The global stainless steel market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industries such as construction, automotive, energy, and consumer goods. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the stainless steel market was valued at USD 137.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is fueled by increased urbanization, infrastructure development, and the material’s corrosion resistance and recyclability. With over 150 grades of stainless steel available, manufacturing expertise has become increasingly specialized, giving rise to dominant players focusing on key categories such as austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, duplex, and precipitation-hardening grades. As industries demand higher performance and sustainability, the leading stainless steel grade manufacturers are differentiating themselves through innovation, scale, and alloy-specific capabilities. Here’s a look at the top 8 types of stainless steel grades and the manufacturers shaping the future of this dynamic market.
Top 8 Types Of Stainless Steel Grades Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Stainless Steel Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: stainlesssteelmanufacturers.org
Key Highlights: Stainless Steel 400 Series: Grades 410 & 416 Series 400 stainless steels are high strength and wear resistant stainless steels due to their high carbon content ……
#2 Stainless Steel Grades
Domain Est. 1999
Website: jindalstainless.com
Key Highlights: These grades are categorised into five types: austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, duplex, and precipitation-hardening stainless steel. The varying compositions ……
#3 Categories, grades and product forms
Domain Est. 2000
Website: worldstainless.org
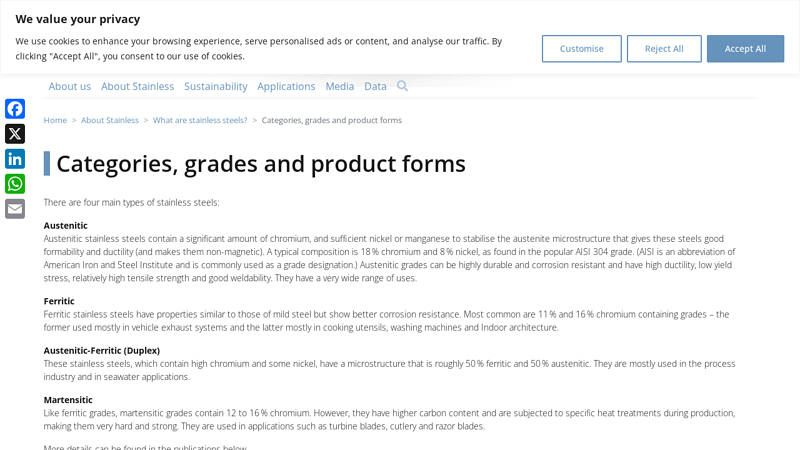
Key Highlights: There are four main types of stainless steels: Austenitic, Ferritic, Austenitic-Ferritic (Duplex) and Martensitic….
#4 Stainless Steel Grades and Families: Explained
Domain Est. 2002
Website: unifiedalloys.com
Key Highlights: Austenitic Stainless Steel · Ferritic Stainless Steel · Duplex Stainless Steel · Martensitic & Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel….
#5 Understanding stainless-steel grades
Domain Est. 2012
Website: essentracomponents.com
Key Highlights: Whether you choose 304 or 316 stainless steel comes down to your application and budget. Learn more about these two grades in our guide, 304 vs ……
#6 The different grades of stainless steel
Domain Est. 2014
Website: beal-inox.com
Key Highlights: According to their composition, inox steels are classified into 4 families: martensitic (group C), ferritic (group F), austenitic (group A), and austeno- ……
#7 Stainless France
Website: stainless.eu
Key Highlights: An adapted stock with Stainless steel grades, Cobalt-based alloys, Titanium and Tantalum alloys in particular. Find out more. The main civil and military ……
#8 Stainless Steel Grades
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1985
Website: continentalsteel.com
Key Highlights: The Stainless Steel Grades Guide: Explore Austenitic, Ferritic, Duplex & More. Get a Quote from Continental Steel, a Leading Supplier Since 1985….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Types Of Stainless Steel Grades
2026 Market Trends for Types of Stainless Steel Grades
The global stainless steel market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and sustainability imperatives. This analysis explores the projected market trends for major types of stainless steel grades, focusing on their applications, regional growth, and emerging innovations.
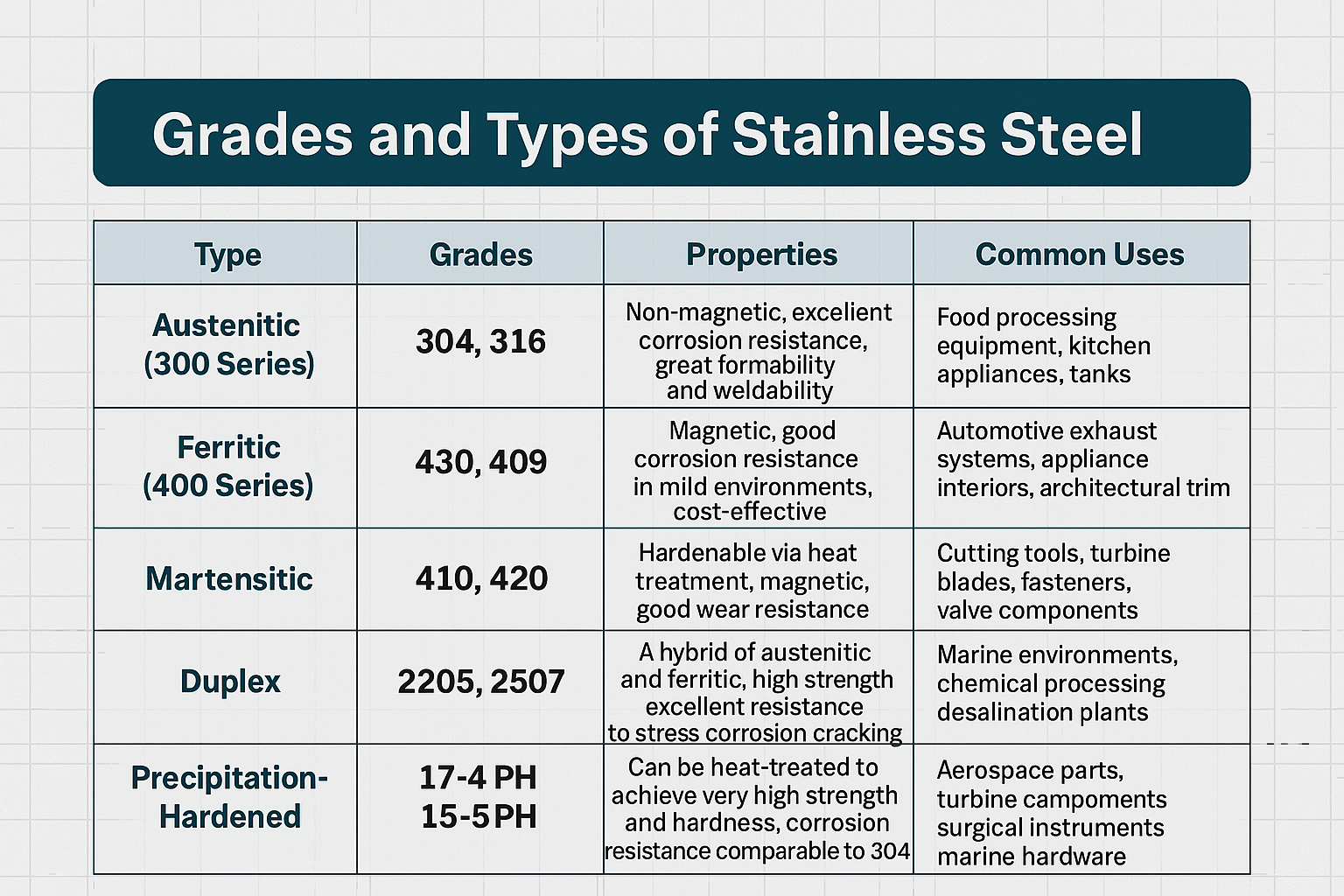
Austenitic Stainless Steel Grades
Austenitic stainless steels, particularly the 300 series (e.g., 304, 316), are expected to maintain dominance in the 2026 market landscape. These grades account for over 70% of global stainless steel consumption due to their excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and weldability. By 2026, demand is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2%, fueled by expanding applications in construction, food processing, and healthcare.
Key trends include:
– Rising adoption of nitrogen-enhanced grades (e.g., 304LN, 316LN) for improved strength and corrosion resistance.
– Increased use of 316L in marine and chemical processing due to superior chloride resistance.
– Growing emphasis on recycled content in austenitic grades, aligning with circular economy goals.
Asia-Pacific, especially China and India, will remain the largest consuming region, driven by urbanization and infrastructure development.
Ferritic Stainless Steel Grades
Ferritic grades (e.g., 430, 409, 444) are anticipated to see moderate growth (CAGR of 3.8%) by 2026, primarily due to cost advantages and good corrosion resistance in mild environments. These grades are increasingly favored in automotive exhaust systems, household appliances, and architectural applications.
Notable developments:
– Expansion of dual-phase ferritic-austenitic grades for improved performance.
– Rising demand for 444 in water treatment and heat exchangers due to molybdenum content enhancing pitting resistance.
– OEMs in the automotive sector shifting toward ferritic grades to reduce material costs without compromising durability.
Europe and North America are expected to lead adoption, supported by stringent emissions regulations and energy efficiency standards.
Martensitic Stainless Steel Grades
Martensitic stainless steels (e.g., 410, 420, 440C) are projected to experience stable demand, with a CAGR of approximately 2.5% through 2026. These grades are valued for their high strength, hardness, and wear resistance, making them ideal for cutlery, surgical instruments, and industrial tools.
Emerging trends:
– Increased use in additive manufacturing (3D printing) for precision components.
– Development of low-carbon variants to improve toughness and weldability.
– Growing demand in the defense and aerospace sectors for high-performance parts.
Technological innovation in heat treatment processes will enhance the mechanical properties of martensitic steels, supporting niche applications.
Duplex Stainless Steel Grades
Duplex grades (e.g., 2205, 2507) are expected to be one of the fastest-growing segments, with a projected CAGR of 6.1% by 2026. Their combination of high strength and excellent corrosion resistance—particularly in chloride-rich environments—makes them ideal for oil & gas, desalination, and chemical processing industries.
Key drivers:
– Expansion of offshore oil and gas projects in the Middle East and Latin America.
– Rising investments in seawater desalination plants due to water scarcity.
– Development of super-duplex and lean duplex grades offering better cost-performance ratios.
Manufacturers are increasingly investing in duplex production capacity to meet surging demand, especially in high-value industrial applications.
Precipitation-Hardening (PH) Stainless Steel Grades
Precipitation-hardening grades (e.g., 17-4 PH, 15-5 PH) are expected to grow steadily (CAGR of 4.3%) by 2026, driven by demand in aerospace, defense, and high-performance engineering sectors. These alloys offer exceptional strength-to-density ratios and can be machined into complex shapes before final heat treatment.
Trends shaping the PH segment:
– Increased use in turbine blades, landing gear, and missile components.
– Advancements in powder metallurgy enabling near-net-shape manufacturing.
– Growing R&D in maraging stainless steels for extreme environments.
North America and Europe will remain key markets due to advanced aerospace and defense industries.
Sustainability and Material Innovation
By 2026, sustainability will play a central role in shaping stainless steel grade selection. Producers are focusing on:
– Reducing carbon footprint through hydrogen-based reduction processes.
– Increasing scrap utilization rates, particularly in electric arc furnace (EAF) production.
– Developing “green” stainless steel with certified low-emission production methods.
Innovations such as nanostructured stainless steels and high-entropy alloys may begin commercial scaling by 2026, offering enhanced performance for specialized applications.
Conclusion
In summary, the 2026 stainless steel market will be characterized by diversified growth across grades, with austenitic and duplex steels leading in volume and value, respectively. Regional dynamics, industry-specific demands, and environmental considerations will shape the adoption of different grades. As industries prioritize performance, cost-efficiency, and sustainability, stainless steel producers must innovate continuously to maintain competitiveness and meet evolving global standards.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Types of Stainless Steel Grades (Quality and IP Concerns)
Sourcing stainless steel grades requires careful attention to material specifications, supplier credibility, and compliance with international standards. Failing to address key quality and intellectual property (IP) issues can lead to performance failures, safety hazards, and legal complications. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
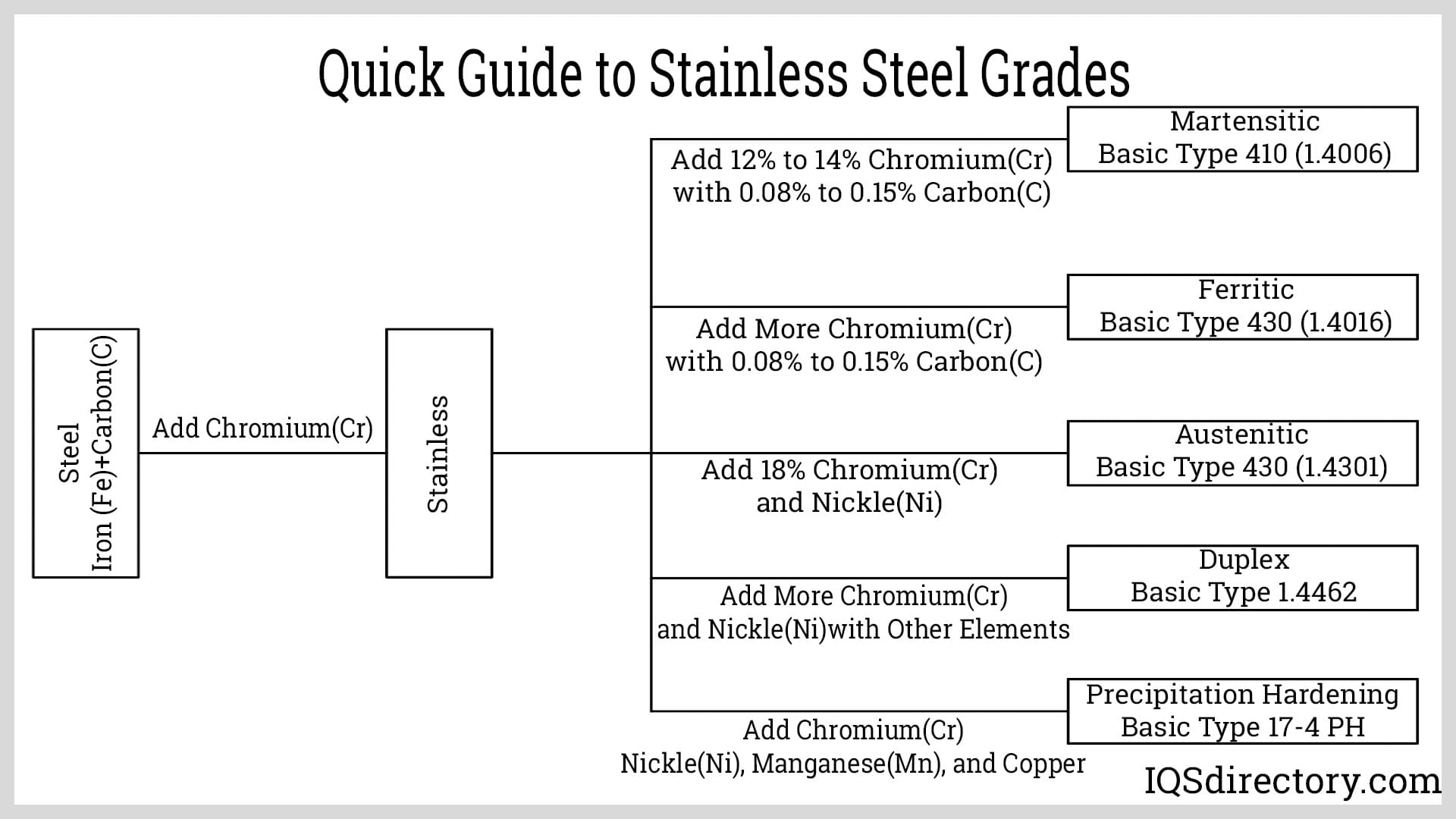
Poor Understanding of Stainless Steel Grade Specifications
One of the most frequent errors is misidentifying or misunderstanding the differences between stainless steel grades (e.g., 304 vs. 316, 430 vs. 410). Each grade has unique chemical compositions and mechanical properties tailored for specific environments. Sourcing the wrong grade—such as using 304 in a highly corrosive marine setting instead of 316—can lead to premature failure. Buyers must verify that the material meets required standards (ASTM, AISI, ISO, etc.) and is suitable for the intended application.
Insufficient Quality Assurance and Certification
Many suppliers, especially in competitive or low-cost markets, may provide substandard materials accompanied by falsified or incomplete mill test certificates (MTCs). Relying on paperwork without third-party verification increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or off-spec materials. Always require Material Test Reports (MTRs) with traceable heat numbers and consider independent testing (e.g., PMI—Positive Material Identification) to confirm alloy composition.
Lack of Supply Chain Transparency
Opaque supply chains can hide the true origin of raw materials. Some suppliers may rebrand lower-quality steel as premium grades. Without clear traceability from mill to end-user, buyers risk receiving material that does not meet required quality benchmarks or may even violate industry regulations (e.g., in food processing or medical devices).
Intellectual Property and Brand Infringement
Some suppliers may falsely claim compliance with proprietary or patented steel formulations (e.g., duplex grades like 2205 or super austenitic grades) without proper licensing. Using counterfeit or unauthorized versions of patented alloys can expose the buyer to intellectual property litigation. Always verify that the supplier is authorized to produce or distribute specific high-performance grades.
Overlooking Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Certain stainless steel grades must meet strict regulatory requirements (e.g., FDA, ASME, PED). Sourcing materials without proper documentation or non-compliant with RoHS, REACH, or other environmental standards can result in project delays, product recalls, or legal penalties, especially in regulated industries.
Cost-Driven Decisions Compromising Quality
Prioritizing low cost over quality often results in sourcing materials with incorrect alloying elements (e.g., reduced chromium or nickel content), leading to poor corrosion resistance and structural integrity. While cost-efficiency is important, it should not come at the expense of material performance and long-term reliability.
Inadequate Supplier Vetting and Due Diligence
Failing to conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers—such as site audits, reference checks, and quality management system certifications (e.g., ISO 9001)—increases the risk of partnering with unreliable vendors. Trustworthy suppliers should offer full transparency, technical support, and consistent quality control practices.
By recognizing and mitigating these common pitfalls, buyers can ensure they source the correct stainless steel grades with guaranteed quality and compliance, avoiding costly errors and protecting against IP and regulatory risks.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Types of Stainless Steel Grades
Overview of Stainless Steel Grades
Stainless steel is a versatile alloy known for its corrosion resistance, durability, and strength. It is categorized into several grades based on composition and properties. These grades are crucial in logistics and compliance due to variations in handling, storage, transportation, and regulatory requirements.
Common Types of Stainless Steel Grades
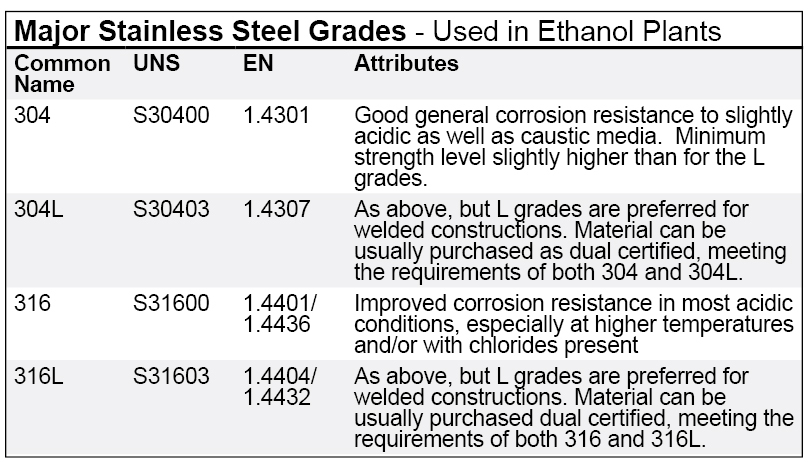
2.1 Austenitic Stainless Steels (Series 200 & 300)
Austenitic stainless steels are the most widely used, offering excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and weldability.
- Examples: 304, 304L, 316, 316L, 321
- Key Characteristics:
- Non-magnetic
- High chromium (16–26%) and nickel (6–22%) content
- Often used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries
Logistics Considerations:
– Handle with clean tools to avoid cross-contamination (especially from carbon steel).
– Protect from chloride exposure during transport (e.g., avoid saltwater proximity).
– Store in dry, ventilated areas to prevent surface staining.
Compliance Requirements:
– Must meet ASTM A240/A240M or EN 10088 standards.
– Traceability required for regulated industries (e.g., 316L in medical devices).
– Material Test Reports (MTRs) must accompany shipments.
2.2 Ferritic Stainless Steels (Series 400 – 430, 446)
Ferritic grades offer moderate corrosion resistance and are magnetic, with lower nickel content.
- Examples: 409, 430, 446
- Key Characteristics:
- Magnetic
- Lower cost due to reduced nickel
- Used in automotive exhausts, appliances
Logistics Considerations:
– Susceptible to embrittlement; avoid impact during handling.
– Less prone to chloride stress corrosion cracking than austenitic grades.
– Can be stored outdoors with protective wrapping.
Compliance Requirements:
– Must comply with ASTM A479 or equivalent.
– Suitable for less stringent environments; not recommended for marine or high-saline zones.
– Certifications may vary based on end-use (e.g., automotive vs. architectural).
2.3 Martensitic Stainless Steels (Series 400 – 410, 420, 440)
These are hardenable steels with high strength and wear resistance.
- Examples: 410, 420, 440C
- Key Characteristics:
- Magnetic
- High carbon content
- Used in cutlery, valves, and fasteners
Logistics Considerations:
– Requires protective coating to prevent rust during transit.
– Avoid moisture exposure; silica gel desiccants recommended in packaging.
– Handle with gloves to prevent fingerprint corrosion.
Compliance Requirements:
– Must meet ASTM A276 or ISO 15510 standards.
– Heat treatment documentation required for quality assurance.
– Restricted in some food-contact applications unless passivated.
2.4 Duplex Stainless Steels (e.g., 2205, 2507)
Duplex steels combine austenitic and ferritic structures for high strength and corrosion resistance.
- Examples: 2205 (S31803), 2507 (S32750)
- Key Characteristics:
- High tensile strength
- Excellent chloride stress corrosion resistance
- Used in offshore oil & gas, desalination plants
Logistics Considerations:
– Sensitive to heat input; avoid welding during handling.
– Store flat to prevent warping; use non-metallic separators.
– Temperature-controlled transport recommended in extreme climates.
Compliance Requirements:
– Must meet NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 for sour service environments.
– Full material certification (e.g., 3.1 or 3.2 per EN 10204) mandatory.
– Third-party inspection often required for critical applications.
2.5 Precipitation-Hardening (PH) Stainless Steels (e.g., 17-4 PH, 15-5 PH)
These offer high strength through heat treatment and are used in aerospace and high-performance applications.
- Examples: 17-4 PH (S17400), 15-5 PH
- Key Characteristics:
- Can be machined in soft state and hardened afterward
- Excellent strength-to-weight ratio
- Used in aerospace, nuclear, and defense sectors
Logistics Considerations:
– Transport in condition-stable packaging to avoid premature aging.
– Keep away from heat sources or UV exposure that could trigger aging.
– Label clearly with heat treatment status.
Compliance Requirements:
– Must comply with AMS (Aerospace Material Specifications) or ASTM A564.
– Full traceability and lot control required.
– ITAR or EAR compliance may apply for export-controlled uses.
Packaging & Labeling Standards
- Packaging: Use moisture-resistant wrapping (e.g., VCI paper), wooden crates for heavy sections, and non-metallic strapping.
- Labeling: Include grade, heat number, dimensions, standards met, and handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Stack”).
- Barcoding/RFID: Recommended for inventory tracking and compliance audits.
Regulatory & Environmental Compliance
- REACH & RoHS: Ensure no restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) exceed limits.
- Export Controls: Verify ITAR, EAR, or other trade restrictions, especially for PH and duplex grades.
- Hazardous Material Classification: Stainless steel is generally non-hazardous but may require documentation if alloyed with controlled elements.
- Sustainability: Recyclability must be declared; stainless steel is 100% recyclable.
Conclusion
Understanding the logistics and compliance requirements for different stainless steel grades ensures safe handling, regulatory adherence, and product integrity. Proper documentation, storage, and transport protocols are essential across all grades, with special considerations for high-performance and regulated applications. Always verify customer and industry-specific requirements before shipment.
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate stainless steel grades requires a comprehensive understanding of material properties, application requirements, environmental conditions, and cost considerations. The most commonly used grades—such as the austenitic 304 and 316, ferritic 430, and martensitic 410—each offer distinct advantages in terms of corrosion resistance, strength, formability, and heat resistance. Selecting the right grade involves balancing performance needs with economic feasibility and supply chain reliability.
It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who provide certified materials, consistent quality, and technical support to ensure compliance with industry standards such as ASTM, AISI, or ISO. Additionally, considerations such as lead times, regional availability, and sustainability practices can significantly impact sourcing decisions.
Ultimately, effective sourcing of stainless steel grades hinges on matching the material’s characteristics to the intended application while maintaining quality, reliability, and cost-efficiency throughout the supply chain. A strategic and informed approach to sourcing ensures long-term performance and value across industrial, architectural, and consumer applications.