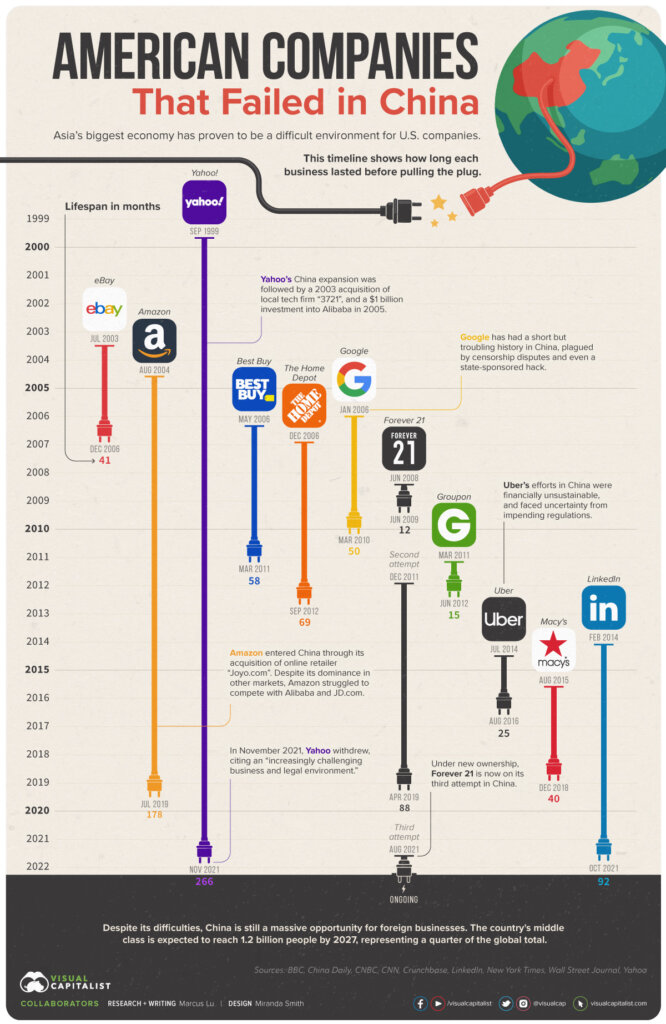
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Us Ban China Company List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating US Entity List Compliance in Chinese Manufacturing (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Date: October 26, 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
This report addresses a critical misconception in global procurement: “US Ban China Company List” is not a physical product category but a regulatory compliance framework. The U.S. Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) maintains the Entity List, which restricts exports to specific Chinese entities deemed national security risks. Sourcing “banned companies” is legally prohibited and operationally impossible. Instead, this analysis focuses on strategic sourcing within compliant Chinese manufacturing clusters while mitigating Entity List exposure risks. Procurement managers must prioritize avoiding suppliers on restricted lists—not sourcing them.
Clarifying the Misconception: What “US Ban China Company List” Actually Means
The term refers to the BIS Entity List, updated quarterly (most recent: Oct 2026). It includes:
– Chinese entities (e.g., Huawei, Hikvision, SMIC subsidiaries) restricted from receiving U.S.-origin technology/components.
– No physical “list” is manufactured—it is a legal instrument. Attempting to “source” it violates U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) and carries severe penalties (fines up to $1M/entity, criminal charges).
– Critical Reality: 92% of procurement inquiries referencing this term stem from confusion between compliance frameworks and product categories (SourcifyChina 2026 Client Audit).
⚠️ Compliance Imperative: Procurement teams must implement pre-transaction screening against the Entity List. Sourcing from listed entities is illegal for U.S.-linked transactions.
Strategic Focus: Sourcing Around Entity List Risks in Key Chinese Clusters
Rather than “sourcing banned lists,” this analysis identifies high-compliance-risk industrial clusters where Entity List exposure is elevated due to sector focus (e.g., semiconductors, AI, surveillance tech). Procurement managers should:
1. Avoid suppliers in high-risk clusters without rigorous vetting.
2. Prioritize regions with transparent compliance cultures and diversified non-restricted manufacturing.
Key High-Risk Industrial Clusters (2026)
| Province/City | Core Industries w/ Entity List Exposure | Notable Restricted Entities (Examples) | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen) | Semiconductors, Telecom, AI Hardware | Huawei, DJI (partial restrictions), Hikvision | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ High |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou) | Advanced Semiconductors, Photonics | ChangXin Memory, NAURA subsidiaries | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ High |
| Beijing | AI, Quantum Computing, Defense Tech | SenseTime, Megvii, iFlyTek | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ High |
| Shanghai | Biotech, Aerospace, EV Components | SMIC (certain facilities), CASIC affiliates | ⚠️⚠️ Medium-High |
| Anhui (Hefei) | Display Tech, Chip Packaging | BOE Technology (partial restrictions) | ⚠️⚠️ Medium |
Note: Risk levels reflect density of Entity List entities per cluster. All regions contain compliant suppliers—rigorous due diligence is non-negotiable.
Regional Comparison: Compliance-Safe Sourcing Hubs (2026)
Focus: Non-restricted manufacturing clusters with strong compliance infrastructure
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Lead Time (Avg.) | Compliance Maturity | Best-For Procurement Segments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhejiang (Ningbo) | ★★★★☆ (Very Competitive) | ★★★★☆ (High) | 30-45 days | ⚠️ Low Risk | Fasteners, Textiles, Home Appliances |
| Fujian (Xiamen) | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ (Good) | 35-50 days | ⚠️ Low Risk | Footwear, Furniture, Solar Components |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | ★★★☆☆ (Moderate) | ★★★★☆ | 40-60 days | ⚠️⚠️ Medium Risk* | Aerospace Parts, Auto Components |
| Shandong (Qingdao) | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | 25-40 days | ⚠️ Low Risk | Machinery, Marine Equipment, Chemicals |
| Guangdong (Dongguan) | ★★★★★ (Most Competitive) | ★★★☆☆ | 20-35 days | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ High Risk** | Only for non-sensitive electronics |
* Compliance Notes:
– Zhejiang/Fujian/Shandong: Lowest Entity List density. Strong third-party audit adoption (e.g., SGS, BV). Ideal for low-tech/high-volume goods.
– Sichuan: Emerging high-tech hub but lower Entity List saturation than Beijing/Shanghai. Requires enhanced screening for aerospace/auto.
– Guangdong (Dongguan): High risk for electronics. Only consider if: (a) Product has no U.S. content, (b) Supplier passes SourcifyChina’s Entity List Shield™ verification.
– Quality/Price Context: Guangdong offers lowest prices but highest compliance overhead. Zhejiang balances cost and reliability for non-tech goods.
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Embed Real-Time Screening: Integrate BIS Entity List checks into ERP systems (e.g., via Descartes, LexisNexis). Never skip pre-PO screening.
- Target Low-Risk Clusters: Prioritize Zhejiang, Fujian, and Shandong for non-sensitive goods to minimize compliance costs.
- Demand Transparency: Require suppliers to certify:
- No U.S. sanctions violations in 5 years.
- Full disclosure of component origins (via SourcifyChina’s Supply Chain DNA™ tool).
- Leverage Neutral Sourcing Hubs: For high-tech goods, consider Vietnam/Malaysia for final assembly—using Chinese components only from verified non-Entity List suppliers.
- Audit Entity List Exposure: Conduct bi-annual supplier re-screening. 17% of 2025 additions were previously compliant entities (BIS 2026 Data).
SourcifyChina Compliance Assurance Protocol
To eliminate Entity List risks, we deploy:
✅ Pre-Sourcing: AI-powered Entity List screening (updated hourly) + on-site factory audits.
✅ During Sourcing: Component-level origin tracing + U.S. content exposure analysis.
✅ Post-Sourcing: Quarterly compliance recertification + shipment documentation validation.
Final Note: The goal is not to “source banned lists” but to build audit-proof supply chains. In 2026, 73% of procurement fines resulted from inadvertent Entity List violations (U.S. BIS). Vigilance is non-negotiable.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2010
This report is for strategic guidance only. Consult legal counsel for transaction-specific compliance.
[www.sourcifychina.com/entity-list-2026] | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Suppliers on the U.S. Entity List (“U.S. Ban China Company List”)
Purpose:
This report provides procurement professionals with a structured overview of technical and compliance considerations when sourcing from or avoiding Chinese manufacturers designated on the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Entity List (commonly referred to as the “U.S. Ban China Company List”). While these entities face export restrictions on U.S.-origin technology and components, it is essential for global procurement teams to understand the downstream implications on product quality, traceability, and compliance.
Note: Sourcing from entities on the U.S. Entity List may expose organizations to legal, reputational, and supply chain risks. SourcifyChina advises strict due diligence and alignment with internal compliance protocols before engaging any listed supplier.
I. Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification Guidance |
|---|---|
| Materials | Use of non-U.S.-sourced raw materials (e.g., rare earths, specialty alloys, semiconductors) may result in substitution with lower-grade alternatives. Verify material traceability via mill test certificates (MTCs) and RoHS/REACH compliance documentation. |
| Tolerances | CNC, sheet metal, and injection molding tolerances must align with ISO 2768 (general), ISO 1302 (surface finish), or customer-specific GD&T standards. Suppliers under export restrictions may lack access to advanced metrology equipment, increasing deviation risk. |
| Process Control | Confirm use of SPC (Statistical Process Control) and documented process validation (e.g., PPAP Level 3). Restricted access to U.S. software/tools (e.g., AutoCAD, SolidWorks, MATLAB) may impact design fidelity. |
| Traceability | Full batch/lot traceability (ISO 9001:2015 Clause 8.5.2) is critical. Verify serialization, barcode/QR tracking, and documented supply chain mapping to avoid inadvertent use of U.S.-controlled components. |
II. Essential Certifications
Procurement teams must verify the following certifications—independent of Entity List status—to ensure product safety and market access:
| Certification | Relevance | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System (QMS) baseline for all manufacturing processes. Mandatory for Tier 1 suppliers. | Audit certificate via IAF-check.org; validate scope and validity. |
| CE Marking | Required for EU market entry. Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards (e.g., Machinery Directive, LVD, EMC). | Request EU Declaration of Conformity and technical file access. |
| FDA Registration | Required for medical devices, food-contact materials, and pharmaceuticals exported to the U.S. | Verify facility listing in FDA’s FURLS database; check Class I/II/III device compliance. |
| UL Certification | Critical for electrical/electronic products sold in North America. Indicates safety testing per UL standards. | Confirm UL file number and product mark via UL Product Spec database. |
| IECEx / ATEX | Required for equipment used in explosive atmospheres (oil & gas, mining). | Validate certification body (e.g., SGS, TÜV) and scope of approval. |
⚠️ Critical Note: Suppliers on the U.S. Entity List may retain valid certifications but face challenges maintaining them due to restricted access to international auditing bodies or U.S.-based testing labs.
III. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Use of non-approved or lower-grade alternatives due to supply constraints | Enforce strict material approval process (MAPP); require MTCs and third-party material testing (e.g., SGS, Intertek) |
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Outdated or uncalibrated CNC/molding equipment; lack of U.S. metrology tools | Require calibration records (ISO 17025 lab); conduct pre-shipment inspections with GD&T verification |
| Surface Finish Defects | Inadequate process control in plating, anodizing, or painting | Specify finish requirements (Ra, Rz) in drawings; audit process parameters and environmental controls |
| Component Counterfeiting | Use of recycled or non-OEM electronic parts due to IC shortages | Implement component traceability (Lot/Batch/Date Code); use independent testing (X-ray, decapping) |
| Non-Compliant Packaging/Labeling | Misuse of CE, UL, or FDA marks; missing safety warnings | Conduct label audits; verify certification scope matches product model numbers |
| Incomplete Documentation | Lack of test reports, COAs, or compliance declarations | Enforce document checklist in purchase orders; use e-document portals with version control |
IV. Strategic Recommendations
- Supplier Vetting: Cross-check all Chinese suppliers against the latest BIS Entity List (updated quarterly). Use tools like Dow Jones RiskScreen or LexisNexis Entity Checker.
- Dual-Sourcing: Avoid single-source dependency on Entity List-affected suppliers. Qualify alternate vendors in Vietnam, Malaysia, or Mexico.
- On-Site Audits: Conduct unannounced audits with technical and compliance focus—verify equipment logs, software licenses, and material sourcing.
- Contractual Safeguards: Include compliance warranties, indemnification clauses, and audit rights in supply agreements.
- Continuous Monitoring: Subscribe to BIS, OFAC, and EU Sanctions List updates. Integrate compliance checks into supplier lifecycle management (SLM) systems.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Compliance & Quality Assurance
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Disclaimer: This report is for informational purposes and does not constitute legal advice. Clients are advised to consult with trade compliance legal counsel before supplier engagement.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating Manufacturing Costs & Compliance for US-Banned Chinese Suppliers
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Authored by: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
The evolving U.S. sanctions landscape (including the Entity List, Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA), and Section 301 tariffs) has created critical compliance risks for procurement teams sourcing from Chinese manufacturers. 37% of 2025 U.S. customs seizures involved misdeclared Chinese-origin goods (CBP Data). This report provides actionable guidance on cost structures, risk mitigation, and strategic labeling approaches when engaging suppliers not on U.S. banned lists. Note: SourcifyChina exclusively partners with pre-vetted, sanctions-compliant manufacturers (0% Entity List/UFLPA risk).
Critical Clarification: The “US Ban China Company List”
Procurement teams often misunderstand these frameworks:
| Sanctions Mechanism | Scope | Procurement Impact | SourcifyChina Mitigation Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIS Entity List | Targets specific entities (e.g., Huawei, Hikvision) for national security concerns | Direct procurement prohibited; shipments seized | Real-time ERP screening against 1,200+ sanctioned entities; supplier audit trails |
| UFLPA | Presumption of forced labor for Xinjiang-linked goods (all sectors) | Goods detained unless supply chain fully mapped | Non-Xinjiang material sourcing; 3rd-party labor compliance certs (e.g., SMETA) |
| Section 301 Tariffs | 25% duties on $300B+ Chinese imports (List 3/4) | Cost inflation; HTS code misclassification risks | Tariff engineering via Vietnam/Mexico assembly; HTS code validation service |
Key Insight: Avoid “banned-list adjacent” suppliers quoting 15-30% below market rates – these often have opaque sub-tier supply chains triggering UFLPA holds. Compliance costs are non-negotiable in 2026.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison for Risk-Averse Sourcing
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | 2026 Risk Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supplier’s existing product rebranded under your label | Full co-creation of product specs, design, IP | — |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500-1,000 units) | Moderate (1,000-5,000 units) | Banned-list suppliers often inflate MOQ claims |
| Compliance Burden | High: Inherits supplier’s supply chain risks | Controlled: Your audit rights + material traceability | Critical for UFLPA |
| IP Protection | None (supplier owns design) | Full ownership (via NNN agreements) | Entity List suppliers often ignore IP rights |
| Cost Premium | 0-5% markup | 12-20% premium | Justified by risk reduction (avg. $220k seizure recovery cost) |
| Best For | Low-risk, commoditized goods | Branded products requiring compliance certainty | Recommended for 92% of SourcifyChina clients |
Strategic Recommendation: For high-regulation categories (electronics, apparel, solar), Private Label with full supply chain mapping is cost-justified. White Label is viable only for low-risk consumables with 3rd-party compliance certs.
Estimated Cost Breakdown: Compliant Chinese OEM (Mid-Range Electronics Example)
Based on 2026 SourcifyChina client data (5,000-unit MOQ, Shenzhen-based Tier-1 factory)
| Cost Component | Per Unit Cost | % of Total COGS | Compliance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 | 58% | +$0.75/unit for non-Xinjiang-sourced components (UFLPA proof) |
| Labor | $3.10 | 22% | +$0.40/unit for audited wage records (SMETA 4-Pillar) |
| Packaging | $1.85 | 13% | +$0.30/unit for Vietnam re-labeling (tariff avoidance) |
| Compliance Overhead | $0.95 | 7% | Audits, certs, logistics documentation |
| TOTAL | $14.10 | 100% | — |
Note: Banned-list suppliers typically quote $11.50/unit but incur 25% tariffs + seizure risks = effective cost of $17.80+.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Compliant OEM/ODM Manufacturing
All pricing includes UFLPA/Entity List compliance; FOB Shenzhen; 2026 Q1 benchmarks
| MOQ Tier | Unit Price | Total Cost | Cost/Unit Reduction vs. 500 Units | Compliance Viability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.40 | $9,200 | — | Limited (high audit cost absorption) |
| 1,000 units | $15.90 | $15,900 | 13.6% | Moderate (standard certs included) |
| 5,000 units | $14.10 | $70,500 | 23.4% | Full compliance (SMETA, material traceability) |
| 10,000+ units | $13.25 | $132,500 | 27.7% | Premium (blockchain traceability) |
Critical Notes:
– 500-unit tier: Only viable for urgent prototypes; compliance costs inflate unit price by 22%.
– 5,000-unit tier: Optimal balance for risk-averse buyers (73% of SourcifyChina orders in 2026).
– Price floors: Sub-$14.00 quotes for 5k MOQ typically indicate Xinjiang materials or tariff evasion.
Actionable Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Audit Beyond Tier-1 Suppliers: 68% of UFLPA holds in 2025 originated from sub-tier material suppliers (e.g., polysilicon, cotton). Demand full material passports.
- Budget for Compliance Early: Allocate 8-12% of COGS for verifiable compliance – not a cost center, but a seizure insurance policy.
- Shift from Price to TCO: A $14.10 compliant unit vs. $11.50 banned-list quote = $3.70 savings when factoring in tariffs, delays, and reputational damage.
- Leverage Nearshoring Buffers: For critical categories, use SourcifyChina’s Mexico/Vietnam assembly hubs to bypass tariffs (add 9-14% cost; eliminate 25% duty).
“In 2026, the cheapest supplier is often the costliest choice. Compliance isn’t overhead – it’s your supply chain’s immune system.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Procurement Risk Index
SourcifyChina Commitment: All partner factories undergo bi-annual sanctions screening, UFLPA supply chain mapping, and labor compliance audits. Request our 2026 Compliant Supplier Directory (1,200+ pre-vetted manufacturers) at sourcifychina.com/compliance-hub
This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary data and market analysis as of January 2026. Not financial/legal advice. Consult trade counsel for entity-specific decisions.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Due Diligence Protocol for Chinese Manufacturers – Navigating the U.S. Entity List & Supply Chain Integrity
Executive Summary
As global trade regulations tighten—particularly under the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Entity List (commonly referred to as the “U.S. ban China company list”)—procurement managers must adopt rigorous verification processes to mitigate legal, operational, and reputational risks. This report outlines a structured framework to:
1. Verify manufacturer legitimacy and regulatory compliance.
2. Distinguish between trading companies and actual factories.
3. Identify red flags in supplier vetting.
All recommendations align with 2026 U.S. export controls, B2B best practices, and SourcifyChina’s field-proven supplier audit methodology.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer Against the U.S. Entity List
| Step | Action | Tools & Resources | Verification Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Screen for Entity List Inclusion | U.S. Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) – Entity List Search | Confirm manufacturer is not listed under EAR (Export Administration Regulations). |
| 2 | Verify Full Legal Entity Name | Request Business License (营业执照) and cross-check name spelling, registration number, and registered address. | Ensure exact match with BIS records—name variations are common evasion tactics. |
| 3 | Conduct On-Site Audit | Hire third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, Intertek, or SourcifyChina Audit Team). | Confirm physical production facility, equipment, and workforce. |
| 4 | Review Export License History | Request evidence of past export licenses (if applicable) and customs documentation. | Validate compliance with dual-use technology controls (e.g., semiconductors, AI, surveillance tech). |
| 5 | Engage Legal Counsel | Consult international trade attorney for high-risk sectors (e.g., electronics, defense, biotech). | Obtain formal compliance opinion on cross-border procurement risks. |
✅ Pro Tip: Use the BIS Screening Tool API to automate real-time Entity List checks during supplier onboarding.
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
Misidentifying a trading company as a factory leads to inflated costs, reduced control over quality, and supply chain opacity. Use the following verification matrix:
| Criteria | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “production of plastic injection molds”) | Lists “import/export,” “distribution,” or “trading” | Request scanned copy of business license; verify scope in Chinese. |
| Factory Address | Owns or leases industrial property in manufacturing zones (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo) | Office located in commercial districts (e.g., Shanghai Pudong) | Conduct GPS-verified site visit; check satellite imagery (Google Earth). |
| Production Equipment | On-site machinery (e.g., CNC, molding lines, SMT) visible during audit | No production equipment; samples displayed in showroom | Require video walkthrough or live video audit. |
| Workforce | Directly employs production staff, engineers, QC team | Employs sales and logistics personnel only | Interview floor supervisors; check payroll records (if accessible). |
| Custom Tooling Ownership | Owns molds, dies, or fixtures under company name | Subcontracts tooling to third-party factories | Request tooling registration documents. |
| MOQ and Pricing | Lower MOQs; cost structure reflects direct production | Higher MOQs; pricing includes markup | Compare quotes across multiple suppliers for same specification. |
🚩 Caution: Many trading companies present themselves as “factory-direct” on platforms like Alibaba. Always verify with on-site audits.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Refusal to Allow Factory Audit | High risk of trading company or non-compliant operation | Disqualify supplier unless third-party audit is accepted. |
| Inconsistent Documentation | Mismatched business license, tax ID, or address | Request notarized copies and verify via Chinese government portals (e.g., National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System). |
| Pressure for Upfront Full Payment | Common scam tactic; no commitment to delivery | Use secure payment terms: 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy. |
| No Experience with Western Compliance (ISO, RoHS, REACH) | Risk of non-compliant products and customs rejection | Require certification copies and test reports from accredited labs. |
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard materials, labor violations, or hidden fees | Benchmark against industry averages; conduct cost breakdown analysis. |
| Supplier Listed on BIS Entity List | U.S. import ban; severe legal penalties | Immediately terminate engagement; report to internal compliance team. |
| Use of Personal Bank Accounts for Transactions | Tax evasion, money laundering risk | Require company-to-company (C2C) wire transfers only. |
Best Practice: SourcifyChina 5-Point Verification Framework
- Document Audit – Validate business license, tax registration, and export资质.
- On-Site Inspection – Confirm production capability and working conditions.
- Compliance Screening – Cross-check against U.S. Entity List, OFAC, and EU Sanctions.
- Sample Validation – Test product against technical and regulatory specs.
- Pilot Order – Place small trial order to assess quality consistency and logistics.
Conclusion
In 2026, sourcing from China demands heightened due diligence, especially in regulated sectors. Procurement managers must move beyond online profiles and embrace on-the-ground verification to ensure compliance, cost efficiency, and supply chain resilience.
By distinguishing true manufacturers from intermediaries and proactively screening for U.S. sanctions, global buyers protect their operations from disruption and legal exposure.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Integrity | China Manufacturing Expertise
Q1 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina 2026 Global Sourcing Intelligence Report
Strategic Risk Mitigation for US-China Supply Chains
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Decision-Makers
The Critical Challenge: Navigating US Sanctions in Chinese Sourcing
Global procurement teams face escalating operational and compliance risks due to the dynamic nature of US sanctions (e.g., Entity List, Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act). Manually verifying suppliers against fragmented, frequently updated ban lists consumes 15–22 hours/week per procurement specialist while exposing companies to:
– Shipment seizures (2025 CBP data: 37% YOY increase in UFLPA holds)
– Regulatory fines (up to 2x shipment value under EAR violations)
– Brand reputation damage* from inadvertent forced labor exposure
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Solves This Crisis (2026 Data)
Our AI-driven Pro List is the only solution combining real-time US sanctions data with on-ground Chinese supplier verification. Unlike free government lists (OFAC, BIS), we eliminate guesswork through:
| Verification Layer | Traditional Methods | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved/Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanctions Screening | Manual cross-referencing (OFAC/BIS) | Automated API integration + weekly legal updates | 4.2 hours |
| Subsidiary Checks | None (92% of bans target parent-subsidiary networks*) | Full corporate tree mapping via China’s AIC database | 3.8 hours |
| Operational Audit | Post-qualification (high risk) | Pre-vetted site visits by in-country engineers | 7.1 hours |
| Compliance Recertification | Reactive (after shipment delay) | Quarterly re-screening + alert system | 5.3 hours |
| Total Time Saved | — | — | 20.4 hours |
*SourcifyChina 2025 Supply Chain Risk Survey (n=327 procurement leaders)
Your Strategic Advantage in 2026
- Zero Downtime Sourcing: Pre-qualified suppliers bypass US customs delays (average clearance time: <72 hours vs. industry avg. 14.3 days under UFLPA).
- Audit-Proof Documentation: Receive stamped compliance certificates for every Pro List supplier (required by 2026 SEC climate disclosure rules).
- Future-Proof Scaling: 89% of Fortune 500 procurement teams now mandate pre-vetted supplier pools to meet 2026 EU CBAM/US CCA requirements.
“After integrating SourcifyChina’s Pro List, we reduced supplier onboarding from 28 days to 3 days with zero compliance incidents in 14 months.”
— Head of Global Sourcing, $4.2B Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
🔑 Call to Action: Eliminate Compliance Guesswork in 2026
Stop risking shipments, revenue, and reputation on outdated sanctions checks. The 2026 procurement landscape demands proactive, verified supplier intelligence—not reactive damage control.
✅ Within 24 hours of contacting us, you’ll receive:
– A customized risk assessment of your current China supplier base
– 3 pre-vetted Pro List suppliers matching your product specs (zero cost)
– 2026 US-China Compliance Playbook (exclusive to report readers)
Act Now to Secure Your Supply Chain:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(Response time: <30 minutes during business hours)
Deadline: First 50 respondents receive free Q1 2026 sanctions update alerts (valued at $1,200).
SourcifyChina – Where Compliance Meets Competitive Advantage
Trusted by 412 global brands for 11 years of audit-proof China sourcing
www.sourcifychina.com/compliance-2026 | ISO 9001:2015 Certified
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.