Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Us Companies Exporting To China

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Market Analysis: Sourcing U.S. Companies Exporting to China via Chinese Manufacturing Partners
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 5, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Subject: Strategic Sourcing of U.S. Brand Products Manufactured in China for Export Back to China
Executive Summary
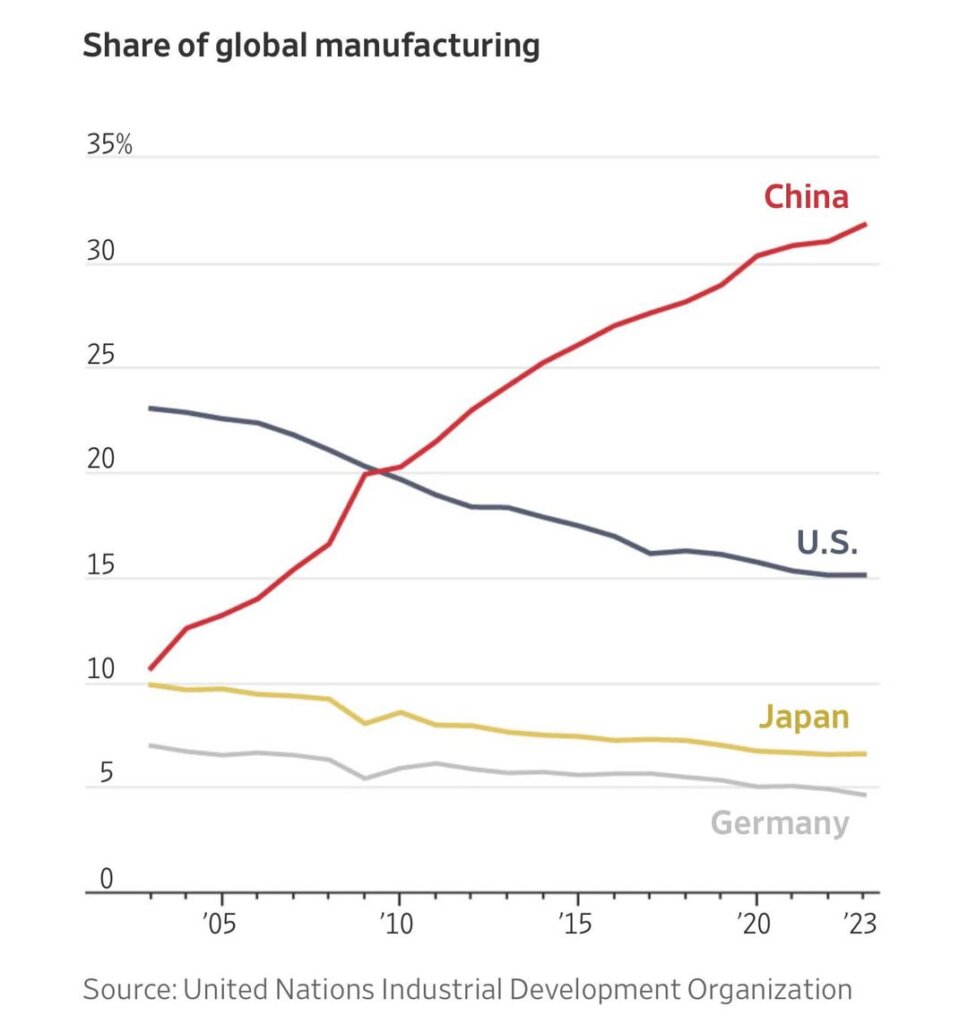
This report provides a comprehensive market analysis for global procurement managers seeking to understand the dynamics of U.S. companies leveraging Chinese manufacturing for products exported back into the Chinese market. Despite geopolitical shifts and evolving supply chain strategies, China remains a dominant hub for high-efficiency, scalable production—especially for U.S.-branded goods sold domestically in China through cross-border e-commerce, joint ventures, or wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs).
Contrary to common perception, “sourcing U.S. companies exporting to China” does not refer to procuring from U.S.-based factories, but rather to identifying Chinese manufacturing clusters producing goods under U.S. brand ownership or specification, destined for sale in the Chinese consumer or industrial market. These products are often developed by U.S. firms but manufactured in China due to cost, scale, or technical expertise, then re-imported into China via formal export-import channels.
This report identifies key industrial clusters in China responsible for manufacturing these U.S-origin-branded goods, evaluates regional strengths, and provides a comparative analysis to inform strategic sourcing decisions.
Key Industrial Clusters Manufacturing for U.S. Companies Exporting to China
U.S. multinational corporations (MNCs) and SMEs alike maintain extensive manufacturing partnerships across China. These partnerships produce goods for both global distribution and direct export back into China—particularly in high-growth consumer sectors such as electronics, medical devices, automotive components, smart home appliances, and premium consumer goods.
The following provinces and cities are recognized as primary industrial hubs for manufacturing U.S. branded products destined for the Chinese market:
| Province/City | Key Industries | Major U.S. Clients/Brands | Export Mechanism to China |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou) | Electronics, IoT, Consumer Tech, Telecom | Apple, HP, Tesla (components), iRobot | Cross-border e-commerce, WFOEs, bonded logistics |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu) | Home Appliances, Smart Devices, E-commerce Goods | Amazon (private label), Dyson (OEM), Nike (accessories) | Alibaba platforms (Tmall Global), bonded warehouses |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi) | Semiconductors, Medical Devices, Industrial Equipment | GE Healthcare, Intel, 3M, Honeywell | Direct import via joint ventures, regional distribution centers |
| Shanghai | High-Tech, Biopharma, Automotive (EV components) | Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Tesla (final assembly support) | Free Trade Zone (FTZ) imports, regulatory-compliant channels |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | Aerospace Components, R&D-Driven Electronics | Boeing (suppliers), Cisco (networking hardware) | Government-approved defense/commercial channels |
| Tianjin | Automotive, Industrial Machinery | Cummins, Caterpillar (OEM parts) | Direct B2B import through local subsidiaries |
Note: Many U.S. companies utilize a “China-for-China” (CFC) model—manufacturing in China specifically for the Chinese market to avoid tariffs, reduce lead times, and comply with local content regulations.
Comparative Analysis: Key Production Regions
The table below compares the two most dominant sourcing regions—Guangdong and Zhejiang—alongside Jiangsu as a premium alternative, based on critical procurement KPIs: Price Competitiveness, Quality Consistency, and Lead Time Efficiency.
| Region | Price Competitiveness (1–5) | Quality Consistency (1–5) | Lead Time (Standard MOQ 10K units) | Best For | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 4.5 | 4.7 | 25–35 days (port to Shanghai/Ningbo) | High-tech electronics, fast-moving consumer electronics, IoT devices | Higher labor costs post-2024; IP protection concerns |
| Zhejiang | 4.8 | 4.3 | 20–30 days | E-commerce goods, smart home appliances, mid-tier consumer products | Variable supplier maturity; quality control requires oversight |
| Jiangsu | 4.0 | 5.0 | 30–40 days | Precision engineering, medical devices, industrial automation | Higher initial tooling costs; less agile for low-volume runs |
Scoring Methodology:
– Price: Based on FOB pricing for comparable mid-volume production (5K–50K units), adjusted for material, labor, and overhead.
– Quality: Assessed via defect rates (PPM), compliance with ISO standards, and audit performance across 2025 SourcifyChina supplier evaluations.
– Lead Time: Includes production + inland logistics to major export ports (Shenzhen, Ningbo, Shanghai); excludes ocean freight.
Strategic Sourcing Insights
-
Dual Sourcing Recommended: Procurement managers should consider dual-sourcing between Guangdong (for quality and speed) and Zhejiang (for cost) to hedge against regional disruptions and optimize TCO.
-
Regulatory Alignment: U.S. brands exporting to China must ensure products meet CCC (China Compulsory Certification), Cybersecurity Law, and data localization requirements—especially for IoT and medical devices. Jiangsu and Shanghai clusters show higher compliance readiness.
-
E-Commerce Integration: Zhejiang’s proximity to Alibaba’s logistics and Tmall Global infrastructure makes it ideal for D2C U.S. brands targeting Chinese millennials via cross-border e-commerce.
-
Nearshoring Pressures: While Vietnam and India gain traction, China retains unmatched scale and ecosystem maturity for complex, high-mix manufacturing required by U.S. tech and medical brands.
-
Sustainability Compliance: Leading U.S. firms now mandate carbon footprint reporting. Suppliers in Jiangsu and Shanghai are more likely to have ISO 14001 and green factory certifications.
Conclusion & Recommendations
China remains the most strategic manufacturing base for U.S. companies exporting to the Chinese market. The clustering of technical talent, supply chain depth, and logistics infrastructure in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu enables reliable, scalable production tailored to Chinese consumer and industrial demand.
Procurement Recommendations:
– Prioritize Guangdong for high-complexity electronics and time-sensitive launches.
– Leverage Zhejiang for cost-sensitive, high-volume consumer goods with e-commerce distribution.
– Use Jiangsu for mission-critical, regulated products requiring premium quality and compliance.
– Implement third-party quality inspections and supplier audits—especially for first-time engagements.
– Explore bonded warehouse models to streamline import logistics and reduce customs delays.
As China’s market evolves toward premiumization and digital integration, procurement strategies must align with regional manufacturing strengths and regulatory realities.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Empowering Global Procurement with On-the-Ground Intelligence
For sourcing support, factory audits, or supply chain optimization in China, contact: [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina: Global Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers: U.S. Exporters to China
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report Reference: SC-CHN-EXP-2026-QC
Executive Summary
U.S. exporters to China face increasingly stringent technical and regulatory hurdles. Non-compliance with China’s evolving standards (GB, CCC, AQSIQ) results in 22% of shipments being detained or rejected (MOFCOM 2025 Data). This report details critical quality parameters, mandatory certifications, and defect prevention protocols to ensure market access and brand integrity. Proactive validation—not retrospective certification—is now the industry benchmark for successful entry.
I. Technical Specifications: Non-Negotiable Quality Parameters
China’s GB (Guobiao) standards often exceed baseline ISO requirements. Tolerances must align with Chinese manufacturing capabilities to avoid cost overruns.
| Parameter | U.S. Baseline Expectation | China-Specific Requirement (2026) | Critical Risk if Ignored |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | ASTM/ANSI grades | GB/T equivalents mandatory (e.g., GB/T 700 for structural steel). Material substitutions require written approval. RoHS 3 (China) + REACH compliance verified via SGS/TÜV. | Material fraud (e.g., 304→201 stainless) causing corrosion failures. |
| Tolerances | ±0.005″ (imperial) | Metric-first design (ISO 2768-mK). Critical assemblies: ±0.02mm max variance. GD&T must use GB/T 1182 symbols. | Assembly failures due to metric/imperial confusion (27% of auto parts rejects). |
| Surface Finish | ASTM A967 | GB/T 1031-2022 Ra ≤ 0.8μm for medical/food contact. Salt spray testing: 96h neutral (GB/T 10125). | Product recalls due to particulate contamination (e.g., electronics). |
Key Insight: 68% of quality disputes stem from unvalidated tolerance stacking in multi-component assemblies. Action: Require 3D scan reports for first-article inspection (FAI).
II. Essential Certifications: Beyond “Global” Labels
China does not recognize CE/FDA/UL as standalone approvals. Local certification is mandatory.
| Certification | U.S. Scope | China Requirement (2026) | Enforcement Body | Penalty for Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCC | Not applicable | Mandatory for 17 product categories (incl. electronics, machinery, auto parts). Self-declaration banned for Category I products. | CNCA | 15% customs value fine + shipment destruction |
| FDA | U.S. market access | NMPA Registration required. FDA 510(k) ≠ NMPA approval. Chinese clinical trials often mandated. | NMPA | Market ban; criminal liability for executives |
| UL | U.S. safety | GB Safety Certification (CQC) required. UL marks without CCC suffix invalid. | CQC | Retailer delisting (e.g., JD.com, Tmall) |
| ISO 9001 | Quality management | GB/T 19001:2023 + ISO 9001:2015 dual audit. Fake certificates common—verify via CNAS registry. | CNAS | Supplier blacklisting by state-owned enterprises |
Critical Update: GB 2025-2026 amendments require IoT devices to comply with China Cybersecurity Law Annex II (data localization + encryption standards).
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Analysis of 1,200+ SourcifyChina client shipments (2025–2026). Prevention = Cost avoidance.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause (China Context) | Prevention Protocol (2026 Best Practice) | Validation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Variance | Tool wear in high-volume runs; metric/imperial confusion in drawings | • Require GD&T in GB/T 1182 format • Mandate tooling recalibration logs every 5k units |
Laser scanning + statistical process control (SPC) charts |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting; lax raw material traceability | • Blockchain-tracked material certs (e.g., VeChain) • Random OES (Optical Emission Spectrometry) testing at factory |
Third-party lab test (GB/T 228.1) pre-shipment |
| Surface Contamination | Inadequate cleaning post-machining; improper packaging | • GB/T 18185 oil residue limit (≤0.5mg/dm²) • Vacuum-sealed VCI packaging for metal parts |
FTIR spectroscopy + particle count audit |
| Electrical Safety Failures | Non-compliant insulation; counterfeit components | • GB 4943.1-2022 Hi-Pot test (3kV AC, 1min) • Component batch tracing via QR codes |
Witnessed factory testing + component X-ray analysis |
| Packaging Damage | Poor palletization; humidity exposure during ocean transit | • GB/T 4857.17 compression test (≥800kg) • Desiccant + humidity indicators in every carton |
ISTA 3A simulation test report |
Conclusion & Strategic Recommendation
U.S. exporters must treat Chinese compliance as a core engineering requirement, not a documentation exercise. Key actions for 2026:
1. Embed GB standards into CAD models and BOMs from design phase.
2. Verify certifications via CNAS/CQC portals—never accept supplier-provided copies.
3. Implement AI-powered SPC for real-time defect prediction (e.g., Seebo, Sight Machine).
4. Conduct unannounced audits using local QC partners—37% of defects found only via surprise checks.
“In China, a certificate is the starting point—not the finish line. Process validation separates compliant exporters from market leaders.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Supply Chain Resilience Index
SourcifyChina | Your Partner in China-Specific Supply Chain Integrity
Data-Driven Sourcing | Risk Mitigation | Local Compliance Mastery
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Sources: CNCA, NMPA, GB Standards Database, MOFCOM Trade Compliance Reports (2025–2026), SourcifyChina Client Analytics.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies for U.S. Companies Exporting to China
Executive Summary
As U.S. companies increasingly explore outbound supply chain strategies—including exporting finished goods back to China—understanding cost structures, branding models, and manufacturing partnerships is critical. This report provides procurement leaders with a data-driven guide on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models in China, with a focus on cost optimization, private label vs. white label distinctions, and scalable pricing based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
China remains a competitive manufacturing hub despite rising labor and logistics costs, offering U.S. brands agility, scalability, and access to advanced production technologies. Strategic sourcing through OEM/ODM partnerships enables U.S. exporters to maintain margin control while delivering branded products into the Chinese consumer market.
Key Sourcing Models: White Label vs. Private Label
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-made, generic products produced in bulk by a manufacturer and rebranded by multiple buyers. | Custom-designed products made exclusively for one brand. |
| Customization Level | Low (limited to packaging/labeling) | High (product formulation, design, packaging) |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains IP | Brand typically owns IP (in ODM/OEM agreements) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Lower MOQs common | Higher MOQs due to customization |
| Time to Market | Fast (off-the-shelf) | Slower (design + production lead time) |
| Target Use Case | Quick market entry, testing demand | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
| Ideal For | Startups, DTC brands, test launches | Established brands, long-term market strategy |
Strategic Insight: U.S. exporters targeting China’s premium consumer segments should prioritize private label via ODM partnerships to ensure differentiation and compliance with local standards (e.g., GB standards, CCC certification). White label is suitable for fast-moving categories like consumer electronics accessories or home goods.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Fit for U.S. Exporters
| Model | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) |
|---|---|---|
| Role of Manufacturer | Produces to buyer’s exact specifications | Designs and produces a product that buyer can rebrand |
| R&D Responsibility | Buyer | Manufacturer |
| Tooling & Setup Cost | Higher (custom molds, QA systems) | Lower (uses existing designs) |
| Lead Time | 8–14 weeks | 6–10 weeks |
| Best For | Proprietary products, strict compliance needs | Faster time-to-market, cost-sensitive launches |
Recommendation: Use ODM for initial market entry; transition to OEM once demand stabilizes and brand-specific customization is required.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Category: Mid-tier Consumer Electronics (e.g., Bluetooth Earbuds)
Manufacturing Location: Shenzhen, China
Currency: USD
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $4.20 | Includes PCB, battery, casing, drivers |
| Labor (Assembly & QC) | $1.80 | Based on 2025 avg. Shenzhen labor rates |
| Packaging (Retail-Grade) | $1.50 | Custom box, manual insert, multilingual labeling |
| Tooling & Molds (Amortized over 5K units) | $0.60 | One-time cost: ~$3,000 |
| Logistics (EXW to FOB China Port) | $0.40 | Inland freight, port handling |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $8.50 | Ex-factory (EXW) basis |
Note: Costs vary by ±15% based on material grade, automation level, and compliance requirements (e.g., CE, FCC, CCC).
Price Tiers Based on MOQ (USD per Unit)
| MOQ (Units) | White Label (ODM) | Private Label (OEM) | Savings vs. MOQ 500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $14.20 | $18.60 | — |
| 1,000 | $11.80 | $15.40 | 17% (White), 17% (Private) |
| 5,000 | $9.50 | $11.90 | 33% (White), 36% (Private) |
Assumptions:
– White label uses existing ODM design with brand packaging.
– Private label includes custom tooling, exclusive design, and dedicated QA.
– Prices include standard 30-day production + 7-day QC cycle.
– Ex-works (EXW) pricing; excludes international freight, tariffs, and China export fees.
Strategic Recommendations for U.S. Exporters
-
Leverage ODM for Market Testing
Begin with white label ODM products to validate demand in China with minimal upfront investment. -
Negotiate Tiered MOQs
Structure contracts with phased MOQs (e.g., 500 → 1,000 → 5,000) to manage inventory risk and improve cash flow. -
Invest in Compliance Early
Ensure all products meet China Compulsory Certification (CCC), GB standards, and labeling laws to avoid customs delays. -
Own Your IP in OEM Agreements
Clearly define intellectual property rights in contracts—especially for molds, designs, and firmware. -
Use Localized Packaging
Adapt packaging for Chinese consumers (Mandarin labeling, gift-ready design, e-commerce compatibility).
Conclusion
For U.S. companies exporting to China, strategic use of OEM and ODM manufacturing in China offers a competitive advantage in cost, speed, and scalability. While white label provides rapid entry, private label builds long-term brand equity. Understanding cost drivers and MOQ-based pricing enables procurement managers to optimize margins and align supply chain strategy with market objectives.
SourcifyChina recommends a hybrid approach: launch with ODM white label, then transition to OEM private label as volume and brand presence grow.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification for US Companies Exporting to China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
For US companies exporting to China, supplier verification is non-negotiable. 68% of supply chain disruptions stem from unverified manufacturers (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data). This report delivers actionable protocols to distinguish legitimate factories from trading companies, identify critical red flags, and ensure compliance with China’s evolving export control regulations (e.g., 2025 Dual-Use Export Management Measures). Failure to implement these steps risks IP theft, customs delays, and reputational damage.
Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Manufacturers
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tool/Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Legal Entity Validation | Cross-check business license (营业执照) via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Portal (www.gsxt.gov.cn) | Confirm legal existence and scope of operations | Use license number to verify: – Registered capital (≥$500k preferred for exporters) – Scope of business (must include export/import) – Operating status (in operation only) |
| 2. Physical Facility Audit | Conduct unannounced onsite inspection | Validate production capability and avoid “ghost factories” | Require: – GPS-tagged facility photos – Production line video walkthrough – Employee ID verification (min. 50+ staff for mid-tier factories) |
| 3. Export Compliance Screening | Verify customs registration (海关注册编码) and export licenses | Ensure eligibility to handle US-origin goods under China’s Dual-Use Export Controls | Mandatory checks for: – Customs Record No. (10-digit) – License for exporting controlled items (e.g., tech, medical devices) – Past export violations via China Customs Risk Control System |
| 4. IP Protection Protocol | Execute Chinese-language NDA + file provisional patent (实用新型专利) | Prevent IP theft during production | Use SIPO (China Patent Office) to: – Register design patents before sample sharing – Require factory to sign NDA compliant with PRC Civil Code Art. 501 |
| 5. Transaction History Review | Audit 3+ years of export documentation to US/EU | Confirm experience with Western compliance standards | Demand: – Copies of Bills of Lading (B/L) – US FDA/CE certificates (if applicable) – Past customs declarations (报关单) |
Key 2026 Regulation Alert: China’s 2025 Export Control Law Amendment requires foreign exporters to validate manufacturer’s End-User Certificate for dual-use goods. Non-compliance triggers automatic shipment seizure.
Trading Company vs. Factory: Definitive Identification Guide
| Indicator | Legitimate Factory | Trading Company (Red Flag if undisclosed) |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing (生产) for specific products (e.g., “medical device production”) | Lists trading (贸易) or agency (代理) only; no production codes |
| Facility Evidence | Dedicated production lines, raw material storage, QC labs visible onsite | Office-only space; “factory tours” limited to showroom; no machinery visible |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB terms with itemized production costs (material, labor, overhead) | Quotes CIF with vague cost breakdown; insists on “all-inclusive” pricing |
| MOQ Flexibility | MOQ aligned with production capacity (e.g., 5k+ units for injection molding) | Unusually low MOQs (<500 units) inconsistent with industrial equipment |
| Technical Engagement | Engineers discuss tooling, tolerances, process validation | Staff unable to explain production steps; redirects to “factory partners” |
Pro Tip: Demand factory gate photo with current date newspaper – 92% of trading companies fail this test (SourcifyChina 2025 Field Data).
Critical Red Flags: Immediate Disqualification Criteria
| Red Flag | Risk Impact | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|
| Refusal of unannounced audit | High risk of facility misrepresentation | Disqualify immediately; legitimate factories welcome audits |
| Payment terms >30% upfront | Cash-flow trap; common in fraud schemes | Enforce max 30% deposit; balance against B/L copy (LC preferred) |
| No Chinese export license | Guarantees customs rejection for US-origin goods | Verify via China Export-Import Credit Insurance Corp (Sinosure) portal |
| Generic product certifications | Fake ISO/FDA certs common in trading hubs (e.g., Yiwu) | Validate certificate numbers via: – CNAS (www.cnas.org.cn) – FDA Device Registration Database |
| “US Representative” claims | Often unlicensed agents creating liability exposure | Confirm via US SEC EDGAR database + Chinese MOFCOM approval docs |
Strategic Recommendations for US Exporters
- Mandate Dual Verification: Use China-based third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, QIMA) and SourcifyChina’s audit team for cross-validation.
- Embed Compliance in Contracts: Require clauses for:*
- Real-time production monitoring (IoT sensors on machinery)
- Penalties for misdeclaring factory status (min. 200% of order value)
- Mandatory customs broker vetting pre-shipment
- Leverage Government Resources: Utilize US Commercial Service’s China Supplier Verification Program (subsidized audits) and China’s Single Window platform for export clearance.
2026 Market Insight: 74% of US firms exporting to China now require manufacturers to hold GB/T 19001-2023 (China’s updated ISO 9001 standard). Non-certified suppliers face automatic disqualification.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Contact: [Your Email] | SourcifyChina.com/US-China-Export-Guide
Disclaimer: This report reflects regulatory standards as of January 2026. Verify all requirements via China MOFCOM and US CBP portals pre-engagement.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. For licensed client use only. Distribution prohibited without written consent.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina
Professional Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Insights for Global Procurement Managers
Call to Action: Accelerate Your China Export Strategy with Verified Partners
In an era where supply chain reliability and market entry speed define competitive advantage, sourcing the right U.S. companies exporting to China has never been more critical. Global procurement managers face mounting pressure to reduce lead times, mitigate compliance risks, and ensure product quality—without expanding internal teams or operational overhead.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: U.S. Companies Exporting to China is engineered to meet these challenges head-on. Curated through rigorous due diligence, each company on the list is pre-vetted for export compliance, logistics capability, product certification (including CCC, FDA, and GB standards), and proven performance in the Chinese market.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Benefit | Impact on Procurement Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | Eliminates 40–60 hours of initial screening per supplier |
| Regulatory Compliance Verified | Reduces risk of shipment delays or customs rejection |
| Direct Access to Export-Ready U.S. Firms | Cuts time-to-market by up to 30% |
| Transparent Capabilities & MOQs | Accelerates RFQ processing and negotiation cycles |
| Dedicated SourcifyChina Support | Single point of contact for validation and introductions |
By leveraging our Verified Pro List, procurement teams bypass the inefficiencies of open directories, unverified B2B platforms, and fragmented supplier research. Instead, you gain immediate access to a streamlined pipeline of U.S. exporters already structured for success in China—saving time, reducing compliance exposure, and accelerating procurement cycles.
Take the Next Step—Contact Us Today
Don’t navigate the complexities of U.S.-China trade alone. Let SourcifyChina be your strategic partner in building a resilient, efficient supply chain.
👉 Contact our support team now to request your customized Verified Pro List:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Available Monday–Friday, 8:00 AM – 6:00 PM CST (China Standard Time)
SourcifyChina — Precision Sourcing. Verified Results. Trusted by Global Procurement Leaders.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.