The global sparkling water market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing consumer preference for healthier beverage alternatives and the rising demand for convenient at-home carbonation solutions. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global sparkling water market was valued at USD 29.27 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 41.85 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 6.2% during the forecast period. This surge is mirrored by growing interest in under sink carbonated water systems, which offer commercial and residential users a space-efficient, high-capacity alternative to countertop and portable units. As sustainability and cost-efficiency become key purchase drivers, manufacturers of under sink carbonation technology are scaling innovation in durability, energy efficiency, and integration capabilities. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and customer adoption metrics, the following nine companies have emerged as leaders in the under sink carbonated water manufacturing space.
Top 9 Under Sink Carbonated Water Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
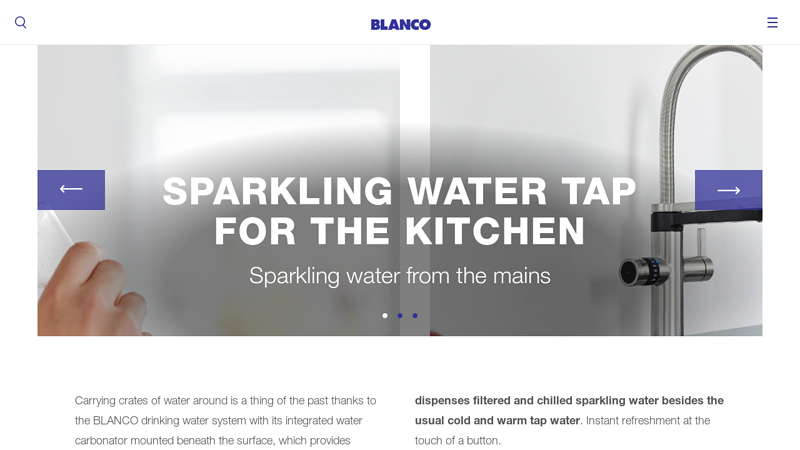
#1 SODA MIXER TAP FOR YOUR KITCHEN
Domain Est. 1996
Website: blanco.com
Key Highlights: The soda mixer tap dispenses filtered and chilled sparkling water besides the usual cold and warm tap water. Instant refreshment at the touch of a button….
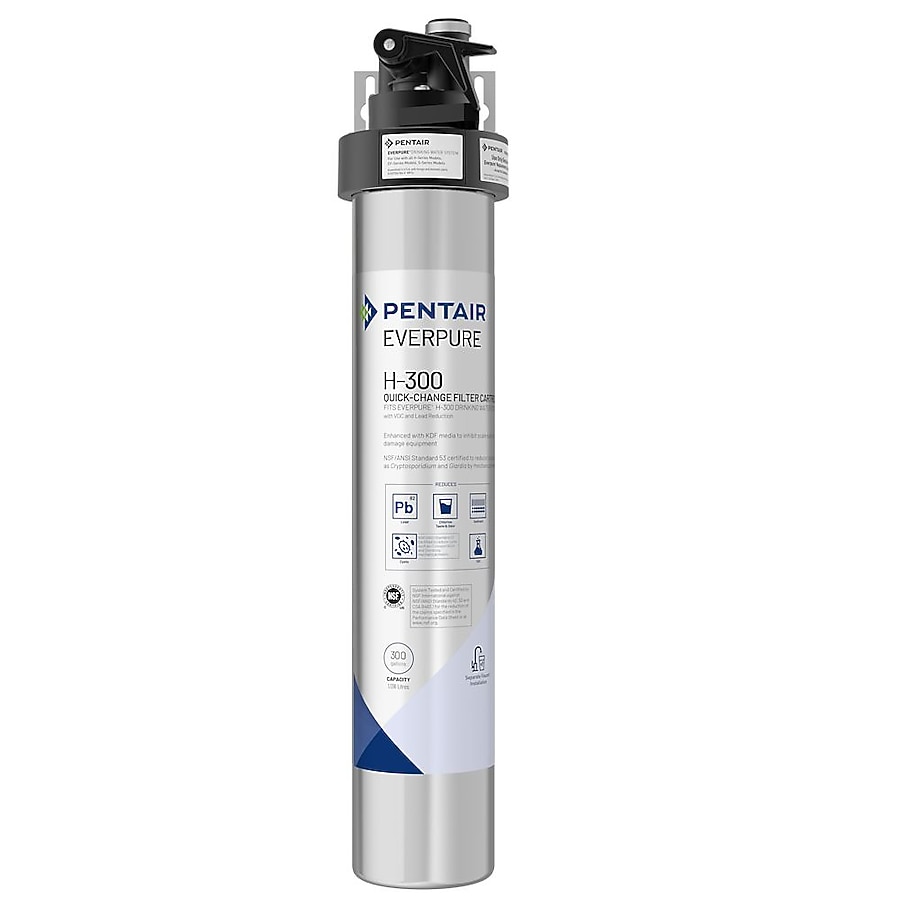
#2 Everpure
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pentair.com
Key Highlights: Pentair Everpure offers an expansive portfolio of technologies and products for commercial water filtration systems in restaurants. These systems are designed ……
#3 GROHE BLUE®Water Filter Kitchen Faucets
Domain Est. 2002
Website: grohe.us
Key Highlights: The GROHE Blue® Chilled & Sparkling water filter system delivers filtered, chilled and carbonated water direct from your kitchen faucet. Simply turn the three- ……
#4 Hot Cold & Sparkling Water
Domain Est. 2005
Website: aqualifeusa.com
Key Highlights: This Hot Cold & Sparkling Water is an under-counter water dispenser connected to your existing water supply. This dispenser delivers fresh-tasting chilled, hot ……
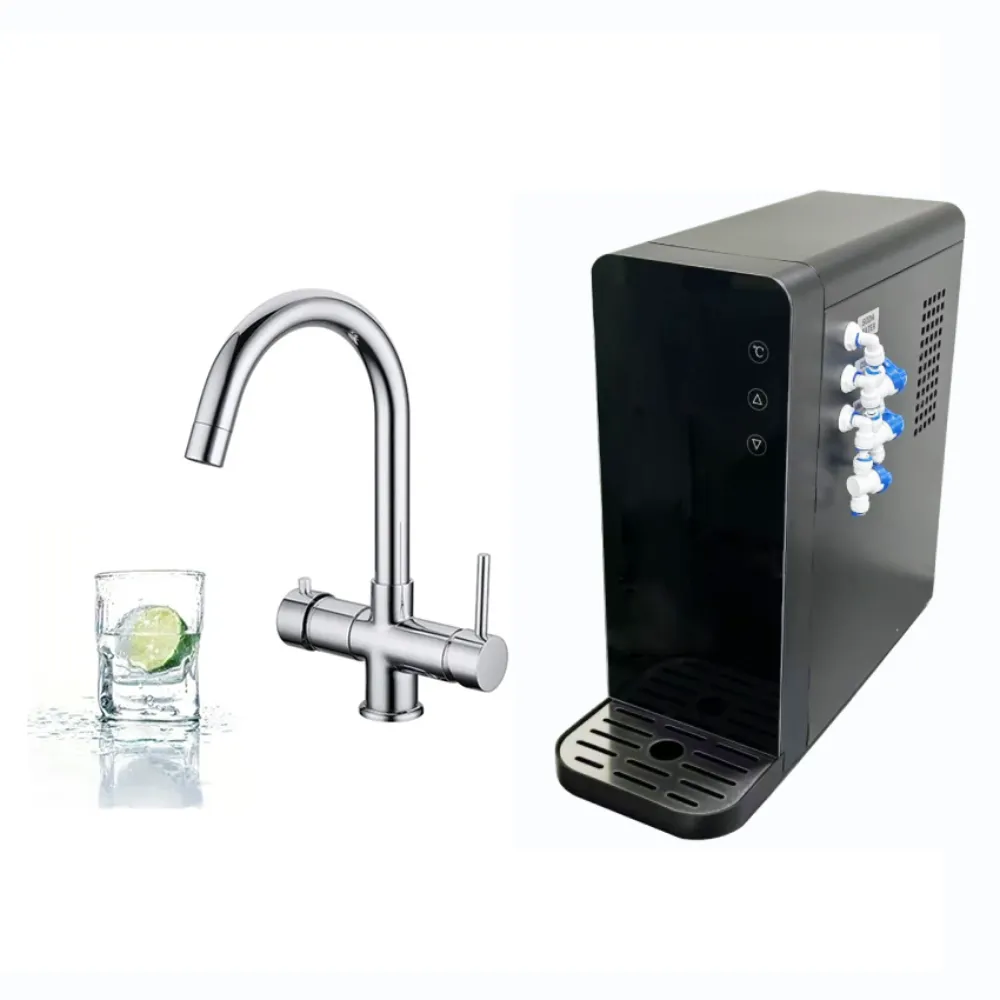
#5 Residential Still & Sparkling
Domain Est. 2012
Website: bluedropwater.com
Key Highlights: Our residential countertop and under-counter water systems are designed to produce up to 30 liters per hour of chilled still or sparkling water while requiring ……
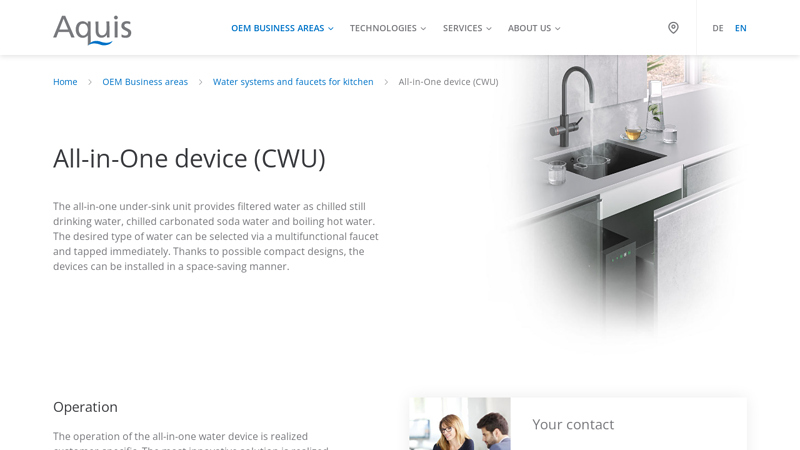
#6 All-in-One device (CWU)
Domain Est. 2017
Website: aquis-systems.com
Key Highlights: The all-in-one under-sink unit provides filtered water as chilled still drinking water, chilled carbonated soda water and boiling hot water….
#7 Chilled, sparkling Water on Tap
Domain Est. 2019
Website: grohe-mena.com
Key Highlights: Our all-in-one home water cooler and carbonation system delivers freshly chilled and filtered water straight from the kitchen faucet….
#8 SeltzaTap
Domain Est. 2021
Website: seltzatap.com
Key Highlights: The SeltzaHub unit lives below your sink, carbonating and chilling sparkling water, ready to be dispensed on demand. A CO2 tank, size of your choosing, is ……
#9 Carbonated Sparkling Water Machine Maker Made by Glacier Fresh
Domain Est. 2022
Website: glacierfreshfilter.com
Key Highlights: Out of stock Rating 5.0 1 Meet USA’s First Cold Soda Maker! Make cold seltzer water in seconds! Easy one-hand operation, just press the rocker, then it will fizz, and pour!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Under Sink Carbonated Water

H2: Market Trends for Under-Sink Carbonated Water Systems in 2026
In 2026, the under-sink carbonated water market is poised for significant expansion, driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and growing sustainability concerns. These systems, which provide continuous access to sparkling water directly from the kitchen tap, are transitioning from niche luxury appliances to mainstream household essentials. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the under-sink carbonated water sector in 2026:
-
Increased Demand for Home Beverage Customization
Consumers are increasingly prioritizing personalized at-home beverage experiences. Under-sink carbonation systems offer precise control over carbonation levels, temperature, and integration with flavor infusion technologies. In 2026, leading brands are expected to introduce smart interfaces and mobile app connectivity, enabling users to customize drinks via smartphones and track consumption patterns. -
Sustainability as a Primary Purchase Driver
With heightened awareness of plastic waste and carbon footprints, consumers are rejecting single-use bottled sparkling water. Under-sink systems eliminate the need for plastic bottles and reduce transportation emissions associated with bottled beverages. By 2026, manufacturers are emphasizing eco-certifications, recyclable components, and energy-efficient compressors to appeal to environmentally conscious buyers. -
Integration with Smart Kitchen Ecosystems
Under-sink carbonators are becoming part of the broader smart home trend. In 2026, integration with voice assistants (e.g., Alexa, Google Assistant), kitchen hubs, and home automation platforms allows for seamless user interaction. These systems can monitor CO₂ levels, predict refill needs, and even sync with grocery delivery apps for automatic cartridge replenishment. -
Expansion of Premium and Built-In Appliance Offerings
High-end kitchen appliance brands are incorporating under-sink carbonation into luxury kitchen designs. In 2026, collaborations between appliance makers (e.g., Sub-Zero, Miele) and beverage technology companies are resulting in sleek, built-in systems that match cabinetry and complement modern kitchen aesthetics. This trend is especially strong in urban markets and among affluent homeowners. -
Growth in Commercial and Multi-Family Applications
Beyond residential use, under-sink carbonation systems are gaining traction in co-working spaces, boutique hotels, and multi-family housing developments. Property developers are installing these systems as value-added amenities to attract tenants and promote sustainable living. By 2026, modular and scalable systems designed for commercial use are expected to represent a growing segment of the market. -
Technological Innovation in CO₂ Management
Advancements in CO₂ delivery—such as recyclable aluminum cartridges, larger-capacity tanks, and closed-loop gas recovery systems—are reducing operating costs and environmental impact. In 2026, some manufacturers are piloting renewable CO₂ sourcing (captured from fermentation or industrial processes), further enhancing the green appeal. -
Regional Market Diversification
While North America and Western Europe remain the largest markets, Asia-Pacific and Latin America are emerging as high-growth regions in 2026. Rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and exposure to Western lifestyle trends are fueling demand in countries like South Korea, Australia, and Brazil. Localized product adaptations, including smaller footprints and bilingual interfaces, are supporting expansion. -
Competitive Pricing and Subscription Models
To lower entry barriers, companies are adopting subscription-based models that bundle the unit, CO₂ refills, and maintenance. In 2026, financing options and trade-in programs for older models are making under-sink systems more accessible. Competitive pricing, driven by increased manufacturing scale and component standardization, is accelerating market penetration.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the under-sink carbonated water market is transforming into a dynamic, tech-enabled segment of the home appliance industry. Fueled by sustainability, convenience, and smart home integration, these systems are redefining how consumers access carbonated beverages. As innovation continues and consumer adoption broadens, the under-sink carbonation market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 12–15% through 2026, establishing itself as a staple in modern kitchens worldwide.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Under-Sink Carbonated Water Systems (Quality & IP Considerations)
Sourcing under-sink carbonated water systems offers convenience and sustainability, but it comes with critical quality and intellectual property (IP) challenges. Overlooking these can lead to subpar performance, legal risks, and reputational damage.
Compromised Water Quality Due to Inadequate Filtration
Many under-sink systems prioritize carbonation over comprehensive filtration. A major pitfall is sourcing units with undersized or low-quality carbon filters that fail to remove chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), or heavy metals. This results in carbonated water that tastes or smells unpleasant despite being bubbly. Ensure the system integrates a multi-stage filtration process—preferably including activated carbon, sediment, and optionally reverse osmosis—to guarantee safe, great-tasting sparkling water.
Use of Substandard CO₂ Cartridges or Proprietary Gas Systems
Some manufacturers lock users into expensive, proprietary CO₂ cylinder systems protected by IP rights. Sourcing such systems limits consumer choice and increases long-term costs. Worse, off-brand or third-party cartridges not designed for the system may leak, under-carbonate, or introduce contaminants due to incompatible seals or gas purity. Always verify CO₂ source compatibility and check whether the design infringes on patented gas delivery mechanisms.
IP Infringement Through Design or Functional Copying
Under-sink carbonation technology often involves patented components—such as pressure-regulated carbonation chambers, automatic shut-off valves, or modular filter designs. Sourcing from suppliers that replicate these features without licensing exposes businesses to litigation. Due diligence is essential: conduct freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses and request IP documentation from suppliers to avoid unintentional infringement.
Inconsistent Carbonation Performance from Poorly Engineered Components
Low-cost systems may use inferior solenoid valves, weak compressors, or ill-designed carbonation tanks, leading to inconsistent fizz levels or system failure over time. These performance issues stem from sourcing based solely on price rather than engineering quality. Evaluate component durability, pressure ratings, and user reviews before procurement.
Lack of Certification and Compliance Documentation
Reputable under-sink systems carry NSF/ANSI certifications for materials safety and performance. Sourcing non-certified units risks exposing consumers to leaching chemicals or microbiological contamination. Always confirm compliance with standards such as NSF/ANSI 42, 53, and 44, and verify that the supplier provides valid certification documentation.
Hidden Costs from Proprietary Filter and Part Ecosystems
Some systems use patented filter housings or electronic control modules, making replacements available only through the original manufacturer at premium prices. This creates long-term dependency and undermines cost savings. Evaluate the availability and pricing of consumables before committing to a supplier.
In summary, sourcing under-sink carbonated water systems demands a balance between performance, safety, and legal compliance. Prioritize suppliers with transparent quality standards, valid certifications, and clear IP status to avoid these common pitfalls.
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Under-Sink Carbonated Water Systems
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for manufacturing, distributing, and selling under-sink carbonated water systems. Designed for manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, this document ensures adherence to international standards, regulatory frameworks, and supply chain best practices.
- Product Classification and Regulatory Oversight
Under-sink carbonated water systems are classified as home appliances that modify drinking water. Key regulatory bodies include:
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Regulates materials in contact with drinking water under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Oversees water quality standards; systems may be subject to Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) requirements.
- NSF International: Certifies products to NSF/ANSI 42 (aesthetic effects), NSF/ANSI 53 (health effects), and NSF/ANSI 400 (carbonation equipment).
- European Union: Must comply with the Drinking Water Directive (98/83/EC) and CE marking under the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
-
Health Canada: Requires compliance with the Canadian Drinking Water Guidelines and CSA B483.1 certification.
-
Material Compliance and Safety
All wetted materials (those in contact with water or CO₂) must be non-toxic and food-grade:
- Use NSF/ANSI 61-certified components for plumbing and seals.
- CO₂ cylinders must meet Department of Transportation (DOT) or Transport Canada (TC) specifications for pressure vessels.
- Plastic components (e.g., tubing, housings) should be BPA-free and comply with FDA 21 CFR 177.
-
Electrical components must meet UL/CSA 1310 (Class 2 power units) or IEC 60335 for household appliances.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) Handling and Transportation
-
CO₂ cylinders are classified as hazardous materials (UN 1013, Compressed Gas, Nonflammable).
- Must be transported in accordance with:
- U.S.: 49 CFR (DOT Hazardous Materials Regulations)
- EU: ADR (European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road)
- International: IMDG Code (for sea freight), IATA DGR (for air transport)
- Cylinders must be secured upright during transit and stored in well-ventilated areas.
-
Retailers and end-users must be provided with CO₂ safety data sheets (SDS) and handling instructions.
-
Electrical and Mechanical Safety
-
Systems with electric compressors or chillers must meet:
- North America: UL/ETL Listing to UL 484 (Room Air Conditioners) or UL 174 (Household Electric Storage Tank Water Heaters), as applicable
- EU: CE marking with compliance to IEC 60335-1 (General Safety) and IEC 60335-2-89 (Particular Requirements for Equipment to Dispense Water)
-
Ground fault protection and low-voltage operation (e.g., 24V DC) are recommended for improved safety.
-
Installation and User Compliance
-
Installation must comply with local plumbing and electrical codes (e.g., IPC, UPC in U.S.; CWC in Canada).
- Systems should include clear installation manuals with:
- Water line connection specifications (e.g., 3/8″ compression fittings)
- Backflow prevention requirements (e.g., air gap or approved device per ASSE 1015)
- Electrical outlet requirements (GFCI protection recommended)
- User manuals must include:
- Routine maintenance instructions
- CO₂ cylinder replacement procedures
- Warranty and registration information
-
Emergency shutdown guidance
-
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance
-
CO₂ sourcing: Use food-grade CO₂ from sustainable or recycled sources where possible (e.g., captured from fermentation or industrial processes).
- End-of-life management:
- Design for disassembly and recyclability (e.g., separate metal, plastic, electronic components)
- Comply with WEEE Directive (EU) or state-level e-waste laws (e.g., California)
- Packaging:
- Minimize plastics; use recyclable cardboard and biodegradable materials
-
Label packaging with recycling instructions (e.g., How2Recycle label)
-
Labeling and Documentation
Mandatory product markings include:
- Manufacturer name and address
- Model and serial number
- Electrical ratings (voltage, amperage, frequency)
- NSF/ANSI certification marks
- CE marking (EU)
- Warning labels (e.g., “Do not use with non-potable water,” “Risk of pressure buildup”)
Documentation must include:
- Installation and operation manual (in local language)
- Warranty statement
- Regulatory compliance statements
-
SDS for CO₂ and any chemical components
-
Supply Chain and Distribution Logistics
-
Inventory management: Maintain buffer stock for CO₂ cylinders and replacement filters.
- Cold chain not required, but store units in climate-controlled environments (0°C–40°C) to protect seals and electronics.
- Last-mile delivery: Coordinate with partners trained in appliance delivery; include unpacking and debris removal as value-added services.
-
Returns and servicing: Establish reverse logistics for defective units and end-of-life returns.
-
Quality Assurance and Audits
-
Implement ISO 9001 (Quality Management) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) where applicable.
- Conduct annual third-party audits for NSF, UL, or CE compliance.
-
Maintain records of batch testing, component sourcing, and customer complaints for traceability.
-
Market-Specific Considerations
-
United States: Comply with state-specific plumbing codes (e.g., CA Title 24 for energy efficiency).
- Canada: Register with Health Canada’s Consumer Product Safety Directorate if required.
- EU: Appoint an Authorized Representative; maintain a Technical File per EU 2019/1020.
- Australia/NZ: Comply with AS/NZS 3500 (Plumbing and Drainage) and register with the Australian Competition & Consumer Commission (ACCC).
Conclusion
Successful deployment of under-sink carbonated water systems requires integrated logistics planning and strict adherence to health, safety, and environmental regulations. By following this guide, stakeholders can ensure product safety, customer satisfaction, and global market access. Regular updates to this guide are recommended to reflect evolving standards and regional requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing an under-sink carbonated water system offers a convenient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solution for enjoying sparkling water at home. By installing a permanent filtration and carbonation unit directly into your kitchen plumbing, you eliminate the need for single-use plastic bottles, reduce long-term beverage expenses, and enjoy consistent, high-quality carbonated water on demand. While the initial investment and installation may require more effort than countertop models or store-bought alternatives, the benefits of space savings, continuous supply, and superior integration with your kitchen make under-sink systems an excellent choice for eco-conscious households seeking sustainable hydration. With proper maintenance and filter replacements, these systems provide a reliable and refreshing source of sparkling water for years to come.