The global turbo impeller market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient compression and pumping systems across industries such as oil & gas, power generation, and HVAC. According to Grand View Research, the global centrifugal compressor market—of which turbo impellers are a critical component—was valued at USD 31.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts sustained growth in turbo machinery demand, citing increased industrial automation and infrastructure development, particularly in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East. As manufacturers strive for improved aerodynamic efficiency and reliability, innovations in turbo impeller design and precision manufacturing have become key differentiators. Against this backdrop, we spotlight the top 10 turbo impeller manufacturers leading technological advancement, market reach, and performance excellence in a competitive and evolving landscape.
Top 10 Turbo Impeller Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Turbochargers
Domain Est. 2005
Website: cooperservices.com
Key Highlights: TSI is the original equipment manufacturer (O.E.M.) for Cooper-Bessemer®, DeLaval®, and Elliott® turbochargers. TSI provides parts, repairs, and full service ……
#2 Turbo Billet Compressor Wheel Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2012
Website: ktsturbobilletx.com
Key Highlights: KTS Turbobillet X (KTS) is a specialty manufacturer of high performance Machined-From-Solid (MFS) Compressor wheel, also known as Billet Impeller. Not all ……
#3 Turbo impeller Manufacturer & Supplier in China
Domain Est. 2024
Website: obtturbine.com
Key Highlights: The turbo impeller design brings the airflow and pressure to the maximum level for great efficient and performance. Using our turbo impellers in your equipment ……
#4 Turbocharger Impellers
Domain Est. 1995
Website: qcforge.com
Key Highlights: Queen City Forging has the expertise to create durable, cost-effective, and high quality turbocharger impellers….
#5 Quality Components & Manufacturing Solutions
Domain Est. 1996
Website: turbocam.com
Key Highlights: TURBOCAM International is a global turbomachinery development and manufacturing company that specializes in 5-axis machining of flowpath components….
#6 Turbotech
Domain Est. 1996
Website: turbotech.co.uk
Key Highlights: Turbotech PRECISION PRODUCTS LTD manufactures impeller and compressor wheel castings in aluminium alloys for a number of industries….
#7 Turbo Machined Products
Domain Est. 2001
Website: turbomp.com
Key Highlights: An impeller is a rotating component equipped with vanes or blades used in turbomachinery. IMPELLERS & BLISKS. Impellers & Bladed Disks up to 30″. Precision ……
#8 Design of impellers of various types
Domain Est. 2004
Website: cfturbo.com
Key Highlights: The core of every turbomachine: the impeller » Design steps for impellers of pumps • Fans • Compressors • Turbines ✓ → Test CFturbo now!…
#9 Next Turbo Technologies
Domain Est. 2014
Website: next-turbo.com
Key Highlights: Next Turbo designs and produces robust and high efficient Integrally geared, single stage, centrifugal turbocompressors with variable diffuser vanes and/or ……
#10 Technical Details of Turbo Compressors
Domain Est. 2018
Website: raettsgroup.com
Key Highlights: A turbo compressor is a type of dynamic compressor that increases the pressure of a gas by imparting kinetic energy through a rotating impeller….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Turbo Impeller

H2: Market Trends for Turbo Impeller in 2026
As industries continue to prioritize energy efficiency, emission reduction, and advanced technological integration, the turbo impeller market is poised for significant evolution by 2026. Turbo impellers—critical components in turbochargers, compressors, blowers, and HVAC systems—are witnessing increased demand driven by advancements in materials, design optimization, and global regulatory pressures. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the turbo impeller landscape in 2026:
-
Rise in Electrification and Hybrid Powertrains
While full vehicle electrification grows, hybrid systems remain crucial for bridging the gap between internal combustion engines (ICEs) and electric vehicles (EVs). Turbo impellers are essential in downsized, high-efficiency engines used in hybrid vehicles. By 2026, demand for high-performance, compact turbo impellers will increase as automakers optimize hybrid engine efficiency. OEMs are investing in advanced turbocharging systems with variable geometry and electrically assisted turbo impellers to reduce lag and improve response. -
Adoption of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
The use of metal additive manufacturing for turbo impeller production is accelerating. 3D printing enables complex geometries, lightweighting, and rapid prototyping, allowing engineers to design impellers with optimized aerodynamic profiles. By 2026, major manufacturers in aerospace and automotive sectors are expected to adopt serial production of 3D-printed turbo impellers, improving performance and reducing lead times. -
Material Innovation: High-Temperature Alloys and Composites
Turbo impellers operate under extreme thermal and mechanical stress. In 2026, the market will see broader adoption of nickel-based superalloys, titanium aluminides, and ceramic matrix composites (CMCs). These materials offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to thermal fatigue, especially in aerospace and high-performance automotive applications. Coating technologies such as thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) will further enhance durability. -
Integration with Digital Twins and Predictive Maintenance
The integration of digital twin technology allows real-time monitoring and simulation of turbo impeller performance. By 2026, predictive analytics and IoT-enabled sensors embedded in turbo systems will provide insights into impeller wear, efficiency, and failure risks. This trend is particularly prominent in industrial and aviation sectors, where unplanned downtime is costly. -
Growth in Industrial and HVAC Applications
Beyond transportation, turbo impellers are gaining traction in industrial air compression, gas processing, and HVAC systems. With global emphasis on energy-efficient buildings and manufacturing, high-efficiency centrifugal compressors using advanced impellers are being deployed. The HVACR (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration) sector is expected to contribute significantly to market growth by 2026. -
Stringent Emission Regulations Driving Innovation
Regulatory frameworks such as Euro 7 (Europe), Bharat Stage VI (India), and EPA Tier 4 (USA) are pushing automakers and industrial operators to reduce NOx and particulate emissions. Turbo impellers play a vital role in improving combustion efficiency and enabling exhaust gas recirculation (EGR). This regulatory push is accelerating R&D in turbocharger systems, directly benefiting the turbo impeller market. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and India, will remain the largest market for turbo impellers due to high automotive production and industrial growth. Europe and North America will focus on high-value, technologically advanced impellers for premium automotive and aerospace applications. Emerging markets in Southeast Asia and Latin America will see rising demand as infrastructure and manufacturing expand. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
By 2026, sustainability will influence material sourcing and end-of-life management. Manufacturers are exploring recyclable alloys and remanufacturing programs for used turbo impellers. Closed-loop production systems and life cycle assessments (LCA) will become standard practices among leading suppliers.
Conclusion
The turbo impeller market in 2026 will be shaped by technological innovation, regulatory demands, and cross-sectoral applications. Companies that invest in advanced materials, digital integration, and sustainable manufacturing will lead the market. As efficiency and performance remain paramount across industries, the turbo impeller will continue to be a critical enabler of next-generation energy systems.
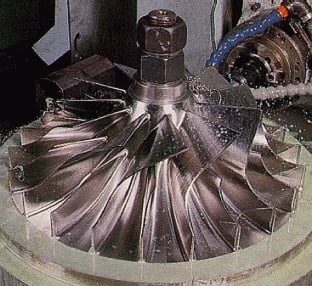
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Turbo Impellers (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing turbo impellers—critical rotating components in turbochargers and compressors—poses unique challenges, especially regarding quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Material Certification and Traceability
A common issue is receiving impellers made from substandard or unverified materials. Without proper material test reports (MTRs) and full traceability (e.g., heat numbers), there’s risk of premature failure due to fatigue, corrosion, or imbalance. Sourcing from suppliers without rigorous metallurgical controls can compromise turbine efficiency and safety.
2. Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Finish
Turbo impellers operate at high speeds (often exceeding 100,000 RPM), making precision paramount. Slight deviations in blade geometry, hub concentricity, or surface roughness can cause imbalance, vibration, and reduced aerodynamic efficiency. Suppliers using outdated tooling or lacking CNC/5-axis machining capabilities often fail to meet tight tolerances.
3. Inconsistent Balancing and Dynamic Testing
Improper balancing—either static or dynamic—leads to excessive vibration, bearing wear, and catastrophic failure. Some suppliers may skip full-speed dynamic balancing or fail to provide certification, increasing field failure rates. Always require documented balance reports to G1.0 or better standards.
4. Lack of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Failure to perform NDT (e.g., fluorescent penetrant inspection, X-ray, or ultrasonic testing) can allow hidden defects like micro-cracks, porosity, or inclusions to go undetected. These flaws may not appear during initial testing but become critical under operational stress.
5. Inadequate Process Control and Quality Documentation
Suppliers without robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949) may lack consistent process controls, leading to batch-to-batch variability. Absence of First Article Inspection (FAI) reports, process capability studies (Cp/Cpk), or PPAP documentation increases risk.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Reverse Engineering and Design Copying
Many turbo impeller designs are proprietary. Sourcing from suppliers who reverse-engineer OEM parts without licensing infringes on patents and design rights. This exposes the buyer to IP litigation and may result in product recalls or import bans.
2. Poorly Defined or Enforced IP Clauses in Contracts
Contracts that lack clear IP ownership, confidentiality, or non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) leave designs vulnerable. Without explicit terms, suppliers may claim co-ownership or reuse design data for competing products.
3. Inadequate Protection of CAD Models and Tooling
Sharing detailed CAD files or investing in tooling without IP safeguards (e.g., watermarking, restricted access, or legal ownership clauses) risks design theft. Some suppliers may clone molds or 3D scan parts for resale.
4. Sourcing from Regions with Weak IP Enforcement
Procuring from jurisdictions with lax IP protection increases the likelihood of counterfeit production and unauthorized distribution. Even if the initial batch is genuine, designs may be replicated and sold globally without consent.
5. Failure to Verify Supplier Design Authority
Using a supplier that claims to manufacture “OEM-equivalent” impellers may still violate patents. Always confirm whether the supplier has legitimate design licenses or has engineered around protected IP through freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Audit suppliers on-site to verify quality systems, equipment, and IP compliance.
- Require full documentation, including MTRs, NDT reports, balance certificates, and FAIs.
- Use legally vetted contracts with strong IP clauses and export controls.
- Work with licensed manufacturers or those offering proprietary, non-infringing designs.
- Consider dual sourcing with IP-protected designs held in-house or under escrow.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, companies can ensure reliable performance, minimize legal exposure, and protect their competitive advantage in the turbo machinery market.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Turbo Impeller
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the transport, handling, and regulatory adherence related to Turbo Impeller components. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safe, efficient, and legally compliant operations throughout the supply chain.
Product Classification & Documentation
Ensure accurate classification of the Turbo Impeller under the Harmonized System (HS) Code for international shipping. Typical classification may fall under HS 8414.90 (Parts of fans, blowers, and similar appliances). Maintain complete technical specifications, material composition, and safety data sheets (SDS) to support customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Package Turbo Impellers in protective, anti-corrosive materials such as VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper, sealed plastic wrapping, and robust wooden crates with internal foam or custom inserts. Clearly label each package with handling instructions including “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” to prevent damage during transit.
Shipping & Transportation
Use freight carriers experienced in handling precision mechanical components. For air freight, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if any lubricants or coatings are classified as hazardous. For sea freight, ensure compliance with IMDG Code where applicable. Secure loads to prevent movement and maintain environmental controls (temperature, humidity) during transit.
Export Controls & Trade Compliance
Verify whether the Turbo Impeller is subject to export control regulations such as ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) or EAR (Export Administration Regulations). Determine licensing requirements based on destination country, end-user, and technical specifications. Conduct regular screening of restricted parties (e.g., Denied Persons List) prior to shipment.
Import Regulations & Duties
Research and comply with import requirements of the destination country, including conformity assessments, certification (e.g., CE, UKCA, or EAC), and payment of applicable tariffs or VAT. Provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin to facilitate customs processing.
Environmental & Safety Compliance
Ensure manufacturing and packaging materials comply with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) directives. Implement proper disposal procedures for packaging waste in accordance with local environmental regulations.
Quality Assurance & Traceability
Maintain full traceability of each Turbo Impeller through serial numbering and documented quality inspections. Retain records of production batches, test results, and shipping data for audit and recall readiness. Comply with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 standards where applicable.
Returns & Reverse Logistics
Establish clear procedures for handling returns, including inspection, refurbishment, or disposal. Ensure returned units are packaged and transported in compliance with safety and environmental standards. Document all reverse logistics activities for compliance and warranty tracking.
Adhering to this guide ensures the Turbo Impeller is managed efficiently and responsibly across all stages of the logistics pipeline while meeting global regulatory requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Turbo Impeller:
After a comprehensive evaluation of technical requirements, supplier capabilities, cost structures, and lead times, sourcing the turbo impeller from a qualified and reliable supplier is a strategic decision that supports operational efficiency and performance excellence. The selected supplier demonstrates proven expertise in precision manufacturing, adherence to industry standards, and a strong track record in delivering high-quality turbo components. By establishing a robust supply chain partnership, we ensure consistent product quality, reduced downtime, and long-term cost savings. Continued collaboration, performance monitoring, and contingency planning will further mitigate risks and support sustained success in meeting project and production goals.