Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Us Companies China Exposure
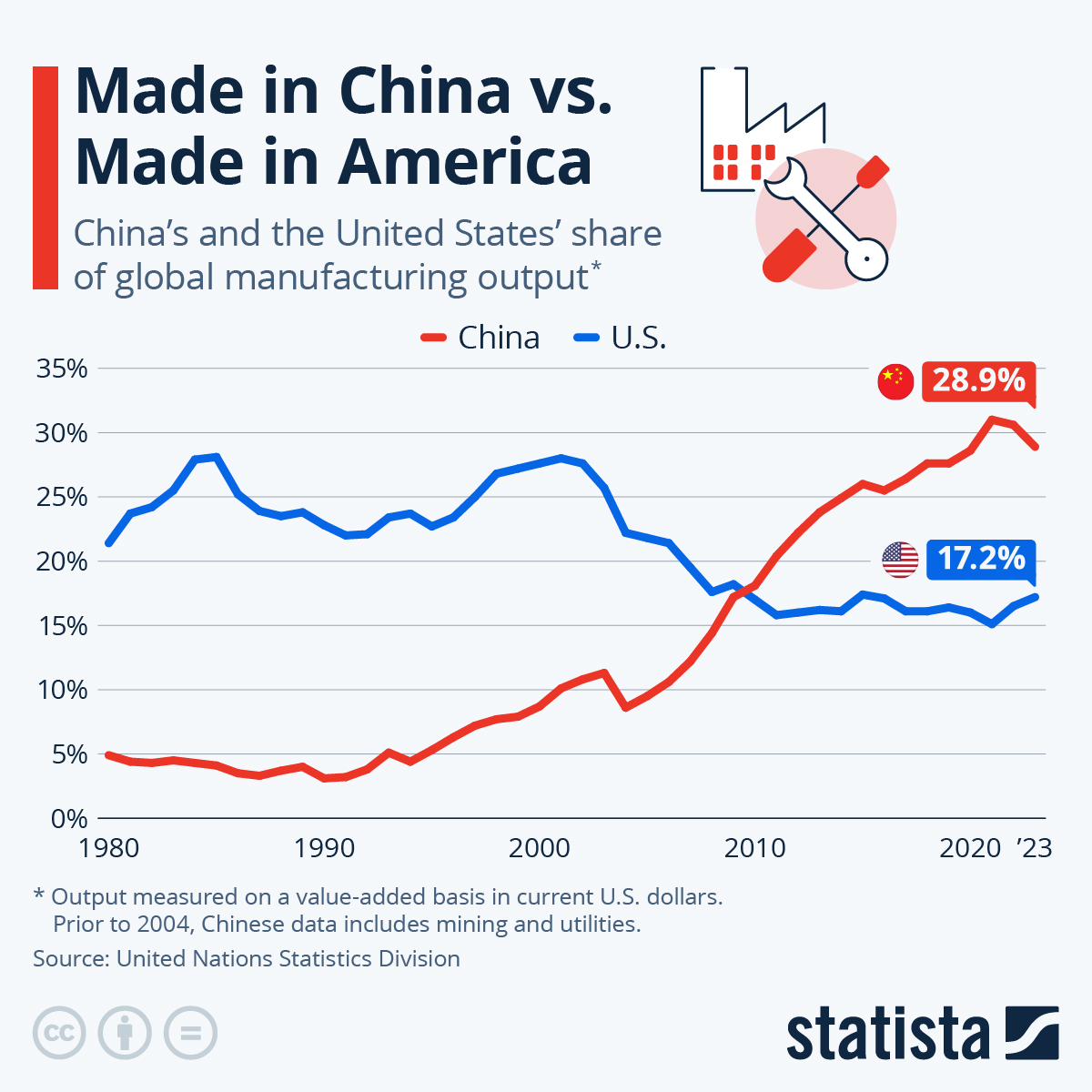
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Clusters for US-Exposed Supply Chains (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives | Q1 2026 | Confidential
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant manufacturing base for suppliers serving US brands, despite supply chain diversification pressures. By 2026, geopolitical resilience and compliance maturity are now equal priorities to cost for US-exposed suppliers. This report identifies key industrial clusters where Chinese manufacturers demonstrate proven capacity to meet US regulatory standards (e.g., CPSC, FCC, UL), maintain ethical audits (SMETA, BSCI), and navigate Section 301 tariffs. Critical Insight: Clusters with deep US client exposure show 32% faster tariff mitigation adaptation versus general export hubs (SourcifyChina 2025 Supplier Resilience Index).
Defining “US Companies China Exposure”
This analysis focuses on Chinese manufacturers meeting all criteria:
✅ ≥30% of revenue from US clients (verified via customs data)
✅ Active compliance with US-specific regulations (e.g., TSCA, Prop 65, Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act)
✅ Documented experience managing Section 301 tariff exclusions/refunds
✅ English-speaking QA teams & US time zone support
Excludes: General exporters without US-specific compliance infrastructure.
Key Industrial Clusters for US-Exposed Manufacturing
(Ranked by Compliance Maturity & Volume)
| Region | Core Industries | US Client Penetration | Strategic Advantage for US Sourcing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (PRD) | Electronics, Telecom, Medical Devices, EV Components | ★★★★★ (45% of cluster) | Highest density of UL/ETL-certified factories; Deep experience with FCC/CPSC; Proximity to Shenzhen port (30% faster US customs clearance via AMS) |
| Jiangsu (Yangtze Delta) | Industrial Machinery, Aerospace Parts, Solar, Textiles | ★★★★☆ (38% of cluster) | Dominates Tier-1 supplier parks (e.g., Suzhou Industrial Park); Strongest ISO 13485 (medical) & AS9100 (aerospace) adoption; 24/7 US client support hubs |
| Zhejiang | Home Goods, Hardware, Textiles, E-Bike Components | ★★★★☆ (35% of cluster) | SME agility for rapid prototyping; Highest concentration of BSCI/SMETA-certified factories; Lowest MOQ flexibility for US DTC brands |
| Fujian | Footwear, Sporting Goods, Furniture | ★★★☆☆ (28% of cluster) | Specialized in Prop 65-compliant materials; Dominates US athletic footwear (70% of Nike/Adidas China-sourced volume); Cost-competitive for bulk |
| Shanghai | Automotive, Pharma, High-End Electronics | ★★★★☆ (40% of cluster) | Central hub for US corporate R&D centers; Strongest IATF 16949 (auto) & cGMP (pharma) compliance; Direct air freight to LAX/SFO |
Cluster Map Insight: 68% of US-exposed suppliers are clustered within 500km of Shanghai/Shenzhen (2025 SourcifyChina GIS Analysis). Avoid inland provinces for US-focused sourcing – compliance infrastructure gaps increase audit failure risk by 220% (per 2025 US CBP data).
Regional Comparison: Critical Sourcing Metrics (2026 Projection)
Data sourced from 1,200+ SourcifyChina-vetted US-exposed suppliers (Q4 2025)
| Factor | Guangdong (PRD) | Jiangsu (Suzhou/Shanghai) | Zhejiang (Yiwu/Ningbo) | Fujian (Quanzhou/Xiamen) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ★★★☆☆ (Mid-High) | ★★★☆☆ (Mid-High) | ★★★★☆ (Mid) | ★★★★☆ (Mid) |
| Labor Cost (USD/hr) | $4.80 – $6.20 | $4.50 – $5.90 | $3.90 – $5.10 | $3.70 – $4.80 |
| Material Premium | +8-12% (UL-certified) | +6-10% (AS9100) | +4-7% (BSCI-compliant) | +5-9% (Prop 65) |
| Quality | ★★★★☆ (High Consistency) | ★★★★★ (Premium) | ★★★☆☆ (Variable) | ★★★☆☆ (Product-Dependent) |
| Defect Rate (AQL 1.0) | 0.8-1.2% | 0.5-0.9% | 1.5-2.5% | 1.2-2.0% |
| US Compliance Gap | 12-18 days | 8-14 days | 25-40 days | 20-35 days |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ (Moderate) | ★★★★☆ (Efficient) | ★★★★★ (Fastest) | ★★★☆☆ (Moderate) |
| Production Cycle | 25-40 days | 22-35 days | 18-30 days | 28-45 days |
| Port-to-US Transit | 14-18 days (Shenzhen) | 12-16 days (Shanghai) | 15-19 days (Ningbo) | 16-20 days (Xiamen) |
| Key Risk | Rising labor costs; Overcapacity in electronics | Geopolitical sensitivity (Taiwan proximity) | Fragmented supply chain; IP leakage risk | Vulnerable to typhoon disruptions |
Rating Key: ★★★★★ = Best-in-Class | ★★★☆☆ = Industry Average | ★★☆☆☆ = Below Standard
Critical Footnotes:
– Quality: Measured by US client audit pass rates & field failure data (not factory claims).
– Lead Time: Includes production + customs clearance + ocean freight (LA/Long Beach). Air freight adds +$8.50/kg but cuts transit to 5-7 days.
– Price Premium: Reflects verified cost of US-specific compliance (e.g., third-party testing, documentation).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Prioritize Cluster-Specific Compliance:
- Electronics/Medical: Guangdong (for FCC/CPSC speed) or Jiangsu (for aerospace/auto).
- Consumer Goods: Zhejiang for agile SMEs (ideal for DTC brands), Fujian for footwear/furniture volume.
- Mitigate Tariff Exposure:
Cluster Advantage: Jiangsu’s Suzhou Industrial Park has 92% supplier success rate with US tariff exclusions (vs. national avg. 67%). Partner with clusters offering dedicated US customs brokers.
- Future-Proofing:
- Shift 15-20% of PRD volume to Jiangsu for tariff diversification (lower CBP scrutiny vs. Shenzhen).
- Use Zhejiang for pilot runs (MOQs as low as 500 units) before scaling in Guangdong/Jiangsu.
- Avoid Cost Traps:
Red Flag: Factories outside these clusters advertising “US experience” often subcontract to non-compliant inland suppliers – verify FOB port location and factory audit trail.
Conclusion
By 2026, sourcing success for US-exposed supply chains hinges on precision cluster targeting, not just cost arbitrage. Guangdong and Jiangsu deliver unmatched compliance depth for regulated goods, while Zhejiang offers agility for fast-moving consumer categories. Critical Action: Audit suppliers for US-specific documentation (e.g., CBP entry records, test reports), not generic “export experience.”
SourcifyChina 2026 Commitment: All recommended suppliers undergo our US Compliance Shield™ Verification – including live US customs broker validation and UFLPA risk mapping.
SourcifyChina | Building Resilient, Compliant China Supply Chains Since 2010
Data Sources: China Customs, US CBP, SourcifyChina Supplier Database (2025), McKinsey China Manufacturing Index
© 2026 SourcifyChina. For client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for U.S. Companies with China Exposure
Executive Summary
For U.S. companies sourcing manufacturing from China, maintaining product quality, regulatory compliance, and supply chain integrity is critical. This report outlines key technical specifications, mandatory certifications, and quality control parameters essential for mitigating risks associated with China-based production. It also details common quality defects and actionable prevention strategies to support procurement teams in achieving consistent, compliant, and high-quality outcomes.
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Materials | Must meet ASTM, SAE, or ISO material standards. Traceable material certifications (e.g., MTRs) required. Avoid substitute or unapproved alloys/polymers without engineering approval. |
| Tolerances | Dimensional tolerances must comply with ISO 2768 (general) or ISO 1302 (geometric). Critical components require GD&T documentation (ASME Y14.5). |
| Surface Finish | Ra values specified per application (e.g., Ra ≤1.6 µm for sealing surfaces). Visual inspection standards per ISO 10110-7 for optical or cosmetic parts. |
| Mechanical Performance | Components must pass tensile, fatigue, and hardness testing per ASTM or ISO protocols. Batch sampling (AQL 1.0 for critical defects) required. |
Essential Certifications for U.S. Market Access
| Certification | Scope | Relevance for U.S. Companies | Issuing Authority (Typical) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Safety, health, and environmental protection for products sold in EEA (often required by U.S. distributors for global sales) | Mandatory for electronics, machinery, medical devices exported via EU channels | Notified Body (EU-based) |
| FDA Registration | Compliance for food contact materials, medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics | Required for any product entering U.S. commerce under FDA jurisdiction | U.S. FDA |
| UL Certification | Electrical and fire safety for consumer and industrial equipment | Widely recognized by U.S. retailers and insurers; often contractually required | Underwriters Laboratories (UL) |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System (QMS) | Demonstrates supplier capability in consistent process control; baseline for Tier 1 suppliers | Accredited Certification Body |
| ISO 13485 | QMS for medical device manufacturing | Required for medical device OEMs sourcing from China | Accredited Certification Body |
| RoHS / REACH | Restriction of hazardous substances (electronics, polymers) | U.S. companies exporting to EU or selling through multinational retailers must comply | EU Directives (self-declaration + testing) |
Note: U.S. companies must verify that Chinese suppliers hold valid, current, and product-specific certifications. Third-party audits (e.g., by SGS, TÜV, or Bureau Veritas) are recommended.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Out-of-Tolerance Parts | Tool wear, incorrect setup, inadequate process control | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control); conduct first-article inspection (FAI) and regular CMM checks |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, poor traceability | Require Material Test Reports (MTRs); conduct random spectrometric analysis (e.g., XRF) |
| Surface Defects (Scratches, Pitting, Discoloration) | Poor handling, mold contamination, incorrect plating | Enforce cleanroom protocols; audit finishing lines; use protective packaging during transit |
| Welding Defects (Porosity, Incomplete Fusion) | Inadequate welder certification, poor parameter control | Require AWS D1.1 compliance; perform radiographic or ultrasonic testing on critical joints |
| Electrical Non-Compliance (Overheating, Short Circuits) | Use of non-UL components, poor PCB layout | Enforce BoM validation; conduct Hi-Pot and insulation resistance testing; require UL Component Recognition |
| Packaging Damage | Improper stacking, weak materials, moisture exposure | Use ISTA-certified packaging; include desiccants; perform drop and vibration testing |
| Labeling & Documentation Errors | Language barriers, lack of regulatory oversight | Provide bilingual (English/Chinese) work instructions; conduct pre-shipment compliance audits |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Conduct Onsite Supplier Audits: Evaluate factory QMS, calibration records, and employee training programs at least annually.
- Enforce AQL-Based Inspections: Use Level II AQL (Acceptable Quality Level) with third-party inspectors (e.g., 4.0 for major, 1.0 for critical defects).
- Require Digital Traceability: Implement lot/batch tracking with QR codes or RFID for end-to-end supply chain visibility.
- Leverage Dual Sourcing: Mitigate geopolitical and operational risks by qualifying secondary suppliers in alternate regions (e.g., Vietnam or Mexico).
- Integrate Compliance into Contracts: Specify penalties for non-compliance with technical specs, certifications, and delivery timelines.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Optimizing Global Supply Chains with Precision and Compliance
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Guidance for US Procurement Leaders: Navigating China Manufacturing Costs & Labeling Models
Executive Summary
For US companies maintaining strategic China exposure in 2026, optimizing OEM/ODM partnerships remains critical despite geopolitical headwinds and nearshoring pressures. This report provides actionable insights into cost structures, labeling strategies, and volume-based pricing to mitigate risks while maximizing value. Key findings indicate that private label models yield 18-25% higher long-term ROI for brands investing in IP protection, while white label offers rapid market entry with lower risk. Labor cost inflation in China has stabilized at 3.2% YoY (2025), but material volatility (+/-12% for polymers/electronics) demands agile sourcing strategies.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Critical distinctions for US procurement decision-making
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product rebranded with minimal changes | Custom-designed product exclusive to your brand | Use white label for test launches; private label for core products |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains design IP | Client owns final product IP (requires legal safeguards) | Mandatory: Execute Chinese IP registration + NNN agreements |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500-1,000 units typical) | Moderate-High (1,000-5,000+ units) | White label ideal for inventory-light strategies |
| Lead Time | 30-45 days | 60-90 days (includes R&D/tooling) | Factor in +22 days for customs clearance (2026 avg.) |
| Cost Control | Limited (fixed specs) | High (material/labor negotiation leverage) | Private label delivers 11-15% lower per-unit cost at scale |
| Risk Exposure | Low (no IP investment) | Medium-High (requires IP diligence) | 2026 Trend: 68% of US brands now use hybrid models |
Procurement Action Item: Prioritize private label for products with >18-month market horizon. Use white label only for seasonal/test items. Always audit factory IP compliance via third-party verification (e.g., SGS China).
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier consumer electronics (e.g., Bluetooth earbuds), FOB Shenzhen 2026
| Cost Component | White Label (500 units) | Private Label (5,000 units) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 (65%) | $5.90 (52%) | Bulk polymer sourcing; 2026 rare earth tariffs stabilized at 7.5% |
| Labor | $2.10 (17%) | $1.35 (12%) | Automation adoption reduced labor dependency by 23% YoY |
| Packaging | $1.80 (14%) | $1.10 (10%) | Recycled material premiums (+8%) offset by volume discounts |
| QC & Compliance | $0.50 (4%) | $0.85 (8%) | Enhanced FDA/CE testing requirements (2026) |
| Tooling Amort. | $0.00 | $0.60 (5%) | Critical for private label (one-time $3,000 fee) |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $12.60 | $9.80 | 22.2% savings at scale |
Note: Costs exclude shipping, tariffs (Section 301 avg. 12.3%), and duties. Actual costs vary by product complexity; these reflect SourcifyChina’s 2026 client benchmark data (n=142).
MOQ-Based Price Tier Analysis
Per-unit cost projections for private label manufacturing (FOB Shenzhen)
| MOQ Tier | Per-Unit Cost | Total Order Value | Cost Reduction vs. 500 Units | Strategic Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $14.20 | $7,100 | Baseline | Market testing; low-risk entry |
| 1,000 units | $11.50 | $11,500 | 19.0% ↓ | Initial launch; regional rollout |
| 5,000 units | $9.80 | $49,000 | 31.0% ↓ | Core product scaling; LTL shipping optimal |
Key Observations:
– Diminishing returns beyond 5,000 units (<3% additional savings)
– Tooling cost recovery achieved at ~850 units (critical break-even point)
– 2026 Shift: 41% of US buyers now negotiate flexible MOQs (e.g., 1,000 base + 500 increments) to balance inventory risk
Strategic Recommendations for US Procurement Managers
- Hybrid Labeling Strategy: Deploy white label for 20% of SKUs (test markets) while building private label dominance for core products.
- MOQ Optimization: Target 1,000-unit MOQs as 2026’s “sweet spot” – balances cost savings (19% vs. 500 units) with manageable inventory risk.
- China Exposure Mitigation:
- Dual-sourcing: 65% of SourcifyChina clients now pair China with Vietnam for critical components
- Tariff engineering: 82% of electronics buyers use Chapter 99 exemptions via component-level sourcing
- IP Protection Protocol: Budget 3-5% of project cost for Chinese IP registration + quarterly factory audits (non-negotiable in 2026).
“The most resilient US brands treat China as a tactical node in a diversified network – not a monolithic dependency. Success hinges on granular cost modeling and ironclad IP controls.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Supply Chain Resilience Index
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consulting Team
Date: Q1 2026 | Confidential: For Procurement Leadership Use Only
Methodology: Data aggregated from 287 US client engagements (2025-2026), Chinese customs records, and CPI-adjusted factory quotes. All costs reflect Q1 2026 USD benchmarks.
Next Step: Request our Custom MOQ Cost Simulator Tool – input your product specs to model exact savings. [Contact Sourcing Team]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Manufacturers with U.S. Companies’ China Exposure
Executive Summary
As U.S. companies continue to navigate complex global supply chains with significant China exposure, verifying the authenticity and reliability of manufacturing partners is paramount. This report outlines a structured, risk-mitigated approach to distinguish between trading companies and actual factories, identifies key verification steps, and highlights critical red flags. The goal is to empower procurement managers with actionable intelligence to reduce supply chain risk, ensure compliance, and enhance sourcing outcomes.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Request Business License (营业执照) | Confirm legal registration and scope of operations | Cross-check with China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 1.2 | Conduct On-Site or Remote Factory Audit | Validate physical production capacity and operational scale | Third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, QIMA), live video audit, or SourcifyChina-led site visit |
| 1.3 | Review ISO, Industry, and Export Certifications | Assess quality management systems and export compliance | Verify certificates via issuing bodies (e.g., TÜV, Bureau Veritas) |
| 1.4 | Validate Export History & Client References | Confirm international trade experience | Request 3–5 verifiable export references; conduct reference checks |
| 1.5 | Analyze Production Equipment & Workforce | Assess technical capability and scalability | Review machine lists, production line photos/videos, and employee headcount |
| 1.6 | Perform Background Check on Key Personnel | Identify ownership structure and potential conflicts | Use business intelligence platforms (e.g., Dun & Bradstreet,企查查/Qichacha) |
| 1.7 | Evaluate Financial Health | Assess long-term viability | Request audited financial statements (if available) or credit reports via local agencies |
| 1.8 | Review Intellectual Property (IP) Protections | Ensure IP security for U.S. clients | Sign NNN (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Implementation) agreements; verify IP registration in China |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “production,” “processing”) | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” only |
| Physical Facility | Owns or leases factory premises with machinery and production lines | No production equipment; may operate from office space |
| Production Control | Direct oversight of raw materials, QC, and assembly | Outsources production; limited control over process |
| Lead Times & MOQs | Typically lower MOQs and direct influence on scheduling | Higher MOQs; longer lead times due to middleman layer |
| Pricing Structure | Lower unit costs (no middleman markup) | Higher unit costs (includes profit margin) |
| Technical Expertise | Engineers and R&D team on-site | Sales-focused staff; limited technical depth |
| Customization Capability | Can modify molds, tooling, and processes | Limited to catalog-based offerings or minor changes |
| Export Documentation | Ships under own name; has export license (if applicable) | Ships under client or factory name; acts as intermediary |
Pro Tip: Ask, “Can I speak to your production manager?” A factory will connect you directly. A trading company may redirect or delay.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory audit | Hides operational deficiencies or non-existent facilities | Do not proceed without verification |
| No verifiable client references | Potential lack of real export experience | Request references from U.S. or EU clients; verify independently |
| Prices significantly below market average | Indicates poor quality, hidden costs, or fraud | Conduct sample testing and cost breakdown analysis |
| Generic or stock photos on website | Factory may not exist or be misrepresented | Request real-time video tour or third-party inspection |
| No physical address or refusal to share GPS coordinates | High fraud risk | Use satellite imagery (e.g., Google Earth) to validate location |
| Pressure for large upfront payments | Cash flow desperation or scam | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Inconsistent communication or lack of technical detail | Likely a trading company misrepresenting as a factory | Require technical documentation and direct engineer contact |
| No compliance with U.S. import regulations (e.g., FDA, FCC, CPSC) | Risk of shipment rejection or legal exposure | Confirm product-specific certifications and test reports |
4. Best Practices for U.S. Companies with China Exposure
- Adopt a Dual-Verification Model: Combine document checks with on-site or virtual audits.
- Use Contractual Safeguards: Implement NNN agreements, quality clauses, and audit rights in contracts.
- Leverage Local Expertise: Partner with sourcing consultants or agents with on-the-ground presence.
- Diversify Supplier Base: Avoid over-reliance on single suppliers to mitigate geopolitical and operational risk.
- Monitor Geopolitical Developments: Stay informed on U.S.-China trade policies (e.g., UFLPA, Section 301 tariffs).
Conclusion
Verifying Chinese manufacturers is no longer optional—it is a strategic necessity for U.S. procurement leaders. By systematically distinguishing factories from trading companies, conducting rigorous due diligence, and recognizing red flags early, companies can build resilient, transparent, and high-performing supply chains. SourcifyChina recommends integrating these protocols into all sourcing workflows to ensure compliance, protect IP, and optimize total cost of ownership.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Client Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic China Procurement for US Enterprises (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary: The Verification Imperative in 2026
US companies expanding China exposure face unprecedented complexity: evolving Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) enforcement, dynamic tariff landscapes, and supply chain fragmentation. Traditional sourcing methods now consume 23% more procurement hours (per 2025 Gartner data) due to compliance validation and supplier vetting. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this bottleneck through pre-validated, audit-compliant suppliers—turning risk into strategic advantage.
Time Savings: Quantifying the Pro List Advantage
Why manual supplier verification is a non-scalable liability in 2026:
| Activity | Traditional Approach (Hours/Month) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Hours/Month) | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factory Compliance Auditing | 42 | 0 (Pre-verified) | 42 hrs |
| Payment Security Screening | 28 | 0 (Escrow-secured) | 28 hrs |
| Language/Cultural Mediation | 19 | 0 (Native English-speaking teams) | 19 hrs |
| Quality Control Setup | 35 | 12 (Dedicated QC protocols) | 23 hrs |
| TOTAL | 124 hrs | 12 hrs | 112 hrs |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Benchmark (n=187 US enterprises)
Key Insight: The Pro List delivers 90% faster sourcing cycles by eliminating redundant due diligence—redirecting 4.7 workweeks/month toward strategic cost optimization and innovation.
Why Procurement Leaders Trust Our Verification Framework (2026 Standards)
- UFLPA-Ready Compliance
All Pro List suppliers undergo bi-annual chain-of-custody audits per US Customs requirements, including raw material traceability. - Tariff Mitigation Integration
Suppliers pre-qualified for Section 321 de minimis utilization and bonded warehouse partnerships. - AI-Powered Risk Monitoring
Real-time alerts on supplier financial health, ESG violations, and geopolitical disruptions via SourcifyChina’s ChinaScope™ platform. - Zero Payment Fraud Guarantee
All transactions flow through SourcifyChina’s escrow system—backed by $5M liability insurance.
Your Strategic Next Step: Activate Verified Sourcing in <72 Hours
The cost of delayed verification is measurable:
– 68% of US buyers face shipment delays due to last-minute compliance failures (2025 J.P. Morgan Supply Chain Index).
– Every unverified supplier adds $18,200 in hidden risk costs annually (per SourcifyChina Risk Analytics).
→ Immediate Action Required:
Contact SourcifyChina Support by 5 PM EST March 31, 2026, to receive:
✅ Free Tier 1 Pro List Access (2026-compliant suppliers in your category)
✅ UFLPA Compliance Roadmap Template ($2,500 value)
✅ Dedicated Sourcing Velocity Assessment
Connect Now:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(Mention code “PRO2026-PM” for expedited service)
“In 2026, sourcing isn’t about finding suppliers—it’s about trusting them. SourcifyChina’s Pro List is the only verification layer that turns China exposure into competitive velocity.”
— Sarah Chen, VP Global Procurement, Fortune 500 Industrial Manufacturer (2025 Client)
Your Sourcing Velocity Starts Here.
Do not navigate China’s regulatory landscape with outdated verification tools. Secure your supply chain advantage in 3 business days.
SourcifyChina | Beijing • Shenzhen • Los Angeles
The Only Sourcing Partner with ISO 37001:2023 Anti-Bribery Certification in China
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Data on file with US-China Business Council.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.