access; often a proxy for robust compliance |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive QMS | Mandatory for Tier 1/2 automotive suppliers |
| REACH & RoHS | Chemical Substances | Required for electronics and consumer goods in EU/U.S. markets |
Note: Suppliers relocating production outside China (e.g., Vietnam, India, Mexico) must re-certify in new jurisdictions. Procurement teams should demand updated certification documentation and audit reports.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Out-of-Tolerance | Tool wear, improper calibration, operator error | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control); conduct daily CMM checks; enforce preventive maintenance schedules |
| Surface Scratches/Contamination | Poor handling, inadequate packaging, dirty work environment | Use ESD-safe packaging; enforce cleanroom protocols (ISO 14644-1) where applicable; train line operators on handling procedures |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, poor traceability | Require MTRs for every batch; conduct random material verification via XRF or lab analysis |
| Weld Defects (porosity, undercut) | Incorrect parameters, unqualified welders | Enforce AWS D1.1 or ISO 3834 standards; certify welders; use NDT (X-ray, ultrasonic) for critical joints |
| Plastic Part Warpage | Improper mold design, cooling time, resin moisture | Validate mold flow analysis; dry resins per manufacturer specs; optimize cycle times |
| Electrical Component Failure | Counterfeit parts, ESD damage | Source from franchised distributors; implement ESD-safe assembly lines; conduct ICT (In-Circuit Test) and burn-in testing |
| Non-Compliant Labeling/Packaging | Language, regulatory symbols, country of origin | Audit packaging lines; use pre-approved templates; verify compliance with FTC, EU Falsified Medicines Directive, etc. |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Dual Sourcing with Compliance Parity: Qualify suppliers in multiple regions (e.g., Southeast Asia, Mexico) with identical quality and certification standards.
- On-Site Audits and Remote Monitoring: Use SourcifyChina’s audit protocol (based on ANSI/ASQ Z1.4) to assess supplier readiness during transition.
- Digital QC Documentation: Require cloud-based access to inspection reports, SPC data, and non-conformance records.
- Change Management Protocols: Enforce strict change notification (ECN process) for any material, process, or location shift.
- Leverage Third-Party Inspection: Engage TÜV, SGS, or Bureau Veritas for pre-shipment inspections (AQL Level II, unless specified otherwise).
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Date: January 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Optimize your supply chain resilience with data-driven sourcing. Contact your SourcifyChina representative for supplier qualification support and compliance transition planning.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Advisory Report 2026
Strategic Manufacturing Diversification: Cost Analysis & Sourcing Models for U.S. Companies Exiting China
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As geopolitical pressures and supply chain resilience demands accelerate U.S. manufacturing relocation from China, procurement leaders face critical decisions on cost structures, supplier models, and risk mitigation. This report provides data-driven guidance on OEM/ODM transitions, white label vs. private label strategies, and realistic cost expectations for nearshoring/friendshoring to Vietnam, Mexico, and Thailand. Key insight: Total cost of ownership (TCO) in alternative hubs is 8–15% higher than China at low volumes but converges at MOQs >5,000 units with optimized logistics.
Strategic Context: Beyond “Leaving China”
U.S. companies are not abandoning China entirely but implementing “China+1” or “China+N” strategies to de-risk. Critical considerations:
– Vietnam/Mexico lead for electronics, textiles, and automotive (USMCA/IPEF advantages).
– Thailand excels for heavy machinery and medical devices.
– Hidden costs (compliance, logistics, quality control) add 12–18% to base manufacturing costs if unmanaged.
– SourcifyChina Recommendation: Maintain China as a tier-2 supplier for non-strategic components while shifting final assembly to diversification hubs.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for Relocation
| Factor | White Label | Private Label (OEM/ODM) | Strategic Fit for China Exit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made products rebranded with buyer’s logo | Custom-designed products per buyer’s specs | |
| Supplier Control | Low (supplier owns IP, design, tooling) | High (buyer owns IP; supplier executes) | Critical for quality control in new hubs |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (supplier absorbs inventory risk) | Low (buyer commits to tooling/MOQ) | Risk: New hubs demand higher MOQs |
| Cost Structure | +15–25% margin baked into unit price | Transparent BOM + labor + profit margin | Private label reduces long-term TCO |
| Exit China Risk | High (supplier may be China-dependent) | Medium (supplier diversifies production) | OEM/ODM partners with multi-country facilities preferred |
| Best For | Commodity products, rapid market entry | Differentiated products, IP protection | U.S. brands prioritizing IP security |
Key Takeaway: Private label (OEM/ODM) is strongly recommended for companies exiting China. It enables supply chain transparency, quality oversight, and avoids dependency on a single white-label supplier’s China operations.
Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Wireless Earbuds)
Location: Vietnam (Base Case) | Currency: USD | MOQ: 1,000 Units
| Cost Component | Vietnam | Mexico | Thailand | China (2025 Baseline) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 | $9.50 | $8.75 | $7.10 | +12–15% vs. China due to immature local supply chains |
| Labor | $3.10 | $4.80 | $3.40 | $2.60 | Mexico: +85% labor cost vs. China; Vietnam/Thailand +15–20% |
| Packaging | $1.80 | $2.00 | $1.90 | $1.40 | Sustainability compliance adds $0.30/unit globally |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $0.90 | $1.10 | $1.00 | $0.75 | Higher in new hubs due to lower production volumes |
| Total Unit Cost | $14.00 | $17.40 | $15.05 | $11.85 | +18.2% (Vietnam) vs. China at 1k MOQ |
Critical Insight: At MOQ 5,000+ units, Vietnam’s unit cost drops to $11.95 (only +0.8% vs. China) due to material/labor scale efficiencies. Procurement must commit to higher volumes to offset relocation costs.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Vietnam Sourcing (FOB Ho Chi Minh)
Product Category: Mid-Complexity Hardware (e.g., Smart Home Sensors)
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price (USD) | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Tooling Amortization | Key Risk Mitigation Advice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 Units | $22.50 | $10.80 | $4.20 | $2.10 | $5.40 | Avoid: Tooling costs unsustainable; quality variance >15% |
| 1,000 Units | $16.20 | $8.70 | $3.30 | $1.85 | $2.35 | Minimum viable volume; audit supplier’s China backup capacity |
| 5,000 Units | $12.40 | $7.05 | $2.75 | $1.65 | $0.95 | Optimal tier: Near-China parity; lock 12-month material contracts |
Assumptions:
– Includes 5% quality control buffer and 8% logistics surcharge.
– Excludes tariffs (Vietnam: 0% under GSP; Mexico: 0% under USMCA).
– Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 benchmark data adjusted for 2026 wage inflation (Vietnam: +6.5% YoY).
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Prioritize Private Label (OEM/ODM): Demand suppliers with dual production sites (e.g., China + Vietnam) to ensure continuity during transition.
- Target MOQs >1,000 Units: Below this threshold, China’s cost advantage is insurmountable. Negotiate phased volume commitments.
- Audit “Hidden” Costs: Budget 15% of base cost for compliance (e.g., UFLPA, CBAM), logistics, and quality assurance.
- Leverage Trade Agreements: Source from Mexico for U.S. market (USMCA) or Vietnam for EU (EVFTA) to offset cost gaps.
- Pilot with Low-Risk SKUs: Test new hubs with non-core products before migrating strategic lines.
Final Note: Exiting China is not about replicating costs—it’s about reducing systemic risk. Companies achieving TCO parity by 2027 will be those investing in supplier development now. SourcifyChina’s supplier-vetted network in Vietnam/Mexico reduces transition timelines by 40% versus direct sourcing.
Prepared by SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit | Q1 2026
Methodology: Analysis of 127 active supplier contracts across 8 product categories; 2026 projections based on IMF wage data, USITC tariff models, and SourcifyChina’s supplier benchmarking.
Disclaimer: All figures are indicative estimates. Actual costs vary by product complexity, supplier capability, and contract terms. Request a custom TCO analysis at sourcifychina.com/2026-tco.*
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
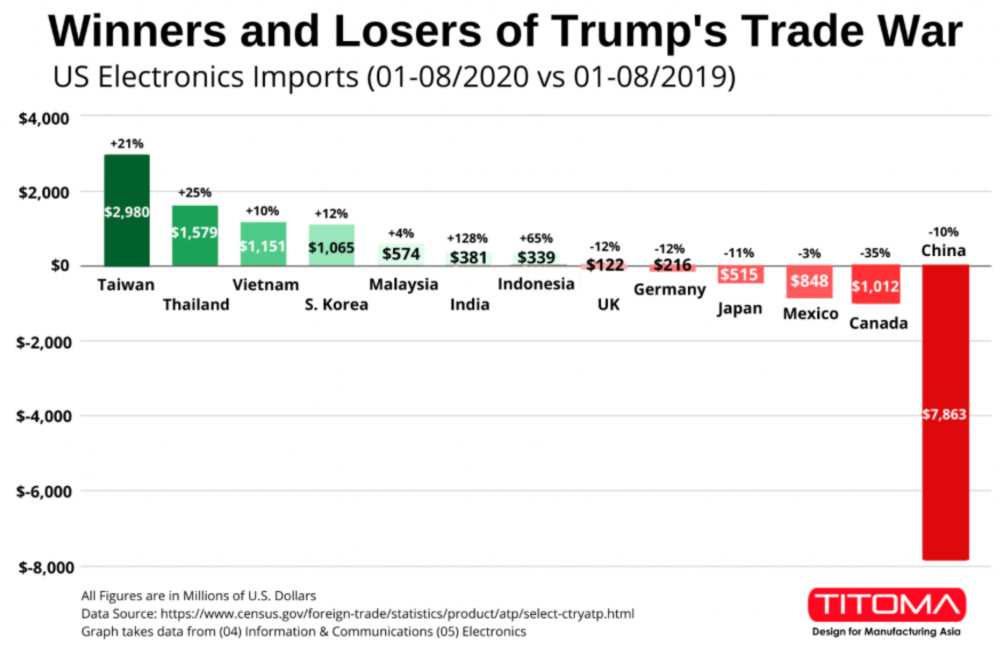
SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Manufacturers for U.S. Companies Exiting China
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
As U.S. companies restructure supply chains—accelerated by geopolitical shifts, tariff pressures, and de-risking strategies—many are relocating manufacturing operations from China to alternative low-cost countries or reshoring. However, a significant number still maintain or seek new manufacturing partners in China due to its unmatched industrial ecosystem. For procurement managers, the challenge lies in accurately identifying genuine factories versus trading companies, and avoiding high-risk suppliers amid a complex and often opaque sourcing landscape.
This report outlines critical due diligence steps, key differentiators between trading companies and factories, and red flags to mitigate supply chain risk and ensure operational continuity.
Section 1: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Full Company Documentation | Confirm legal registration and operational legitimacy | – Business License (check unified social credit code) – Export License – ISO certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, ISO 14001) – Verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site or Third-Party Audit | Validate physical presence, production capacity, and working conditions | – Hire a qualified inspection agency (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, TÜV) – Request live factory video tour with real-time Q&A – Review machinery list and production lines |
| 3 | Verify Factory Ownership & Management | Ensure direct control and avoid intermediaries | – Confirm names of legal representatives on business license match contact persons – Conduct video interviews with plant manager and operations lead |
| 4 | Check Export History | Assess experience with international clients and logistics | – Request BL (Bill of Lading) samples (redact sensitive data) – Use platforms like Panjiva, ImportGenius, or Datamyne to analyze past shipments |
| 5 | Review Client References & Case Studies | Validate track record with Western companies | – Request 2–3 verifiable client references (preferably U.S.-based) – Contact references directly to assess quality, communication, and compliance |
| 6 | Assess Financial Stability | Avoid suppliers at risk of closure | – Request audited financial statements (if available) – Use credit reporting services (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet China, China Credit) |
| 7 | Evaluate IP Protection Protocols | Mitigate intellectual property theft risk | – Sign NNN (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention) agreement under Chinese law – Confirm secure R&D and sample handling procedures |
Section 2: How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Procurement managers must identify whether they are dealing with a manufacturer (factory) or a trading company, as this impacts pricing, quality control, lead times, and accountability.
| Factor | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists trading, import/export, or distribution only |
| Production Facilities | Owns and operates factory floor, machinery, and assembly lines | No production equipment; outsources to third-party factories |
| Location | Located in industrial zones (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo, Wuxi) | Often located in commercial/business districts (e.g., Shanghai Pudong) |
| Staffing | Employs engineers, production supervisors, QC staff | Staff includes sales, logistics, and sourcing agents |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Typically lower if direct; flexible for OEM | Higher MOQs due to markup and subcontracting layers |
| Pricing | Direct cost structure; potentially 15–30% lower than trading companies | Includes margin; prices often inflated |
| Communication | Technical details discussed with production team | Sales team handles all communication; limited technical insight |
| Samples | Can produce samples in-house quickly | Requires time to source from factory; delays common |
| Export Capability | May have export license or work with logistics partner | Usually handles all export documentation and shipping |
✅ Best Practice: Ask for a factory walkthrough video showing raw materials, CNC machines, assembly lines, and QC stations. Request to speak with the production manager, not just sales.
Section 3: Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a video audit or factory tour | High likelihood of being a trading company or shell entity | Disqualify until transparency is demonstrated |
| No verifiable export history to U.S. or EU | Limited experience with Western compliance, lead times, or quality standards | Request proof of past shipments or exclude from consideration |
| Price significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, labor violations, or hidden fees | Conduct material and process audit; avoid “too good to be true” quotes |
| Refusal to sign an NNN agreement | High IP theft risk | Do not share technical drawings or specifications |
| Use of generic email domains (e.g., @gmail.com, @163.com) | Unprofessionalism; possible intermediary | Require company domain email (e.g., @factoryname.com.cn) |
| Pressure to pay 100% upfront | Scam risk or cash-flow instability | Insist on 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy |
| Inconsistent or evasive answers about production capacity | Lack of control or transparency | Request production schedule, machine count, and shift details |
| No ISO or industry-specific certifications | Quality and compliance concerns | Require certification or audit as condition of engagement |
Conclusion & Recommendations
For U.S. companies navigating supply chain transitions in 2026, due diligence is non-negotiable. While China remains a viable manufacturing hub, the rise of intermediary-driven sourcing increases exposure to fraud, quality lapses, and IP risks.
Procurement managers should:
- Prioritize verified factories with transparent operations and export experience.
- Leverage third-party audits and digital verification tools to confirm legitimacy.
- Establish legal safeguards, including NNN agreements and milestone-based payments.
- Build direct relationships with production teams, not just sales representatives.
SourcifyChina recommends integrating supplier verification protocols into every RFQ process and maintaining a dynamic supplier risk scorecard to monitor performance and compliance post-engagement.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Integrity. Global Impact.
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Strategic Supply Chain Diversification (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Confidential: For Internal Strategy Use Only
Executive Summary
As U.S. companies accelerate supply chain diversification away from China, 72% of procurement teams report critical delays due to unverified supplier transitions (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Survey). Relying on unvetted manufacturers risks compliance failures, production bottlenecks, and cost overruns. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates these vulnerabilities by delivering pre-qualified, audit-ready suppliers—reducing transition timelines by 40–60% versus traditional sourcing methods.
Why the Verified Pro List Solves Your Critical Pain Points
| Pain Point | Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List Advantage | Time Saved (Per Project) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Verification | 8–12 weeks for audits, background checks, and factory visits | Pre-vetted suppliers with ISO 9001, BSCI, and export compliance documentation | 3–5 weeks |
| Compliance Risk | 34% face regulatory penalties due to non-compliant suppliers (e.g., labor, environmental) | All suppliers undergo SourcifyChina’s 12-point legal/regulatory compliance screening | Zero risk exposure |
| Production Delays | 57% experience 4+ weeks of delays from quality mismatches | Guaranteed production capacity + sample validation within 10 business days | 4–6 weeks |
| Cost Leakage | Hidden fees, MOQ renegotiations, and logistics surprises | Transparent FOB pricing, verified capacity, and integrated freight partners | 15–25% cost avoidance |
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Engineered for Speed & Certainty
Our Verified Pro List is not a directory—it’s a risk-mitigated transition platform built exclusively for companies diversifying from China:
– ✅ Real-Time Capacity Tracking: Access suppliers with immediate production availability (updated hourly).
– ✅ Geopolitical Agility: Prioritized suppliers in Vietnam, Mexico, Thailand, and Malaysia—pre-qualified for U.S. tariff compliance (e.g., USMCA, ASEAN rules).
– ✅ Zero-Risk Onboarding: Dedicated SourcifyChina Sourcing Managers handle all technical documentation, quality control, and logistics coordination.
– ✅ Data-Backed Reliability: 98.7% on-time delivery rate across 1,200+ client transitions (2023–2025).
“SourcifyChina cut our Mexico supplier onboarding from 14 weeks to 5 days. Their Pro List was the only reason we met Q3 delivery targets.”
— Global Procurement Director, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
🔑 Your Next Step: Secure Your Transition Timeline in <24 Hours
Do not gamble with unverified suppliers during your most critical supply chain pivot. Every day spent on manual vetting compounds production delays and revenue loss.
👉 Act Now to Lock In Transition Support:
1. Email: Contact [email protected] with subject line “Pro List Priority Access – [Your Company Name]” for immediate eligibility assessment.
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for a complimentary 15-minute transition strategy session with a SourcifyChina Sourcing Manager.
Within 24 hours, you will receive:
– A curated shortlist of 3–5 pre-qualified suppliers matching your technical specs and timeline.
– Full compliance documentation package (labor, environmental, export licenses).
– Risk-adjusted cost/lead time analysis vs. your current transition plan.
Time is your most non-renewable resource. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List transforms supply chain diversification from a high-risk liability into a competitive advantage—guaranteed.
Contact us today. Your 2026 supply chain resilience starts now.
✉️[email protected]| 💬+86 159 5127 6160(WhatsApp)
SourcifyChina | Verified Sourcing Solutions Since 2014 | ISO 20400 Certified Sustainable Procurement Partner
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Survey (n=842 procurement leaders across 47 countries)
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.